从上一篇笔记的记录, 大致感觉到了 YYModel 整个流程啦,但还不是很清晰,至此对整体进行一个梳理,方便理解。
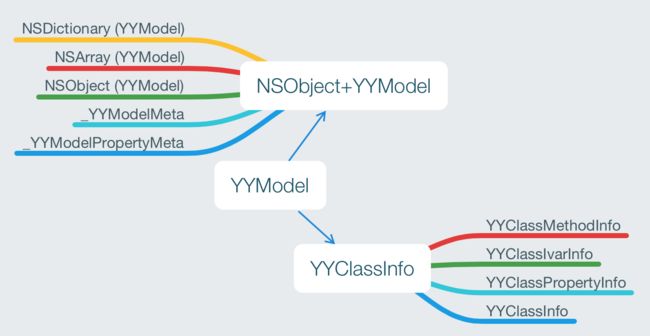
从目录可以看出YYModel分为两块,一个是对 NSObject 的处理,一个是对Class的封装。
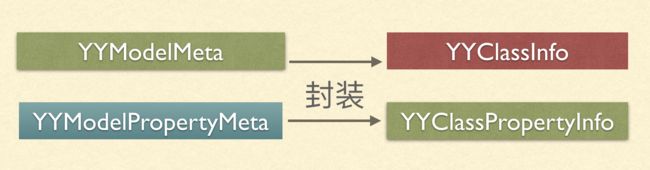
正是 YYModelMeta 对 YYClassInfo 进一步的封装,将两个类连合起来,也是将 YYClassInfo 里面所做的成果的体现。
我想从新带着下面的问题去了解。。。
- 1、YYModel 是干什么的?
- 2、YYClassInfo 和 NSObject + YYModel分别起什么作用?
- 3、**YYModelMeta和 YYModelProperty在NSObject + YYModel 中起了什么作用? **
----
此时再来了解YYClassInfo,会有新的感受。下面通过其中的类来先了解下:
YYClassIvarInfo
// 增加对 ivar (实例变量) 的描述
@interface YYClassIvarInfo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) Ivar ivar; ///< ivar
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *name; ///< 变量名字
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) ptrdiff_t offset; ///< 变量偏移量
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *typeEncoding; ///< 变量编码类型
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) YYEncodingType type; ///< 转化 YYType
- (instancetype)initWithIvar:(Ivar)ivar;
@end
@implementation YYClassIvarInfo
- (instancetype)initWithIvar:(Ivar)ivar {
if (!ivar) return nil;
self = [super init];
_ivar = ivar;
// 获取 实例变量的名字
const char *name = ivar_getName(ivar);
if (name) {
// 转化维我们需要的 NSString
_name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:name];
}
// 获取 偏移量
_offset = ivar_getOffset(ivar);
// 获取编码类型
const char *typeEncoding = ivar_getTypeEncoding(ivar);
if (typeEncoding) {
_typeEncoding = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:typeEncoding];
// 转化为 YYType 方便后面判断
_type = YYEncodingGetType(typeEncoding);
}
return self;
}
这样一下来,就很好的转化成了我们可以用的实例变量啦。
YYClassMethodInfo
在此我们先粗略的补充一下关于 Method,详细可以看南峰子写的Objective-C Runtime 运行时之三:方法与消息
struct objc_method {
SEL method_name; // 选择子(方法名字)
char \\*method_types; // 方法的参数列表
IMP method_imp; // 函数指针(方法实现)
}
id (*IMP)(id, SEL, ...)
