1、什么是多标签分类?
在图像分类领域,对象可能会存在多个属性的情况。例如,这些属性可以是类别,颜色,大小等。与通常的图像分类相反,此任务的输出将包含2个或更多属性。本文考虑的是多输出问题,即预先知道属性数量,这是一种特殊情况的多标签分类问题。
2、本文使用的数据集?
在Kaggle网站上提供的“ Fashion Product Images”数据集的低分辨率子集中进行练习。在本文中,我们将使用Fashion Product Images数据集。它包含超过44000张衣服和配饰图像,每个图像带有9个标签。我们从kaggle上讲其下载下来,同时将其放置在如下目录下:
. ├── fashion-product-images │ ├── images │ └── styles.csv ├── dataset.py ├── model.py ├── requirements.txt ├── split_data.py ├── test.py └── train.py
styles.csv包含了对象的标签信息.为了方便,我们只使用三个标签:ender, articleType and baseColour.
我们还从数据注释中提取类别的所有唯一标签。总共,我们将拥有:
- 5个性别值(男孩,女孩,男性,中性,女性),
- 47种颜色
- 和143篇物件(例如运动凉鞋,钱包或毛衣)。
我们的目标是创建和训练神经网络模型,以预测数据集中图像的三个标签(性别,物品和颜色)。
3、处理数据
(1)可视化部分数据
(2) 划分训练集和测试集
总共,我们将使用40 000张图像。我们将其中的32,000个放入训练集中,其余的8 000个将用于测试。要分割数据,请运行split_data.py脚本:
import argparse import csv import os import numpy as np from PIL import Image from tqdm import tqdm def save_csv(data, path, fieldnames=['image_path', 'gender', 'articleType', 'baseColour']): with open(path, 'w', newline='') as csv_file: writer = csv.DictWriter(csv_file, fieldnames=fieldnames) writer.writeheader() for row in data: writer.writerow(dict(zip(fieldnames, row))) if __name__ == '__main__': parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Split data for the dataset') parser.add_argument('--input', type=str, required=True, help="Path to the dataset") parser.add_argument('--output', type=str, required=True, help="Path to the working folder") args = parser.parse_args() input_folder = args.input output_folder = args.output annotation = os.path.join(input_folder, 'styles.csv') # open annotation file all_data = [] with open(annotation) as csv_file: # parse it as CSV reader = csv.DictReader(csv_file) # tqdm shows pretty progress bar # each row in the CSV file corresponds to the image for row in tqdm(reader, total=reader.line_num): # we need image ID to build the path to the image file img_id = row['id'] # we're going to use only 3 attributes gender = row['gender'] articleType = row['articleType'] baseColour = row['baseColour'] img_name = os.path.join(input_folder, 'images', str(img_id) + '.jpg') # check if file is in place if os.path.exists(img_name): # check if the image has 80*60 pixels with 3 channels img = Image.open(img_name) if img.size == (60, 80) and img.mode == "RGB": all_data.append([img_name, gender, articleType, baseColour]) # set the seed of the random numbers generator, so we can reproduce the results later np.random.seed(42) # construct a Numpy array from the list all_data = np.asarray(all_data) print(len(all_data)) # Take 40000 samples in random order inds = np.random.choice(40000, 40000, replace=False) # split the data into train/val and save them as csv files save_csv(all_data[inds][:32000], os.path.join(output_folder, 'train.csv')) save_csv(all_data[inds][32000:40000], os.path.join(output_folder, 'val.csv'))
开始划分数据:
!python split_data.py --input ./fashion-product-images/ --output ./fashion-product-images/
(3)读取数据集
import csv import numpy as np from PIL import Image from torch.utils.data import Dataset mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406] std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225] class AttributesDataset(): def __init__(self, annotation_path): color_labels = [] gender_labels = [] article_labels = [] with open(annotation_path) as f: reader = csv.DictReader(f) for row in reader: color_labels.append(row['baseColour']) gender_labels.append(row['gender']) article_labels.append(row['articleType']) self.color_labels = np.unique(color_labels) self.gender_labels = np.unique(gender_labels) self.article_labels = np.unique(article_labels) self.num_colors = len(self.color_labels) self.num_genders = len(self.gender_labels) self.num_articles = len(self.article_labels) self.color_id_to_name = dict(zip(range(len(self.color_labels)), self.color_labels)) self.color_name_to_id = dict(zip(self.color_labels, range(len(self.color_labels)))) self.gender_id_to_name = dict(zip(range(len(self.gender_labels)), self.gender_labels)) self.gender_name_to_id = dict(zip(self.gender_labels, range(len(self.gender_labels)))) self.article_id_to_name = dict(zip(range(len(self.article_labels)), self.article_labels)) self.article_name_to_id = dict(zip(self.article_labels, range(len(self.article_labels)))) class FashionDataset(Dataset): def __init__(self, annotation_path, attributes, transform=None): super().