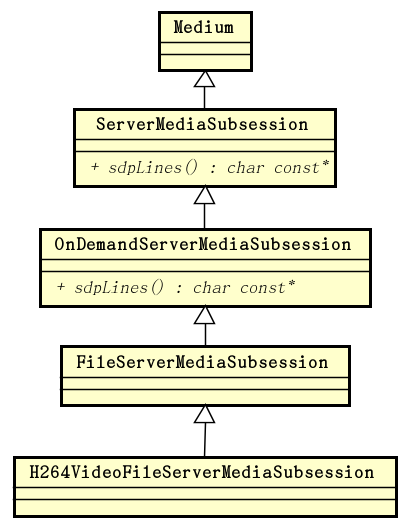
如我们在前文 live555 源码分析:ServerMediaSession 中看到的,H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession 的继承层次体系如下图:
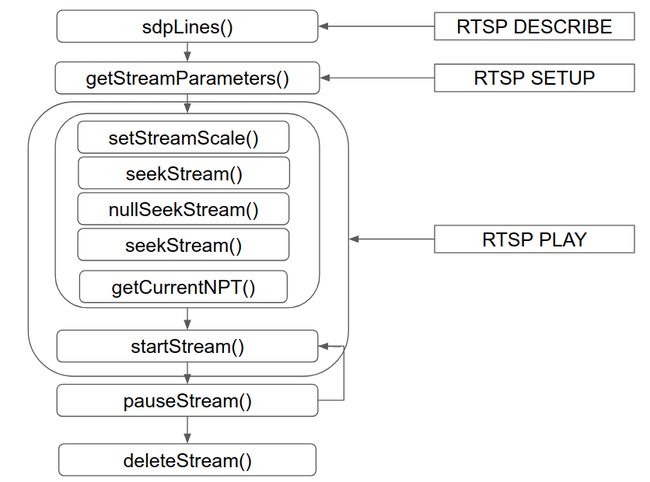
在这个继承层次体系中,ServerMediaSubsession 定义了可以对流媒体的单个子会话执行的操作,它有着如下这样的生命周期:
对于这些操作的实现则是由 OnDemandServerMediaSubsession 完成的,本文分析这个类的定义和实现。
我们再来看一下产生 SDP 消息行的 sdpLines(),它在处理 RTSP DESCRIBE 消息时会用到:
char const*
OnDemandServerMediaSubsession::sdpLines() {
if (fSDPLines == NULL) {
// We need to construct a set of SDP lines that describe this
// subsession (as a unicast stream). To do so, we first create
// dummy (unused) source and "RTPSink" objects,
// whose parameters we use for the SDP lines:
unsigned estBitrate;
FramedSource* inputSource = createNewStreamSource(0, estBitrate);
if (inputSource == NULL) return NULL; // file not found
struct in_addr dummyAddr;
dummyAddr.s_addr = 0;
Groupsock* dummyGroupsock = createGroupsock(dummyAddr, 0);
unsigned char rtpPayloadType = 96 + trackNumber()-1; // if dynamic
RTPSink* dummyRTPSink = createNewRTPSink(dummyGroupsock, rtpPayloadType, inputSource);
if (dummyRTPSink != NULL && dummyRTPSink->estimatedBitrate() > 0) estBitrate = dummyRTPSink->estimatedBitrate();
setSDPLinesFromRTPSink(dummyRTPSink, inputSource, estBitrate);
Medium::close(dummyRTPSink);
delete dummyGroupsock;
closeStreamSource(inputSource);
}
fprintf(stderr, "OnDemandServerMediaSubsession::sdpLines(): %s\n", fSDPLines);
return fSDPLines;
}
这个函数执行的步骤如下:
第 1 步,调用 createNewStreamSource() 函数,创建 FramedSource。createNewStreamSource() 函数在 H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession 中定义:
FramedSource* H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession::createNewStreamSource(unsigned /*clientSessionId*/, unsigned& estBitrate) {
estBitrate = 500; // kbps, estimate
// Create the video source:
ByteStreamFileSource* fileSource = ByteStreamFileSource::createNew(envir(), fFileName);
if (fileSource == NULL) return NULL;
fFileSize = fileSource->fileSize();
// Create a framer for the Video Elementary Stream:
return H264VideoStreamFramer::createNew(envir(), fileSource);
}
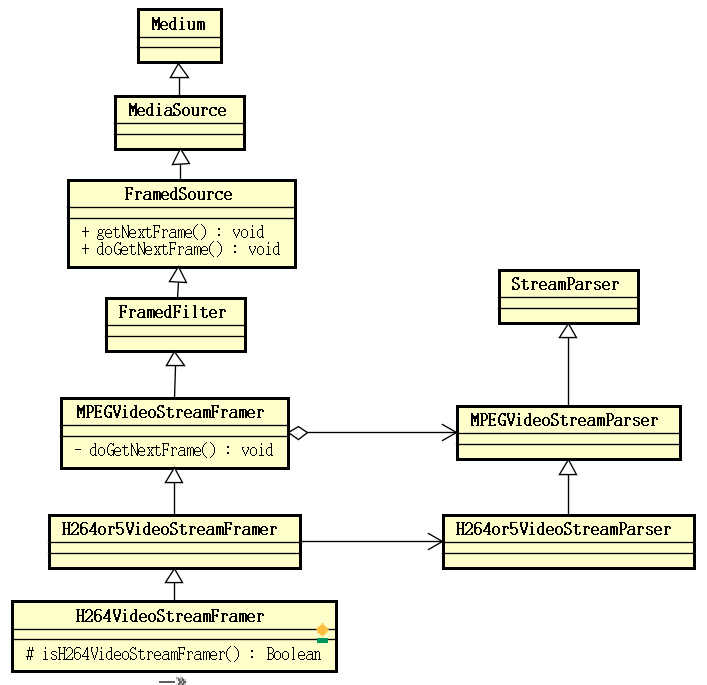
返回的 FramedSource 为 ByteStreamFileSource。FramedSource 用于获取视频流中的单个帧,它有着如下这样的继承层次结构:
第 2 步,调用 createGroupsock() 函数创建 Groupsock。
Groupsock* OnDemandServerMediaSubsession
::createGroupsock(struct in_addr const& addr, Port port) {
fprintf(stderr, "OnDemandServerMediaSubsession::createGroupsock().\n");
// Default implementation; may be redefined by subclasses:
return new Groupsock(envir(), addr, port, 255);
}
第 3 步,计算 RTP 载荷类型。
第 4 步,调用 createNewRTPSink() 创建 RTPSink,createNewRTPSink() 同样在 H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession 中实现:
RTPSink* H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession
