(Java Native Interface,Java本地接口)
我们直接新建一个工程,勾选上Include C++ support,生成的内容跟上节
描述的相同。
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_example_huozhenpeng_myapplication_MainActivity_stringFromNative(JNIEnv *env,
jobject instance) {
std::string hello = "Hello from";
return env->NewStringUTF(hello.c_str());
}
看下生成的文件,有个extern "C",如果去掉这个会发现调不通。
extern "C"
(简单来说,这个extern“C”用于C++代码调用C的函数)
百度百科:
extern "C"的主要作用就是为了能够正确实现C++代码调用其他C语言代码。加上extern "C"后,会指示编译器这部分代码按C语言的进行编译,而不是C++的。由于C++支持函数重载,因此编译器编译函数的过程中会将函数的参数类型也加到编译后的代码中,而不仅仅是函数名;而C语言并不支持函数重载,因此编译C语言代码的函数时不会带上函数的参数类型,一般只包括函数名。
JNIEnv
上面的代码中有个很关键的东西JNIEnv,这个是什么呢?
看下声明:
#if defined(__cplusplus)
typedef _JNIEnv JNIEnv;
typedef _JavaVM JavaVM;
#else
typedef const struct JNINativeInterface* JNIEnv;
typedef const struct JNIInvokeInterface* JavaVM;
#endif
(JNIEvn的定义对于c和c++做了区分)
typedef const struct JNINativeInterface* JNIEnv;
/*
* Table of interface function pointers.
*/
struct JNINativeInterface {
void* reserved0;
void* reserved1;
void* reserved2;
void* reserved3;
jint (*GetVersion)(JNIEnv *);
jclass (*DefineClass)(JNIEnv*, const char*, jobject, const jbyte*,
jsize);
...省略很多...
}
JNIEnv本身是个指向一个结构体的指针,所以JNIEnv *env这儿的env变量是个二级指针。
struct _JNIEnv {
/* do not rename this; it does not seem to be entirely opaque */
const struct JNINativeInterface* functions;
#if defined(__cplusplus)
jint GetVersion()
{ return functions->GetVersion(this); }
...省略很多...
}
在C++中JNIEnv就是个结构体
静态本地方法与非静态本地方法
public native String stringFromNative();
public static native String stringFromstaticNative();
看下生成的c++文件的区别:
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_example_huozhenpeng_myapplication_MainActivity_stringFromstaticNative(JNIEnv *env,
jclass type) {
std::string hello = "Hello from C++pppppppp2";
return env->NewStringUTF(hello.c_str());
}
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_example_huozhenpeng_myapplication_MainActivity_stringFromNative(JNIEnv *env,
jobject instance) {
std::string hello = "Hello from";
return env->NewStringUTF(hello.c_str());
}
区别就是方法的第二个参数,静态本地方法生成的是jclass,非静态本地方法生成的是jobject(一个代表的是class,另一个代表的是调用该方法的对象)
在JNI中动态修改java代码中的值
修改非静态成员变量
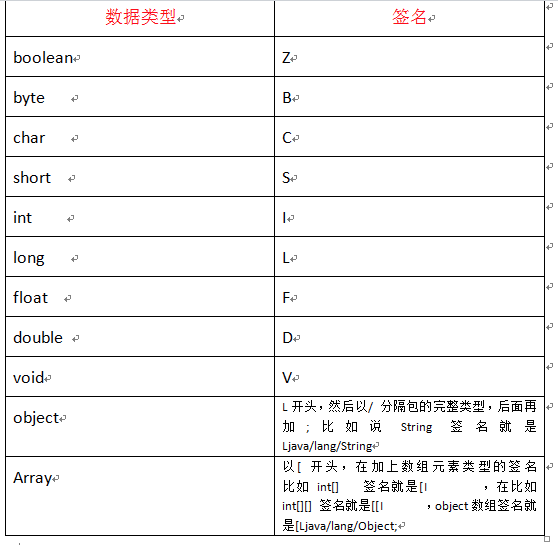
先看下java数据类型在jni中对应的签名,下面要用到
操作引用类型
做个demo,在jni中改变java成员变量的值并返回:
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_example_huozhenpeng_myapplication_MainActivity_updateValueFromJNI(JNIEnv *env,
