1. 实验目的
- 掌握多线程服务器的编写模板。
- 掌握多线程程序的编写方法。
2. 实验要求
- 认真阅读和掌握本实验的相关知识点。
- 上机编写并运行本程序。
- 保存程序的运行结果,并结合程序进行分析。
3. 实验内容
采用多线程并发服务器技术,服务器可以同时接受多个客户的请求。具体要求如下:
客户端:
- 根据客户输入的服务器IP地址,向服务器发起建立连接的请求。
- 接收客户输入的客户端名称,并把该客户端名称发给服务器。
- 接收客户输入的字符串,将字符串发送给服务器。
- 接收服务器发回的处理后(如何处理不做具体要求,自己可以随意发挥)的字符串并显示。继续接受客户输入的字符串,直到用户输入quit时退出。
服务器端:
- 接收并显示与之连接的客户端的名称。
- 接收客户端发来的字符串,显示出来,并对字符串做处理(如何处理不做具体要求,自己可以随意发挥),最后将处理后的字符串发回给客户。
4. 实验代码和结果
1. 实验代码
服务端代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define PORT 1234
#define BACKLOG 5
#define MAXDATASIZE 1000
void process_cli(int connfd,struct sockaddr_in client);
void* function(void* arg);
struct ARG
{
int connfd;
struct sockaddr_in client;
};
int main()
{
int listenfd,connfd;
pthread_t tid;
struct ARG *arg;
struct sockaddr_in server;
struct sockaddr_in client;
socklen_t len;
if ((listenfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0)) == -1)
{
perror("socket() error.\n");
exit(1);
}
int opt = SO_REUSEADDR;
setsockopt(listenfd,SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR,&opt,sizeof(opt));
bzero(&server,sizeof(server));
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(PORT);
server.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
if (bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&server, sizeof(server)) == -1)
{
perror("bind() error.\n");
exit(1);
}
if(listen(listenfd, BACKLOG) == -1)
{
perror("listen() error.\n");
exit(1);
}
len = sizeof(client);
while(1)
{
if((connfd = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &len)) == -1)
{
perror("accept() error.\n");
exit(1);
}
arg = (struct ARG *)malloc(sizeof(struct ARG));
arg->connfd = connfd;
memcpy((void *)&arg->client, &client,sizeof(client));
if(pthread_create(&tid, NULL, function, (void*)arg))
{
perror("pthread_create() error.\n");
exit(1);
}
}
close(listenfd);
return 0;
}
void process_cli(int connfd,struct sockaddr_in client)
{
int num, i, j, n;
char recvbuf[MAXDATASIZE],sendbuf[MAXDATASIZE],cli_name[MAXDATASIZE];
int code[10] = {2, 0, 1, 5, 1, 2, 2, 0, 7, 5};
printf("[!] You got a connection from: %s, the port is: %d\n", inet_ntoa(client.sin_addr), ntohs(client.sin_port));
num = recv(connfd, cli_name, MAXDATASIZE, 0);
if(num == 0)
{
close(connfd);
printf("[!] Client disconnected.\n");
return;
}
cli_name[num - 1] = '\0';
printf("[>] Client's name is %s.\n",cli_name);
while (num = recv(connfd, recvbuf, MAXDATASIZE, 0))
{
recvbuf[num] = '\0';
printf("[>] Received client (%s) message: %s",cli_name,recvbuf);
if((i = (num - 1) % 10) != 0)
{
for(j = 0; j < (10 - i); j++)
{
recvbuf[num - 1] = '0';
num++;
}
}
for(n = 0; n < num / 10; n++)
{
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if(recvbuf[10 * n + i] >= '0' && recvbuf[10 * n + i] <= '9')
{
recvbuf[10 * n + i] += code[i];
if(recvbuf[10 * n + i]>'9')
{
recvbuf[10 * n + i] -= 10;
}
}
else if(recvbuf[10 * n + i] >= 'a' && recvbuf[10 * n + i] <= 'z')
{
recvbuf[10 * n + i] += code[i];