::createNewRTPSink(Groupsock* rtpGroupsock,
unsigned char rtpPayloadTypeIfDynamic,
FramedSource* /*inputSource*/) {
return H264VideoRTPSink::createNew(envir(), rtpGroupsock, rtpPayloadTypeIfDynamic);
}
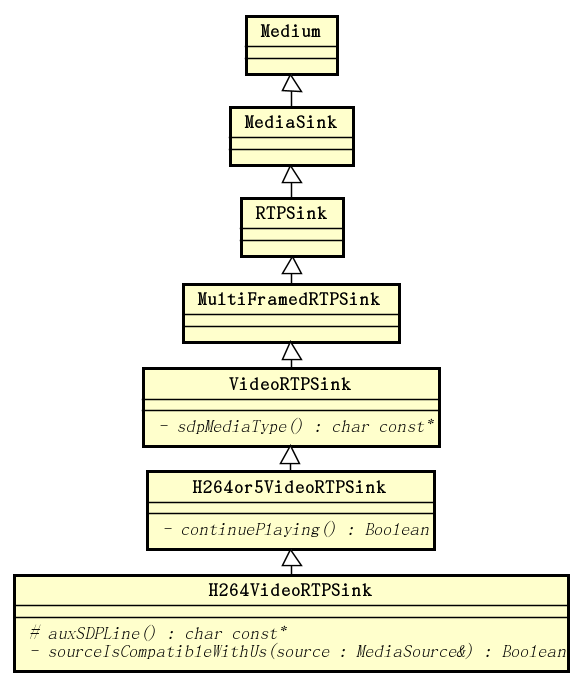
传进来的 FramedSource 并没有被用到。返回的 RTPSink 为 H264VideoRTPSink。H264VideoRTPSink 的继承层次结构如下图所示:
第 5 步,调用 setSDPLinesFromRTPSink() 生成 SDP 行。前面的几步都是在为这一步的执行做准备。这个函数实现如下:
void OnDemandServerMediaSubsession
::setSDPLinesFromRTPSink(RTPSink* rtpSink, FramedSource* inputSource, unsigned estBitrate) {
fprintf(stderr, "OnDemandServerMediaSubsession::setSDPLinesFromRTPSink().\n");
if (rtpSink == NULL) return;
char const* mediaType = rtpSink->sdpMediaType();
unsigned char rtpPayloadType = rtpSink->rtpPayloadType();
AddressString ipAddressStr(fServerAddressForSDP);
char* rtpmapLine = rtpSink->rtpmapLine();
char const* rtcpmuxLine = fMultiplexRTCPWithRTP ? "a=rtcp-mux\r\n" : "";
char const* rangeLine = rangeSDPLine();
char const* auxSDPLine = getAuxSDPLine(rtpSink, inputSource);
if (auxSDPLine == NULL) auxSDPLine = "";
char const* const sdpFmt =
"m=%s %u RTP/AVP %d\r\n"
"c=IN IP4 %s\r\n"
"b=AS:%u\r\n"
"%s"
"%s"
"%s"
"%s"
"a=control:%s\r\n";
unsigned sdpFmtSize = strlen(sdpFmt)
+ strlen(mediaType) + 5 /* max short len */ + 3 /* max char len */
+ strlen(ipAddressStr.val())
+ 20 /* max int len */
+ strlen(rtpmapLine)
+ strlen(rtcpmuxLine)
+ strlen(rangeLine)
+ strlen(auxSDPLine)
+ strlen(trackId());
char* sdpLines = new char[sdpFmtSize];
sprintf(sdpLines, sdpFmt,
mediaType, // m=
fPortNumForSDP, // m=
rtpPayloadType, // m=
ipAddressStr.val(), // c= address
estBitrate, // b=AS:
rtpmapLine, // a=rtpmap:... (if present)
rtcpmuxLine, // a=rtcp-mux:... (if present)
rangeLine, // a=range:... (if present)
auxSDPLine, // optional extra SDP line
trackId()); // a=control:
delete[] (char*) rangeLine; delete[] rtpmapLine;
fSDPLines = strDup(sdpLines);
delete[] sdpLines;
}
在这个函数中,获取生成 SDP 消息所需的数据,然后生成 SDP 消息。mediaType 来自于 VideoRTPSink:
char const* VideoRTPSink::sdpMediaType() const {
return "video";
}
这也是 VideoRTPSink 提供的仅有的功能了。
rtpPayloadType 来自于 RTPSink:
unsigned char rtpPayloadType() const { return fRTPPayloadType; }
前面在 sdpLines() 中计算得到 RTP 载荷类型,在创建 RTPSink 时计算的值会被传递给它。这里返回的正是前面计算得到的值。对于 H.264 视频流,这个值为 96。
map 行来自于 RTPSink:
char* RTPSink::rtpmapLine() const {
if (rtpPayloadType() >= 96) { // the payload format type is dynamic
char* encodingParamsPart;
if (numChannels() != 1) {
encodingParamsPart = new char[1 + 20 /* max int len */];
sprintf(encodingParamsPart, "/%d", numChannels());
} else {
encodingParamsPart = strDup("");
}
char const* const rtpmapFmt = "a=rtpmap:%d %s/%d%s\r\n";
unsigned rtpmapFmtSize = strlen(rtpmapFmt)
+ 3 /* max char len */ + strlen(rtpPayloadFormatName())
+ 20 /* max int len */ + strlen(encodingParamsPart);