jobject instance) {
//1.得到jclass
jclass jcs=env->GetObjectClass(instance);
//2.根据jclas得到fieldId(JNI为java中的每个变量都分配了一个fieldId) //参数(jclass,java中要修改的变量名,变量在jni中的签名)
jfieldID fieldid=env->GetFieldID(jcs,"value","Ljava/lang/String;");
//3.得到java中变量
jstring string= (jstring) env->GetObjectField(instance, fieldid);
//4.得到变量的值
const char *value=env->GetStringUTFChars(string,NULL);
//5.修改(拼一个2010吧)
char c[50]="2010";//注意这儿写char *c="2010"、char[]="2010"、char[10]="2010"都不行
//6.拼接新值
strcat(c,value);
//7.生成新字符串
jstring newValue=env->NewStringUTF(c);
//8.设置到对象中
env->SetObjectField(instance,fieldid,newValue);
//9.释放资源
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(newValue,value);
return newValue;
}
private String value="jinzhongxueyuan";
public native String updateValueFromJNI();
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sample_text);
String s1=value;
updateValueFromJNI();
String s2=value;
tv.setText(s1+"\n"+s2);
测试结果:
操作基本类型
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_com_example_huozhenpeng_myapplication_MainActivity_updateIntValueFromJNI(JNIEnv *env,
jobject instance) {
//1.得到jclass
jclass jcs=env->GetObjectClass(instance);
//2.根据jclas得到fieldId(JNI为java中的每个变量都分配了一个fieldId) //参数(jclass,java中要修改的变量名,变量在jni中的签名)
jfieldID fieldid=env->GetFieldID(jcs,"value2","I");
//3.得到java中变量
jint jt=env->GetIntField(instance,fieldid);
int result=jt+50;
//设置新值
env->SetIntField(instance,fieldid,result);
return result;
}
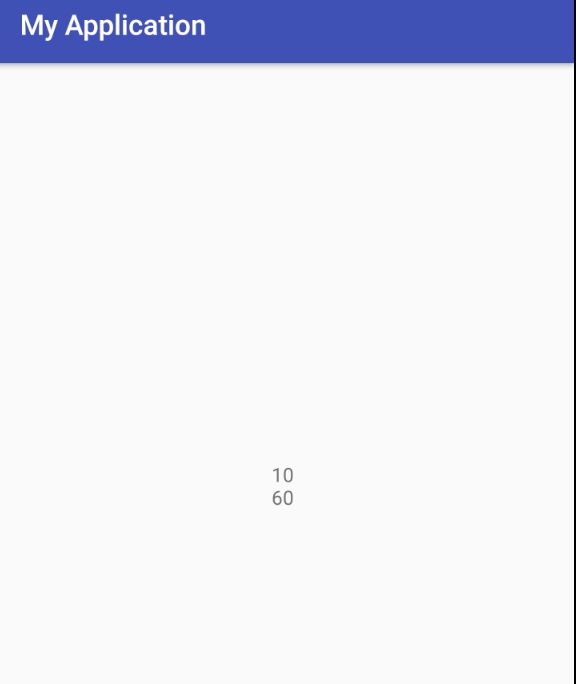
public int value2=10;
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sample_text);
int s1=value2;
updateIntValueFromJNI();
int s2=value2;
tv.setText(s1+"\n"+s2);
操作静态成员变量
其实跟上面大致差不多,只是大部分方法名多了static
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_com_example_huozhenpeng_myapplication_MainActivity_updateStaticValue(JNIEnv *env,
jobject instance) {
//1.得到jclass
jclass jcs=env->GetObjectClass(instance);
//2.根据jclas得到fieldId(JNI为java中的每个变量都分配了一个fieldId) //参数(jclass,java中要修改的变量名,变量在jni中的签名)
jfieldID fieldid=env->GetStaticFieldID(jcs,"value3","I");
//3.得到java中变量
jint jt=env->GetStaticIntField(jcs,fieldid);
int result=jt+50;
//设置新值
env->SetStaticIntField(jcs,fieldid,result);
}
public static int value3=50;
public native void updateStaticValue();
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sample_text);
int s1=value3;
updateStaticValue();
int s2=value3;
tv.setText(s1+"\n"+s2);