不用 postman 也能学, 但用 postman 更简单.
目标
目标很简单, 也很明确, 能够使用 cURL 发送常用的 GET, POST, DELETE, PATCH 请求.
方法
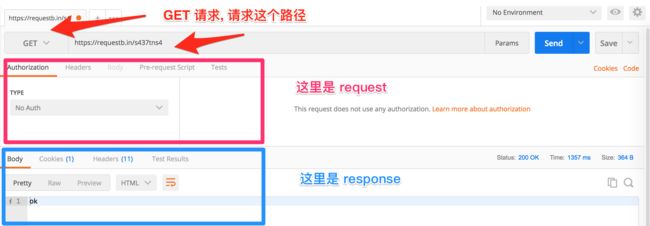
首先打开 postman, 在地址栏输入 https://requestb.in/s437tns4. 这是我从 https://requestb.in/ 临时生成的一个 url, 可以用来接受并显示我们的 request. 它就像一个回声, 你 ping 它就 pong.
点击发送, 有:
看到已经返回了状态码 200 以及 ok.
到 request bin 刷新一下, 可以看到刚才从 postman 发出的请求:
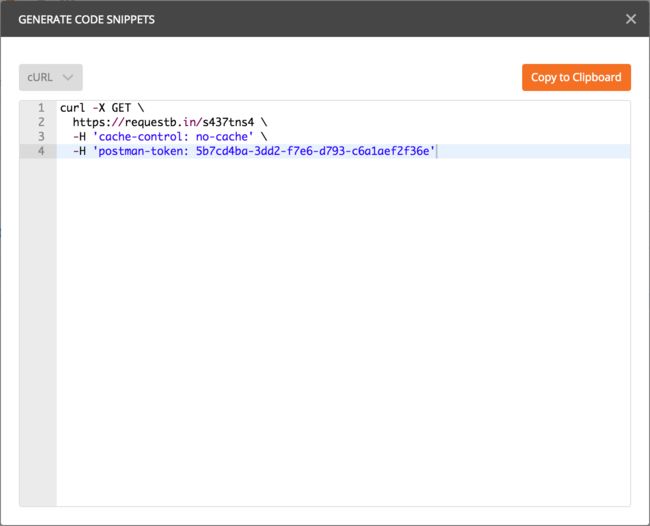
下面用 cURL 来做同样的事. 点击 postman 右上角的 code, 可以看到这个 request 在多种语言的代码, 我们选择 cURL, 得到代码:
curl -X GET \
https://requestb.in/s437tns4 \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'postman-token: 5b7cd4ba-3dd2-f7e6-d793-c6a1aef2f36e'
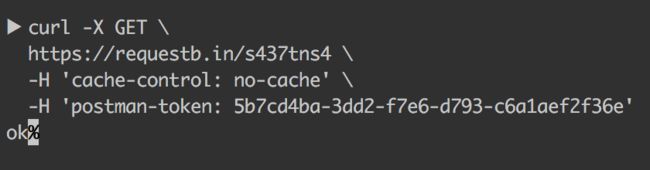
在 shell 下发送这个请求:
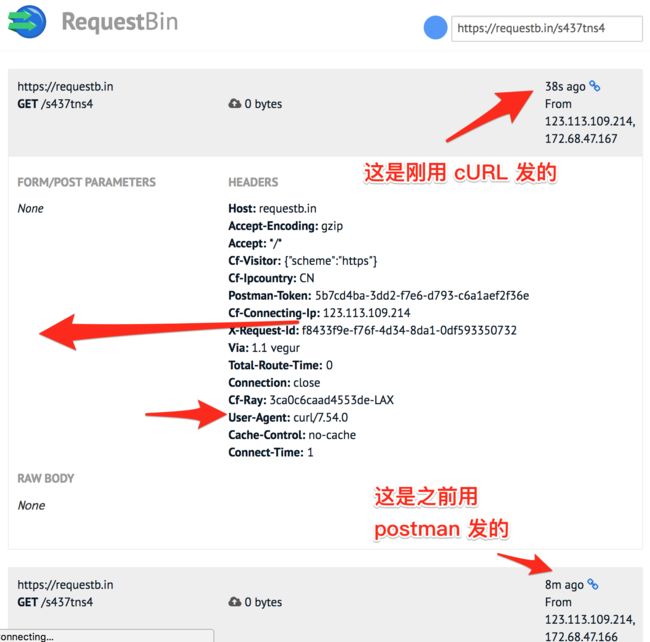
再去 request bin 刷新一下, 收到了第二个请求!