对比一下其中常用到的一个方法,objc_msgSend(receiver, SEL op, ...);
/**
model: 谁执行
meta->_setter: 执行的方法
value: 传的值
*/
((void (*)(id, SEL, id))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, value);
此时我们再来看看 YYClassMethodInfo 的实现
/** 对 Method (方法) 的描述*/
@interface YYClassMethodInfo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) Method method; ///< method
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *name; ///< 方法名
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) SEL sel; ///< 方法选择器
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) IMP imp; ///< 方法的函数名
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *typeEncoding; ///< 方法的编码
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *returnTypeEncoding; ///< 方法返回值的类型
@property (nullable, nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSArray *argumentTypeEncodings; ///< 方法参数的类型
- (instancetype)initWithMethod:(Method)method;
@end
@implementation YYClassMethodInfo
- (instancetype)initWithMethod:(Method)method {
if (!method) return nil;
self = [super init];
_method = method;
// 获取 SEL
_sel = method_getName(method);
// 获取 函数地址
_imp = method_getImplementation(method);
// 获取 方法的名字
const char *name = sel_getName(_sel);
if (name) {
_name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:name];
}
const char *typeEncoding = method_getTypeEncoding(method);
if (typeEncoding) {
_typeEncoding = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:typeEncoding];
}
char *returnType = method_copyReturnType(method);
if (returnType) {
_returnTypeEncoding = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:returnType];
free(returnType);
}
unsigned int argumentCount = method_getNumberOfArguments(method);
if (argumentCount > 0) {
NSMutableArray *argumentTypes = [NSMutableArray new];
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < argumentCount; i++) {
char *argumentType = method_copyArgumentType(method, i);
NSString *type = argumentType ? [NSString stringWithUTF8String:argumentType] : nil;
// 将参数的类型,加入到数组中
[argumentTypes addObject:type ? type : @""];
if (argumentType) free(argumentType);
}
_argumentTypeEncodings = argumentTypes;
}
return self;
}
@end
从上面大致可以看出来,YYClassInfo 这块就是那些需要runtime获取的东东,直接转化为我们可以正常使用的。
YYClassPropertyInfo
首先注意“属性” (property)有两大概念:
- ivar(实例变量)
- 存取方法(access method = getter + setter)。
@property = getter + setter;
struct property_t {
const char *name; // 名字
const char *attributes; // 属性的声明描述,例如 strong nonatomic之类的
};
陈宜龙为了搞清属性是怎么实现的,曾经反编译过相关的代码,他大致生成了五个东西
-
OBJC_IVAR_$类名$属性名称:该属性的“偏移量” (offset),这个偏移量是“硬编码” (hardcode),表示该变量距离存放对象的内存区域的起始地址有多远。 -
setter与getter方法对应的实现函数 -
ivar_list:成员变量列表 -
method_list:方法列表 -
prop_list:属性列表
也就是说我们每次在增加一个属性,系统都会在 ivar_list中添加一个成员变量的描述,在method_list中增加 setter与 getter方法的描述,在prop_list中增加一个属性的描述,然后计算该属性在对象中的偏移量,然后给出 setter 与 getter 方法对应的实现,在 setter 方法中从偏移量的位置开始赋值,在 getter方法中从偏移量开始取值,为了能够读取正确字节数,系统对象偏移量的指针类型进行了类型强转。
通过上述陈宜龙的解释,对 property 又有了很好的认识。
@interface YYClassPropertyInfo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) objc_property_t property; ///< property
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *name; ///< 属性名
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) YYEncodingType type; ///< 属性类型
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *typeEncoding; ///< 属性编码
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *ivarName; ///< 属性实例变量米刮腻子
@property (nullable, nonatomic, assign, readonly) Class cls; ///< 属性 class
@property (nullable, nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSArray *protocols; ///< 可能为空的协议数组
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) SEL getter; ///< getter 方法
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) SEL setter; ///< setter 方法
- (instancetype)initWithProperty:(objc_property_t)property;
@end
@implementation YYClassPropertyInfo
- (instancetype)initWithProperty:(objc_property_t)property {
if (!property) return nil;
self = [super init];
_property = property;
const char *name = property_getName(property);
if (name) {
_name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:name];
}
YYEncodingType type = 0;
unsigned int attrCount;
// 获取属性的声明描述的列表
objc_property_attribute_t *attrs = property_copyAttributeList(property, &attrCount);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < attrCount; i++) {
switch (attrs[i].name[0]) {
case 'T': { // Type encoding
if (attrs[i].value) {
// 获取 编码类型
_typeEncoding = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:attrs[i].value];
// 获取 YYYType
type = YYEncodingGetType(attrs[i].value);
// 判断 YYType 是否属于 id 类型
if ((type & YYEncodingTypeMask) == YYEncodingTypeObject && _typeEncoding.length) {
// 通过编码类型 初始化 NSSCanner
NSScanner *scanner = [NSScanner scannerWithString:_typeEncoding];
if (![scanner scanString:@"@\\"" intoString:NULL]) continue;
NSString *clsName = nil;
if ([scanner scanUpToCharactersFromSet: [NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString:@"\\"<"] intoString:&clsName]) {
