Android Activity
标签(空格分隔): android
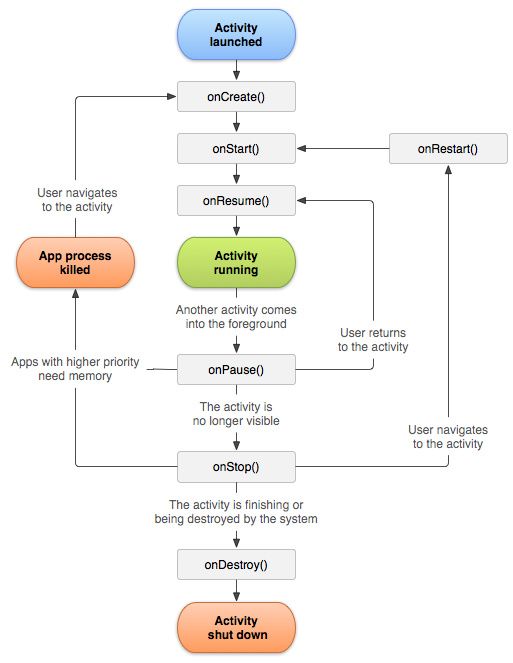
生命周期
- 单个Activity的生命周期
可见状态:onCreate、onStart、onResume
不可见状态:onStop、onPause、onRestart
销毁状态:onDestroy
Activity生命周期图
场景:
- Activity启动:onCreate->onStart->onResume
- 单Activity下app按back键:
onPause->onStop->onDestroy - 一个Activity到另一个Activty:
onPause->onCreate->onStart->onResume->onStop - 从一个Activity返回到前一个Activity:(正常返回)
onPause->onRestart->onStart->onResume->onStop->onDestroy
生命周期设计思想:
1、在多个Activity进行交互的时候,为什么要先暂停(onPause()方法)当前的Activity,执行新的Activity的onCreate()方法,onStart()方法,onResume()方法?
答:比如当你正在一个页面(Activity)上看视频,此时,页面正处于onResume()方法。正在这个时候,突然来了一个电话。此时Android的处理是:首先把第一个视频的页面暂停(onPause()方法),然后再执行第二个页面的onCreate()方法,onStart()方法,onRsume()方法。当第二个页面获得焦点(onResume()方法)的时候,新的页面成功开启的时候,才停止(onStop()方法)第一个页面。如果在新打开的页面onCreate()方法执行之前,就停止(onStop()方法)的话,如果第二个页面由于其它原因开启失败,那就会出现黑屏状态。
2.Activity横竖屏切换:
首先Activity先执行一个生命周期的函数,然后再重新创建一个新的Activity。
- 一般情况大体流程:
onSaveInstanceState-->
onPause-->
onStop-->
onDestroy-->
onCreate-->
onStart-->
onRestoreInstanceState-->
onResume--> - 修改AndroidManifest.xml,把该Activity添加 android:configChanges="orientation"
onSaveInstanceState-->
onPause-->
onStop-->
onDestroy-->
onCreate-->
onStart-->
onRestoreInstanceState-->
onResume-->
- 把android:configChanges="orientation" 改成 android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden",就只打印onConfigChanged
onConfigurationChanged-->
总结:1、不设置Activity的android:configChanges时,切屏会重新调用各个生命周期,切横屏时会执行一次,切竖屏时会执行两次
2、设置Activity的android:configChanges="orientation"时,切屏还是会重新调用各个生命周期,切横、竖屏时只会执行一次
3、设置Activity的android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden"时,切屏不会重新调用各个生命周期,只会执行onConfigurationChanged方法
(参考自这篇博客)
3.onDestory()方法:释放掉与Activity相关的一些属性,为了防止内存泄漏,在优化等方面很重要。
Activity的启动
两种启动方式:隐式启动、显示启动。
应用场景:隐式启动:系统程序或者其他app中的Activity。
显示启动:本app中的Activity。
显示调用
Intent intent = new Intent(FirstActivity.this,SecondActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("person_data",person);
startActivity(intent);
隐式调用
manifest
在MainActivity中调用:
Intent intent = new Intent("www.baidu.com");
- 系统常见系统Activity:启动浏览器、启动图库、启动电话等。
如拨打电话:
//onCreate方法
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_DIAL);
intent.setData(Uri.parse("tel:10086"));
startActivity(intent);
//manifest里面
我们观察到intentFilter里面有三种属性:action、category、data
一个Activity可以有多个intent-filter,一个Intent只要能匹配其中一组intent-filter就可以成功启动。
匹配原则:
- action:
action是一个字符串,系统预定一些action,同时我们也可以自定义一些action。action的匹配规则要求Intent中必须有action且必须和过滤规则中的其中一个action匹配相同。注意action的匹配区分大小写,所以大小写不同的字符串不能被匹配。 - category:
category是一个字符串,系统预定一些category,同时也可以自定义category。category匹配原则要求如果Intent中含有category,那么所有的category都必须和过滤原则其中一个category相同。也就是说没有category也可被匹配,(原因就是系统在调用startActivity或者startActivityForResult的时候会默认为Intent加入“android.intent.category.DEFAULT”这个category)。 - data:
data的语法:
data是由两个部分构成,mimeType和URI。
1、minmeType:是指媒体类型。如image/jpeg、audio/mpeg4-generic等。
2、URI:
Scheme:URI的模式。比如http、file、content等。如果参数没有URI没有指定scheme,其他参数无效。
Host:URI的主机名。如果host未指定,整个URI中的其他参数无效,这也意味着URI是无效。
Port:URI中的端口号。
Path、pathPattern、pathPrefix:这三个参数的路径信息。path表示完整的路径信息,pathPattern表示完整的路径信息,但它里面包括通配符“*”。
例子:
intent.setDataAndType(Uri.parse("file://abc"),"image/png");
