进程间通信系列
AIDL的入门使用(一)
AIDL的入门使用(二)
AIDL的入门使用(三)
Messenger的入门使用
目录
序言
什么概念都省了,直接看怎么使用,主要分两部分,一个是服务端,一个是客户端。更多使用请持续关注。
AIDL通信的服务端
1、创建AIDL 的服务端的Moudle ;
2、在aidl包下创建需要传递的对象Book类,并实现Parcelable 接口(使用Android Studio 的Parcelable 接口生成插件)
package com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
/**
* Created by yuxue on 2017/11/28.
*/
public class Book implements Parcelable {
public int id;
public String name;
public double price;
//省略set 、get、构造、toString等方法
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeInt(this.id);
dest.writeString(this.name);
dest.writeDouble(this.price);
}
public Book() {
}
protected Book(Parcel in) {
this.id = in.readInt();
this.name = in.readString();
this.price = in.readDouble();
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator() {
@Override
public Book createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
return new Book(source);
}
@Override
public Book[] newArray(int size) {
return new Book[size];
}
};
}
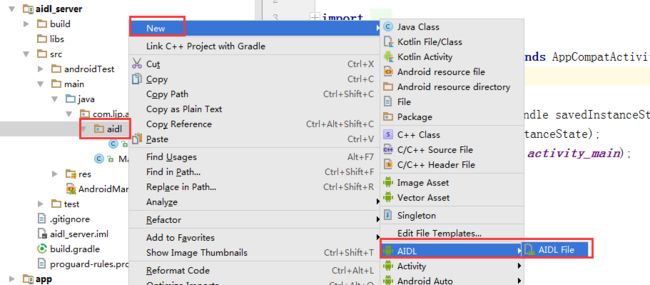
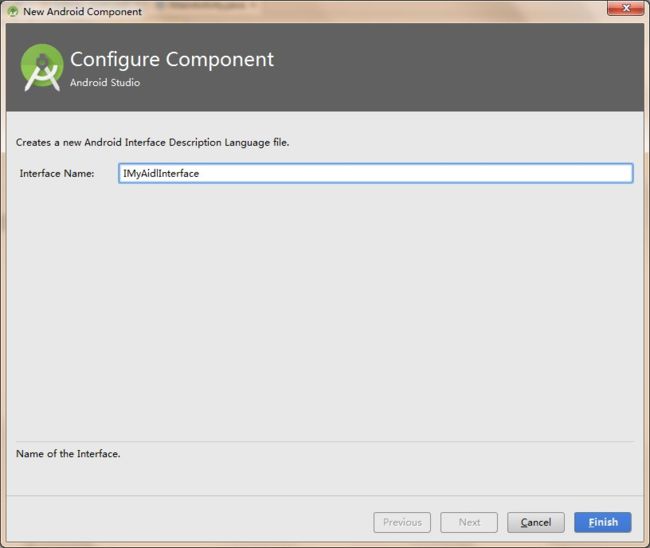
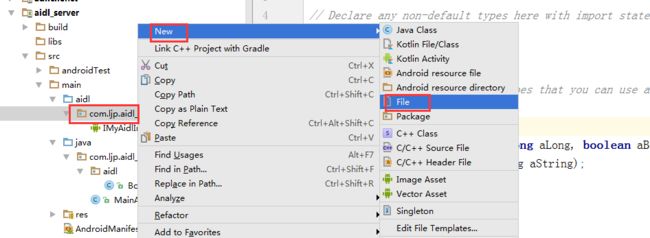
3、鼠标右键单击aidl包——>new ——>AIDL——>AIDL File——>输入接口名称:IMyAidlInterface——>Finish
//Book.aidl文件
package com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl;//在这里一定要标注包名,与 IMyAidlInterface.aidl文件中的包名相同,否则编译报错
//注意 parcelable的p字母是小写 ,声明已序列化的类
parcelable Book;
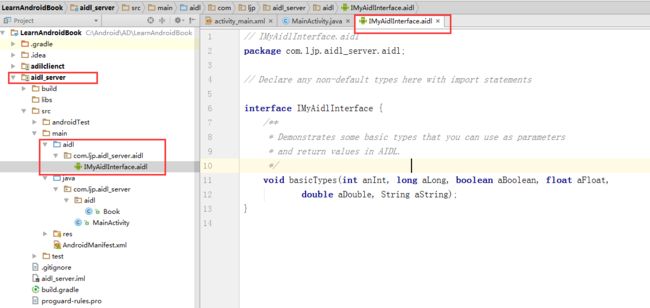
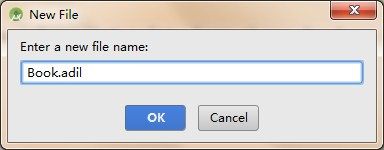
4、在新生成的aidl包上鼠标右键新建文件要传递的类名.adil文件,这里要传递的对象为Book类,因此新建Book.aidl,在Book.aidl文件中声明包名和已序列化对应的类。
5、编写IMyAidlInterface.aidl文件,声明客户端调用AIDL的接口,编写好IMyAidlInterface.aidl文件以后 Build——>Make Project(一定要先Make Project以后编译器才不会报错)
// IMyAidlInterface.aidl
package com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
import com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.Book;//虽然在同一个包中,但还是要进行导包操作,否则会报错。
interface IMyAidlInterface {
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat,
double aDouble, String aString);
//编写客户端可以调用的AIDL接口,
void addBook(in Book book);//一定要加 in
List getBooks();
void setTag(in String tag);
String getTag();
void setNum(in int num);
int getNum();
}
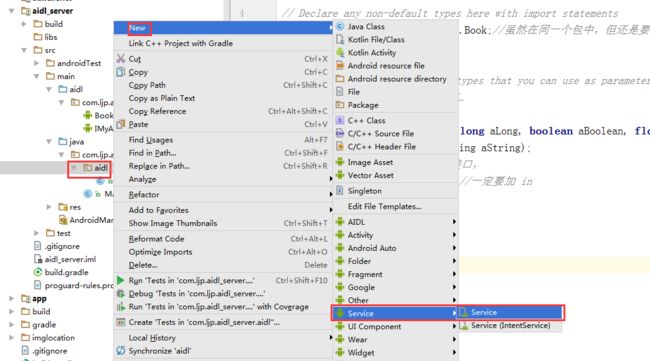
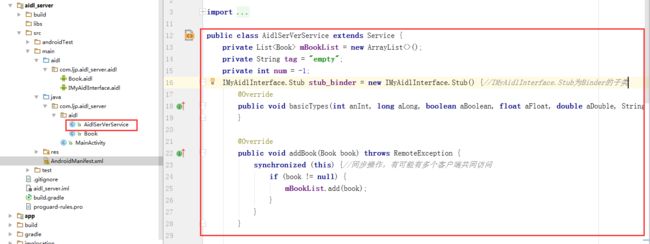
6、创建服务端的Service并编写内容,右键单击aidl包——>New ——> Service——> Service——>输入文件名AidlSerVerService,创建IMyAidlInterface.Stub的对象并在onBind方法中返回。(注:IMyAidlInterface.java文件有编译器在Make Project 过程中自动生成,即我们可以不编写前面的aidl文件,只需要编写IMyAidlInterface.java文件也是可以进行进程间通信的)