if(recvbuf[10 * n + i] > 'z')
{
recvbuf[10 * n + i] -= 26;
}
}
else if(recvbuf[10 * n + i] >= 'A' && recvbuf[10 * n + i] <= 'Z')
{
recvbuf[10 * n + i] += code[i];
if(recvbuf[10 * n + i] > 'Z')
{
recvbuf[10 * n + i] -= 26;
}
}
sendbuf[10 * n + i] = recvbuf[10 * n + i];
}
}
sendbuf[num - 1] = '\0';
send(connfd, sendbuf, strlen(sendbuf),0);
printf("[>] Send message:%s\n",sendbuf);
if(!strcmp(sendbuf, "sujy122075"))
{
printf("[>] Client (%s) quit.\n", cli_name);
close(connfd);
break;
}
}
close(connfd);
}
void* function(void* arg)
{
struct ARG *info;
info = (struct ARG *)arg;
process_cli(info->connfd, info->client );
free(arg);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
客户端代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define PORT 1234
#define MAXDATASIZE 1000
void process(FILE *fp,int sockfd);
char* getMessage(char* sendline,int len,FILE *fp);
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int sockfd;
struct hostent* he;
struct sockaddr_in server;
if(argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage:%s\n",argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
if((he = gethostbyname(argv[1])) == NULL)
{
printf("gethostbyname() error\n");
exit(1);
}
if((sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0)) == -1)
{
printf("socket() error\n");
exit(1);
}
bzero(&server, sizeof(server));
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(PORT);
server.sin_addr = *((struct in_addr *)he->h_addr);
if(connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&server, sizeof(server)) == -1)
{
printf("connect() error\n");
exit(1);
}
process(stdin,sockfd);
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
void process(FILE *fp,int sockfd)
{
char sendline[MAXDATASIZE],recvline[MAXDATASIZE];
int num;
printf("[!] Connected to server.\n");
printf("[*] Please input client's name:");
if(fgets(sendline, MAXDATASIZE, fp) == NULL)
{
printf("[!] Exit.\n");
return;
}
send(sockfd, sendline, strlen(sendline), 0);
while(getMessage(sendline, MAXDATASIZE, fp) != NULL)
{
send(sockfd, sendline, strlen(sendline), 0);
if((num = recv(sockfd, recvline, MAXDATASIZE, 0)) == 0)
{
printf("[!] Server terminated.\n");
return;
}
recvline[num] = '\0';
printf("[>] Server Message:%s\n", recvline);
if(!strcmp(recvline, "sujy122075"))
{
close(sockfd);
break;
}
}
printf("[!] Exit.\n");
}
char* getMessage(char* sendline, int len, FILE* fp)
{
printf("[*] Please input string to server:");
return(fgets(sendline,MAXDATASIZE,fp));
}
2. 实验结果
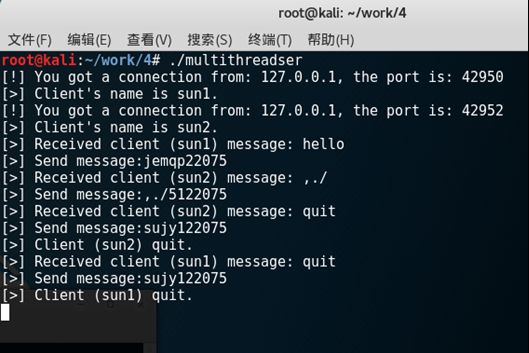
服务端运行结果:
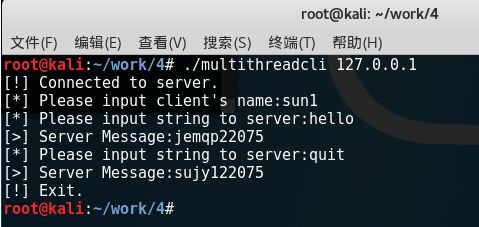
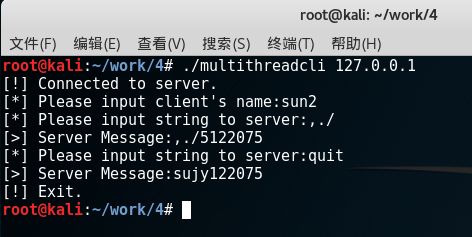
客户端运行结果:
线程1:
线程2:
5. 实验心得
- 在编译时需要加上-pthread,不然的话会编译失败,因为linux中gcc不自带pthread库;
- 线程是进程内独立执行实体和调度单元,创建线程比进程快很多倍;
- 一个进程内的所有线程共享相同的内存空间、全局变量等信息;
- pthread_create创建线程成功后都由一个线程ID标识;
- 如果要传递多个参数,需要将所有数据封装在一个结构中。
6. 附件
下面给出客户端和服务端的c文件
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/19oS960n5VDxEl_x5rhZuGw 密码:d2u3