__init__() self.transform = transform self.attr = attributes # initialize the arrays to store the ground truth labels and paths to the images self.data = [] self.color_labels = [] self.gender_labels = [] self.article_labels = [] # read the annotations from the CSV file with open(annotation_path) as f: reader = csv.DictReader(f) for row in reader: self.data.append(row['image_path']) self.color_labels.append(self.attr.color_name_to_id[row['baseColour']]) self.gender_labels.append(self.attr.gender_name_to_id[row['gender']]) self.article_labels.append(self.attr.article_name_to_id[row['articleType']]) def __len__(self): return len(self.data) def __getitem__(self, idx): # take the data sample by its index img_path = self.data[idx] # read image img = Image.open(img_path) # apply the image augmentations if needed if self.transform: img = self.transform(img) # return the image and all the associated labels dict_data = { 'img': img, 'labels': { 'color_labels': self.color_labels[idx], 'gender_labels': self.gender_labels[idx], 'article_labels': self.article_labels[idx] } } return dict_data
4、建立模型
(1)首先我们看看Mobilenetv2的结构:使用以下代码查看
import torchvision.models as models model=models.mobilenet_v2()
结果:
MobileNetV2( (features): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=32, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): Conv2d(32, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (2): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (2): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(16, 96, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(96, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(96, 96, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), groups=96, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(96, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(96, 24, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(24, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (3): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(24, 144, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(144, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(144, 144, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=144, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(144, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(144, 24, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(24, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (4): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(24, 144, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(144, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(144, 144, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), groups=144, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(144, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(144, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (5): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(32, 192, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(192, 192, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=192, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(192, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (6): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(32, 192, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(192, 192, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=192, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(192, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (7): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(32, 192, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(192, 192, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), groups=192, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(192, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (8): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(64, 384, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(384, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=384, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(384, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(384, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (9): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(64, 384, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(384, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=384, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(384, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(384, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (10): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(64, 384, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(384, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=384, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(384, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(384, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (11): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(64, 384, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(384, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=384, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(384, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(384, 96, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(96, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (12): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(96, 576, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(576, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(576, 576, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=576, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(576, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(576, 96, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(96, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (13): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(96, 576, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(576, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(576, 576, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=576, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(576, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(576, 96, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(96, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (14): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(96, 576, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(576, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(576, 576, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), groups=576, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(576, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(576, 160, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(160, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (15): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(160, 960, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(960, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(960, 960, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=960, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(960, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(960, 160, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(160, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (16): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(160, 960, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(960, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(960, 960, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=960, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(960, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(960, 160, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(160, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (17): InvertedResidual( (conv): Sequential( (0): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(160, 960, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(960, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (1): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(960, 960, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=960, bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(960, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) (2): Conv2d(960, 320, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (3): BatchNorm2d(320, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) ) ) (18): ConvBNReLU( (0): Conv2d(320, 1280, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False) (1): BatchNorm2d(1280, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) (2): ReLU6(inplace=True) ) ) (classifier): Sequential( (0): Dropout(p=0.2, inplace=False) (1): Linear(in_features=1280, out_features=1000, bias=True) ) )
