Apache服务器SSL双向认证配置
以Win32版Apache与OpenSSL为例,介绍从创建数字证书到Apache配置的整个过程,希望对读者有所帮助。
Apache是目前最流行的WEB服务器之一,借助OpenSSL库,我们可以在Apache上建立SSL通道,提供SSL连接服务。OpenSSL库除提供Apache的SSL模块外,还提供了一套数字证书工具,可以创建、转换数字证书。
1 环境准备
软件下载
l Apache:apache_2.2.4-win32-x86-openssl-0.9.8d.msi
l openSSL:Win32 OpenSSL v0.9.8e
apache_2.2.4-win32-x86-openssl-0.9.8d.msi是一个捆绑的软件包,包含了apache与openssl必选组件,apache的版本是2.2.4,OpenSSL版本是0.9.8d。如不必使用最新的openssl,则仅下载此软件包即可。
软件安装
(1) 运行Win32OpenSSL-0_9_8e.exe安装OpenSSL;
(2) 运行apache_2.2.4-win32-x86-openssl-0.9.8d.msi安装apache。
如果想使用最新版的OpenSSL,则应删除apache安装目录下的libeay32.dll与ssleay32.dll两个文件,迫使Apache使用OpenSSL安装在c:"windows"system32下的两个最新文件。
软件配置
1.3.1 Apache配置
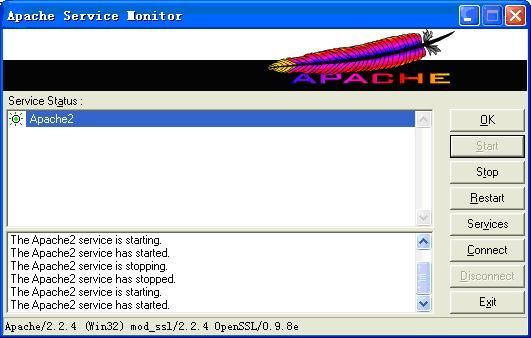
编辑apache的conf目录下的httpd.conf文件,将#LoadModule ssl_module modules/mod_ssl.so前的#删除,使得Apache启动时加载mod_ssl.so模块。重新启动apache,如果看到下列画面,说明mod_ssl.so已经加载成功。
1.3.2 OpenSSL配置
(1)创建证书管理目录与文件;
l 创建C:"CA作为证书管理主目录;
l C:"CA下创建certs与keys两个目录,存储证书与私钥;
l C:"CA下创建crl目录,存储证书注销列表文件;
l C:"CA下创建一个空文件index.txt,存储证书清单;
l C:"CA下创建一个index.txt.attr文件,内容为unique_subject = no;
l C:"CA下创建证书序列号文件serial,内容为01;
l C:"CA下创建证书注销列表序号文件crlnumber,内容为01。
(2)编辑OpenSSL的bin/openssl.cnf文件,修改下列内容:
| # # OpenSSL example configuration file. # This is mostly being used for generation of certificate requests. # # This definition stops the following lines choking if HOME isn't # defined. HOME = . RANDFILE = $ENV::HOME/.rnd # Extra OBJECT IDENTIFIER info: #oid_file = $ENV::HOME/.oid oid_section = new_oids # To use this configuration file with the "-extfile" option of the # "openssl x509" utility, name here the section containing the # X.509v3 extensions to use: # extensions = # (Alternatively, use a configuration file that has only # X.509v3 extensions in its main [= default] section.) [ new_oids ] # We can add new OIDs in here for use by 'ca' and 'req'. # Add a simple OID like this: # testoid1=1.2.3.4 # Or use config file substitution like this: # testoid2=${testoid1}.5.6 #################################################################### [ ca ] default_ca = CA_default # The default ca section #################################################################### [ CA_default ] dir = C:/CA # Where everything is kept certs = $dir/certs # Where the issued certs are kept crl_dir = $dir/crl # Where the issued crl are kept database= $dir/index.txt # database index file. #unique_subject = no # Set to 'no' to allow creation of # several ctificates with same subject. new_certs_dir= $dir/certs # default place for new certs. certificate = $dir/certs/CA.YOUR.COM.crt # The CA certificate serial = $dir/serial # The current serial number crlnumber= $dir/crlnumber # the current crl number # must be commented out to leave a V1 CRL crl = $dir/crl.pem # The current CRL private_key = $dir/keys/CA.YOUR.COM.key # The private key RANDFILE= $dir/keys/.rand # private random number file x509_extensions = usr_cert # The extentions to add to the cert # Comment out the following two lines for the "traditional" # (and highly broken) format. name_opt = ca_default # Subject Name options cert_opt = ca_default # Certificate field options # Extension copying option: use with caution. # copy_extensions = copy # Extensions to add to a CRL. Note: Netscape communicator chokes on V2 CRLs # so this is commented out by default to leave a V1 CRL. # crlnumber must also be commented out to leave a V1 CRL. # crl_extensions = crl_ext default_days = 365 # how