如果要为Intent指定完整的Data,必须调用setDataAndType方法不能先调用setData在调用setType方法。因为这两个方法会彼此清除对方的值。
源码中
public Intent setData(Uri uri){
mData = data;
mType = null;
return this;
}
Activity的启动模式
默认情况下,当我们多次启动后同一个Activity的时候,系统会创建多个实例并把它们放入任务栈,当我们点击back键,会发现Activity一个一个回退。任务栈是一个栈结构,后进先出,当栈空时,系统回收这个任务栈。
-
四种启动模式:
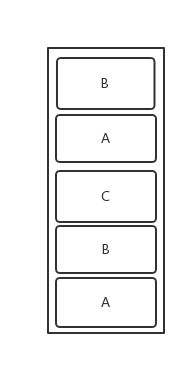
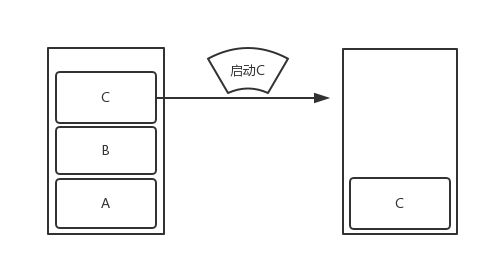
1)standard
Android创建Activity时的默认模式,假设没有为Activity设置启动模式的话,默认标准模式。每次启动一个Activity都会又一次创建一个新的实例入栈,无论这个实例是否存在。
如图:
2)singleTop
栈顶复用模式,在这种模式下,如果新Activity已经位于任务栈顶,此activity不会被重新创建,同时它的onNewIntent方法会被回掉,通过此方法的参数我们可以取出当前请求的信息。
如图
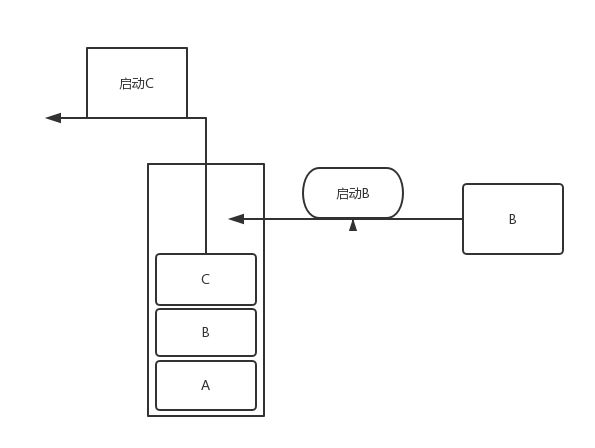
3)singleTask
栈内复用模式,一种单实例模式,只要Activity在一个栈中存在,那么启动此Activity都不会创建实例,在系统中调用onNewIntent。例如ABDC任务栈,singleTask具有clearTop的效果,如果你想去取出B Activity,你的D、C Activity也会出栈。
如图:
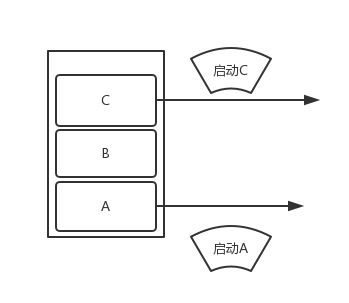
4)singleInstance
具有singleTask的所有属性,并在此模式下,Activity只能单独的位于一个任务栈里面。例如:Activity A运用此模式,当启动A后,系统会为它创建一个任务栈,然后A独自在这个新的任务栈里面,由于栈内复用,后续就不会创建新的Activity了。
如图:
指定启动模式
1、在manifest里面的Activity中指定:
2、通过Intent中设置标志位指定启动模式:(setClass是运用与本app的跳转,setClassName是用于与不同应用程序的Activity的跳转)。
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this,SecondActivity.class);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
startActivity(intent);
第二种方式的优先级高于第一种方式,两者都存在时,取决于第二种方式。两种方式的限定范围不同。
Android中的Flags:
FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK:singleTask
FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP:sinfleTop
FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP:singleTask启动模式会具有此标志位效果。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_EXCLUDE_FROM_RECENTS:相当于android:excludeFromRecents="true".被标记的Activity不会出现在历史列表中。
Actvity传递数据(参考自这篇博客)
1)intent
发送方:
//onCreate方法中
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.putExtra("name", "诸葛亮");
intent.putExtra("age", 50);
intent.putExtra("IQ", 200.0f);
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, SecondActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
接受者:
Intent intent = getIntent();
String name = intent.getStringExtra("name");
int age = intent.getIntExtra("age", 0);
float IQ = intent.getFloatExtra("IQ", 0.0f);
textview2.setText("name:"+name+",age:"+age+",IQ:"+IQ);
2)Bundle
在onCreate方法中的参数就有Bundle。
发送方:
Intent intent = new Intent();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("name", "杨过");
bundle.putInt("age", 30);
bundle.putFloat("weight", 70.9f);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, SecondActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
接受方:
Intent intent = getIntent();
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
String name = bundle.getString("name");
int age = bundle.getInt("age");
float weight = bundle.getFloat("weight");
textview.setText(name+","+age+","+weight);
3)Application
首先要新建一个继承Application的MyApp类,补充属性的get/set方法
AndroidManifest.xml也要配置application的属性android:name=".MyApp"
发送方:
MyApp myApp = (MyApp) getApplication();
myApp.setName("周星驰");
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, SecondActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
接受方:
MyApp myApp = (MyApp) getApplication();
