C语言中,在编译期,函数的调用就会决定调用哪个函数,而OC的函数,属于动态调用过程,在编译期并不能决定真正调用哪个函数,只有在真正运行时才会根据函数的名称找到对应的函数来调用,我们写的代码在程序运行过程中都会被转化成runtime的C代码执行,例如[target doSomething];会被转化成objc_msgSend(target, @selector(doSomething)),调用方法其实就是给对象发送消息。
一、对象、类、元类
OC中一切都被设计成了对象,一个类被初始化成一个实例,这个实例是一个对象。objc_class继承于objc_object,所以类也是一个对象。
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
typedef struct objc_object *id;
@interface Object{
Class isa;
}
@interface NSObject {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
}
structobjc_object {
private:
isa_t isa;
}
struct objc_class : objc_object {
// Class ISA;
Class superclass;
cache_t cache;//
formerly cache pointer and vtable
class_data_bits_t bits;// class_rw_t * plus custom
rr/alloc flags
}
unionisa_t
{
isa_t() { }
isa_t(uintptr_t value) : bits(value) { }
Class cls;
uintptr_t bits;
}
当一个对象的实例方法被调用的时候,会通过isa找到相应的类,然后在该类的class_data_bits_t中去查找方法。class_data_bits_t是指向了类对象的数据区域。在该数据区域内查找相应方法的对应实现
类对象的类方法调用时,通过类的isa在元类中获取方法的实现。
meta-class存储着一个类的所有类方法。每个类都会有一个单独的meta-class,因为每个类的类方法基本不可能完全相同。
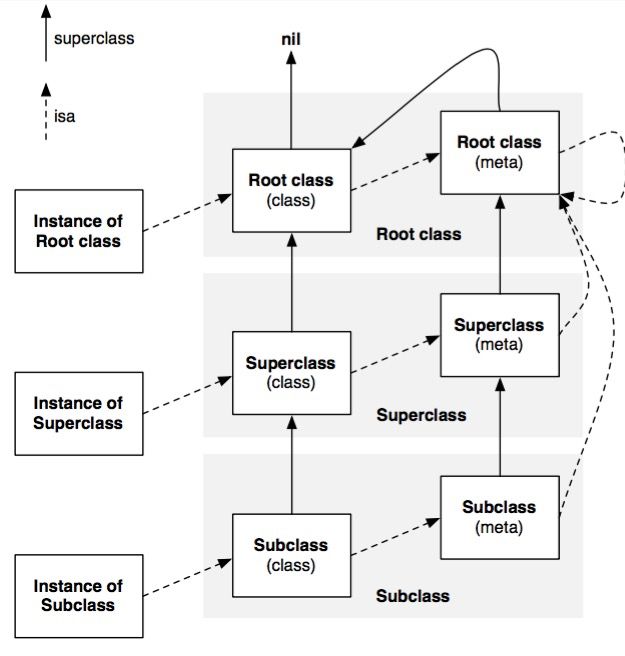
实线是super_class指针,虚线是isa指针
Root class (class)其实就是NSObject,NSObject是没有超类的,所以Root class(class)的superclass指向nil。
每个Class都有一个isa指针指向唯一的Meta class
Root class(meta)的superclass指向Root class(class),也就是NSObject,形成一个回路
每个Meta class的isa指针都指向Root class (meta)
二、获取类的信息
//获取属性列表class_copyPropertyList([self class], &count);
//获取方法列表
class_copyMethodList([self class], &count);
//获取成员变量列表
class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
//获取协议列表
class_copyProtocolList([self class], &count);
1、自动归档解档
获取类的成员变量列表,把变量名称当做key值进行归档解档
2、字典转模型
获取模型类的属性列表,根据属性字符串去字典里边取值,利用KVC赋值
三、关联对象
分类不能添加属性,因为添加了@property之后并不会自动帮我们生成实例变量以及存取方法,我们可以通过关联对象来给分类添加属性
- (void)setAssociatedObject:(id)associatedObject {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self,AssociatedKey, associatedObject, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
- (id)associatedObject {
returnobjc_getAssociatedObject(self, AssociatedKey);
}
objc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key,id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy)
id object给谁设置关联对象
const void *key关联对象唯一的key,获取时会用到
id value关联对象
objc_AssociationPolicy关联策略
四、动态加载方法
我们知道发送消息是通过objc_msgSend(id, SEL, ...)来实现的,首先通过对象的isa指针找到对象所在的类,在Class中先去cache中通过SEL查找对应函数method,若cache中未找到,再去methodList中查找,若methodlist中未找到,则取superClass中查找。若能找到,则将method加入到cache中,以方便下次查找,并通过method中的函数指针跳转到对应的函数中去执行。若是一直查找到根类还是没有找到,就会执行resolveInstanceMethod方法。在这个方法里面,我们可以动态的给类对象或者实例对象动态的增加方法。
1、动态添加实例方法
void dynamicAddressMethod(id self,SEL _cmd) {
NSLog(@"Address --->百子湾");
}
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel{
if(sel ==@selector(address)){
class_addMethod([self class], sel, (IMP)dynamicAddressMethod,"v@:");
returnYES;
}
return[super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}
2、动态添加类方法
void dynamicNameMethod(id self,SEL sel,NSString *n) {
NSLog(@"Name ---> %@",n);
}
+ (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel {
//方法1添加到当前类的元类