long to certify for default_crl_days= 30 # how long before next CRL default_md = sha1 # which md to use. preserve= no # keep passed DN ordering # A few difference way of specifying how similar the request should look # For type CA, the listed attributes must be the same, and the optional # and supplied fields are just that :-) policy = policy_match # For the CA policy [ policy_match ] countryName = match stateOrProvinceName = match organizationName = match organizationalUnitName= optional commonName = supplied emailAddress = optional # For the 'anything' policy # At this point in time, you must list all acceptable 'object' # types. [ policy_anything ] countryName = optional stateOrProvinceName = optional localityName = optional organizationName = optional organizationalUnitName= optional commonName = supplied emailAddress = optional #################################################################### [ req ] default_bits = 1024 default_keyfile = privkey.pem distinguished_name= req_distinguished_name attributes = req_attributes x509_extensions = v3_ca # The extentions to add to the self signed cert # Passwords for private keys if not present they will be prompted for # input_password = secret # output_password = secret # This sets a mask for permitted string types. There are several options. # default: PrintableString, T61String, BMPString. # pkix : PrintableString, BMPString. # utf8only: only UTF8Strings. # nombstr : PrintableString, T61String (no BMPStrings or UTF8Strings). # MASK:XXXX a literal mask value. # WARNING: current versions of Netscape crash on BMPStrings or UTF8Strings # so use this option with caution! string_mask = nombstr # req_extensions = v3_req # The extensions to add to a certificate request [ req_distinguished_name ] countryName = Country Name (2 letter code) countryName_default = CN countryName_min = 2 countryName_max = 2 stateOrProvinceName = State or Province Name (full name) stateOrProvinceName_default= BeiJing localityName = Locality Name (eg, city) 0.organizationName = Organization Name (eg, company) 0.organizationName_default = COM # we can do this but it is not needed normally :-) #1.organizationName = Second Organization Name (eg, company) #1.organizationName_default= World Wide Web Pty Ltd organizationalUnitName = Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) organizationalUnitName_default = YOUR commonName = Common Name (eg, YOUR name) commonName_max = 64 emailAddress = Email Address emailAddress_max = 64 # SET-ex3 = SET extension number 3 [ req_attributes ] challengePassword = A challenge password challengePassword_min = 4 challengePassword_max = 20 unstructuredName = An optional company name [ usr_cert ] # These extensions are added when 'ca' signs a request. # This goes against PKIX guidelines but some CAs do it and some software # requires this to avoid interpreting an end user certificate as a CA. basicConstraints=CA:FALSE # Here are some examples of the usage of nsCertType. If it is omitted # the certificate can be used for anything *except* object signing. # This is OK for an SSL server. # nsCertType = server # For an object signing certificate this would be used. # nsCertType = objsign # For normal client use this is typical # nsCertType = client, email # and for everything including object signing: # nsCertType = client, email, objsign # This is typical in keyUsage for a client