package com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class AidlSerVerService extends Service {
private List mBookList = new ArrayList<>();
private String tag = "empty";
private int num = -1;
IMyAidlInterface.Stub stub_binder = new IMyAidlInterface.Stub() {//IMyAidlInterface.Stub实际为android.os.Binder 的子类并实现了com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.IMyAidlInterface接口
@Override
public void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, String aString) throws RemoteException {
}
@Override
public void addBook(Book book) throws RemoteException {
synchronized (this) {//同步操作,有可能有多个客户端共同访问
if (book != null) {
mBookList.add(book);
}
}
}
@Override
public List getBooks() throws RemoteException {
return mBookList;
}
@Override
public void setTag(String tag) throws RemoteException {
synchronized (this) {
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(tag)) {
AidlSerVerService.this.tag = tag;
}
}
}
@Override
public String getTag() throws RemoteException {
return tag;
}
@Override
public void setNum(int num) throws RemoteException {
synchronized (this) {
AidlSerVerService.this.num = num;
}
}
@Override
public int getNum() throws RemoteException {
return num;
}
};
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
return stub_binder;
}
}
7、在AndroidMainfest文件中注册服务端的Service并对外暴露,至此服务端的代码就编写完成了。
AIDL通信的客户端
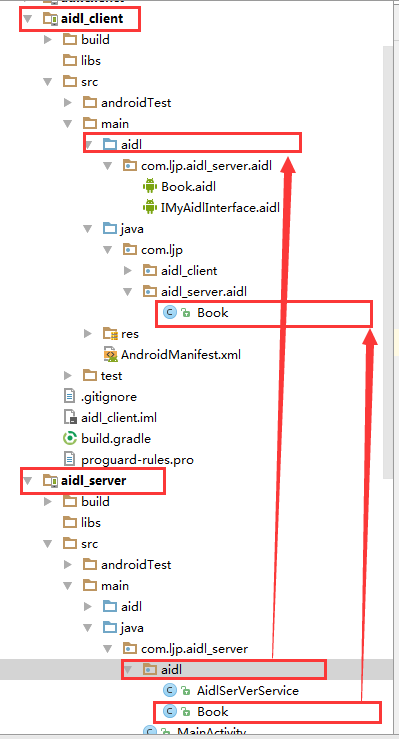
1、将服务端 main文件夹下的aidl文件夹复制到客户端的main文件夹下,将服务端的Book类复制到客户端的对应包名下,然后Build——>Make Project ;
2、测试调用服务端的AIDL接口进行通信;
package com.ljp.aidl_client;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.Book;
import com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.IMyAidlInterface;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
private IMyAidlInterface mService_face;
private static final String TAG = "Main_Client";
ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
Log.e(TAG, "onServiceConnected: ");
mService_face = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Log.e(TAG, "onServiceDisconnected: ");
}
};
public void bindAidlService(View view) {
Intent intent_service = new Intent();
intent_service.setPackage("com.ljp.aidl_server"); //设置需要绑定的服务端的包名,不是服务端Service的包名
intent_service.setAction("server.aidl.service.action");//设置你所需调用服务的意图
boolean successful = bindService(intent_service, mConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
Log.e(TAG, "bindAidlService: successful=" + successful);
}
public void UnbindAidlService(View view) {