ClassmetaClass = objc_getMetaClass(class_getName(self));
if (sel ==@selector(name)) {
class_addMethod(metaClass,sel, (IMP)dynamicNameMethod, "v@:");
returnYES;
}
//方法2添加到NSObject类的元类
//ClassmetaClass = objc_getMetaClass(object_getClassName((id)[NSObject class]));
//if (sel== @selector(name)) {
//class_addMethod(metaClass,sel, (IMP)dynamicNameMethod, "v@:@");
//return YES;
//}
////方法3添加到NSObject
//if (sel== @selector(name)) {
//class_addMethod([NSObject class], sel, (IMP)dynamicNameMethod,"v@:@");
//return YES;
//}
//
return[super resolveClassMethod:sel];
}
六、消息转发
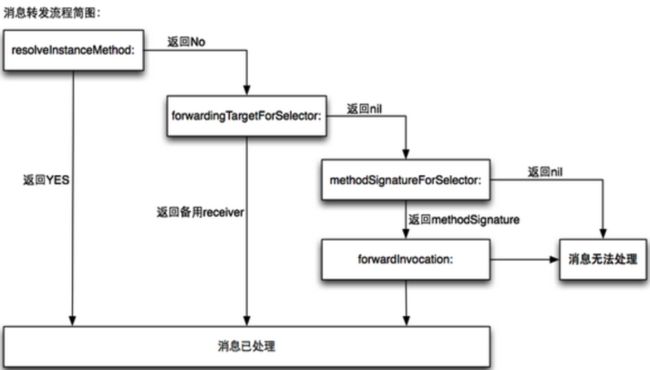
向一个对象发送其无法处理的消息,如果我们在resolve...Method方法里边添加方法,就会执行消息转发
forwardingTargetForSelector可以返回一个可以执行方法的对象
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if(aSelector == @selector(run)){
return[RunMethod new];
}
return[super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
如果我们不实现forwardingTargetForSelector,就会调用methodSignatureForSelector和forwardInvocation
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
NSLog(@"对象方法方法签名");
if(aSelector == @selector(run)) {
return[NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v@:"];
}
return[super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
关于生成签名的类型"v@:",每一个方法会默认隐藏两个参数,self、_cmd,self代表方法调用者,_cmd代表这个方法的SEL,签名类型就是用来描述这个方法的返回值、参数的,v代表返回值为void,@表示self,:表示_cmd。
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation*)anInvocation {
//自定义转发逻辑1
SEL sel =anInvocation.selector;
RunMethod*runM = [RunMethod new];
if ([runM respondsToSelector:sel]){
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:runM];
}else {
[superforwardInvocation:anInvocation];
}
////自定义转发逻辑2
////在这里可以改变方法选择器
//[anInvocation setSelector:@selector(unknown)];
////改变方法选择器后,需要指定消息的接收者
//[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:self];
//[anInvocation setSelector:@selector(run)];
//[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[RunMethod new]];
}
七、方法交换
Method one = class_getInstanceMethod([Method_1
class], @selector(eat));
Method two = class_getInstanceMethod([Mehtod_2class], @selector(eat));
method_exchangeImplementations(one, two);
Method_1 *onem = [[Method_1 alloc]init];
[onem eat];
Mehtod_2 *twom = [[Mehtod_2 alloc]init];
[twom eat];
页面统计:
@implementation UIViewController (statistics)
+load会在类初始加载时调用,+initialize方法是以懒加载的方式被调用的,如果程序一直没有给某个类或它的子类发送消息,那么这个类的+initialize方法是永远不会被调用的
+ (void)load {
MethodoriginalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod([self class],@selector(viewWillAppear:));
Method swizzledMethod= class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(statistics_viewWillAppear:));
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
- (void)statistics_viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated {
NSString*pageName = NSStringFromClass([self class]);
NSLog(@"pageName = %@",pageName);
[selfstatistics_viewWillAppear:animated];
}
- (void)statistics_viewWillDisappear:(BOOL)animated {
[selfstatistics_viewWillDisappear:animated];
}
@end