char* rtpmapLine = new char[rtpmapFmtSize];
sprintf(rtpmapLine, rtpmapFmt,
rtpPayloadType(), rtpPayloadFormatName(),
rtpTimestampFrequency(), encodingParamsPart);
delete[] encodingParamsPart;
return rtpmapLine;
} else {
// The payload format is staic, so there's no "a=rtpmap:" line:
return strDup("");
}
}
对于 RFC 3551 分配了载荷类型的媒体类型,无需 map 行。对于动态的载荷类型,则需要该行,其中包含了载荷类型、载荷格式名称,时间戳频率等,当通道个数大于 1 时,还包含通道个数。
通道个数来自于 MultiFramedRTPSink:
MultiFramedRTPSink(UsageEnvironment& env,
Groupsock* rtpgs, unsigned char rtpPayloadType,
unsigned rtpTimestampFrequency,
char const* rtpPayloadFormatName,
unsigned numChannels = 1);
载荷格式名称和时间戳频率来自于 H264or5VideoRTPSink,对于 H.264 的视频流而言,载荷格式名称为 "H264",时间戳频率为 90000:
H264or5VideoRTPSink
::H264or5VideoRTPSink(int hNumber,
UsageEnvironment& env, Groupsock* RTPgs, unsigned char rtpPayloadFormat,
u_int8_t const* vps, unsigned vpsSize,
u_int8_t const* sps, unsigned spsSize,
u_int8_t const* pps, unsigned ppsSize)
: VideoRTPSink(env, RTPgs, rtpPayloadFormat, 90000, hNumber == 264 ? "H264" : "H265"),
fHNumber(hNumber), fOurFragmenter(NULL), fFmtpSDPLine(NULL) {
回到 setSDPLinesFromRTPSink()。然后是 range SDP 行,它来自于 ServerMediaSubsession:
char const*
ServerMediaSubsession::rangeSDPLine() const {
// First, check for the special case where we support seeking by 'absolute' time:
char* absStart = NULL; char* absEnd = NULL;
getAbsoluteTimeRange(absStart, absEnd);
if (absStart != NULL) {
char buf[100];
if (absEnd != NULL) {
sprintf(buf, "a=range:clock=%s-%s\r\n", absStart, absEnd);
} else {
sprintf(buf, "a=range:clock=%s-\r\n", absStart);
}
return strDup(buf);
}
if (fParentSession == NULL) return NULL;
// If all of our parent's subsessions have the same duration
// (as indicated by "fParentSession->duration() >= 0"), there's no "a=range:" line:
if (fParentSession->duration() >= 0.0) return strDup("");
// Use our own duration for a "a=range:" line:
float ourDuration = duration();
if (ourDuration == 0.0) {
return strDup("a=range:npt=0-\r\n");
} else {
char buf[100];
sprintf(buf, "a=range:npt=0-%.3f\r\n", ourDuration);
return strDup(buf);
}
}
所需获取的最后的 SDP 信息是 aux SDP 行,这些信息需要从视频流数据中解析获得,通过 H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession 的 getAuxSDPLine() 函数获得:
char const* H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession::getAuxSDPLine(RTPSink* rtpSink, FramedSource* inputSource) {
if (fAuxSDPLine != NULL) return fAuxSDPLine; // it's already been set up (for a previous client)
if (fDummyRTPSink == NULL) { // we're not already setting it up for another, concurrent stream
// Note: For H264 video files, the 'config' information ("profile-level-id" and "sprop-parameter-sets") isn't known
// until we start reading the file. This means that "rtpSink"s "auxSDPLine()" will be NULL initially,