截了这么久的图... 现在我们学到了三个知识点:
- curl 的一般格式是
curl <一个url> - 用
-X GET指定 request 类型位 GET 请求 (An HTTP Method (verb)) - 用
-H 'key=value'指定 header 键值对
实践
过程你懂了. 现在把 postman 的 GET 换成 POST, 得到 cURL 代码:
curl -X POST \
https://requestb.in/s437tns4 \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'postman-token: a645c3f7-fe70-3e2a-213e-5651826cd735'
再刷新 request bin 页面, 得到一个 post 请求:
但你啥东西都没有 post 啊, 我们给 body 加上点文本:
curl -X POST \
https://requestb.in/s437tns4 \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'postman-token: f5cdd615-db24-0add-d278-8928560b1313' \
-d '{
"ping": "pong"
}'
哒哒, 收到了数据:
现在, 我们很确定 -X 后面指定的是 request 方法. 还学到了加 payload 的方法: -d '<字符串>'. (这个 -d 是 --data 的意思.)
The request body can be in multiple formats. These formats are defined by the MIME type of the request. The MIME Type can be set using the Content-Type HTTP header. The most commonly used MIME types are:
- multipart/form-data
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- application/json
有几种 post:
- POST Raw Text:
-d 'string' - POST Form Data:
-d 'foo=bar&foo2=baz'
再多一点实践
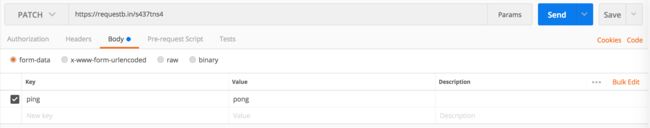
- form data
curl -X PATCH \
https://requestb.in/s437tns4 \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'content-type: multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW' \
-H 'postman-token: 17a4727a-cfbd-8ec3-e139-e484270158b2' \
-F ping=pong
哈哈, 我居然是 patch 的一个 form data... 好像哪里不对.
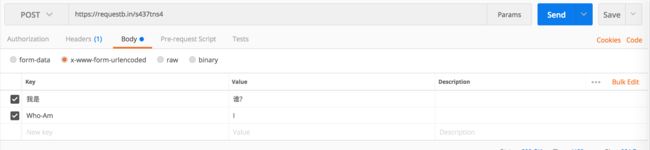
- form url encoded
curl -X POST \
https://requestb.in/s437tns4 \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
-H 'postman-token: 1b1ccc0d-e3a4-73ed-366c-b9d30dc9238c' \
-d '%E6%88%91%E6%98%AF=%E8%B0%81%3F&Who-Am=I'
看看 request bin 收到的 request:
再举一个例子:
HTML 里的这样一个 POST
等价于
curl --data "birthyear=1905&press=%20OK%20" \
http://www.example.com/when.cgi
This kind of POST will use the Content-Type application/x-www-form-urlencoded and is the most widely used POST kind.
这个 %20 很常见, 是空格键, 看 ASCII 表 就知道.
现在的 cURL 可以不用手工转义:
curl --data-urlencode "name=I am Daniel" \
http://www.example.com
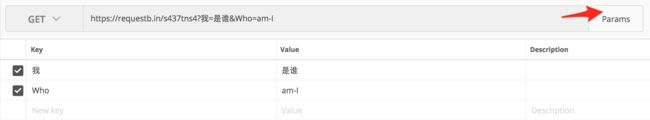
- params
curl -X GET \
'https://requestb.in/s437tns4?%E6%88%91=%E6%98%AF%E8%B0%81&Who=am-I' \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'postman-token: 1be0f58e-fa8b-9a1e-79e4-2dbae11f14f7' \
-d '%E6%88%91%E6%98%AF=%E8%B0%81%3F&Who-Am=I'
再看再学把. postman 虽然好用, 但实在是太卡了! 所以要 GET cURL.
