搭建hibernate
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_22329521/article/details/74330968
需要导入的hibernate的包
其中所需要的依赖包
需要的配置文件
一个是元数据orm的配置文件
例如
package com.fmt.hibernate;
public class Customer {
/*
* CREATE TABLE `cst_customer` (
`cust_id` BIGINT(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '客户编号(主键)',
`cust_name` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '客户名称(公司名称)',
`cust_source` VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '客户信息来源',
`cust_industry` VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '客户所属行业',
`cust_level` VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '客户级别',
`cust_linkman` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系人',
`cust_phone` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '固定电话',
`cust_mobile` VARCHAR(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '移动电话',
PRIMARY KEY (`cust_id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
*/
private Long cust_id;
private String cust_name;
private String cust_source;
private String cust_industry;
private String cust_level;
private String cust_linkman;
private String cust_phone;
private String cust_mobile;
public Long getCust_id() {
return cust_id;
}
public void setCust_id(Long cust_id) {
this.cust_id = cust_id;
}
public String getCust_name() {
return cust_name;
}
public void setCust_name(String cust_name) {
this.cust_name = cust_name;
}
public String getCust_source() {
return cust_source;
}
public void setCust_source(String cust_source) {
this.cust_source = cust_source;
}
public String getCust_industry() {
return cust_industry;
}
public void setCust_industry(String cust_industry) {
this.cust_industry = cust_industry;
}
public String getCust_level() {
return cust_level;
}
public void setCust_level(String cust_level) {
this.cust_level = cust_level;
}
public String getCust_linkman() {
return cust_linkman;
}
public void setCust_linkman(String cust_linkman) {
this.cust_linkman = cust_linkman;
}
public String getCust_phone() {
return cust_phone;
}
public void setCust_phone(String cust_phone) {
this.cust_phone = cust_phone;
}
public String getCust_mobile() {
return cust_mobile;
}
public void setCust_mobile(String cust_mobile) {
this.cust_mobile = cust_mobile;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [cust_id=" + cust_id + ", cust_name=" + cust_name + "]";
}
}
当前一个Customer对象 需要建立他相应的xml文件
接下啦是hibernate的主配置文件最重要的该文件的文件名字必须是hibernate.cfg.xml,同时在src的目录
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc:mysql:///hibernate?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
root
123456
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
true
true
update
代码的增删改查
@Test
public void fun1(){
//1创建,调用空参构造
Configuration conf=new Configuration();
//2读取配置文件,j加载src下的Hibernate.cfg.xml文件
conf.configure();
//根据配置,创建SessionFactory对象
//SessionFaction就是用来创建Session的
//sessionFactory 负责保存和使用所有配置信息,消耗内存资源较大
//sessionFactory 属于线程安全的对象设计
//所以SessionnFactory全局唯一
SessionFactory sessionFactory = conf.buildSessionFactory();
//session对象是表达hibernate框架与数据库之间的连接可以理解为JDBC中的connection对象,但同时可以操作sql,是hibernate的核心对象
//获取Session
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
//获取线程绑定的session
// Session currentSession = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
//获取操作事务
// Transaction transaction = session.getTransaction();
//开启事务病获得操作事务(建议使用)
Transaction transaction1 = session.beginTransaction();
/*
保存
Customer customer=new Customer();
customer.setCust_name("jd");
session.save(customer);
*/
/*
查询
session.get 第一个参数是类,第二个是主键id
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 1l);
System.out.println(customer);
*/
/*
修改
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 1l);
customer.setCust_name("百度");
session.update(customer);
*/
/*
删除
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 1l);
customer.setCust_name("百度");
session.delete(customer);
*/
transaction1.commit();//提交
// transaction1.rollback();//回滚
session.close();//释放资源
sessionFactory.close();//释放资源
}
实体类创建注意事项
- 持久化提供无参构造
- 成员变量私有,提供共有get/set方法访问,需提供属性
- 持久化类的属性,应尽量使用包装类型
- 持久化需要提供oid,与数据库中的主键列对应(如果一个表没有主键,无法映射到hibernate表中,主键相同hibernate认为对象相同)
- 不要用final修饰class(hibernate使用cglib代理生成代理对象,代理对象是继承被代理对象,如果被final修改将无法生成代理)
主键生成策略
在元对象xml中
.....