// and we need to start reading data from our file until this changes.
fDummyRTPSink = rtpSink;
// Start reading the file:
fDummyRTPSink->startPlaying(*inputSource, afterPlayingDummy, this);
// Check whether the sink's 'auxSDPLine()' is ready:
checkForAuxSDPLine(this);
}
envir().taskScheduler().doEventLoop(&fDoneFlag);
return fAuxSDPLine;
}
这个函数在首次调用时,会通过 RTPSink 启动对流媒体文件帧数据的读取,即调用 RTPSink 的 startPlaying() 函数。
startPlaying() 函数执行一个长长的调用链,最终调用 ByteStreamFileSource 的 doGetNextFrame() 函数,这个调用栈如下:
#0 ByteStreamFileSource::doGetNextFrame (this=0x6e4f10) at ByteStreamFileSource.cpp:96
#1 0x00000000004308b4 in FramedSource::getNextFrame (this=0x6e4f10, to=0x7ffff7fd1010 "", maxSize=150000,
afterGettingFunc=0x4740c2 ,
afterGettingClientData=0x6e5020, onCloseFunc=0x47424c , onCloseClientData=0x6e5020) at FramedSource.cpp:78
#2 0x0000000000474096 in StreamParser::ensureValidBytes1 (this=0x6e5020, numBytesNeeded=4) at StreamParser.cpp:159
#3 0x0000000000434fe1 in StreamParser::ensureValidBytes (this=0x6e5020, numBytesNeeded=4) at StreamParser.hh:118
#4 0x0000000000434d75 in StreamParser::test4Bytes (this=0x6e5020) at StreamParser.hh:54
#5 0x000000000047918e in H264or5VideoStreamParser::parse (this=0x6e5020) at H264or5VideoStreamFramer.cpp:951
#6 0x0000000000435de9 in MPEGVideoStreamFramer::continueReadProcessing (this=0x6e4710) at MPEGVideoStreamFramer.cpp:159
#7 0x0000000000435d51 in MPEGVideoStreamFramer::doGetNextFrame (this=0x6e4710) at MPEGVideoStreamFramer.cpp:142
#8 0x00000000004308b4 in FramedSource::getNextFrame (this=0x6e4710, to=0x6ff241 "", maxSize=100000,
afterGettingFunc=0x47c788 ,
afterGettingClientData=0x6e5540, onCloseFunc=0x43092e , onCloseClientData=0x6e5540) at FramedSource.cpp:78
#9 0x000000000047c2c0 in H264or5Fragmenter::doGetNextFrame (this=0x6e5540) at H264or5VideoRTPSink.cpp:181
#10 0x00000000004308b4 in FramedSource::getNextFrame (this=0x6e5540, to=0x6e69cc "", maxSize=100452,
afterGettingFunc=0x45d09c ,
afterGettingClientData=0x6e5220, onCloseFunc=0x45da86 , onCloseClientData=0x6e5220) at FramedSource.cpp:78
#11 0x000000000045d07b in MultiFramedRTPSink::packFrame (this=0x6e5220) at MultiFramedRTPSink.cpp:224
#12 0x000000000045cec8 in MultiFramedRTPSink::buildAndSendPacket (this=0x6e5220, isFirstPacket=1 '\001') at MultiFramedRTPSink.cpp:199
#13 0x000000000045cd07 in MultiFramedRTPSink::continuePlaying (this=0x6e5220) at MultiFramedRTPSink.cpp:159
#14 0x000000000047bfe0 in H264or5VideoRTPSink::continuePlaying (this=0x6e5220) at H264or5VideoRTPSink.cpp:127
#15 0x0000000000405d2a in MediaSink::startPlaying (this=0x6e5220, source=..., afterFunc=0x422a12 , afterClientData=0x6e4aa0)
at MediaSink.cpp:78
#16 0x0000000000422c5f in H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession::getAuxSDPLine (this=0x6e4aa0, rtpSink=0x6e5220, inputSource=0x6e4710)