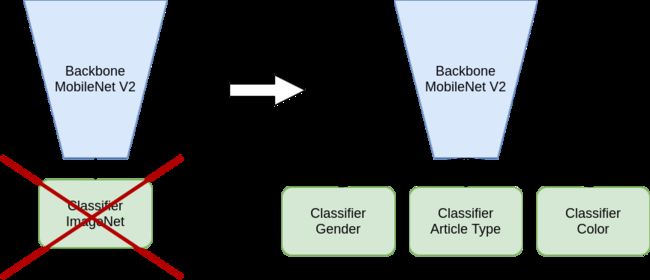
(2)需要对MobileNetv2进行改造以适应多标签分类,我们只需要获取到features中的特征,不使用classifier,同时加入我们自己的分类器。
完整代码:
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torchvision.models as models class MultiOutputModel(nn.Module): def __init__(self, n_color_classes, n_gender_classes, n_article_classes): super().__init__() self.base_model = models.mobilenet_v2().features # take the model without classifier last_channel = models.mobilenet_v2().last_channel # size of the layer before classifier # the input for the classifier should be two-dimensional, but we will have # [batch_size, channels, width, height] # so, let's do the spatial averaging: reduce width and height to 1 self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # create separate classifiers for our outputs self.color = nn.Sequential( nn.Dropout(p=0.2), nn.Linear(in_features=last_channel, out_features=n_color_classes) ) self.gender = nn.Sequential( nn.Dropout(p=0.2), nn.Linear(in_features=last_channel, out_features=n_gender_classes) ) self.article = nn.Sequential( nn.Dropout(p=0.2), nn.Linear(in_features=last_channel, out_features=n_article_classes) ) def forward(self, x): x = self.base_model(x) x = self.pool(x) # reshape from [batch, channels, 1, 1] to [batch, channels] to put it into classifier x = torch.flatten(x, 1) return { 'color': self.color(x), 'gender': self.gender(x), 'article': self.article(x) } def get_loss(self, net_output, ground_truth): color_loss = F.cross_entropy(net_output['color'], ground_truth['color_labels']) gender_loss = F.cross_entropy(net_output['gender'], ground_truth['gender_labels']) article_loss = F.cross_entropy(net_output['article'], ground_truth['article_labels']) loss = color_loss + gender_loss + article_loss return loss, {'color': color_loss, 'gender': gender_loss, 'article': article_loss}
5、开始训练
训练代码:
import argparse import os from datetime import datetime import torch import torchvision.transforms as transforms from dataset import FashionDataset, AttributesDataset, mean, std from model import MultiOutputModel from test import calculate_metrics, validate, visualize_grid from torch.utils.data import DataLoader from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter def get_cur_time(): return datetime.strftime(datetime.now(), '%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M') def checkpoint_save(model, name, epoch): f = os.path.join(name, 'checkpoint-{:06d}.pth'.format(epoch)) torch.save(model.state_dict(), f) print('Saved checkpoint:', f) if __name__ == '__main__': parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Training pipeline') parser.add_argument('--attributes_file', type=str, default='./fashion-product-images/styles.csv', help="Path to the file with attributes") parser.add_argument('--device', type=str, default='cuda', help="Device: 'cuda' or 'cpu'") args = parser.parse_args() start_epoch = 1 N_epochs = 50 batch_size = 16 num_workers = 8 # number of processes to handle dataset loading device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() and args.device == 'cuda' else "cpu") # attributes variable contains labels for the categories in the dataset and mapping between string names and IDs attributes = AttributesDataset(args.attributes_file) # specify image transforms for augmentation during training train_transform = transforms.Compose([ transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5), transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.3, contrast=0.3, saturation=0.3, hue=0), transforms.RandomAffine(degrees=20, translate=(0.1, 0.1), scale=(0.8, 1.2), shear=None, resample=False, fillcolor=(255, 255, 255)), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean, std) ]) # during validation we use only tensor and normalization