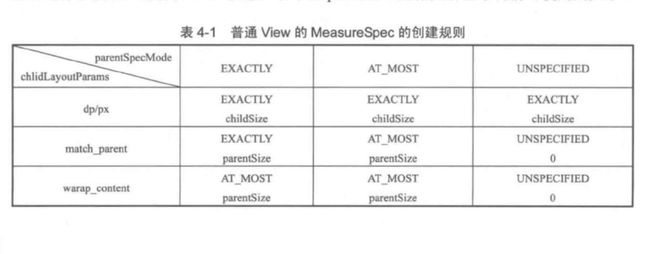
Android View 的测量过程中使用到了MeasureSpec,正如其字面意思所表达的那个-“测量规格”。View根据该规格从而决定自己的大小。MeasureSpec由俩部分组成,一部分是SpecMode(测量模式),另一部分是SpecSize(规格大小)。View的MeasureSpec由父容器和自己布局参数共同决定,这个后面会具体解释。
一.MeasureSpec组成
MeasureSpec是由一个32位 int 值来表示的。其中该 int 值对应的二进制的高2位代表SpecMode,低30位代表SpecSize。这种方法设计很巧妙,减少了空间占用。
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static int makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
}
makeMeasureSpec是用来构建MeasureSpec,可以看出MeasueSpec的确是由Size和Mode 组成起来构建的
二. SpecMode 测量模式
在说具体模式前,有必要大概讲下MeasureSpec是如何来用到View的测量中的。
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
上面是View的measure测量方法。View的测量是一层一层去进行绘制的。首先会绘制ViewGroup,然后由ViewGroup去绘制子View。从View的measure方法,可以看到这里已经传入了widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec。也就是说父ViewGroup去测量子View的时候,已经知道了子View的测量规格。也就是子View的测量模式和测量大小。
- UNSPECIFIED:父容器不对子View有限制,子View要多大给多大,这种一般我们不会接触到
- EXACTLY: 表示精确模式,View的大小已经确认,为SpecSize所指定的值。
- AT_MOST:表示子View的大小不确认,指定了该子View最大可以为多少。子View可以在该范围内设定自己的大小。
可以这样去理解:MeasureSpec是系统提供给了我们一种能力(范围)。View可以在允许的范围内,绘制自己的东西。
三. MeasureSpec的创建发生在何时
- View的测量是由ViewGroup去进行的。以FrameLayout为例。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
...
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
...
}
}
...
}
2 . FrameLayout的onMeasure方法会遍历自己所有的子View,然后调用measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0)去测量子View。
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
可以发现measureChildWithMargins方法的getChildMeasureSpec方法创建了子View的MeasureSpec方法。然后调用child.measure执行子View的测量
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//noinspection ResourceType
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
3 . getChildMeasureSpec方法参数的spec是父容器的测量规格。childDimension则是通过getLayoutParams获取的。所以说子View的MeasureSpec是由 父容器和子View的布局参数共同决定的。
- 下面具体来分析上面方法的情况
由于上面方法情况很多,就只分析父ViewGroup为Exactly模式。
父容器为Exactly模式,那么就可以知道父容器的大小,其值为SpecSize。在来考虑子View的布局参数。
a. 如果子MATCH_PARENT时,那么子View的大小也就确认了,其值和父View一样大,为SpecSize。 子View的大小是确认的,故子View属于Exactly模式,最后通过MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec方法创建即可.
b.View的布局参数如果是具体的值,也是同理的。
c. View的布局参数是WRAP_CONTENT的情况,那么子View在大也不能大过父容器SpecSize的大小。此时由于View的布局是根据自己的内容的,所以大小是不确认的,所以测量模式应该为AT_MOST模式。
下面包含了所有情况