at H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession.cpp:92
#17 0x0000000000464cd4 in OnDemandServerMediaSubsession::setSDPLinesFromRTPSink (this=0x6e4aa0, rtpSink=0x6e5220, inputSource=0x6e4710, estBitrate=500)
at OnDemandServerMediaSubsession.cpp:456
#18 0x000000000046378b in OnDemandServerMediaSubsession::sdpLines (this=0x6e4aa0) at OnDemandServerMediaSubsession.cpp:76
#19 0x000000000042198b in ServerMediaSession::generateSDPDescription (this=0x6e4900) at ServerMediaSession.cpp:240
ByteStreamFileSource 的 doGetNextFrame() 启动对流媒体数据的读取,这个函数的实现如下:
void ByteStreamFileSource::doGetNextFrame() {
if (feof(fFid) || ferror(fFid) || (fLimitNumBytesToStream && fNumBytesToStream == 0)) {
handleClosure();
return;
}
#ifdef READ_FROM_FILES_SYNCHRONOUSLY
doReadFromFile();
#else
if (!fHaveStartedReading) {
// Await readable data from the file:
envir().taskScheduler().turnOnBackgroundReadHandling(fileno(fFid),
(TaskScheduler::BackgroundHandlerProc*)&fileReadableHandler, this);
fHaveStartedReading = True;
}
#endif
}
对于异步读取来说,是注册一个文件读取处理程序 fileReadableHandler,对于同步读取,则是直接通过 doReadFromFile() 读取文件数据。
回到 H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession 的 getAuxSDPLine()。执行了 RTPSink 的 startPlaying() 之后,就会通过 checkForAuxSDPLine(void* clientData) 检查一下视频流元数据的读取是否结束:
static void checkForAuxSDPLine(void* clientData) {
H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession* subsess = (H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession*)clientData;
subsess->checkForAuxSDPLine1();
}
void H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession::checkForAuxSDPLine1() {
nextTask() = NULL;
char const* dasl;
if (fAuxSDPLine != NULL) {
// Signal the event loop that we're done:
setDoneFlag();
} else if (fDummyRTPSink != NULL && (dasl = fDummyRTPSink->auxSDPLine()) != NULL) {
fAuxSDPLine = strDup(dasl);
fDummyRTPSink = NULL;
// Signal the event loop that we're done:
setDoneFlag();
} else if (!fDoneFlag) {
// try again after a brief delay:
int uSecsToDelay = 100000; // 100 ms
nextTask() = envir().taskScheduler().scheduleDelayedTask(uSecsToDelay,
(TaskFunc*) checkForAuxSDPLine, this);
}
}
这个函数在执行的时候,若发现 aux SDP 行还没有获取到,就会注册一个定时器任务过一段时间继续检查。
aux SDP 行通过 RTPSink 的 auxSDPLine() 获取,该函数实际的实现位于 H264VideoRTPSink 中:
char const* H264VideoRTPSink::auxSDPLine() {
// Generate a new "a=fmtp:" line each time, using our SPS and PPS (if we have them),
// otherwise parameters from our framer source (in case they've changed since the last time that
// we were called):
H264or5VideoStreamFramer* framerSource = NULL;
u_int8_t* vpsDummy = NULL; unsigned vpsDummySize = 0;
u_int8_t* sps = fSPS; unsigned spsSize = fSPSSize;
u_int8_t* pps = fPPS; unsigned ppsSize = fPPSSize;
if (sps == NULL || pps == NULL) {
