iOS开发中截取相机部分画面,切割sampleBuffer(Crop sample buffer)
本例需求:在类似直播的功能界面,二维码扫描,人脸识别或其他需求中的功能界面或其他需求中需要从相机捕获的画面中单独截取出一部分区域。
原理:由于需要截取相机捕获整个画面其中一部分,所以也就必须拿到那一部分画面的数据,又因为相机AVCaptureVideoDataOutputSampleBufferDelegate中的sampleBuffer为系统私有的数据结构不可直接操作,所以需要将其转换成可以切割的数据结构再进行切割,网上有种思路说将sampleBuffer间接转换为UIImage再对图片切割,这种思路繁琐且性能低,本例将sampleBuffer转换为CoreImage中的CIImage,性能相对较高且降低代码繁琐度。
最终效果如下, 绿色框中即为截图的画面,长按可以移动。
GitHub地址(附代码) : Crop sample buffer
地址 : Crop sample buffer
博客地址 : Crop sample buffer
掘金地址 : Crop sample buffer
注意:使用ARC与MRC下代码有所区别,已经在项目中标注好,主要为管理全局的CIContext对象,它在初始化的方法中编译器没有对其进行retain,所以,调用会报错。
使用场景
- 本项目中相机捕捉的背景分辨率默认设置为2K(即1920*1080),可切换为4K ,所以需要iPhone 6s以上的设备才支持。
- 本例可以使用CPU/GPU切割,在VC中需要在cropView初始化前设置isOpenGPU的值,打开则使用GPU,否则CPU
- 本例只实现了横屏下的Crop功能,本例默认始终为横屏状态,未做竖屏处理。
基本配置
1.配置相机基本环境(初始化AVCaptureSession,设置代理,开启),在示例代码中有,这里不再重复。
2.通过AVCaptureVideoDataOutputSampleBufferDelegate代理中拿到原始画面数据(CMSampleBufferRef)进行处理
实现途径
1.利用CPU软件截取(CPU进行计算并切割,消耗性能较大)
- (CMSampleBufferRef)cropSampleBufferBySoftware:(CMSampleBufferRef)sampleBuffer;
2.利用 硬件截取(利用Apple官方公开的方法利用硬件进行切割,性能较好, 但仍有问题待解决)
- (CMSampleBufferRef)cropSampleBufferByHardware:(CMSampleBufferRef)buffer;
解析
// Called whenever an AVCaptureVideoDataOutput instance outputs a new video frame. 每产生一帧视频帧时调用一次
- (void)captureOutput:(AVCaptureOutput *)captureOutput didOutputSampleBuffer:(CMSampleBufferRef)sampleBuffer fromConnection:(AVCaptureConnection *)connection {
CMSampleBufferRef cropSampleBuffer;
#warning 两种切割方式任选其一,GPU切割性能较好,CPU切割取决于设备,一般时间长会掉帧。
if (self.isOpenGPU) {
cropSampleBuffer = [self.cropView cropSampleBufferByHardware:sampleBuffer];
}else {
cropSampleBuffer = [self.cropView cropSampleBufferBySoftware:sampleBuffer];
}
// 使用完后必须显式release,不在iOS自动回收范围
CFRelease(cropSampleBuffer);
}
- 以上方法为每产生一帧视频帧时调用一次的相机代理,其中sampleBuffer为每帧画面的原始数据,需要对原始数据进行切割处理方可达到本例需求。注意最后一定要对cropSampleBuffer进行release避免内存溢出而发生闪退。
利用CPU截取
- (CMSampleBufferRef)cropSampleBufferBySoftware:(CMSampleBufferRef)sampleBuffer {
OSStatus status;
// CVPixelBufferRef pixelBuffer = [self modifyImage:buffer];
CVImageBufferRef imageBuffer = CMSampleBufferGetImageBuffer(sampleBuffer);
// Lock the image buffer
CVPixelBufferLockBaseAddress(imageBuffer,0);
// Get information about the image
uint8_t *baseAddress = (uint8_t *)CVPixelBufferGetBaseAddress(imageBuffer);
size_t bytesPerRow = CVPixelBufferGetBytesPerRow(imageBuffer);
size_t width = CVPixelBufferGetWidth(imageBuffer);
// size_t height = CVPixelBufferGetHeight(imageBuffer);
NSInteger bytesPerPixel = bytesPerRow/width;
// YUV 420 Rule
if (_cropX % 2 != 0) _cropX += 1;
NSInteger baseAddressStart = _cropY*bytesPerRow+bytesPerPixel*_cropX;
static NSInteger lastAddressStart = 0;
lastAddressStart = baseAddressStart;
// pixbuffer 与 videoInfo 只有位置变换或者切换分辨率或者相机重启时需要更新,其余情况不需要,Demo里只写了位置更新,其余情况自行添加
// NSLog(@"demon pix first : %zu - %zu - %@ - %d - %d - %d -%d",width, height, self.currentResolution,_cropX,_cropY,self.currentResolutionW,self.currentResolutionH);