transforms val_transform = transforms.Compose([ transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean, std) ]) train_dataset = FashionDataset('./fashion-product-images/train.csv', attributes, train_transform) train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=num_workers) val_dataset = FashionDataset('./fashion-product-images/val.csv', attributes, val_transform) val_dataloader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=num_workers) model = MultiOutputModel(n_color_classes=attributes.num_colors, n_gender_classes=attributes.num_genders, n_article_classes=attributes.num_articles)\ .to(device) optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters()) logdir = os.path.join('./logs/', get_cur_time()) savedir = os.path.join('./checkpoints/', get_cur_time()) os.makedirs(logdir, exist_ok=True) os.makedirs(savedir, exist_ok=True) logger = SummaryWriter(logdir) n_train_samples = len(train_dataloader) # Uncomment rows below to see example images with ground truth labels in val dataset and all the labels: # visualize_grid(model, val_dataloader, attributes, device, show_cn_matrices=False, show_images=True, # checkpoint=None, show_gt=True) # print("\nAll gender labels:\n", attributes.gender_labels) # print("\nAll color labels:\n", attributes.color_labels) # print("\nAll article labels:\n", attributes.article_labels) print("Starting training ...") for epoch in range(start_epoch, N_epochs + 1): total_loss = 0 accuracy_color = 0 accuracy_gender = 0 accuracy_article = 0 for batch in train_dataloader: optimizer.zero_grad() img = batch['img'] target_labels = batch['labels'] target_labels = {t: target_labels[t].to(device) for t in target_labels} output = model(img.to(device)) loss_train, losses_train = model.get_loss(output, target_labels) total_loss += loss_train.item() batch_accuracy_color, batch_accuracy_gender, batch_accuracy_article = \ calculate_metrics(output, target_labels) accuracy_color += batch_accuracy_color accuracy_gender += batch_accuracy_gender accuracy_article += batch_accuracy_article loss_train.backward() optimizer.step() print("epoch {:4d}, loss: {:.4f}, color: {:.4f}, gender: {:.4f}, article: {:.4f}".format( epoch, total_loss / n_train_samples, accuracy_color / n_train_samples, accuracy_gender / n_train_samples, accuracy_article / n_train_samples)) logger.add_scalar('train_loss', total_loss / n_train_samples, epoch) if epoch % 5 == 0: validate(model, val_dataloader, logger, epoch, device) if epoch % 25 == 0: checkpoint_save(model, savedir, epoch)
训练开始:
!python train.py --attributes_file ./fashion-product-images/styles.csv --device cuda
训练结果:
2020-04-08 06:29:00.254385: I tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:44] Successfully opened dynamic library libcudart.so.10.1 Starting training ... epoch 1, loss: 5.8528, color: 0.2588, gender: 0.5042, article: 0.2475 epoch 2, loss: 4.5602, color: 0.3409, gender: 0.6014, article: 0.4370 epoch 3, loss: 3.9851, color: 0.4036, gender: 0.6471, article: 0.5129 epoch 4, loss: 3.6513, color: 0.4293, gender: 0.6729, article: 0.5560 epoch 5, loss: 3.4301, color: 0.4493, gender: 0.6840, article: 0.5907 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Validation loss: 2.9477, color: 0.4920, gender: 0.7140, article: 0.6561 epoch 6, loss: 3.2782, color: 0.4629, gender: 0.6943, article: 0.6175 epoch 7, loss: 3.1310, color: 0.4765, gender: 0.7055, article: 0.6365 epoch 8, loss: 3.0227, color: 0.4833, gender: 0.7176, article: 0.6537 epoch 9, loss: 2.9306, color: 0.4956, gender: 0.7206, article: 0.6697 epoch 10, loss: 2.8473, color: 0.5013, gender: 0.7277, article: 0.6796 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Validation loss: 2.6451, color: 0.4930, gender: 0.7387, article: 0.7163 epoch 11, loss: 2.7843, color: 0.5049, gender: 0.7338, article: 0.6893 epoch 12, loss: 2.7196, color: 0.5108, gender: 0.7365, article: 0.6979 epoch 13, loss: 2.6629, color: 0.5202, gender: 0.7424, article: 0.7080 epoch 14, loss: 2.6081, color: 0.5248, gender: 0.7484, article: 0.7135 epoch 15, loss: 2.5597, color: 0.5279, gender: 0.7506, article: 0.7218 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Validation loss: 