// We need to get SPS and PPS from our framer source:
if (fOurFragmenter == NULL) return NULL; // we don't yet have a fragmenter (and therefore not a source)
framerSource = (H264or5VideoStreamFramer*)(fOurFragmenter->inputSource());
if (framerSource == NULL) return NULL; // we don't yet have a source
framerSource->getVPSandSPSandPPS(vpsDummy, vpsDummySize, sps, spsSize, pps, ppsSize);
if (sps == NULL || pps == NULL) return NULL; // our source isn't ready
}
// Set up the "a=fmtp:" SDP line for this stream:
u_int8_t* spsWEB = new u_int8_t[spsSize]; // "WEB" means "Without Emulation Bytes"
unsigned spsWEBSize = removeH264or5EmulationBytes(spsWEB, spsSize, sps, spsSize);
if (spsWEBSize < 4) { // Bad SPS size => assume our source isn't ready
delete[] spsWEB;
return NULL;
}
u_int32_t profileLevelId = (spsWEB[1]<<16) | (spsWEB[2]<<8) | spsWEB[3];
delete[] spsWEB;
char* sps_base64 = base64Encode((char*)sps, spsSize);
char* pps_base64 = base64Encode((char*)pps, ppsSize);
char const* fmtpFmt =
"a=fmtp:%d packetization-mode=1"
";profile-level-id=%06X"
";sprop-parameter-sets=%s,%s\r\n";
unsigned fmtpFmtSize = strlen(fmtpFmt)
+ 3 /* max char len */
+ 6 /* 3 bytes in hex */
+ strlen(sps_base64) + strlen(pps_base64);
char* fmtp = new char[fmtpFmtSize];
sprintf(fmtp, fmtpFmt,
rtpPayloadType(),
profileLevelId,
sps_base64, pps_base64);
delete[] sps_base64;
delete[] pps_base64;
delete[] fFmtpSDPLine; fFmtpSDPLine = fmtp;
return fFmtpSDPLine;
}
要产生 SDP 行,需要用到视频流数据的 SPS 帧和 PPS 帧,这两帧数据有两种来源,一种是在对象构造时,由调用者传入:
H264or5VideoRTPSink
::H264or5VideoRTPSink(int hNumber,
UsageEnvironment& env, Groupsock* RTPgs, unsigned char rtpPayloadFormat,
u_int8_t const* vps, unsigned vpsSize,
u_int8_t const* sps, unsigned spsSize,
u_int8_t const* pps, unsigned ppsSize)
: VideoRTPSink(env, RTPgs, rtpPayloadFormat, 90000, hNumber == 264 ? "H264" : "H265"),
fHNumber(hNumber), fOurFragmenter(NULL), fFmtpSDPLine(NULL) {
if (vps != NULL) {
fVPSSize = vpsSize;
fVPS = new u_int8_t[fVPSSize];
memmove(fVPS, vps, fVPSSize);
} else {
fVPSSize = 0;
fVPS = NULL;
}
if (sps != NULL) {
fSPSSize = spsSize;
fSPS = new u_int8_t[fSPSSize];
memmove(fSPS, sps, fSPSSize);
} else {
fSPSSize = 0;
fSPS = NULL;
}
if (pps != NULL) {
fPPSSize = ppsSize;
fPPS = new u_int8_t[fPPSSize];
memmove(fPPS, pps, fPPSSize);
} else {
fPPSSize = 0;
fPPS = NULL;
}
}
另外一种则是从数据源中获取:
class H264or5VideoStreamFramer: public MPEGVideoStreamFramer {
public:
void getVPSandSPSandPPS(u_int8_t*& vps, unsigned& vpsSize,
u_int8_t*& sps, unsigned& spsSize,
u_int8_t*& pps, unsigned& ppsSize) const {
// Returns pointers to copies of the most recently seen VPS (video parameter set)
// SPS (sequence parameter set) and PPS (picture parameter set) NAL units.
// (NULL pointers are returned if the NAL units have not yet been seen.)