文件上传
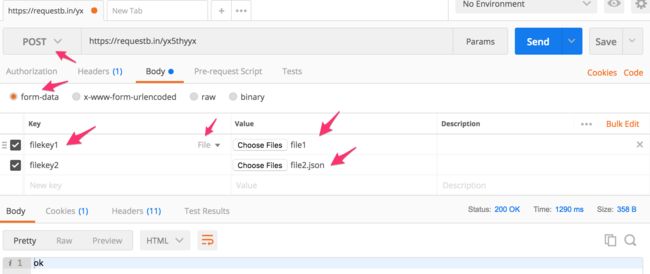
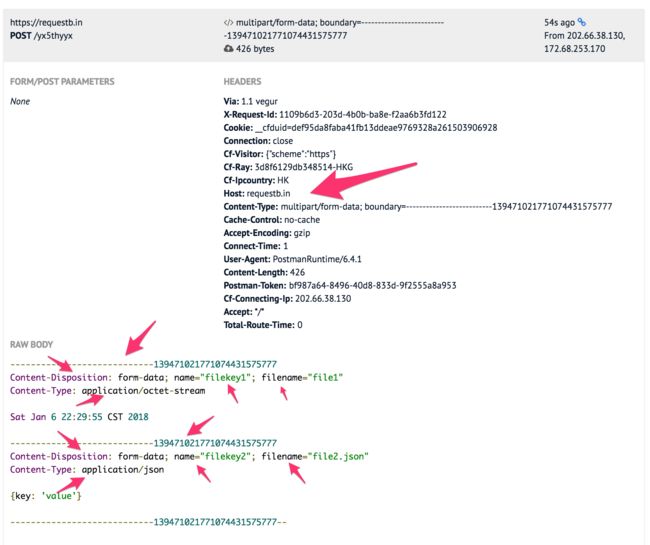
post form-data:
注意到上面最后一个 boundry 后面还有两个 --.
对应的 cURL:
curl -X POST \
https://requestb.in/yx5thyyx \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'content-type: multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW' \
-H 'postman-token: 8a19e97d-2cac-2783-402e-b0a1b17f048b' \
-F filekey1=@/private/tmp/file1 \
-F filekey2=@/private/tmp/file2.json
那个 boundry 是个 随机 的.
put file:
Perhaps the best way to upload data to a HTTP server is to use PUT. Then again, this of course requires that someone put a program or script on the server end that knows how to receive a HTTP PUT stream.
试了一下和 post 看上去没啥区别.
其他
用 referer 来看人家傻不傻:
A HTTP request may include a 'referer' field (yes it is misspelled, 哈哈, 就是拼错了), which can be used to tell from which URL the client got to this particular resource. Some programs/scripts check the referer field of requests to verify that this wasn't arriving from an external site or an unknown page. While this is a stupid way to check something so easily forged, many scripts still do it. Using curl, you can put anything you want in the referer-field and thus more easily be able to fool the server into serving your request.
Use curl to set the referer field with:
curl --referer http://www.example.come \
http://www.example.com
user agent:
--user-agent, 还是看傻不傻.
TODO
更多实例.
Notes
- mulitple requests:
curl -I http://example.com --next http://example.com
PUT
The HTTP PUT request method is similar to HTTP POST. It too is meant to transfer data to a server (and elicit a response). What data is returned depends on the implementation of the server.
A PUT request can pass parameters to the server using "Query String Parameters", as well as the Request Body. For example, in the following raw HTTP request,
PUT /hi/there?hand=wave
PATCH
The HTTP PATCH method is used to update resources on a server. The exact use of PATCH requests depends on the server in question. There are a number of server implementations which handle PATCH differently. Technically, PATCH supports both Query String parameters and a Request Body.
references
- curl - Tutorial
- Introduction · Everything curl
- Postman Echo