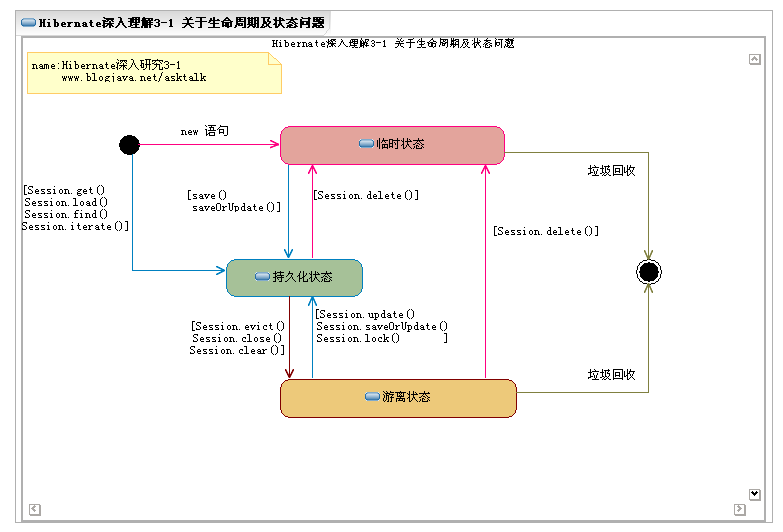
hibernate实体对象的状态
三种状态:瞬时状态,持久化状态,游离状态
Configuration conf=new Configuration();
conf.configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = conf.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Customer customer=new Customer();//没有id,没有与session关联
customer.setCust_name("jd");//瞬时状态
session.save(customer);//持久化状态,由id,有关联
transaction.commit();//提交
session.close();//游离|托管状态。有id。没关联
sessionFactory.close();
持久化状态的特点持久化对象的任何变化都会自动同步到数据库中
Configuration conf=new Configuration();
conf.configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = conf.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 2l);
customer.setCust_name("tianmao");//这里没有设置update的操作,仍然修改了数据库
transaction.commit();//提交
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
hibernate一级缓存
Test
public void fun1() {
Configuration conf = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = conf.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//这里这回进行一次的查询 session缓存了 id位2l的custion到内存中,第二次查询不会走数据库查询
Customer customer1 = session.get(Customer.class, 2l);
Customer customer2 = session.get(Customer.class, 2l);
Customer customer3 = session.get(Customer.class, 2l);
System.out.println(customer1==customer2);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
@Test
public void fun2() {
Configuration conf = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = conf.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Customer customer1 = session.get(Customer.class, 2l);//tianmao
customer1.setCust_name("jd");
customer1.setCust_name("tianmao");
//这里不会进行update操作,值进行了查询的sql
//seesion保存了查询出来后的快照,对比当时的快照是否发生变化同步到数据库
transaction.commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
Hibernate的隔离级别设置
在主配置文件中
加入
4
调用获取当前线程中的session对象调用sessionFactory.getCurrentSession(); 注意点需要在配置文件中声明,同时通过getCurrentSession方法获得到的session当事务提交时,session会自动关闭,不要手动close关闭
thread
Hql查询
hql查询:HQL是Hibernate Query Language的简写,HQL采用面向对象的查询方式
Session session= HibernateUtils.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//书写HQL语句
// String hql="from com.fmt.hibernate.Customer";
// String hql="from Customer ";//查询所有Custom对象
/**
//查询id位2的
String hql="from Customer where cust_id =2";
Query query = session.createQuery(hql);
*/
/**
条件查询
String hql="from Customer where cust_id =?";
Query query = session.createQuery(hql);
//query.setLong(0,2l);
query.setParameter(0,2l);//这个不用的参数做具体设置较为方便
*/
/**
命名查询
String hql="from Customer where cust_id =:cust_id";//冒号后面的字符串是setParamerter中的第一个参数
Query query = session.createQuery(hql);
query.setParameter("cust_id",2l);
*/
/**
分页查询
String hql="from Customer ";
Query query = session.createQuery(hql);
query.setFirstResult(1);//第几页
query.setMaxResults(3);//每次返回最大多少
*/
List list = query.list();//返回list
System.out.print(list);
// Object o = query.uniqueResult();//接受唯一的查询
//根据HQL语句创建查询对象
//根据查询对象获取查询结果
/**
//内链接
// String hql="from Customer c inner join c.linkMens";
// Query query = session.createQuery(hql);
// List list = query.list();
// for (Object[] arr:list){
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
// }
//迫切内链接(与上述多了个fetch,同时query.list返回返现不在是Object[]),同理左外右外