vps = fLastSeenVPS; vpsSize = fLastSeenVPSSize;
sps = fLastSeenSPS; spsSize = fLastSeenSPSSize;
pps = fLastSeenPPS; ppsSize = fLastSeenPPSSize;
}
对于从数据源获取 SPS 帧和 PPS 帧的情况,在从文件中获取数据之后,这些数据会被推给 framerSource,推 SPS 的过程如下:
#0 H264or5VideoStreamFramer::saveCopyOfSPS (this=0x6e4710, from=0x6ff241 "gB\200*\332\001\020\017\036^R\n\f\n\r\241Bj", size=18)
at H264or5VideoStreamFramer.cpp:110
#1 0x00000000004798c4 in H264or5VideoStreamParser::parse (this=0x6e5020) at H264or5VideoStreamFramer.cpp:1069
#2 0x0000000000435de9 in MPEGVideoStreamFramer::continueReadProcessing (this=0x6e4710) at MPEGVideoStreamFramer.cpp:159
#3 0x0000000000435db4 in MPEGVideoStreamFramer::continueReadProcessing (clientData=0x6e4710) at MPEGVideoStreamFramer.cpp:155
#4 0x0000000000474249 in StreamParser::afterGettingBytes1 (this=0x6e5020, numBytesRead=150000, presentationTime=...) at StreamParser.cpp:191
#5 0x0000000000474112 in StreamParser::afterGettingBytes (clientData=0x6e5020, numBytesRead=150000, presentationTime=...) at StreamParser.cpp:170
#6 0x000000000043092a in FramedSource::afterGetting (source=0x6e4f10) at FramedSource.cpp:92
#7 0x0000000000431494 in ByteStreamFileSource::doReadFromFile (this=0x6e4f10) at ByteStreamFileSource.cpp:182
#8 0x0000000000431233 in ByteStreamFileSource::fileReadableHandler (source=0x6e4f10) at ByteStreamFileSource.cpp:126
#9 0x0000000000483a49 in BasicTaskScheduler::SingleStep (this=0x6d9c20, maxDelayTime=0) at BasicTaskScheduler.cpp:171
#10 0x00000000004864b4 in BasicTaskScheduler0::doEventLoop (this=0x6d9c20, watchVariable=0x6e4bb0 "") at BasicTaskScheduler0.cpp:80
#11 0x0000000000422c9c in H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession::getAuxSDPLine (this=0x6e4aa0, rtpSink=0x6e5220, inputSource=0x6e4710)
at H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession.cpp:98
#12 0x0000000000464cd4 in OnDemandServerMediaSubsession::setSDPLinesFromRTPSink (this=0x6e4aa0, rtpSink=0x6e5220, inputSource=0x6e4710, estBitrate=500)
at OnDemandServerMediaSubsession.cpp:456
#13 0x000000000046378b in OnDemandServerMediaSubsession::sdpLines (this=0x6e4aa0) at OnDemandServerMediaSubsession.cpp:76
#14 0x000000000042198b in ServerMediaSession::generateSDPDescription (this=0x6e4900) at ServerMediaSession.cpp:240
推 PPS 的过程如下:
#0 H264or5VideoStreamFramer::saveCopyOfPPS (this=0x6e4710, from=0x6ff241 "h\316\006\342\332\001\020\017\036^R\n\f\n\r\241Bj", size=4)
at H264or5VideoStreamFramer.cpp:119
#1 0x0000000000479ad9 in H264or5VideoStreamParser::parse (this=0x6e5020) at H264or5VideoStreamFramer.cpp:1090
#2 0x0000000000435de9 in MPEGVideoStreamFramer::continueReadProcessing (this=0x6e4710) at MPEGVideoStreamFramer.cpp:159
#3 0x0000000000435d51 in MPEGVideoStreamFramer::doGetNextFrame (this=0x6e4710) at MPEGVideoStreamFramer.cpp:142
#4 0x00000000004308b4 in FramedSource::getNextFrame (this=0x6e4710, to=0x6ff241 "h\316\006\342\332\001\020\017\036^R\n\f\n\r\241Bj", maxSize=100000,
afterGettingFunc=0x47c788 ,
afterGettingClientData=0x6e5540, onCloseFunc=0x43092e , onCloseClientData=0x6e5540) at FramedSource.cpp:78
#5 0x000000000047c2c0 in H264or5Fragmenter::doGetNextFrame (this=0x6e5540) at H264or5VideoRTPSink.cpp:181
#6 0x00000000004308b4 in FramedSource::getNextFrame (this=0x6e5540, to=0x6e69cc "gB\200*\332\001\020\017\036^R\n\f\n\r\241Bj", maxSize=100452,
afterGettingFunc=0x45d09c ,
