事件传递
一个点击事件产生后,传递顺序是:Activity(Window) -> ViewGroup -> View
事件分发过程由dispatchTouchEvent()、onInterceptTouchEvent()和onTouchEvent()三个方法协助完成。
dispatchTouchEvent()
返回值不同则情况不同。
- 默认情况:根据当前对象的不同而返回方法不同
| 对象 | 返回方法 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| Activity | super.dispatchTouchEvent() | 即调用父类ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent() |
| ViewGroup | onIntercepTouchEvent() | 即调用自身的onIntercepTouchEvent() |
| View | onTouchEvent() | 即调用自身的onTouchEvent() |
- 返回true
- 消费事件
- 事件不会往下传递
- 后续事件(Move、Up)会继续分发到该View
- 返回false
- 不消费事件
- 事件不会往下传递
- 将事件回传给父控件的onTouchEvent()处理.(Activity例外:返回false=消费事件)
- 后续事件(Move、Up)会继续分发到该View(与onTouchEvent()区别)
onTouchEvent()
- 返回true
- 自己处理(消费)该事情
- 事件停止传递
- 该事件序列的后续事件(Move、Up)让其处理;
- 返回false
- 不处理(消费)该事件
- 事件往上传递给父控件的onTouchEvent()处理
- 当前View不再接受此事件列的其他事件(Move、Up);
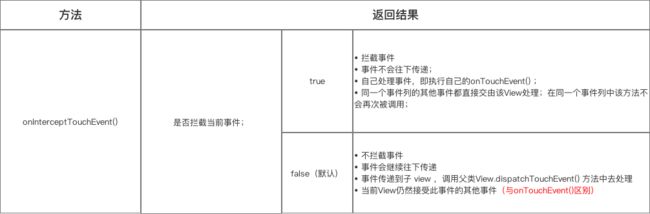
onInterceptTouchEvent
事件分发机制源码分析
Activity 事件分发机制
从上面分析可以知道,当点击屏幕上的一个事件,首先处理的是Activity。由Activity的dispatchTouchEvent()方法首先拦截。而Activity真正执行事件的是Window。
Activity的dispatchTouchEvent方法。
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
//当按钮事件是ACTION_DOWN时候执行,一般我们的事件都是按下开始的,所以这里是true。
if (ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
//空方法,无实现.
onUserInteraction();
}
//getWindow将获取PhoneWindow对象。这里调用的是PhoneWindow的superDispatchTouchEvent
if (getWindow().superDispatchTouchEvent(ev)) {
return true;
}
return onTouchEvent(ev);
}
首先判断if(ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) ,一般我们事件都是从按下屏幕开始的,也就是说事件一般情况下都是从ACTION_DOWN开始,所以这里返回true。
-
返回ture之后执行onUserInteraction():
/** * Called whenever a key, touch, or trackball event is dispatched to the * activity. Implement this method if you wish to know that the user has * interacted with the device in some way while your activity is running. * This callback and {@link #onUserLeaveHint} are intended to help * activities manage status bar notifications intelligently; specifically, * for helping activities determine the proper time to cancel a notfication. * *All calls to your activity's {@link #onUserLeaveHint} callback will * be accompanied by calls to {@link #onUserInteraction}. This * ensures that your activity will be told of relevant user activity such * as pulling down the notification pane and touching an item there. * *
Note that this callback will be invoked for the touch down action * that begins a touch gesture, but may not be invoked for the touch-moved * and touch-up actions that follow. * * @see #onUserLeaveHint() */ public void onUserInteraction() { }
onUserInteraction是一个空方法。从注释中可以看出,如果想知道当前Activity中用户和设备进行某种交互,你就要重写该方法。也就是说当Activity处于栈顶的时候,用户的按键操作(home,menu,back等)都会触发改方法。
-
getWindow().superDispatchTouchEvent(ev):
首先getWindow()返回的是一个Window对象,我们知道Android中Window是一个抽象类,也就是说真正的实现在它的子类里面,而Window的子类只有一个就是大名鼎鼎的PhoneWindow。
-
也就是说这里实际调用的是PhoneWindow的superDispatchTouchEvent。
PhoneWindow的superDispatchTouchEvent
@Override
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
return mDecor.superDispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
这里返回的是mDecor.superDispatchTouchEvent(event),而mDecor是DecorView的对象。DecorView又是Android 的根视图对象,也就是顶层视图。
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
DecorView中又执行super.dispatchTouchEvent(event),我们知道DecorView继承于FrameLayout,属于一个ViewGroup。也就是执行了ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent()方法。
总结:
- 到这里我们可以知道Activity.dispatchTouchEvent()经过调用最后调用的是ViewGroup.dispatchTouchEvent().
- Activity.dispatchTouchEvent()如果自定义返回true或者false,改事件都将结束。
- 这样调用之后事件将进入ViewGroup中去。
汇总:当一个点击事件发生时,调用顺序如下
- 事件最先传到Activity的dispatchTouchEvent()进行事件分发
- 调用Window类实现类PhoneWindow的superDispatchTouchEvent()
- 调用DecorView的superDispatchTouchEvent()
- 最终调用DecorView父类的dispatchTouchEvent(),即ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent()
ViwGroup事件分发机制
ViwGroup dispatchTouchEvent方法
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
...
//处理结果.
boolean handled = false;
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(ev)) {
final int action = ev.getAction();
final int actionMasked = action & MotionEvent.ACTION_MASK;
...
// Check for interception.