certificate. # keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment # This will be displayed in Netscape's comment listbox. nsComment = "OpenSSL Generated Certificate" # PKIX recommendations harmless if included in all certificates. subjectKeyIdentifier=hash authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer # This stuff is for subjectAltName and issuerAltname. # Import the email address. # subjectAltName=email:copy # An alternative to produce certificates that aren't # deprecated according to PKIX. # subjectAltName=email:move # Copy subject details # issuerAltName=issuer:copy #nsCaRevocationUrl = http://www.domain.dom/ca-crl.pem #nsBaseUrl #nsRevocationUrl #nsRenewalUrl #nsCaPolicyUrl #nsSslServerName [ v3_req ] # Extensions to add to a certificate request basicConstraints = CA:FALSE keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment [ v3_ca ] # Extensions for a typical CA # PKIX recommendation. subjectKeyIdentifier=hash authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid:always,issuer:always # This is what PKIX recommends but some broken software chokes on critical # extensions. #basicConstraints = critical,CA:true # So we do this instead. basicConstraints = CA:true # Key usage: this is typical for a CA certificate. However since it will # prevent it being used as an test self-signed certificate it is best # left out by default. # keyUsage = cRLSign, keyCertSign # Some might want this also # nsCertType = sslCA, emailCA # Include email address in subject alt name: another PKIX recommendation # subjectAltName=email:copy # Copy issuer details # issuerAltName=issuer:copy # DER hex encoding of an extension: beware experts only! # obj=DER:02:03 # Where 'obj' is a standard or added object # You can even override a supported extension: # basicConstraints= critical, DER:30:03:01:01:FF [ crl_ext ] # CRL extensions. # Only issuerAltName and authorityKeyIdentifier make any sense in a CRL. # issuerAltName=issuer:copy authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid:always,issuer:always [ proxy_cert_ext ] # These extensions should be added when creating a proxy certificate # This goes against PKIX guidelines but some CAs do it and some software # requires this to avoid interpreting an end user certificate as a CA. basicConstraints=CA:FALSE # Here are some examples of the usage of nsCertType. If it is omitted # the certificate can be used for anything *except* object signing. # This is OK for an SSL server. # nsCertType = server # For an object signing certificate this would be used. # nsCertType = objsign # For normal client use this is typical # nsCertType = client, email # and for everything including object signing: # nsCertType = client, email, objsign # This is typical in keyUsage for a client certificate. # keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment # This will be displayed in Netscape's comment listbox. nsComment = "OpenSSL Generated Certificate" # PKIX recommendations harmless if included in all certificates. subjectKeyIdentifier=hash authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer:always # This stuff is for subjectAltName and issuerAltname. # Import the email address. # subjectAltName=email:copy # An alternative to produce certificates that aren't # deprecated according to PKIX. # subjectAltName=email:move # Copy subject details # issuerAltName=issuer:copy #nsCaRevocationUrl = http://www.domain.dom/ca-crl.pem #nsBaseUrl #nsRevocationUrl #nsRenewalUrl #nsCaPolicyUrl #nsSslServerName # This really needs to be in place for it to be a proxy certificate. proxyCertInfo=critical,language:id-ppl-anyLanguage,pathlen:3,policy:foo |