static CVPixelBufferRef pixbuffer = NULL;
static CMVideoFormatDescriptionRef videoInfo = NULL;
// x,y changed need to reset pixbuffer and videoinfo
if (lastAddressStart != baseAddressStart) {
if (pixbuffer != NULL) {
CVPixelBufferRelease(pixbuffer);
pixbuffer = NULL;
}
if (videoInfo != NULL) {
CFRelease(videoInfo);
videoInfo = NULL;
}
}
if (pixbuffer == NULL) {
NSDictionary *options = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:
[NSNumber numberWithBool : YES], kCVPixelBufferCGImageCompatibilityKey,
[NSNumber numberWithBool : YES], kCVPixelBufferCGBitmapContextCompatibilityKey,
[NSNumber numberWithInt : g_width_size], kCVPixelBufferWidthKey,
[NSNumber numberWithInt : g_height_size], kCVPixelBufferHeightKey,
nil];
status = CVPixelBufferCreateWithBytes(kCFAllocatorDefault, g_width_size, g_height_size, kCVPixelFormatType_32BGRA, &baseAddress[baseAddressStart], bytesPerRow, NULL, NULL, (__bridge CFDictionaryRef)options, &pixbuffer);
if (status != 0) {
NSLog(@"Crop CVPixelBufferCreateWithBytes error %d",(int)status);
return NULL;
}
}
CVPixelBufferUnlockBaseAddress(imageBuffer,0);
CMSampleTimingInfo sampleTime = {
.duration = CMSampleBufferGetDuration(sampleBuffer),
.presentationTimeStamp = CMSampleBufferGetPresentationTimeStamp(sampleBuffer),
.decodeTimeStamp = CMSampleBufferGetDecodeTimeStamp(sampleBuffer)
};
if (videoInfo == NULL) {
status = CMVideoFormatDescriptionCreateForImageBuffer(kCFAllocatorDefault, pixbuffer, &videoInfo);
if (status != 0) NSLog(@"Crop CMVideoFormatDescriptionCreateForImageBuffer error %d",(int)status);
}
CMSampleBufferRef cropBuffer = NULL;
status = CMSampleBufferCreateForImageBuffer(kCFAllocatorDefault, pixbuffer, true, NULL, NULL, videoInfo, &sampleTime, &cropBuffer);
if (status != 0) NSLog(@"Crop CMSampleBufferCreateForImageBuffer error %d",(int)status);
lastAddressStart = baseAddressStart;
return cropBuffer;
}
- 以上方法为切割sampleBuffer的对象方法
首先从CMSampleBufferRef中提取出CVImageBufferRef数据结构,然后对CVImageBufferRef进行加锁处理,如果要进行页面渲染,需要一个和OpenGL缓冲兼容的图像。用相机API创建的图像已经兼容,您可以马上映射他们进行输入。假设你从已有画面中截取一个新的画面,用作其他处理,你必须创建一种特殊的属性用来创建图像。对于图像的属性必须有Crop宽高, 作为字典的Key.因此创建字典的关键几步不可省略。
位置的计算
在软切中,我们拿到一帧图片的数据,通过遍历其中的数据确定真正要Crop的位置,利用如下公式可求出具体位置,具体切割原理在[YUV介绍]中有提到,计算时所需的变量在以上代码中均可得到。
`NSInteger baseAddressStart = _cropY*bytesPerRow+bytesPerPixel*_cropX;
`
注意:
- 1.对X,Y坐标进行校正,因为CVPixelBufferCreateWithBytes是按照像素进行切割,所以需要将点转成像素,再按照比例算出当前位置。即为上述代码的int cropX = (int)(currentResolutionW / kScreenWidth * self.cropView.frame.origin.x); currentResolutionW为当前分辨率的宽度,kScreenWidth为屏幕实际宽度。
- 2.根据YUV 420的规则,每4个Y共用1个UV,而一行有2个Y,所以取点必须按照偶数取点。利用CPU切割中使用的方法为YUV分隔法,具体切割方式请参考YUV介绍
- 3.本例中声明pixelBuffer与videoInfo均为静态变量,为了节省每次创建浪费内存,但是有三种情况需要重置它们:位置变化,分辨率改变,重启相机。文章最后注意详细提到。
// hardware crop
- (CMSampleBufferRef)cropSampleBufferByHardware:(CMSampleBufferRef)buffer {
// a CMSampleBuffer's CVImageBuffer of media data.