if(mConnection!=null){
unbindService(mConnection);
Log.e(TAG, "UnbindAidlService: ");
}
}
public void addBook_AidlService(View view) {
try {
if (mService_face != null) {
mService_face.addBook(new Book(0, "book0", 30.5));
Log.e(TAG, "addBook_AidlService: ");
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void getBooks_AidlService(View view) {
try {
if (mService_face != null) {
List books = mService_face.getBooks();
Log.e(TAG, "addBook_AidlService: books[0]=" + books.get(0));
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void setTag_AidlService(View view) {
try {
if (mService_face != null) {
mService_face.setTag("setTag_AidlService");
Log.e(TAG, "setTag_AidlService: ");
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void getTag_AidlService(View view) {
try {
if (mService_face != null) {
String tag = mService_face.getTag();
Log.e(TAG, "getTag_AidlService: tag=" + tag);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void setNum_AidlService(View view) {
try {
if (mService_face != null) {
mService_face.setNum(27);
Log.e(TAG, "setNum_AidlService: ");
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void getNum_AidlService(View view) {
try {
if (mService_face != null) {
int num = mService_face.getNum();
Log.e(TAG, "getNum_AidlService: num=" + num);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
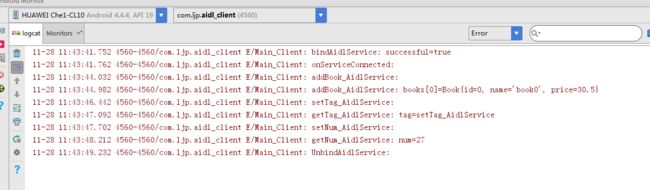
测试结果如下:
IMyAidlInterface.java 文件详解,实际有用的是这个文件,有编写的aidl文件经过编译器自动生成(注:可以单独编写该文件那就不需要aidl文件了)
package com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl;
public interface IMyAidlInterface extends android.os.IInterface {
/**
* Stub是存根,Proxy是代理,Stub是服务端实现的存根,而Proxy则是Stub的代理。
* Local-side IPC implementation stub class.
*/
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.IMyAidlInterface {
//Binder的唯一标识,一般使用类名标识
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.IMyAidlInterface";
/**
* Construct the stub at attach it to the interface.
*/
public Stub() {
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
/**
* 将服务端的Binder对象转换为客户端需要的AIDL接口类型的对象,
* 如果在同一个进程下的话,那么asInterface()将返回服务端的Stub对象本身,因为此时根本不需要跨进称通信,那么直接调用Stub对象的接口就可以了,返回的实现就是服务端的Stub实现,也就是根本没有跨进程通信;
* 如果不是同一个进程,那么asInterface()返回是Stub.Proxy对象,该对象持有着远程的Binder引用(服务端),因为现在需要跨进程通信,所以如果调用Stub.Proxy的接口的话,那么它们都将是IPC调用,它会通过调用Stub.Proxy的transact方法去与服务端通信
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.IMyAidlInterface interface,generating a proxy if needed.