// 如果扫描"\\"<"之外的数据成功,转化为 clsName,则返回 ClassName
if (clsName.length) _cls = objc_getClass(clsName.UTF8String);
}
// 判断是否 是协议
NSMutableArray *protocols = nil;
while ([scanner scanString:@"<" intoString:NULL]) {
NSString* protocol = nil;
if ([scanner scanUpToString:@">" intoString: &protocol]) {
if (protocol.length) {
if (!protocols) protocols = [NSMutableArray new];
[protocols addObject:protocol];
}
}
[scanner scanString:@">" intoString:NULL];
}
_protocols = protocols;
}
}
} break;
case 'V': { // Instance variable
if (attrs[i].value) {
_ivarName = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:attrs[i].value];
}
} break;
case 'R': {
type |= YYEncodingTypePropertyReadonly;
} break;
case 'C': {
type |= YYEncodingTypePropertyCopy;
} break;
case '&': {
type |= YYEncodingTypePropertyRetain;
} break;
case 'N': {
type |= YYEncodingTypePropertyNonatomic;
} break;
case 'D': {
type |= YYEncodingTypePropertyDynamic;
} break;
case 'W': {
type |= YYEncodingTypePropertyWeak;
} break;
case 'G': {
type |= YYEncodingTypePropertyCustomGetter;
if (attrs[i].value) {
_getter = NSSelectorFromString([NSString stringWithUTF8String:attrs[i].value]);
}
} break;
case 'S': {
type |= YYEncodingTypePropertyCustomSetter;
if (attrs[i].value) {
_setter = NSSelectorFromString([NSString stringWithUTF8String:attrs[i].value]);
}
} // break; commented for code coverage in next line
default: break;
}
}
if (attrs) {
free(attrs);
attrs = NULL;
}
_type = type;
if (_name.length) {
if (!_getter) {
_getter = NSSelectorFromString(_name);
}
if (!_setter) {
// if name = age 转化为我们需要的方法名:setAge
_setter = NSSelectorFromString([NSString stringWithFormat:@"set%@%@:", [_name substringToIndex:1].uppercaseString, [_name substringFromIndex:1]]);
}
}
return self;
}
@end
YYClassInfo,最后,YYClassInfo 讲上述综合起来,构成了一个很好操纵 ivar,method,property 的 Class。
@interface YYClassInfo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) Class cls; ///< class object
@property (nullable, nonatomic, assign, readonly) Class superCls; ///< super class object
@property (nullable, nonatomic, assign, readonly) Class metaCls; ///< class's meta class object
@property (nonatomic, readonly) BOOL isMeta; ///< whether this class is meta class
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *name; ///< class name
@property (nullable, nonatomic, strong, readonly) YYClassInfo *superClassInfo; ///< super class's class info
@property (nullable, nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSDictionary *ivarInfos; ///< ivars
@property (nullable, nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSDictionary *methodInfos; ///< methods
@property (nullable, nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSDictionary *propertyInfos; ///< properties
- (void)setNeedUpdate;
- (BOOL)needUpdate;
+ (nullable instancetype)classInfoWithClass:(Class)cls;
+ (nullable instancetype)classInfoWithClassName:(NSString *)className;
@end
其中特别要注意的是 ClassInfo 的初始化
+ (instancetype)classInfoWithClass:(Class)cls {
if (!cls) return nil;
// 定义缓存
static CFMutableDictionaryRef classCache;
static CFMutableDictionaryRef metaCache;
//dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{})确保了初始化过程只有一次。
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
// 定义锁
static dispatch_semaphore_t lock;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
//使用CFDictionary创建了cache缓存
classCache = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(CFAllocatorGetDefault(), 0, &kCFTypeDictionaryKeyCallBacks, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
metaCache = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(CFAllocatorGetDefault(), 0, &kCFTypeDictionaryKeyCallBacks, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
// 创建锁
lock = dispatch_semaphore_create(1);
});
// 等待锁,当信号总量少于0的时候就会一直等待,否则就可以正常的执行,并让信号总量-1
dispatch_semaphore_wait(lock, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER);
// 初始化 classInfo ,通过 key 获取 value
YYClassInfo *info = CFDictionaryGetValue(class_isMetaClass(cls) ? metaCache : classCache, (__bridge const void *)(cls));
if (info && info->_needUpdate) {
[info _update];
}
// 信号锁,信号总量加1
dispatch_semaphore_signal(lock);
if (!info) {
info = [[YYClassInfo alloc] initWithClass:cls];
if (info) {
dispatch_semaphore_wait(lock, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER);
// 设置字典 key == bridge class value == _bridge info
CFDictionarySetValue(info.isMeta ? metaCache : classCache, (__bridge const void *)(cls), (__bridge const void *)(info));
dispatch_semaphore_signal(lock);
}
}
return info;
}
就这样粗略记录了一下,成了一个性能有保障,安全性高的 YYClassInfo,然后 YYmodelMeta 再对其进行封装,配上不同的映射关系,巧妙的通过 runtime 处理一系列问题啦。
话说回来,我们一直要记住它做的一个核心功能就是取出 JOSN中对应的 value 设置 model 中属性设置值就 OK 了,这样就可以更好的理解。
((void (*)(id, SEL, id))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, value);
然后,就很方便我们使用 Model 取值啦。
PS :刚刚看到一个系列 YYModel 解读的博客,很赞,推荐下Blog Archive,发现自己必须再次学习啊~~~