// String hql="from Customer c inner join fetch c.linkMens";
// Query query = session.createQuery(hql);
// List list = query.list();
// for (Customer arr:list){
// System.out.println(arr);
// }
*/
transaction.commit();
session.close();
Criteria查询
Criteria是一种比hql更面向对象的查询方式。Criteria 可使用 Criterion 和 Projection 设置查询条件
Session session= HibernateUtils.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
/**
基本查询
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Customer.class);
List list = criteria.list();
*/
/**
* 条件查询
* HQL中,不可能出现任何数据库相关的信息
* > gt
* >= ge
* < lt
* <= le
* == eq
* != ne
* in in
* between and between
* like like
* is not null isNotNull
* is null isNull
* or or
* and and
//查询所有Customer
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Customer.class);
criteria.add(Restrictions.ne("cust_id",2l));//这里的ne就是Resctirction提供的方法
List list = criteria.list();
*/
/**
分页
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Customer.class);
criteria.setFirstResult(0);
criteria.setMaxResults(2);
List list = criteria.list();
*/
/**
聚合函数
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Customer.class);
criteria.setProjection(Projections.rowCount());//Projections
Long number = (Long) criteria.uniqueResult();
*/
System.out.println(list);
/**
transaction.commit();
session.close();
//离线查询
@Test
public void fun5(){
//上层构建查询条件
DetachedCriteria dc=DetachedCriteria.forClass(Customer.class);
dc.add(Restrictions.idEq(61));
//dao层代码基本不动
Session session= HibernateUtils.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Criteria executableCriteria = dc.getExecutableCriteria(session);
List list = executableCriteria.list();
System.out.print(list);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
}
原生sql查询
Session session= HibernateUtils.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
String sql="select * from cst_customer";
SQLQuery sqlQuery = session.createSQLQuery(sql);
//因为查询查来的是有几行几行里面有几列
List list = sqlQuery.list();
for (Object[] objs:list){
for (Object o:objs){
System.out.println(o);
}
}
transaction.commit();
session.close();
Session session= HibernateUtils.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
/**
条件查询
String sql="select * from cst_customer where cust_id =?";
SQLQuery sqlQuery = session.createSQLQuery(sql);
sqlQuery.setParameter(0,2l);
*/
/**
分页查询
String sql="select * from cst_customer limit ?,?";
SQLQuery sqlQuery = session.createSQLQuery(sql);
sqlQuery.setParameter(0,0);
sqlQuery.setParameter(1,1);
*/
//这里是给添加实体,查询后就会出该实体
sqlQuery.addEntity(Customer.class);
List list = sqlQuery.list();
System.out.print(list);
懒加载
Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
/**
//立即获得
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 18l);
*/
/**
//返回一个代理对象 只有对对象使用了才会进行查询
Customer customer = session.load(Customer.class, 18l);
System.out.println(customer);//这里才会进行查询如果不操作对象,最后也不会进行数据查询
*/
//返回一个代理对象 如果当期对象呗使用了才会进行查询
Customer customer = session.load(Customer.class, 18l);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
如果要关闭懒加载,建议是开启懒加载
在对象的xml表中配置
//lazy 是关闭懒加载这样load也是当即查询,默认是true
懒加载注意事项,在懒加载的使用要调用懒加载出来的对象,确保seesion并未关闭!!
