1、何为指针?
简单来说就是指向存储对象的内存地址。
2、单链表的插入
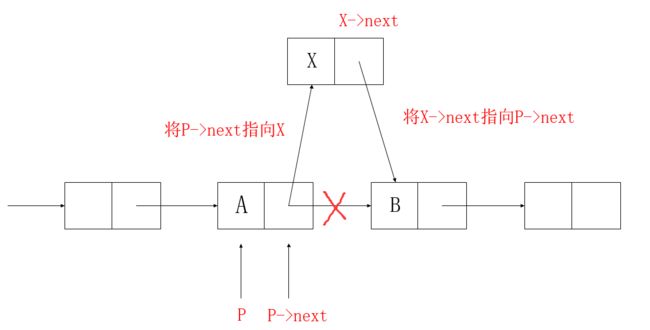
如图所示单链表,当前指针P指向结点A,请在A、B结点之间插入一个结点X:
第一步:先将X的next的指针指向P的next
x->next = p->next
因为p->next指向B,所以将x->next赋值成p->next,从而x->next也指向B结点
注意:
(1)要先将X的next指针指向B,再将A的next指针即P的next指针指向X结点。
(2)P指的是A结点,P->next指的是A->next,而A->next指向B结点,即P->next指向B结点。
第二步:再将P->next指向X结点,从而完成插入功能
p->next = x
3、利用哨兵减少时间开销
哨兵即解决数据结构中的边界问题
例:给定字符key,在数组中查找该key,若有,返回相应的位置,反之,返回false
不用「哨兵」:
function findKeyLocaltion(array,arrayLength,key) {
//边界处理
if(!array&&arrayLength<=0) return false
let i=0
while(iwhile循环每次都要判断key与数组中的item是否相等,当数据量大时,会非常耗时。
使用「哨兵」:
《数据结构与算法之美》举的例子可读性差,我给简化了下
//哨兵处理
function findKeyLocaltion2(array,arrayLength,key) {
//边界处理
if(!array&&arrayLength<=0) return false
array.push(key)
let i=0
while(array[i]!==key){
++i
}
array.pop()
if(i===arrayLength){
return false
}
return i
}
4、检查链表代码是否正确的几大条件
(1)当链表为空时,代码是否正常工作?
(2)当链表只包含一个结点时,代码是否正常工作?
(3)当链表只包含两个结点时,代码是否正常工作?
(4)在处理链表的头结点和尾结点的时候,代码是否能正常工作?
5、头节点
head节点即哨兵,作用就是使所有链表,包括空链表的头节点不为null,并使对单链表的插入、删除操作不需要区分是否为空表或是否在第一个位置进行,从而与其他位置的插入、删除操作一致。
6、单链表反转
一定要看注释!思路全在注释里!
//反转单链表
//尾插法
reverseList(){
//head节点即哨兵,作用就是使所有链表,
// 包括空链表的头节点不为null,并使对单链表的插入、
//删除操作不需要区分是否为空表或是否在第一个位置进行,
// 从而与其他位置的插入、删除操作一致
//所以反转链表的时候不需要带上head节点
let currentNode=this.head.next
//第一个节点头结点让其指向null
let previousNode=null
while(currentNode!==null){
// while(currentNode.value!=="three"){
//务必先保留下一节点的指针地址
let nextNode=currentNode.next
//第一次是null
currentNode.next=previousNode
//此时将previousNode赋值为当前节点,
// 那么下次循环的时候,方便下次的currentNode指向previousNode
previousNode=currentNode
//抬走,下一个!
currentNode=nextNode
}
//最后将反转好的链表加上头节点
this.head.next=previousNode
}
6、链表中环的检测
为什么快指针fast要从 this.head.next 开始?