CVImageBufferRef imageBuffer = CMSampleBufferGetImageBuffer(buffer);
CGRect cropRect = CGRectMake(_cropX, _cropY, g_width_size, g_height_size);
// log4cplus_debug("Crop", "dropRect x: %f - y : %f - width : %zu - height : %zu", cropViewX, cropViewY, width, height);
/*
First, to render to a texture, you need an image that is compatible with the OpenGL texture cache. Images that were created with the camera API are already compatible and you can immediately map them for inputs. Suppose you want to create an image to render on and later read out for some other processing though. You have to have create the image with a special property. The attributes for the image must have kCVPixelBufferIOSurfacePropertiesKey as one of the keys to the dictionary.
如果要进行页面渲染,需要一个和OpenGL缓冲兼容的图像。用相机API创建的图像已经兼容,您可以马上映射他们进行输入。假设你从已有画面中截取一个新的画面,用作其他处理,你必须创建一种特殊的属性用来创建图像。对于图像的属性必须有kCVPixelBufferIOSurfacePropertiesKey 作为字典的Key.因此以下步骤不可省略
*/
OSStatus status;
/* Only resolution has changed we need to reset pixBuffer and videoInfo so that reduce calculate count */
static CVPixelBufferRef pixbuffer = NULL;
static CMVideoFormatDescriptionRef videoInfo = NULL;
if (pixbuffer == NULL) {
NSDictionary *options = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:
[NSNumber numberWithInt:g_width_size], kCVPixelBufferWidthKey,
[NSNumber numberWithInt:g_height_size], kCVPixelBufferHeightKey, nil];
status = CVPixelBufferCreate(kCFAllocatorSystemDefault, g_width_size, g_height_size, kCVPixelFormatType_420YpCbCr8BiPlanarFullRange, (__bridge CFDictionaryRef)options, &pixbuffer);
// ensures that the CVPixelBuffer is accessible in system memory. This should only be called if the base address is going to be used and the pixel data will be accessed by the CPU
if (status != noErr) {
NSLog(@"Crop CVPixelBufferCreate error %d",(int)status);
return NULL;
}
}
CIImage *ciImage = [CIImage imageWithCVImageBuffer:imageBuffer];
ciImage = [ciImage imageByCroppingToRect:cropRect];
// Ciimage get real image is not in the original point after excute crop. So we need to pan.
ciImage = [ciImage imageByApplyingTransform:CGAffineTransformMakeTranslation(-_cropX, -_cropY)];
static CIContext *ciContext = nil;
if (ciContext == nil) {
// NSMutableDictionary *options = [[NSMutableDictionary alloc] init];
// [options setObject:[NSNull null] forKey:kCIContextWorkingColorSpace];
// [options setObject:@0 forKey:kCIContextUseSoftwareRenderer];
EAGLContext *eaglContext = [[EAGLContext alloc] initWithAPI:kEAGLRenderingAPIOpenGLES3];