(3)创建随机数种子rand文件:
| cd c:"openssl"bin openssl rand -out c:/ca/keys/.rand 1024 |
2 创建数字证书
创建根证书(CA.COM)
(1)创建根证书的私钥与证书申请;
| openssl genrsa -des3 -out c:/ca/keys/CA.COM.key 2048 ** 创建时需要指定根私钥保护密码,请牢记此密码。 openssl req -new -out CA.COM.csr -key c:/ca/keys/CA.COM.key -config openssl.cnf ** 创建时需要指定下列内容,其他内容使用默认值。 Country Name : CN State or Province Name: BeiJing Organization Name:COM Organizational Unit Name:COM Common Name:CA.COM |
或:
| openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout c:/ca/Keys/CA.COM.key -out CA.COM.csr -config openssl.cnf ** 创建时需要指定下列内容,其他内容使用默认值。 Country Name : CN State or Province Name: BeiJing Organization Name:COM Organizational Unit Name:COM Common Name:CA.COM |
(2)使用根私钥对根证书自签名;
| openssl ca -in CA.COM.csr -out c:/ca/certs/CA.COM.crt -selfsign -keyfilec:/ca/keys/CA.COM.key -days 7305 -extensions v3_ca -config openssl.cnf ** 确认证书主题是: countryName = CN stateOrProvinceName = BeiJing organizationName = COM organizationalUnitName = COM commonName = CA.COM |
或:
| openssl x509 -in CA.COM.csr -out c:/ca/certs/CA.COM.crt -req -signkeyc:/ca/keys/CA.COM.key -days 7305 -extensions v3_ca -config openssl.cnf ** 确认证书主题是: countryName = CN stateOrProvinceName = BeiJing organizationName = COM organizationalUnitName = COM commonName = CA.COM |
(3)删除根证书申请文件CA.COM.csr。
创建二级根证书(CA.YOUR.COM)
创建完根证书后,我们可以使用根证书创建二级根证书。
(1)创建二级根证书的证书申请;
| openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout c:/ca/keys/CA.YOUR.COM.key -outCA.YOUR.COM.csr -config openssl.cnf ** 创建时需要指定二级证书私钥的保护密码,请牢记此密码; ** 创建时需要指定下列内容,其他内容使用默认值。 Country Name : CN State or Province Name: BeiJing Organization Name:COM Organizational Unit Name:YOUR Common Name:CA.YOUR.COM |
(2)使用根证书对二级根证书进行签名;
| openssl ca -in CA.YOUR.COM.csr -out c:/ca/certs/CA.YOUR.COM.crt -keyfilec:/ca/keys/CA.COM.key -cert c:/ca/certs/CA.COM.crt -days 7305 -extensions v3_ca -config openssl.cnf ** 输入根私钥的保护密码; ** 确认证书主题是: countryName = CN stateOrProvinceName = BeiJing organizationName = COM organizationalUnitName = YOUR commonName = CA.YOUR.COM |
(3)删除二级根证书申请文件CA.YOUR.COM.csr。
至此我们创建完二级根证书,后续的服务器证书与个人证书,我们都使用二级根证书做签名。当然,我们也可以使用根证书签名,但为模拟更现实的情况,我们使用二级根证书做主要的签名证书。
创建服务器证书
(1)创建服务器证书的证书申请;
| openssl req -newkey rsa:1024 -keyout c:/ca/keys/www.your.com.key -outwww.your.com.csr -config openssl.cnf ** 创建时需要指定服务器证书私钥的保护密码,请牢记此密码; ** 创建时需要指定下列内容,其他内容使用默认值。 Country Name : CN State or Province Name: BeiJing Organization Name:COM Organizational Unit Name:YOUR Common Name:www.your.com |
(2)使用二级根证书对服务器证书签名;
| openssl ca -in www.your.com.csr -out c:/ca/certs/www.your.com.crt -config openssl.cnf ** 输入二级证书的私钥保护密码; ** 确认证书主题是: countryName = CN stateOrProvinceName = BeiJing organizationName = COM organizationalUnitName = YOUR commonName = www.your.com 注意:本步骤中我们使用了配置文件openssl.cnf中指定的签名证书ca.your.com.crt与签名证书私钥ca.your.com.key以及有效期365,因而命令比2.2节命令要简洁许多。 |
(3)删除服务器证书申请文件www.your.com.csr。
创建个人证书
(1)创建个人证书的证书申请;
| openssl req -newkey rsa:1024 -keyout my.key -out my.csr -config openssl.cnf ** 创建时需要指定个人证书私钥的保护密码,请牢记此密码; ** 创建时需要指定下列内容,其他内容使用默认值。 Country Name : CN State or Province Name: BeiJing Organization Name:COM Organizational Unit Name:YOUR Common Name:[email protected] |