一对多,多对一
public class
Customer {
/*
* CREATE TABLE `cst_customer` (
`cust_id` BIGINT(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '客户编号(主键)',
`cust_name` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '客户名称(公司名称)',
`cust_source` VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '客户信息来源',
`cust_industry` VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '客户所属行业',
`cust_level` VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '客户级别',
`cust_linkman` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系人',
`cust_phone` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '固定电话',
`cust_mobile` VARCHAR(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '移动电话',
PRIMARY KEY (`cust_id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
*/
private Long cust_id;
private String cust_name;
private String cust_source;
private String cust_industry;
private String cust_level;
private String cust_linkman;
private String cust_phone;
private String cust_mobile;
private Set linkMens=new HashSet<>();
public Long getCust_id() {
return cust_id;
}
public void setCust_id(Long cust_id) {
this.cust_id = cust_id;
}
public String getCust_name() {
return cust_name;
}
public void setCust_name(String cust_name) {
this.cust_name = cust_name;
}
public String getCust_source() {
return cust_source;
}
public void setCust_source(String cust_source) {
this.cust_source = cust_source;
}
public String getCust_industry() {
return cust_industry;
}
public void setCust_industry(String cust_industry) {
this.cust_industry = cust_industry;
}
public String getCust_level() {
return cust_level;
}
public void setCust_level(String cust_level) {
this.cust_level = cust_level;
}
public String getCust_linkman() {
return cust_linkman;
}
public void setCust_linkman(String cust_linkman) {
this.cust_linkman = cust_linkman;
}
public String getCust_phone() {
return cust_phone;
}
public void setCust_phone(String cust_phone) {
this.cust_phone = cust_phone;
}
public String getCust_mobile() {
return cust_mobile;
}
public void setCust_mobile(String cust_mobile) {
this.cust_mobile = cust_mobile;
}
public Set getLinkMens() {
return linkMens;
}
public void setLinkMens(Set linkMens) {
this.linkMens = linkMens;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [cust_id=" + cust_id + ", cust_name=" + cust_name + "]";
}
}
//联系人实体
public class LinkMan {
/*
* CREATE TABLE `cst_linkman` (
`lkm_id` bigint(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '联系人编号(主键)',
`lkm_name` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系人姓名',
`lkm_cust_id` bigint(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '客户id',
`lkm_gender` char(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系人性别',
`lkm_phone` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系人办公电话',
`lkm_mobile` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系人手机',
`lkm_email` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系人邮箱',
`lkm_qq` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系人qq',
`lkm_position` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系人职位',
`lkm_memo` varchar(512) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '联系人备注',
PRIMARY KEY (`lkm_id`),
KEY `FK_cst_linkman_lkm_cust_id` (`lkm_cust_id`),
CONSTRAINT `FK_cst_linkman_lkm_cust_id` FOREIGN KEY (`lkm_cust_id`) REFERENCES `cst_customer` (`cust_id`) ON DELETE NO ACTION ON UPDATE NO ACTION
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
*/
private Long lkm_id;
private Character lkm_gender;
private String lkm_name;
private String lkm_phone;
private String lkm_email;
private String lkm_qq;
private String lkm_mobile;
private String lkm_memo;
private String lkm_position;
//表达多对一关系
private Customer customer ;
//----------------------------------------------
//不与数据库中的列对应,只为了接收表单参数
private Long cust_id;
public Long getCust_id() {
return cust_id;
}
public void setCust_id(Long cust_id) {
this.cust_id = cust_id;
}
public Customer getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
public void setCustomer(Customer customer) {
this.customer = customer;
}
public Long getLkm_id() {
return lkm_id;
}
public void setLkm_id(Long lkm_id) {
this.lkm_id = lkm_id;
}
public Character getLkm_gender() {
return lkm_gender;
}
public void setLkm_gender(Character lkm_gender) {
this.lkm_gender = lkm_gender;
}
public String getLkm_name() {
return lkm_name;
}
public void setLkm_name(String lkm_name) {
this.lkm_name = lkm_name;
}
public String getLkm_phone() {
return lkm_phone;
}
public void setLkm_phone(String lkm_phone) {
this.lkm_phone = lkm_phone;
}
public String getLkm_email() {
return lkm_email;
}
public void setLkm_email(String lkm_email) {
this.lkm_email = lkm_email;
}
public String getLkm_qq() {
return lkm_qq;
}
public void setLkm_qq(String lkm_qq) {
this.lkm_qq = lkm_qq;
}
public String getLkm_mobile() {
return lkm_mobile;
}
public void setLkm_mobile(String lkm_mobile) {
this.lkm_mobile = lkm_mobile;
}
public String getLkm_memo() {
return lkm_memo;
}
public void setLkm_memo(String lkm_memo) {
this.lkm_memo = lkm_memo;
}
public String getLkm_position() {