ciContext = [CIContext contextWithEAGLContext:eaglContext options:nil];
}
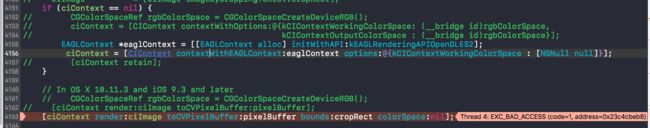
[ciContext render:ciImage toCVPixelBuffer:pixbuffer];
// [ciContext render:ciImage toCVPixelBuffer:pixbuffer bounds:cropRect colorSpace:nil];
CMSampleTimingInfo sampleTime = {
.duration = CMSampleBufferGetDuration(buffer),
.presentationTimeStamp = CMSampleBufferGetPresentationTimeStamp(buffer),
.decodeTimeStamp = CMSampleBufferGetDecodeTimeStamp(buffer)
};
if (videoInfo == NULL) {
status = CMVideoFormatDescriptionCreateForImageBuffer(kCFAllocatorDefault, pixbuffer, &videoInfo);
if (status != 0) NSLog(@"Crop CMVideoFormatDescriptionCreateForImageBuffer error %d",(int)status);
}
CMSampleBufferRef cropBuffer;
status = CMSampleBufferCreateForImageBuffer(kCFAllocatorDefault, pixbuffer, true, NULL, NULL, videoInfo, &sampleTime, &cropBuffer);
if (status != 0) NSLog(@"Crop CMSampleBufferCreateForImageBuffer error %d",(int)status);
return cropBuffer;
}
以上为硬件切割的方法,硬件切割利用GPU进行切割,主要利用CoreImage中CIContext 对象进行渲染。
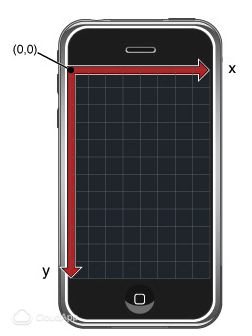
CoreImage and UIKit coordinates (CoreImage 与 UIKit坐标系问题):我在开始做的时候跟正常一样用设定的位置对图像进行切割,但是发现,切出来的位置不对,通过上网查阅发现一个有趣的现象CoreImage 与 UIKit坐标系不相同
如下图:
正常UIKit坐标系是以左上角为原点:
而CoreImage坐标系是以左下角为原点:(在CoreImage中,每个图像的坐标系是独立于设备的)
所以切割的时候一定要注意转换Y,X的位置是正确的,Y是相反的。
- 如果要进行页面渲染,需要一个和OpenGL缓冲兼容的图像。用相机API创建的图像已经兼容,您可以马上映射他们进行输入。假设你从已有画面中截取一个新的画面,用作其他处理,你必须创建一种特殊的属性用来创建图像。对于图像的属性必须有宽高 作为字典的Key.因此创建字典的关键几步不可省略。
- 对CoreImage进行切割有两种切割的方法均可用:
-
ciImage = [ciImage imageByCroppingToRect:cropRect];如果使用此行代码则渲染时用[ciContext render:ciImage toCVPixelBuffer:pixelBuffer]; - 或者直接使用:
[ciContext render:ciImage toCVPixelBuffer:pixelBuffer bounds:cropRect colorSpace:nil];
- 注意:CIContext 中包含图像大量上下文信息,不能在回调中多次调用,官方建议只初始化一次。但是注意ARC,MRC区别。
注意:
1. 使用ARC与MRC下代码有所区别,已经在项目中标注好,主要为管理全局的CIContext对象,它在初始化的方法中编译器没有对其进行retain,所以,调用会报错。
2.切换前后置摄像头:因为不同机型的前后置摄像头差别较大,一种处理手段是在记录iphone机型crop的plist文件中增加前后置摄像头支持分辨率的属性,然后在代码中根据plist映射出来的模型进行分别引用。另一种方案是做自动降级处理,例如后置支持2K,前置支持720P,则转换后检测到前置不支持2K就自动将前置降低一个等级,直到找到需要的等级。如果这样操作处理逻辑较多且初看不易理解,而前置切割功能适用范围不大,所以暂时只支持后置切割。
补充说明
- 屏幕逻辑分辨率与视频分辨率
Point and pixel的区别
因为此类说明网上很多,这里就不做太多具体阐述,仅仅简述一下
Point 即是设备的逻辑分辨率,即[UIScreen mainScreen].bounds.size.width 得到的设备的宽高,所以点可以简单理解为iOS开发中的坐标系,方便对界面元素进行描述。Pixel: 像素则是比点更精确的单位,在普通屏中1点=1像素,Retina屏中1点=2像素。
分辨率 分辨率需要根据不同机型所支持的最大分辨率进行设置,例如iPhone 6S以上机型支持4k(3840 * 2160)分辨率拍摄视频。而当我们进行Crop操作的时候调用的API正是通过像素来进行切割,所以我们操作的单位是pixel而不是point.下面会有详细介绍。
- ARC, MRC下所做工作不同