*
* @param obj
* @return 若位于同一进程中则返回的是服务端的Stub对象本身,否则返回的是系统封装后的Stub.Proxy对象
*/
public static com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.IMyAidlInterface asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.IMyAidlInterface))) {
return ((com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.IMyAidlInterface) iin);
}
return new com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
/**
* 返回当前的Binder对象,在客户端连接成功时使用:IMyAidlInterface iMyAidlInterface = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
* 检索与此接口相关联的绑定器对象。您必须使用这个而不是普通的cast,这样代理对象才能返回正确的结果。
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return this;
}
/**
* 运行在服务端的Binder线程池中,当客户端发起跨进程请求时,远程请求会通过底层封装后交由此方法处理
* 默认实现是返回false的存根。您将希望覆盖此操作,以完成事务的适当解组。 如果你想调用这个,调用交易()。
*
* @param code
* @param data
* @param reply
* @param flags
* @return 如果返回false客户端就会请求失败可用作权限验证
* @throws android.os.RemoteException
*/
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: {
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_basicTypes: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
int _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readInt();
long _arg1;
_arg1 = data.readLong();
boolean _arg2;
_arg2 = (0 != data.readInt());
float _arg3;
_arg3 = data.readFloat();
double _arg4;
_arg4 = data.readDouble();
java.lang.String _arg5;
_arg5 = data.readString();
this.basicTypes(_arg0, _arg1, _arg2, _arg3, _arg4, _arg5);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_addBook: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.Book _arg0;
if ((0 != data.readInt())) {
_arg0 = com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.Book.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);//调用Book类中的Parcelable的工厂方法生成一个Book对象,下同
} else {
_arg0 = null;
}
this.addBook(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_getBooks: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
java.util.List _result = this.getBooks();
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeTypedList(_result);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_setTag: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
java.lang.String _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readString();
this.setTag(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_getTag: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
java.lang.String _result = this.getTag();
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeString(_result);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_setNum: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
int _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readInt();
this.setNum(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_getNum: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
int _result = this.getNum();
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(_result);
return true;
}
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
/**
* 一个运行在客户端的代理,持有服务端的Binder应用
* Stub是存根,Proxy是代理,Stub是服务端实现的存根,而Proxy则是Stub的代理。
*/
private static class Proxy implements com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.IMyAidlInterface {
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor() {
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
@Override
public void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, java.lang.String aString) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeInt(anInt);
_data.writeLong(aLong);
_data.writeInt(((aBoolean) ? (1) : (0)));
_data.writeFloat(aFloat);
_data.writeDouble(aDouble);
_data.writeString(aString);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_basicTypes, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public void addBook(com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.Book book) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
if ((book != null)) {
_data.writeInt(1);
book.writeToParcel(_data, 0);
} else {
_data.writeInt(0);
}
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_addBook, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public java.util.List getBooks() throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
java.util.List _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_getBooks, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.createTypedArrayList(com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.Book.CREATOR);
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
@Override
public void setTag(java.lang.String tag) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeString(tag);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_setTag, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public java.lang.String getTag() throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
java.lang.String _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_getTag, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readString();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
@Override
public void setNum(int num) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeInt(num);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_setNum, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public int getNum() throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
int _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_getNum, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readInt();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
}
//声明binder接口的方法的ID,用于标志方法
static final int TRANSACTION_basicTypes = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
static final int TRANSACTION_addBook = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 1);
static final int TRANSACTION_getBooks = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 2);
static final int TRANSACTION_setTag = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 3);
static final int TRANSACTION_getTag = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 4);
static final int TRANSACTION_setNum = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 5);
static final int TRANSACTION_getNum = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 6);
}
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
public void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, java.lang.String aString) throws android.os.RemoteException;
//下面是Binder 通信的接口
public void addBook(com.ljp.aidl_server.aidl.Book book) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public java.util.List getBooks() throws android.os.RemoteException;
public void setTag(java.lang.String tag) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public java.lang.String getTag() throws android.os.RemoteException;
public void setNum(int num) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public int getNum() throws android.os.RemoteException;
}
我的CSDN博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/wo_ha/article/details/78655896