//注意1:用于判断是否拦截,即interception。
final boolean intercepted;
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| mFirstTouchTarget != null) {
//是否设置不拦截
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0;
if (!disallowIntercept) {
//执行onInterceptTouchEvent方法.
intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed
} else {
intercepted = false;
}
} else {
// There are no touch targets and this action is not an initial down
// so this view group continues to intercept touches.
intercepted = true;
}
// If intercepted, start normal event dispatch. Also if there is already
// a view that is handling the gesture, do normal event dispatch.
//如果intercepted拦截
if (intercepted || mFirstTouchTarget != null) {
ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
}
...
//如果intercepted 返回true,则不会进入这个条件。即没有取消,并且拦截了
if (!canceled && !intercepted) {
// If the event is targeting accessiiblity focus we give it to the
// view that has accessibility focus and if it does not handle it
// we clear the flag and dispatch the event to all children as usual.
// We are looking up the accessibility focused host to avoid keeping
// state since these events are very rare.
//大致意思是如果设置拦截,则子ViewGroup等将不处理。
View childWithAccessibilityFocus = ev.isTargetAccessibilityFocus()
? findChildWithAccessibilityFocus() : null;
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN)
|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) {
...
final int childrenCount = mChildrenCount;
//当有有child的时候
if (newTouchTarget == null && childrenCount != 0) {
final float x = ev.getX(actionIndex);
final float y = ev.getY(actionIndex);
// Find a child that can receive the event.
// Scan children from front to back.
//查询一个可以接收该事件的Child
final ArrayList preorderedList = buildOrderedChildList();
final boolean customOrder = preorderedList == null
&& isChildrenDrawingOrderEnabled();
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final int childIndex = customOrder
? getChildDrawingOrder(childrenCount, i) : i;
final View child = (preorderedList == null)
? children[childIndex] : preorderedList.get(childIndex);
...
//注意2:传入的child有值,将执行child.dispatchTouchEvent(event)
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) {
// Child wants to receive touch within its bounds.
//child 想要去接收在这个范围内的touch
mLastTouchDownTime = ev.getDownTime();
if (preorderedList != null) {
// childIndex points into presorted list, find original index
for (int j = 0; j < childrenCount; j++) {
if (children[childIndex] == mChildren[j]) {
mLastTouchDownIndex = j;
break;
}
}
} else {
mLastTouchDownIndex = childIndex;
}
mLastTouchDownX = ev.getX();
mLastTouchDownY = ev.getY();
newTouchTarget = addTouchTarget(child, idBitsToAssign);
alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = true;
break;
}
...
}
if (preorderedList != null) preorderedList.clear();
}
...
}
}
// Dispatch to touch targets.
if (mFirstTouchTarget == null) {
// No touch targets so treat this as an ordinary view.
//注意3:如果拦截了,则这个child为空,则会调用super.dispatchTouchEvent(event),从而执行onTouchEvent().
handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null,
TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS);
} else {
...
}
...
}
if (!handled && mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(ev, 1);
}
return handled;
}
-
注意1:判断是否拦截。
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { return false; }默认返回false,表示不拦截,则!intercepted为true进入条件语句,关注注意点2,如果ViewGroup重写该方法并返回true,则不会进入条件判断,则直接关注注意点3.
注意2:当ViewGroup不拦截的时候,则会遍历ViewGroup的Child,取得一个可接受到事件的子View通过调用dispatchTransformedTouchEvent去执行child.dispatchTouchEvent(event)。
-
注意3:如果ViewGroup拦截了,则直接dispatchTransformedTouchEvent 中的super.dispatchTouchEvent(event),则会执行View的dispatchTouchEvent中的onTouch方法,也就是执行改ViewGroup的onTouch方法。
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel, View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) { final boolean handled; // Canceling motions is a special case. We don't need to perform any transformations // or filtering. The important part is the action, not the contents. final int oldAction = event.getAction(); if (cancel || oldAction == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL) { event.setAction(MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL); if (child == null) { handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event); } else { handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event); } event.setAction(oldAction); return handled; } ... if (newPointerIdBits == oldPointerIdBits) { if (child == null || child.hasIdentityMatrix()) { if (child == null) { handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event); } else { final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft; final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop; event.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY); handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event); event.offsetLocation(-offsetX, -offsetY); } return handled; } transformedEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(event); } else { transformedEvent = event.split(newPointerIdBits); } ... return handled; }结论
- Android事件分发是先传递到ViewGroup,再由ViewGroup传递到View
- 在ViewGroup中通过onInterceptTouchEvent()对事件传递进行拦截:
- onInterceptTouchEvent方法返回true代表拦截事件,即不允许事件继续向子View传递;
- 返回false代表不拦截事件,即允许事件继续向子View传递;(默认返回false)
- 子View中如果将传递的事件消费掉,ViewGroup中将无法接收到任何事件。
View 事件分发机制
View dispatchTouchEvent
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
...
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
//满足这3个条件,result才返回true。
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
//如果result 为true则不会执行onTouchEvent()。
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
}
...
return result;
}
这里如果想要执行onTouchEvent(),则必须让result为true,而result为true需满足3个条件。
-
li.mOnTouchListener != null: mOnTouchListener 事件不能为空:mOnTouchListener 事件是在setOnTouchListener方法里面设置:
public void setOnTouchListener(OnTouchListener l) { getListenerInfo().mOnTouchListener = l; }也就是说必须在View中设置setOnTouchListener(l)事件。
(mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED: 控件必须是enable,view默认的是true。
-
li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event): onTouch方法的返回值。
- onTouch 返回true时,就会让上述三个条件全部成立,从而整个方法直接返回true。则不会执行onTouchEvent().
- onTouch 返回false时,则会执行onTouchEvent().
回调控件注册Touch事件时的onTouch方法
//手动调用设置 button.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() { @Override public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) { return false; } });