2.3961, color: 0.5315, gender: 0.7714, article: 0.7491 epoch 16, loss: 2.5190, color: 0.5321, gender: 0.7544, article: 0.7290 epoch 17, loss: 2.4800, color: 0.5365, gender: 0.7594, article: 0.7332 epoch 18, loss: 2.4462, color: 0.5391, gender: 0.7597, article: 0.7373 epoch 19, loss: 2.4088, color: 0.5436, gender: 0.7608, article: 0.7437 epoch 20, loss: 2.3739, color: 0.5429, gender: 0.7659, article: 0.7473 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Validation loss: 2.2869, color: 0.5514, gender: 0.7711, article: 0.7690 epoch 21, loss: 2.3389, color: 0.5473, gender: 0.7690, article: 0.7507 epoch 22, loss: 2.3178, color: 0.5519, gender: 0.7702, article: 0.7565 epoch 23, loss: 2.2882, color: 0.5575, gender: 0.7739, article: 0.7588 epoch 24, loss: 2.2743, color: 0.5598, gender: 0.7737, article: 0.7605 epoch 25, loss: 2.2319, color: 0.5587, gender: 0.7779, article: 0.7687 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Validation loss: 2.1797, color: 0.5543, gender: 0.7922, article: 0.7912 Saved checkpoint: ./checkpoints/2020-04-08_06-29/checkpoint-000025.pth epoch 26, loss: 2.2222, color: 0.5597, gender: 0.7790, article: 0.7670 epoch 27, loss: 2.1937, color: 0.5692, gender: 0.7772, article: 0.7713 epoch 28, loss: 2.1812, color: 0.5667, gender: 0.7835, article: 0.7746 epoch 29, loss: 2.1546, color: 0.5710, gender: 0.7849, article: 0.7777 epoch 30, loss: 2.1379, color: 0.5775, gender: 0.7836, article: 0.7806 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Validation loss: 2.1563, color: 0.5629, gender: 0.7917, article: 0.7952 epoch 31, loss: 2.1177, color: 0.5753, gender: 0.7886, article: 0.7811 epoch 32, loss: 2.1005, color: 0.5736, gender: 0.7862, article: 0.7831 epoch 33, loss: 2.0771, color: 0.5786, gender: 0.7883, article: 0.7898 epoch 34, loss: 2.0599, color: 0.5811, gender: 0.7927, article: 0.7902 epoch 35, loss: 2.0510, color: 0.5809, gender: 0.7911, article: 0.7916 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Validation loss: 2.1351, color: 0.5688, gender: 0.8005, article: 0.7991 epoch 36, loss: 2.0240, color: 0.5823, gender: 0.7955, article: 0.7924 epoch 37, loss: 2.0013, color: 0.5909, gender: 0.8005, article: 0.7971 epoch 38, loss: 2.0063, color: 0.5872, gender: 0.7968, article: 0.7971 epoch 39, loss: 1.9837, color: 0.5904, gender: 0.8035, article: 0.8011 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Validation loss: 2.0680, color: 0.5907, gender: 0.8272, article: 0.8051 epoch 41, loss: 1.9650, color: 0.5939, gender: 0.8028, article: 0.8038 epoch 42, loss: 1.9456, color: 0.5937, gender: 0.8015, article: 0.8045 epoch 43, loss: 1.9259, color: 0.5960, gender: 0.8036, article: 0.8065 epoch 44, loss: 1.9200, color: 0.6020, gender: 0.8066, article: 0.8109 epoch 45, loss: 1.9001, color: 0.6047, gender: 0.8045, article: 0.8104 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Validation loss: 2.0689, color: 0.5907, gender: 0.8132, article: 0.8018 epoch 46, loss: 1.8828, color: 0.5989, gender: 0.8107, article: 0.8158 epoch 47, loss: 1.8747, color: 0.6025, gender: 0.8115, article: 0.8122 epoch 48, loss: 1.8623, color: 0.6080, gender: 0.8102, article: 0.8169 epoch 49, loss: 1.8594, color: 0.6056, gender: 0.8109, article: 0.8189 epoch 50, loss: 1.8409, color: 0.6073, gender: 0.8126, article: 0.8211 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Validation loss: 2.0269, color: 0.5832, gender: 0.8236, article: 0.8155 Saved checkpoint: ./checkpoints/2020-04-08_06-29/checkpoint-000050.pth
6、进行测试
测试代码:
import argparse import os import warnings import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import torch import torchvision.transforms as transforms from dataset import FashionDataset, AttributesDataset, mean, std from model import MultiOutputModel from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, ConfusionMatrixDisplay, balanced_accuracy_score from torch.utils.data import DataLoader def checkpoint_load(model, name): print('Restoring checkpoint: {}'.format(name)) model.load_state_dict(torch.load(name, map_location='cpu')) epoch = int(os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(name))[0].split('-')[1]) return epoch def