CIContext 的初始化
首先应该将CIContext声明为全局变量或静态变量,因为CIContext初始化一次内部含有大量信息,比较耗内存,且只是渲染的时候使用,无需每次都初始化,然后如下如果在MRC中初始化完成后并未对ciContext发出retain的消息,所以需要手动retain,但在ARC下系统会自动完成此操作。
ARC:
static CIContext *ciContext = NULL;
ciContext = [CIContext contextWithOptions:nil];
MRC:
static CIContext *ciContext = NULL;
ciContext = [CIContext contextWithOptions:nil];
[ciContext retain];
- 坐标问题
1. 理解点与像素的对应关系
首先CropView需要在手机显示出来,所以坐标系还是UIKit的坐标系,左上角为原点,宽高分别为不同手机的宽高(如iPhone8 : 375*667, iPhone8P : 414 * 736, iPhoneX : 375 * 816),但是我们需要算出实际分辨率下CropView的坐标,即我们可以把当前获取的cropView的x,y点的位置转换成对应pixel的位置。
// 注意这里求的是X的像素坐标,以iPhone 8 为例 (点为375 * 667),分辨率为(1920 * 1080)
_cropX = (int)(_currentResolutionW / _screenWidth * (cropView.frame.origin.x);
即
_cropX = (int)(1920 / 375 * 当前cropView的x点坐标;
2. CPU / GPU 两种方式切割时坐标系的位置不同
原点位置
CPU : UIKit为坐标系,原点在左上角
GPU : CoreImage为坐标系,原点在左下角
因此计算时如果使用GPU, y的坐标是相反的,我们需要通过如下公式转换,即将点对应转为正常以左上角为原点坐标系中的点。
_cropY = (int)(_currentResolutionH / _screenHeight * (_screenHeight - self.frame.origin.y - self.frame.size.height));
3. 当手机屏幕不是16:9时,如果将视频设置为填充满屏幕则会出现偏差
需要注意的是,因为部分手机或iPad屏幕尺寸并不为16:9(iPhone X, 所有iPad (4 : 3)),如果我们在2k(1920 * 1080) , 4k (3840 * 2160 ) 分辨率下对显示的View设置了 captureVideoPreviewLayer.videoGravity = AVLayerVideoGravityResizeAspectFill; 那么屏幕会牺牲一部分视频填充视图,即相机捕获的视频数据并没有完整展现在手机视图里,所以再使用我们的crop功能时,由于我们使用的是UIKit的坐标系,也就是说原点(0,0)并不是该帧图片真正像素的(0,0),而如果计算则需要写很多额外代码,所以我们可以在Crop功能下设置captureVideoPreviewLayer.videoGravity = AVLayerVideoGravityResizeAspect; 这样的话video视图会根据分辨率调整为显示完整视频。但是设置后如果设备是iPhoneX (比例大于16:9,X轴会缩小,黑边填充),iPad(比例小于16:9,y轴缩小,黑边填充)。
按照如上解析,我们之前计算的点会出现偏差,因为相当于x或y轴会缩小一部分,而我们拿到的cropView的坐标仍然是相对于整个父View而言。
这时,如果我们通过不断更改cropView则代码量较大,所以我在这里定义了一个videoRect属性用来记录Video真正的Rect,因为当程序运行时我们可以得到屏幕宽高比例,所以通过确定宽高比可以拿到真正Video的rect,此时在后续代码中我们只需要传入videoRect的尺寸进行计算,即时是原先正常16:9的手机后面API也无须更改。
4. 为什么用int
在软切中,我们在创建pixelBuffer时需要使用
CV_EXPORT CVReturn CVPixelBufferCreateWithBytes(
CFAllocatorRef CV_NULLABLE allocator,
size_t width,
size_t height,
OSType pixelFormatType,
void * CV_NONNULL baseAddress,
size_t bytesPerRow,
CVPixelBufferReleaseBytesCallback CV_NULLABLE releaseCallback,
void * CV_NULLABLE releaseRefCon,
CFDictionaryRef CV_NULLABLE pixelBufferAttributes,
CV_RETURNS_RETAINED_PARAMETER CVPixelBufferRef CV_NULLABLE * CV_NONNULL pixelBufferOut)
这个API,我们需要将x,y的点放入baseAddress中,这里又需要使用公式NSInteger baseAddressStart = _cropY*bytesPerRow+bytesPerPixel*_cropX;,但是这里根据YUV 420的规则我们我们传入的X的点不能为奇数,所以我们需要if (_cropX % 2 != 0) _cropX += 1;,而只有整型才能求余,所以这里的点我们均定义为int,在视图展示中忽略小数点的误差。