(2)使用二级根证书对个人证书签名;
| openssl ca -in my.csr -out my.crt -config openssl.cnf ** 输入二级证书的私钥保护密码; ** 确认证书主题是: countryName = CN stateOrProvinceName = BeiJing organizationName = COM organizationalUnitName = YOUR commonName = [email protected] |
(3)添加证书链到个人证书。编辑my.crt文件,将CA.YOUR.COM.crt和CA.COM.crt文件从BEGIN CERTIFICATE开始的内容按序复制到my.crt文件中;
(4)合并编辑后的my.crt与my.key为个人证书文件my.pfx;
| openssl pkcs12 -export -in my.crt -inkey my.key -out c:/ca/certs/my.pfx ** 输入my的证书私钥保护密码; ** 重新指定个人证书的保护密码,请牢记此密码; |
(5)删除个人证书申请文件my.csr、私钥文件my.key、证书文件my.crt。
注意:第3、4两步可以使用下列命令一步完成:
| openssl pkcs12 -export -in my.crt -inkey my.key -out c:/ca/certs/my.pfx -certfile c:/ca/certs/ca.your.com.crt -certfile c:/ca/certs/ca.com.crt |
再按以上步骤,创建另外一张个人证书my1.pfx,Common Name为my1。后面我们将注销这张证书,演示证书注销列表的使用。
创建证书链文件
Web服务器与客户端建立SSL通信通道前,要交换双方的证书,并使用本方的证书链文件(P7B-PKCS7)与证书注销列表文件(CRL)验证对方证书的合法性。
证书链文件,实际上就是多个CA的证书(公钥),有两种格式:一是文本格式(Privacy Enhanced Mail,PEM),即使用BASE64转码后的格式;二是二进制格式(Distinguished Encoding Rules,DER),即P7B文件。其中,PEM格式仅需将各CA的证书从枝到根的顺序合并在一起即可。而P7B格式的证书链文件,则需要特殊处理。
使用OpenSSL创建P7B格式的证书链文件的命令如下:
| openssl crl2pkcs7 -out c:/ca/your.p7b -nocrl -certfilec:/ca/certs/CA.YOUR.COM.crt -certfile c:/ca/certs/CA.COM.crt |
创建证书注销列表文件
(1)注销证书my1.pfx;
编辑c:/ca/index.txt文件,查阅/C=CN /ST=BeiJing /O=COM /OU=YOUR /CN=lny对应的证书序号为05。创建证书时,openssl自动将新创建的证书存储在certs目录下,文件名为<证书序号>.pem,因此05.pem即为my1.pfx对应的证书。使用下列命令可以显示证书的主题信息进行确认:
| openssl x509 -in c:/ca/certs/05.pem -text ** 确认主题是:Subject: C=CN, ST=BeiJing, O=COM, OU=YOUR, CN=my1 |
然后,使用下列命令注销此证书:
| openssl ca -revoke c:/ca/certs/05.pem ** 输入二级根证书的私钥保护密码。 |
再次编辑c:/ca/index.txt,可以看到05号证书的状态已经修改为R,即注销了。
(2)生成证书注销列表文件;
| openssl ca -gencrl -crldays 7 -crlexts crl_ext -out c:/ca/crl/your.crl -config openssl.cnf ** 输入二级证书的私钥保护密码; |
(3)转换PEM格式证书列表文件为DER格式;
本步骤是可选的。如果客户端或服务器需要DER格式的证书注销列表文件,则可以使用下列命令进行格式转换:
| openssl crl -inform PEM -outform DER -in c:/ca/crl/your.crl -outc:/ca/crl/your_bin.crl |
注意:上述操作中,我们可以注销多个证书后再生成证书注销列表。生成证书注销列表时,我们指定了下次发布证书注销列表的日期为7日后(-crldays 7)。
3 配置Apache
准备好需要的各种证书及配套的文件后,我们可以配置Apache,启用SSL连接服务。
(1)编辑apache/conf/httpd.conf,删除#Include conf/extra/ httpd-ssl.conf前的#,激活httpd-ssl.conf;
(2)编辑apache/conf/extra/httpd-ssl.conf,将全部包含C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2的项编辑为使用""括(兰色字体部分),修改如下:
| # # This is the Apache server configuration file providing SSL support. # It contains the configuration directives to instruct the server how to # serve pages over an https connection. For detailing information about these # directives see <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/mod_ssl.html> # # Do NOT simply read the instructions in here without understanding # what they do. They're here only as hints or reminders. If you are unsure # consult the online docs. You have been warned. # # # Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG): # Configure one or more sources to seed the PRNG of the SSL library. # The seed data should be of good random quality. # WARNING! On some platforms /dev/random blocks if not enough entropy # is available. This means you then cannot use the /dev/random device # because it would lead to very long connection times (as long as # it requires to make more entropy available). But usually those # platforms additionally provide a /dev/urandom device which doesn't # block. So, if available, use this one instead. Read the mod_ssl User # Manual for more details. # #SSLRandomSeed startup file:/dev/random 512 #SSLRandomSeed startup file:/dev/urandom 512 #SSLRandomSeed connect file:/dev/random 512 #SSLRandomSeed connect file:/dev/urandom 512 # # When we also provide SSL we have to listen to the # standard HTTP port (see above) and to the HTTPS port # # Note: Configurations that use IPv6 but not IPv4-mapped addresses need two # Listen directives: "Listen [::]:443" and "Listen 0.0.0.0:443" # Listen 443 ## ## SSL Global Context ## ## All SSL configuration in this context applies both to ## the main server and all SSL-enabled virtual hosts. ## # # Some MIME-types for downloading Certificates and CRLs # AddType application/x-x509-ca-cert .crt AddType application/x-pkcs7-crl .crl # Pass Phrase Dialog: # Configure the pass phrase gathering process. # The filtering dialog program (`builtin' is a internal # terminal dialog) has to provide the pass phrase on stdout. SSLPassPhraseDialog builtin # Inter-Process Session Cache: # Configure the SSL Session Cache: First the mechanism # to use and second the expiring timeout (in seconds). #SSLSessionCache dbm:C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/logs/ssl_scache SSLSessionCache "shmcb:C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/logs/ssl_scache(512000)" SSLSessionCacheTimeout 300 # Semaphore: # Configure the path to the mutual exclusion semaphore the # SSL engine uses internally for inter-process synchronization. SSLMutex default ## ## SSL Virtual Host Context ## <VirtualHost _default_:443>
# General setup for the virtual host DocumentRoot "C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/htdocs" ServerName lny.your.com:443 ServerAdmin [email protected] ErrorLog "C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/logs/error_log" TransferLog "C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/logs/access_log" # SSL Engine Switch: # Enable/Disable SSL for this virtual host. SSLEngine on # SSL Cipher Suite: # List the ciphers that the client is permitted to negotiate. # See the mod_ssl documentation for a complete list. SSLCipherSuite ALL:!ADH:!EXPORT56:RC4+RSA:+HIGH:+MEDIUM:+LOW:+SSLv2:+EXP:+eNULL # Server Certificate: # Point SSLCertificateFile at a PEM encoded certificate. If # the certificate is encrypted, then you will be prompted for a # pass phrase. Note that a kill -HUP will prompt again. Keep # in mind that if you have both an RSA and a DSA certificate you # can configure both in parallel (to also allow the use of DSA # ciphers, etc.) SSLCertificateFile "C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/conf/server.crt" #SSLCertificateFile C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/conf/server-dsa.crt # Server Private Key: # If the key is not combined with the certificate, use this # directive to point at the key file. Keep in mind that if # you've both a RSA and a DSA private key you can configure # both in parallel (to also allow the use of DSA ciphers, etc.) SSLCertificateKeyFile "C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/conf/server.key" #SSLCertificateKeyFile C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/conf/server-dsa.key # Server Certificate Chain: # Point SSLCertificateChainFile at a file containing the # concatenation of PEM encoded CA certificates which form the # certificate chain for the server certificate. Alternatively # the referenced file can be the same as SSLCertificateFile # when the CA certificates are directly