afterGettingClientData=0x6e5220, onCloseFunc=0x45da86 , onCloseClientData=0x6e5220) at FramedSource.cpp:78
#7 0x000000000045d07b in MultiFramedRTPSink::packFrame (this=0x6e5220) at MultiFramedRTPSink.cpp:224
#8 0x000000000045cec8 in MultiFramedRTPSink::buildAndSendPacket (this=0x6e5220, isFirstPacket=0 '\000') at MultiFramedRTPSink.cpp:199
#9 0x000000000045da83 in MultiFramedRTPSink::sendNext (firstArg=0x6e5220) at MultiFramedRTPSink.cpp:422
#10 0x0000000000486c1b in AlarmHandler::handleTimeout (this=0x6e5760) at BasicTaskScheduler0.cpp:34
#11 0x0000000000484d1e in DelayQueue::handleAlarm (this=0x6d9c28) at DelayQueue.cpp:187
#12 0x0000000000483c4c in BasicTaskScheduler::SingleStep (this=0x6d9c20, maxDelayTime=0) at BasicTaskScheduler.cpp:212
#13 0x00000000004864b4 in BasicTaskScheduler0::doEventLoop (this=0x6d9c20, watchVariable=0x6e4bb0 "") at BasicTaskScheduler0.cpp:80
#14 0x0000000000422c9c in H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession::getAuxSDPLine (this=0x6e4aa0, rtpSink=0x6e5220, inputSource=0x6e4710)
at H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession.cpp:98
#15 0x0000000000464cd4 in OnDemandServerMediaSubsession::setSDPLinesFromRTPSink (this=0x6e4aa0, rtpSink=0x6e5220, inputSource=0x6e4710, estBitrate=500)
at OnDemandServerMediaSubsession.cpp:456
#16 0x000000000046378b in OnDemandServerMediaSubsession::sdpLines (this=0x6e4aa0) at OnDemandServerMediaSubsession.cpp:76
#17 0x000000000042198b in ServerMediaSession::generateSDPDescription (this=0x6e4900) at ServerMediaSession.cpp:240
SPS 和 PPS 帧数据要都拿到才能产生
SDP 行。H264VideoRTPSink::auxSDPLine() 在拿不到 SDP 行数据时,会返回 null 给调用者。
对于 H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession 的 checkForAuxSDPLine() 而言,在拿不到 SDP 的情况下,则是再次调度一个定时器任务执行,等待下一次检查的到来。
在 H264VideoRTPSink::auxSDPLine() 中,如果已经有了 SPS 和 PPS 数据的话则会先移除 SPS 中的 Emulation 字节,然后计算 SPS 帧数据和 PPS 帧数据的 Base64 编码,并最终产生 SDP 行。
移除 SPS 中的 Emulation 字节的过程就像下面这样:
unsigned removeH264or5EmulationBytes(u_int8_t* to, unsigned toMaxSize,
u_int8_t const* from, unsigned fromSize) {
unsigned toSize = 0;
unsigned i = 0;
while (i < fromSize && toSize+1 < toMaxSize) {
if (i+2 < fromSize && from[i] == 0 && from[i+1] == 0 && from[i+2] == 3) {
to[toSize] = to[toSize+1] = 0;
toSize += 2;
i += 3;
} else {
to[toSize] = from[i];
toSize += 1;
i += 1;
}
}
return toSize;
}
所谓的 Emulation 字节,是由于 H.264 流数据中,通过 0x00000001 和 0x000001 字节序列作为帧数据的分割序列,为了避免解码器将编码的帧数据中的这样的序列误认为是帧之间的分割序列,而强制在出现两个 0x00 字节的帧数据时,插入一个 0x03 字节。而在计算 SPS 的 Base64 时需要先移除这些字节。
H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession 的 getAuxSDPLine() 在拿到 aux SDP 行之后,就把它返回给调用者 OnDemandServerMediaSubsession::setSDPLinesFromRTPSink()。aux SDP 行通常像下面这样:
a=rtpmap:96 H264/90000
a=fmtp:96 packetization-mode=1;profile-level-id=42802A;sprop-parameter-sets=Z0KAKtoBEA8eXlIKDAoNoUJq,aM4G4g==
OnDemandServerMediaSubsession::setSDPLinesFromRTPSink() 利用所有的信息,生成最终的子会话 SDP 行。最终的子会话 SDP 行通常像下面这样:
m=video 0 RTP/AVP 96
c=IN IP4 0.0.0.0
b=AS:500
a=rtpmap:96 H264/90000
a=fmtp:96 packetization-mode=1;profile-level-id=42802A;sprop-parameter-sets=Z0KAKtoBEA8eXlIKDAoNoUJq,aM4G4g==
a=control:track1
Done.
live555 源码分析系列文章
live555 源码分析:简介
live555 源码分析:基础设施
live555 源码分析:MediaSever
Wireshark 抓包分析 RTSP/RTP/RTCP 基本工作过程
live555 源码分析:RTSPServer
live555 源码分析:DESCRIBE 的处理
live555 源码分析:SETUP 的处理
live555 源码分析:PLAY 的处理
live555 源码分析:RTSPServer 组件结构
live555 源码分析:ServerMediaSession
live555 源码分析:子会话 SDP 行生成
live555 源码分析:子会话 SETUP
live555 源码分析:播放启动