因为如果fast和slow一样,都从this.head开始的话,那么fast从起跑线就慢了一步,从而使得fast与slow的相遇慢了一步,代码执行时间增加了。
//环验证
checkCircle(){
let fast=this.head.next
let slow=this.head
while(fast!==null && fast.next!==null){
fast=fast.next.next
slow=slow.next
if(fast===slow) {
console.log(fast)
return true
}
}
return false
}
7、删除链表倒数第n个结点
//删除倒数第K个节点(位置)
deleteFromEndByIndex(index){
//务必先判断是否是 环链表=========================PR
if(this.checkCircle()) return false
let position=1
//反转链表,那么倒数第三个就是正数第三个
this.reverseList()
let currentNode=this.head.next
while(currentNode!==null && position8、求链表的中间结点
//求中间节点,思想也是快慢指针
findMiddleNode(){
let fast=this.head
let slow=this.head
//如果fast.next.next ===null,
// 就证明它是偶数链表,没有中间节点
while(fast.next!==null && fast.next.next!==null){
fast=fast.next.next
slow=slow.next
}
//偶数链表返回中间偏左的节点
console.log(slow)
return slow
}
9、两个有序的链表合并
这个放到下篇讲,我太累了,明天搞
10、链表完整代码
window.onload=function () {
//链表结点类
class Node{
constructor(value){
//value即当前节点的值
this.value=value
//next即当前节点的指针
this.next=null
}
}
//链表类
class LinkedList{
constructor(){
//初始化,新建头结点
this.head=new Node("head")
}
//根据value查找节点
findNodeByValue(value){
//让指针指向头结点
let currentNode=this.head
while(currentNode!==null && currentNode.value!==value){
//当 当前节点的值不是要找的item时,依次查找下一个节点
currentNode=currentNode.next
}
return currentNode===null?false:currentNode
}
//根据index查找节点
findNodeByIndex(index){
let currentNode=this.head
//查找的位置
let position=0
while(currentNode!==null && position!==index){
currentNode=currentNode.next
position++
}
return currentNode===null?false:currentNode
}
//在指定节点后方插入新节点
insertBehind(newValue,value){
let currentNode = this.findNodeByValue(value)
if(!currentNode){
console.log("指定节点不存在,请重新选择!")
return false
}
let newNode=new Node(newValue)
//插入节点,务必先调整后一节点的指针
newNode.next=currentNode.next
currentNode.next=newNode
}
//查找指定节点的前一个节点
findPreNode(value){
let currentNode=this.head
if(currentNode!==null && currentNode.next!==null && currentNode.next.value !== value){
currentNode=currentNode.next
}else if(currentNode.next === null){
console.log("未找到指定节点,请重新赋值!")
return false
}
return currentNode
}
//删除指定节点
deleteNode(value){
let deleteNode=this.findNodeByValue(value)
if(!deleteNode){
console.log("指定删除的节点不存在,请重新赋值!")
return false
}
let previousNode=this.findPreNode(value)
previousNode.next=deleteNode.next
}
//遍历并打印所有节点
showAllNode(){
//务必先检查是否为环========================PR
if(this.checkCircle()) return false
let currentNode=this.head
while(currentNode!==null){
console.log(currentNode.value)
currentNode=currentNode.next
}
}
//反转单链表
//尾插法==================================PR
reverseList(){
//head节点即哨兵,作用就是使所有链表,
// 包括空链表的头节点不为null,并使对单链表的插入、删除操作不需要区分是否为空表或是否在第一个位置进行,
// 从而与其他位置的插入、删除操作一致
//所以反转链表的时候不需要带上head节点
let currentNode=this.head.next
//第一个节点头结点让其指向null
let previousNode=null
while(currentNode!==null){
// while(currentNode.value!=="three"){
//务必先保留下一节点的指针地址
let nextNode=currentNode.next
//第一次是null
currentNode.next=previousNode
//此时将previousNode赋值为当前节点,
// 那么下次循环的时候,方便下次的currentNode指向previousNode
previousNode=currentNode
//抬走,下一个!
currentNode=nextNode
}
//最后将反转好的链表加上头节点
this.head.next=previousNode
}
//环验证
checkCircle(){
let fast=this.head.next
let slow=this.head
while(fast!==null && fast.next!==null){
fast=fast.next.next
slow=slow.next
if(fast===slow) {
console.log(fast)
return true
}
}
return false
}
//删除倒数第K个节点(位置)
deleteFromEndByIndex(index){
//务必先判断是否是 环链表=========================PR
if(this.checkCircle()) return false
let position=1
//反转链表,那么倒数第三个就是正数第三个
this.reverseList()
let currentNode=this.head.next
while(currentNode!==null && position(完)