appended to the server # certificate for convinience. SSLCertificateChainFile "C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/conf/ca.crt" # Certificate Authority (CA): # Set the CA certificate verification path where to find CA # certificates for client authentication or alternatively one # huge file containing all of them (file must be PEM encoded) # Note: Inside SSLCACertificatePath you need hash symlinks # to point to the certificate files. Use the provided # Makefile to update the hash symlinks after changes. SSLCACertificatePath "C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/conf" SSLCACertificateFile "C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/conf/ca.crt" # Certificate Revocation Lists (CRL): # Set the CA revocation path where to find CA CRLs for client # authentication or alternatively one huge file containing all # of them (file must be PEM encoded) # Note: Inside SSLCARevocationPath you need hash symlinks # to point to the certificate files. Use the provided # Makefile to update the hash symlinks after changes. SSLCARevocationPath "C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/conf" SSLCARevocationFile "C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/conf/ca.crl" # Client Authentication (Type): # Client certificate verification type and depth. Types are # none, optional, require and optional_no_ca. Depth is a # number which specifies how deeply to verify the certificate # issuer chain before deciding the certificate is not valid. SSLVerifyClient require SSLVerifyDepth 10 # Access Control: # With SSLRequire you can do per-directory access control based # on arbitrary complex boolean expressions containing server # variable checks and other lookup directives. The syntax is a # mixture between C and Perl. See the mod_ssl documentation # for more details. #<Location /> #SSLRequire ( %{SSL_CIPHER} !~ m/^(EXP|NULL)/ " # and %{SSL_CLIENT_S_DN_O} eq "Snake Oil, Ltd." " # and %{SSL_CLIENT_S_DN_OU} in {"Staff", "CA", "Dev"} " # and %{TIME_WDAY} >= 1 and %{TIME_WDAY} <= 5 " # and %{TIME_HOUR} >= 8 and %{TIME_HOUR} <= 20 ) " # or %{REMOTE_ADDR} =~ m/^192".76".162".[0-9]+$/ #</Location> # SSL Engine Options: # Set various options for the SSL engine. # o FakeBasicAuth: # Translate the client X.509 into a Basic Authorisation. This means that # the standard Auth/DBMAuth methods can be used for access control. The # user name is the `one line' version of the client's X.509 certificate. # Note that no password is obtained from the user. Every entry in the user # file needs this password: `xxj31ZMTZzkVA'. # o ExportCertData: # This exports two additional environment variables: SSL_CLIENT_CERT and # SSL_SERVER_CERT. These contain the PEM-encoded certificates of the # server (always existing) and the client (only existing when client # authentication is used). This can be used to import the certificates # into CGI scripts. # o StdEnvVars: # This exports the standard SSL/TLS related `SSL_*' environment variables. # Per default this exportation is switched off for performance reasons, # because the extraction step is an expensive operation and is usually # useless for serving static content. So one usually enables the # exportation for CGI and SSI requests only. # o StrictRequire: # This denies access when "SSLRequireSSL" or "SSLRequire" applied even # under a "Satisfy any" situation, i.e. when it applies access is denied # and no other module can change it. # o OptRenegotiate: # This enables optimized SSL connection renegotiation handling when SSL # directives are used in per-directory context. #SSLOptions +FakeBasicAuth +ExportCertData +StrictRequire <FilesMatch "".