String name = myApp.getName();
textview = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textview);
textview.setText(name);
4)传递对象用Parclelable接口
首先新建一个对象类:
package com.example.intenttest;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Person implements Parcelable {
private String name;
private int age;
private String hobby;
//补全get、set方法
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getHobby() {
return hobby;
}
public void setHobby(String hobby) {
this.hobby = hobby;
}
//必须重写以下方法
/**
* 返回当前对象的内容描述,如果含有文件描述,返回1(常量CONTENTS_FILE_DESCRIPTOR),否则返回0
* @return
*/
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
/**
* 该方法实现序列化
* @param dest
* @param flags 有两个值0(基本上都是0)/1(常量PARCELABLE_WRITE_RETURN_VALUE,表示当前对象需要作为返回值返回,不能立即释放对象)
*/
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeString(name);
dest.writeInt(age);
dest.writeString(hobby);
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator(){
/**
* 从序列化的对象创建原始对象
* @param source 序列化后的对象
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public Person createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
Person person = new Person();
person.name = source.readString();
person.age = source.readInt();
person.hobby = source.readString();
return person;
}
//初始化原始数组的长度
@Override
public Person[] newArray(int size) {
return new Person[size];
}
};
}
发送者:
package com.example.intenttest;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.PersistableBundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.ToggleButton;
public class FirstActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
Person person = new Person();
private final static String TAG = "FirstActivity";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_first);
person.setAge(20);
person.setName("Jack");
person.setHobby("football");
Button sendIntent = (Button)findViewById(R.id.send_intent);
sendIntent.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.send_intent:
Intent intent = new Intent(FirstActivity.this,SecondActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("person_data",person);
startActivity(intent);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
接收者:
Person person = (Person)getIntent().getParcelableExtra("person_data");
textView.setText("年龄:"+person.getAge()+",姓名:"+person.getName()+",爱好:"+person.getHobby());
5)页面返回传值
被返回方:
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,SecondActivity.class);
startActivityForResult(intent, 38);
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
//requstCode邀请码,result返回码;
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
Bundle bundle = data.getExtras();
String name = bundle.getString("name");
int age = bundle.getInt("age");
float weight = bundle.getFloat("weight");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, name+age+weight, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
返回方:
Intent data = new Intent();
data.setClass(SecondActivity.this, MainActivity.class);
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("name", "张天师");
bundle.putInt("age", 30);
bundle.putFloat("weight", 120.5f);
data.putExtras(bundle);
setResult(250, data);
finish();