validate(model, dataloader, logger, iteration, device, checkpoint=None): if checkpoint is not None: checkpoint_load(model, checkpoint) model.eval() with torch.no_grad(): avg_loss = 0 accuracy_color = 0 accuracy_gender = 0 accuracy_article = 0 for batch in dataloader: img = batch['img'] target_labels = batch['labels'] target_labels = {t: target_labels[t].to(device) for t in target_labels} output = model(img.to(device)) val_train, val_train_losses = model.get_loss(output, target_labels) avg_loss += val_train.item() batch_accuracy_color, batch_accuracy_gender, batch_accuracy_article = \ calculate_metrics(output, target_labels) accuracy_color += batch_accuracy_color accuracy_gender += batch_accuracy_gender accuracy_article += batch_accuracy_article n_samples = len(dataloader) avg_loss /= n_samples accuracy_color /= n_samples accuracy_gender /= n_samples accuracy_article /= n_samples print('-' * 72) print("Validation loss: {:.4f}, color: {:.4f}, gender: {:.4f}, article: {:.4f}\n".format( avg_loss, accuracy_color, accuracy_gender, accuracy_article)) logger.add_scalar('val_loss', avg_loss, iteration) logger.add_scalar('val_accuracy_color', accuracy_color, iteration) logger.add_scalar('val_accuracy_gender', accuracy_gender, iteration) logger.add_scalar('val_accuracy_article', accuracy_article, iteration) model.train() def visualize_grid(model, dataloader, attributes, device, show_cn_matrices=True, show_images=True, checkpoint=None, show_gt=False): if checkpoint is not None: checkpoint_load(model, checkpoint) model.eval() imgs = [] labels = [] gt_labels = [] gt_color_all = [] gt_gender_all = [] gt_article_all = [] predicted_color_all = [] predicted_gender_all = [] predicted_article_all = [] accuracy_color = 0 accuracy_gender = 0 accuracy_article = 0 with torch.no_grad(): for batch in dataloader: img = batch['img'] gt_colors = batch['labels']['color_labels'] gt_genders = batch['labels']['gender_labels'] gt_articles = batch['labels']['article_labels'] output = model(img.to(device)) batch_accuracy_color, batch_accuracy_gender, batch_accuracy_article = \ calculate_metrics(output, batch['labels']) accuracy_color += batch_accuracy_color accuracy_gender += batch_accuracy_gender accuracy_article += batch_accuracy_article # get the most confident prediction for each image _, predicted_colors = output['color'].cpu().max(1) _, predicted_genders = output['gender'].cpu().max(1) _, predicted_articles = output['article'].cpu().max(1) for i in range(img.shape[0]): image = np.clip(img[i].permute(1, 2, 0).numpy() * std + mean, 0, 1) predicted_color = attributes.color_id_to_name[predicted_colors[i].item()] predicted_gender = attributes.gender_id_to_name[predicted_genders[i].item()] predicted_article = attributes.article_id_to_name[predicted_articles[i].item()] gt_color = attributes.color_id_to_name[gt_colors[i].item()] gt_gender = attributes.gender_id_to_name[gt_genders[i].item()] gt_article = attributes.article_id_to_name[gt_articles[i].item()] gt_color_all.append(gt_color) gt_gender_all.append(gt_gender) gt_article_all.append(gt_article) predicted_color_all.append(predicted_color) predicted_gender_all.append(predicted_gender) predicted_article_all.append(predicted_article) imgs.append(image) labels.append("{}\n{}\n{}".format(predicted_gender, predicted_article, predicted_color)) gt_labels.append("{}\n{}\n{}".format(gt_gender, gt_article, gt_color)) if not show_gt: n_samples = len(dataloader) print("\nAccuracy:\ncolor: {:.4f}, gender: {:.4f}, article: {:.4f}".format( accuracy_color / n_samples, accuracy_gender / n_samples, accuracy_article / n_samples)) # Draw confusion matrices if show_cn_matrices: # color cn_matrix = confusion_matrix( y_true=gt_color_all, y_pred=predicted_color_all, labels=attributes.color_labels, normalize='true') ConfusionMatrixDisplay(cn_matrix, attributes.color_labels).plot( include_values=False, xticks_rotation='vertical') plt.title("Colors") plt.tight_layout() plt.show() # gender cn_matrix = confusion_matrix( y_true=gt_gender_all, y_pred=predicted_gender_all, labels=attributes.gender_labels, normalize='true') ConfusionMatrixDisplay(cn_matrix, attributes.gender_labels).plot( xticks_rotation='horizontal') plt.title("Genders") plt.tight_layout() plt.show() # Uncomment