return lkm_position;
}
public void setLkm_position(String lkm_position) {
this.lkm_position = lkm_position;
}
}
在原先的hibernate.cfg.xml
在添加
同时配置LinkMan.cfg.xml
@Test
public void fun1(){
Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setCust_name("阿里");
LinkMan linkMan=new LinkMan();
linkMan.setLkm_name("马云1");
LinkMan linkMan1=new LinkMan();
linkMan1.setLkm_name("马云2");
customer.getLinkMens().add(linkMan);
customer.getLinkMens().add(linkMan1);
/**
session.save(customer);
//这里没有添加保存linman对象是因为使用级联操作,在之前Customer的配置中,级联操作会顺带保存
// session.save(linkMan);
// session.save(linkMan1);
*/
/**
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 18l);
LinkMan linkMan = new LinkMan();
linkMan.setLkm_name("马云3");
customer.getLinkMens().add(linkMan);
*/
/**
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 18l);
LinkMan linkMan = session.get(LinkMan.class, 9l);
customer.getLinkMens().remove(linkMan);
//如果不调用delete 在数据库id为9的linman还存在,但是指向Customer外键为null
//session.delete(linkMan);
如果需要删除customer 同时删除linkman 在linkman的配置文件中也添加级联操作
*/
transaction.commit();
session.close();
}
Inverse 属性
http://blog.csdn.net/lzgs_4/article/details/45844045(这篇讲的比较通俗易懂)
多对多操作
//角色对象
public class Role {
/*
*
CREATE TABLE `sys_role` (
`role_id` bigint(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`role_name` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '角色名称',
`role_memo` varchar(128) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '备注',
PRIMARY KEY (`role_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
*/
private Long role_id;
private String role_name;
private String role_memo;
//表达多对多
private Set users = new HashSet();
public Long getRole_id() {
return role_id;
}
public void setRole_id(Long role_id) {
this.role_id = role_id;
}
public String getRole_name() {
return role_name;
}
public void setRole_name(String role_name) {
this.role_name = role_name;
}
public String getRole_memo() {
return role_memo;
}
public void setRole_memo(String role_memo) {
this.role_memo = role_memo;
}
public Set getUsers() {
return users;
}
public void setUsers(Set users) {
this.users = users;
}
}
public class User {
/*
* CREATE TABLE `sys_user` (
`user_id` bigint(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户id',
`user_code` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户账号',
`user_name` varchar(64) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户名称',
`user_password` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户密码',
`user_state` char(1) NOT NULL COMMENT '1:正常,0:暂停',
PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=9 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
*/
private Long user_id;
private String user_code;
private String user_name;
private String user_password;
private Character user_state;
//表达多对多
private Set roles = new HashSet();
public Long getUser_id() {
return user_id;
}
public void setUser_id(Long user_id) {
this.user_id = user_id;
}
public String getUser_code() {
return user_code;
}
public void setUser_code(String user_code) {
this.user_code = user_code;
}
public String getUser_name() {
return user_name;
}
public void setUser_name(String user_name) {
this.user_name = user_name;
}
public String getUser_password() {
return user_password;
}
public void setUser_password(String user_password) {
this.user_password = user_password;
}
public Character getUser_state() {
return user_state;
}
public void setUser_state(Character user_state) {
this.user_state = user_state;
}
public Set getRoles() {
return roles;
}
public void setRoles(Set roles) {
this.roles = roles;
}
}
User和Role的配置文件里 set内容是几乎是镜像的
在User的配置文件中配置
在Role的配置文件中配置
Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
/**
如果不设置inverse属性会报错查看上面配置
User u1=new User();
u1.setUser_name("小明");
User u2=new User();
u2.setUser_name("小红");
Role r1=new Role();
r1.setRole_name("保洁");
Role r2=new Role();
r2.setRole_name("教师");
//用户表达关系
u1.getRoles().add(r1);
u1.getRoles().add(r2);
u2.getRoles().add(r1);
u2.getRoles().add(r2);
//角色表达关系(如果配置了invser下面r1,r2的操作可以不用操作)
r1.getUsers().add(u1);
r1.getUsers().add(u2);
r2.getUsers().add(u1);
r2.getUsers().add(u2);
session.save(u1);
session.save(u2);
session.save(r1);
session.save(r2);
*/
/**
//新增角色
User user = session.get(User.class, 13l);
Role role = new Role();
role.setRole_name("运动员");
user.getRoles().add(role);
//用不用可以根据是否已经设置了联级属性
// session.save(role);
*/
/**
//删除角色
User user = session.get(User.class, 13l);
Role role1 = session.get(Role.class, 11l);
Role role2 = session.get(Role.class, 12l);
user.getRoles().remove(role1);
user.getRoles().remove(role2);
*/
transaction.commit();
session.close();
在一对多的关联中,在一的一方设置inverse=”true”让多的一方来维护关联关系更有助于优化,因为可以减少执行update语句
关联查询中的懒加载
http://blog.csdn.net/csdn_gia/article/details/54694910(案例充足)
批量抓取
List list = query.list();
for (Customer c:list)
{ //如果不设置批量抓取,每次都会查询,根据需求设置batch-size
System.out.println(c.getLinkMens());
}
参考文章:http://blog.csdn.net/fg2006/article/details/6436517
http://blog.csdn.net/lzgs_4/article/details/45844045
http://blog.csdn.net/csdn_gia/article/details/54694910