前言:YOLOv3代码中也提供了参数搜索,可以为对应的数据集进化一套合适的超参数。本文建档分析一下有关这部分的操作方法以及其参数的具体进化方法。
1. 超参数
YOLOv3中的 超参数在train.py中提供,其中包含了一些数据增强参数设置,具体内容如下:
hyp = {'giou': 3.54, # giou loss gain
'cls': 37.4, # cls loss gain
'cls_pw': 1.0, # cls BCELoss positive_weight
'obj': 49.5, # obj loss gain (*=img_size/320 if img_size != 320)
'obj_pw': 1.0, # obj BCELoss positive_weight
'iou_t': 0.225, # iou training threshold
'lr0': 0.00579, # initial learning rate (SGD=1E-3, Adam=9E-5)
'lrf': -4., # final LambdaLR learning rate = lr0 * (10 ** lrf)
'momentum': 0.937, # SGD momentum
'weight_decay': 0.000484, # optimizer weight decay
'fl_gamma': 0.5, # focal loss gamma
'hsv_h': 0.0138, # image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
'hsv_s': 0.678, # image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
'hsv_v': 0.36, # image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
'degrees': 1.98, # image rotation (+/- deg)
'translate': 0.05, # image translation (+/- fraction)
'scale': 0.05, # image scale (+/- gain)
'shear': 0.641} # image shear (+/- deg)
2. 使用方法
在训练的时候,train.py提供了一个可选参数--evolve, 这个参数决定了是否进行超参数搜索与进化(默认是不开启超参数搜索的)。
具体使用方法也很简单:
python train.py --data data/voc.data
--cfg cfg/yolov3-tiny.cfg
--img-size 416
--epochs 273
--evolve
实际使用的时候,需要进行修改,train.py中的约444行:
for _ in range(1): # generations to evolve
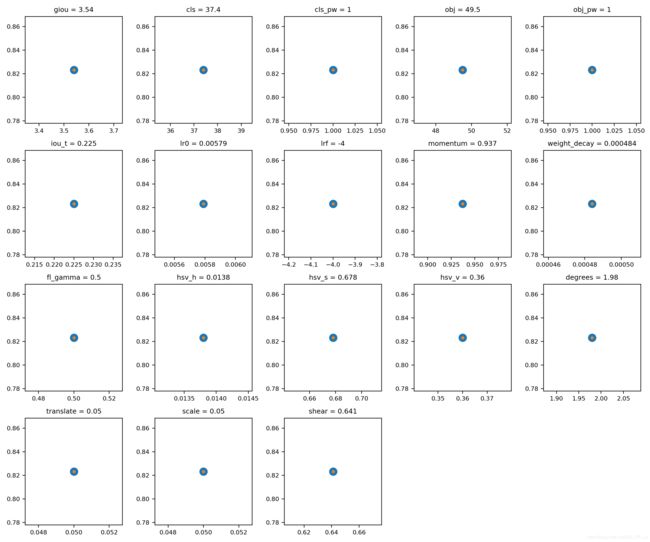
将其中的1修改为你想设置的迭代数,比如200代,如果不设置,结果将会如下图所示,实际上就是只有一代。
3. 原理
整个过程比较简单,对于进化过程中的新一代,都选了了适应性最高的前一代(在前几代中)进行突变。以上所有的参数将有约20%的 1-sigma的正态分布几率同时突变。
s = 0.2 # sigma
整个进化过程需要搞清楚两个点:
- 如何评判其中一代的好坏?
- 下一代如何根据上一代进行进化?
第一个问题:判断好坏的标准。
def fitness(x):
w = [0.0, 0.0, 0.8, 0.2]
# weights for [P, R, mAP, F1]@0.5
return (x[:, :4] * w).sum(1)
YOLOv3进化部分是通过以上的适应度函数判断的,适应度越高,代表这一代的性能越好。而在适应度中,是通过Precision,Recall ,mAP,F1这四个指标作为适应度的评价标准。
其中的w是设置的加权,如果更关心mAP的值,可以提高mAP的权重;如果更关心F1,则设置更高的权重在对应的F1上。这里分配mAP权重为0.8、F1权重为0.2。
第二个问题:如何进行进化?
进化过程中有两个重要的参数:
第一个参数为parent, 可选值为single或者weighted,这个参数的作用是:决定如何选择上一代。如果选择single,代表只选择上一代中最好的那个。
if parent == 'single' or len(x) == 1:
x = x[fitness(x).argmax()]
如果选择weighted,代表选择得分的前10个加权平均的结果作为下一代,具体操作如下:
elif parent == 'weighted': # weighted combination
n = min(10, len(x)) # number to merge
x = x[np.argsort(-fitness(x))][:n] # top n mutations
w = fitness(x) - fitness(x).min() # weights
x = (x * w.reshape(n, 1)).sum(0) / w.sum() # new parent
第二个参数为method,可选值为1,2,3, 分别代表使用三种模式来进化:
# Mutate
method = 2
s = 0.2 # 20% sigma
np.random.seed(int(time.time()))
g = np.array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, .1, \
1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]) # gains
# 这里的g类似加权
ng = len(g)
if method == 1:
v = (np.random.randn(ng) *
np.random.random() * g * s + 1) ** 2.0
elif method == 2:
v = (np.random.randn(ng) *
np.random.random(ng) * g * s + 1) ** 2.0
elif method == 3:
v = np.ones(ng)
while all(v == 1):
# 为了防止重复,直到有变化才停下来
r = (np.random.random(ng) < 0.1) * np.random.randn(ng)
# 10% 的突变几率
v = (g * s * r + 1) ** 2.0
for i, k in enumerate(hyp.keys()):
hyp[k] = x[i + 7] * v[i]
# 进行突变
另外,为了防止突变过程,导致参数出现明显不合理的范围,需要用一个范围进行框定,将超出范围的内容剪切掉。具体方法如下:
# Clip to limits
keys = ['lr0', 'iou_t', 'momentum',
'weight_decay', 'hsv_s',
'hsv_v', 'translate',
'scale', 'fl_gamma']
limits = [(1e-5, 1e-2), (0.00, 0.70),
(0.60, 0.98), (0, 0.001),
(0, .9), (0, .9), (0, .9),
(0, .9), (0, 3)]
for k, v in zip(keys, limits):
hyp[k] = np.clip(hyp[k], v[0], v[1])
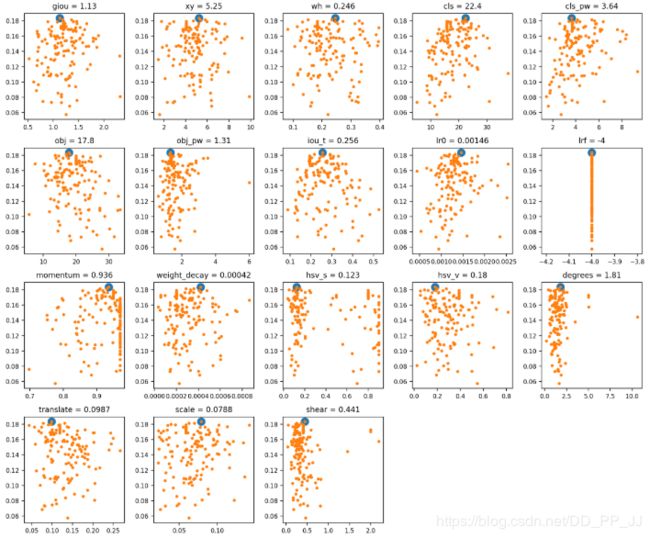
最终训练的超参数搜索的结果可视化:
参考资料:
官方issue: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/392
官方代码:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3