code below to see the article confusion matrix (it may be too big to display) cn_matrix = confusion_matrix( y_true=gt_article_all, y_pred=predicted_article_all, labels=attributes.article_labels, normalize='true') plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 1.8}) plt.rcParams.update({'figure.dpi': 300}) ConfusionMatrixDisplay(cn_matrix, attributes.article_labels).plot( include_values=False, xticks_rotation='vertical') plt.rcParams.update({'figure.dpi': 100}) plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 5}) plt.title("Article types") plt.show() if show_images: labels = gt_labels if show_gt else labels title = "Ground truth labels" if show_gt else "Predicted labels" n_cols = 5 n_rows = 3 fig, axs = plt.subplots(n_rows, n_cols, figsize=(10, 10)) axs = axs.flatten() for img, ax, label in zip(imgs, axs, labels): ax.set_xlabel(label, rotation=0) ax.get_xaxis().set_ticks([]) ax.get_yaxis().set_ticks([]) ax.imshow(img) plt.suptitle(title) plt.tight_layout() plt.show() model.train() def calculate_metrics(output, target): _, predicted_color = output['color'].cpu().max(1) gt_color = target['color_labels'].cpu() _, predicted_gender = output['gender'].cpu().max(1) gt_gender = target['gender_labels'].cpu() _, predicted_article = output['article'].cpu().max(1) gt_article = target['article_labels'].cpu() with warnings.catch_warnings(): # sklearn may produce a warning when processing zero row in confusion matrix warnings.simplefilter("ignore") accuracy_color = balanced_accuracy_score(y_true=gt_color.numpy(), y_pred=predicted_color.numpy()) accuracy_gender = balanced_accuracy_score(y_true=gt_gender.numpy(), y_pred=predicted_gender.numpy()) accuracy_article = balanced_accuracy_score(y_true=gt_article.numpy(), y_pred=predicted_article.numpy()) return accuracy_color, accuracy_gender, accuracy_article if __name__ == '__main__': parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Inference pipeline') parser.add_argument('--checkpoint', type=str, required=True, help="Path to the checkpoint") parser.add_argument('--attributes_file', type=str, default='./fashion-product-images/styles.csv', help="Path to the file with attributes") parser.add_argument('--device', type=str, default='cuda', help="Device: 'cuda' or 'cpu'") args = parser.parse_args() device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() and args.device == 'cuda' else "cpu") # attributes variable contains labels for the categories in the dataset and mapping between string names and IDs attributes = AttributesDataset(args.attributes_file) # during validation we use only tensor and normalization transforms val_transform = transforms.Compose([ transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean, std) ]) test_dataset = FashionDataset('./fashion-product-images/val.csv', attributes, val_transform) test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=False, num_workers=8) model = MultiOutputModel(n_color_classes=attributes.num_colors, n_gender_classes=attributes.num_genders, n_article_classes=attributes.num_articles).to(device) # Visualization of the trained model visualize_grid(model, test_dataloader, attributes, device, checkpoint=args.checkpoint)
开始执行:
!python test.py --checkpoint ./checkpoints/2020-04-08_06-29/checkpoint-000050.pth --attributes_file ./fashion-product-images/styles.csv --device cuda
在谷歌colab中显示不出图。加了%matplotlib inline报错,这里只能引用原文的图了:
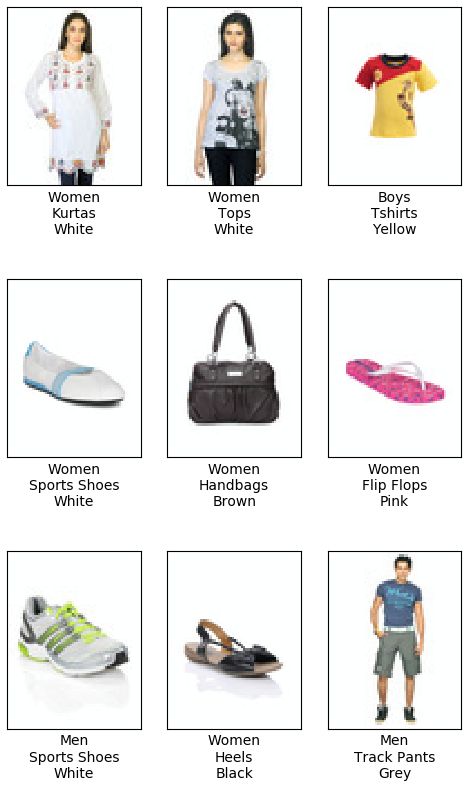
首先是测试集预测的标签:
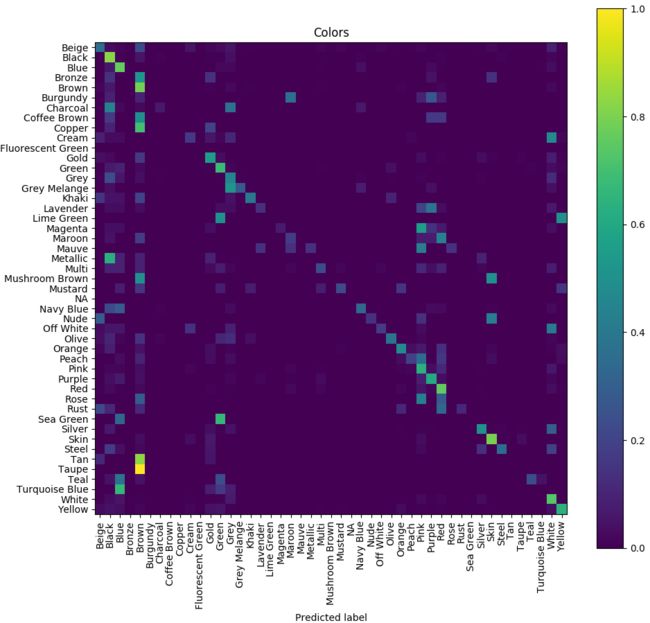
大体上是正确的,但是colors的识别准确率较低,使用混淆矩阵看看:
Now it’s clear that the model confuses similar colors like, for example, magenta, pink, and purple. Even for humans it would be difficult to recognize all the 47 colors represented in the dataset.
如我们所见,低颜色精度是一个大问题。如果要改善它,可以将数据集中的颜色数量减少到例如10种,将相似的颜色重新映射到一个类,然后重新训练模型。应该获得更好的结果。
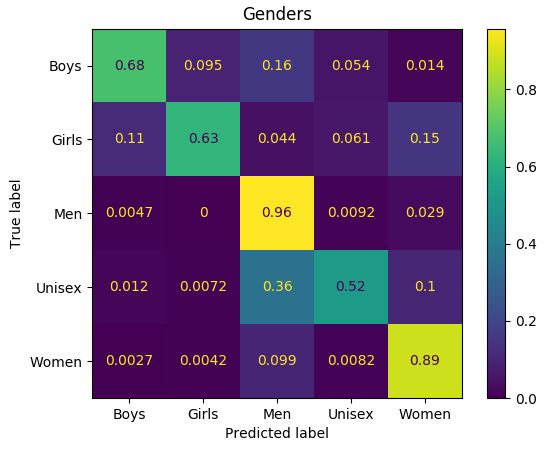
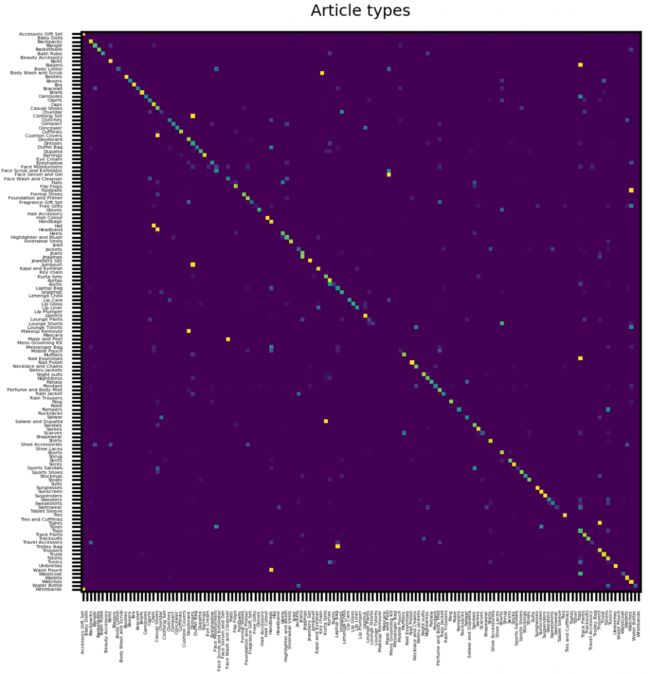
对于类别的混淆矩阵:
该模型使“女孩”和“妇女”标签,“男人”和“男女通用”混淆。同样,对于人类而言,在这些情况下有时可能也很难检测出正确的衣服标签。
最后,这是衣服和配饰的混淆矩阵。在大多数情况下,预测的标签与真实值重合:
同样,有些物件很难区分–下面的这些袋子是很好的例子:
参考:https://www.learnopencv.com/multi-label-image-classification-with-pytorch/