(cgi|shtml|phtml|php)$"> SSLOptions +StdEnvVars </FilesMatch> <Directory "C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/cgi-bin"> SSLOptions +StdEnvVars </Directory> # SSL Protocol Adjustments: # The safe and default but still SSL/TLS standard compliant shutdown # approach is that mod_ssl sends the close notify alert but doesn't wait for # the close notify alert from client. When you need a different shutdown # approach you can use one of the following variables: # o ssl-unclean-shutdown: # This forces an unclean shutdown when the connection is closed, i.e. no # SSL close notify alert is send or allowed to received. This violates # the SSL/TLS standard but is needed for some brain-dead browsers. Use # this when you receive I/O errors because of the standard approach where # mod_ssl sends the close notify alert. # o ssl-accurate-shutdown: # This forces an accurate shutdown when the connection is closed, i.e. a # SSL close notify alert is send and mod_ssl waits for the close notify # alert of the client. This is 100% SSL/TLS standard compliant, but in # practice often causes hanging connections with brain-dead browsers. Use # this only for browsers where you know that their SSL implementation # works correctly. # Notice: Most problems of broken clients are also related to the HTTP # keep-alive facility, so you usually additionally want to disable # keep-alive for those clients, too. Use variable "nokeepalive" for this. # Similarly, one has to force some clients to use HTTP/1.0 to workaround # their broken HTTP/1.1 implementation. Use variables "downgrade-1.0" and # "force-response-1.0" for this. BrowserMatch ".*MSIE.*" " nokeepalive ssl-unclean-shutdown " downgrade-1.0 force-response-1.0 # Per-Server Logging: # The home of a custom SSL log file. Use this when you want a # compact non-error SSL logfile on a virtual host basis. CustomLog "C:/Program Files/Apache Software Foundation/Apache2.2/logs/ssl_request_log" " "%t %h %{SSL_PROTOCOL}x %{SSL_CIPHER}x ""%r"" %b" </VirtualHost> |
(3)取消www.your.com.key的私钥保护密码;
此操作仅Win32的Apache需要。
Linux的Apache启动时自动提示要求输入服务器证书私钥的保护密码,而Win32的Apache没有此功能,因此必须取消证书私钥的保护密码。
| openssl rsa -in c:/ca/keys/www.your.com.key -outc:/ca/keys/www.your.com1.key ** 输入lny.your.com的私钥保护密码。 |
(4)复制证书文件;
移动c:/ca/keys/www.your.com1.key到conf/server.key;
复制c:/ca/certs/www.your.com.crt到conf/server.crt;
合并c:/ca/certs/CA.YOUR.COM.crt和c:/ca/certs/CA.COM. crt证书从BEGIN CERTIFICATE开始的内容到PEM格式的证书链文件中,复制该证书链文件到conf/ca.crt。如果有P7B格式的证书链文件,可以使用下列命名转换成PEM格式的证书链文件。
| openssl pkcs7 -in c:/ca/your.p7b -out ca.crt -print_certs |
复制c:/ca/crl/your.crl到conf/ca.crl。
4 测试
(1)编辑客户端hosts文件,增加服务器的域名;
| 192.168.100.1 www.your.com |
注: windows上hosts文件位于C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc目录。
(2)复制并安装个人证书my.pfx和my1.pfx;
(3)使用ie浏览器访问服务器https://www.your.com,在弹出的证书选择窗口中选择[email protected]证书,应能连接到服务器,输出如下内容。
(4)使用ie浏览器访问服务器https://www.your.com,在弹出的证书选择窗口中选择my1证书,应弹出下列错误窗口。
5 其他证书管理
从个人证书中获取私钥
| openssl pkcs12 -in c:/ca/certs/my.pfx -out my.key –nocerts ** 输入个人证书的保护密码; ** 指定个人证书私钥的保护密码。 |
从个人证书中获取证书
| openssl pkcs12 -in c:/ca/certs/my.pfx -out my.crt -nokeys ** 输入个人证书的保护密码。 |