20一个自定义集合的自述
大家好,我是集合,可能大家对我已经很熟悉了,IEnumerable<T>, IList<T>,List<T>,IQueryable<T>......我就这样被大家使用着,今天,我想与大家走进一步,让您了解更真实的我。
我们就专门为Book类来打造一个集合类吧:
public class Book
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return String.Format("ID:{0},Name:{1}", Id, Name);
}
}
为什么我可以被遍历?
很多朋友问我:为什么我们可以遍历你?其实,我之所以能被遍历,是因为我实现了IEnumerable<T>接口:
public interface IEnumerable<out T> : IEnumerable
{
IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator();
}
而IEnumerable<T>接口实现了IEnumerable接口:
public interface IEnumerable
{
IEnumerator GetEnuemrator();
}
既然我实现了2个接口,那这2个接口的方法IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator()和IEnumerator GetEnuemrator(),我都需要实现,稍后会为大家呈现。我大致上是这样的:
public class BookCollection : IEnumerable<Book>
{
}
我是怎样被初始化的?
在我的内部,我会把所有的元素放到一个容器里,我就把这个容器叫做哈希表,是以键值对存放的,键是字符串,值是object类型:
//key是字符串,value是object类型
private Hashtable table;
每次你们创建我的时候,我都会初始化这个哈希表:
public BookCollection()
{
table = new Hashtable();
}
有些朋友喜欢在初始化我的时候,就把元素添加进来,比如这样:
public static BookCollection GetInitialCollection()
{
return new BookCollection()
{
new Book(){Id="1",Name = "阳光灿烂的日子"},
new Book(){Id = "2", Name = "痛并快乐着"}
};
}
是的,你确实可以这么做,因为我为大家准备了:
public BookCollection(params Book[] array)
{
table = new Hashtable();
foreach (Book item in array)
{
this.Add(item);
}
}
//添加把Book的Id作为哈希表的key
public void Add(Book book)
{
foreach (string key in table.Keys)
{
if(key == book.Id)
throw new Exception("不能重复");
}
table.Add(book.Id, book);
}
为什么可以通过元素位置找到对应元素?
有时候,大家希望通过报上某个位置来获取集合中的元素,对于这点,我提供了索引:
public Book this[int index]
{
get
{
string key = getKey(index);
return table[key] as Book;
}
set
{
string key = getKey(index);
table[key] = value;
}
}
//根据整型获得哈希表中的字符串索引
private string getKey(int index)
{
//边界考虑
if (index < 0 || index > table.Keys.Count)
{
throw new Exception("索引超出了范围");
}
string selected = "";
int i = 0;
foreach (string key in table.Keys)
{
if (i == index)
{
selected = key;
break;
}
i++;
}
return selected;
}
//根据字符串类型获得哈希表中的字符串索引
private string getKey(string key)
{
foreach (string k in table.Keys)
{
if (key == k)
{
return key;
}
}
throw new Exception("不存在此键");
}
public Book this[string key]
{
get
{
string selected = getKey(key);
return table[selected] as Book;
}
set
{
string selected = getKey(key);
table.Remove(table[selected]);
this.Add(value);
}
}
我所倚重的迭代器
大家已经知道,之所以能遍历我,是因为我实现了IEnumerable<T>接口,而IEnumerable<T>接口的作用就是通过方法返回一个迭代器。
迭代器实现了IEnumerator<T>接口:
public interface IEnumerator<out T> : IDisposable, IEnuemrator
{
T Current{get;}
}
而IEnumerator<T>接口又实现了IEnuemrator接口和IDisposabe接口:
public intterface IEnuemrator
{
object Current {get;}
bool MoveNext();
void Reset();
}
public interfac IDisposabe
{
void Dispose();
}
所以,我自身的迭代器需要同时实现IEnumerator<T>和IEnuemrator这2个接口的方法。
什么是迭代器呢?简单地说,迭代器维护了一个集合和指针,通过指针位置的移动来遍历集合的元素。
//迭代器维护着集合和指针
public class BookEnumerator : IEnumerator<Book>
{
private BookCollection collection;
private int index;
//迭代器的初始化
public BookEnumerator(BookCollection bc)
{
this.collection = bc;
index = -1;
}
public BookCollection Collection
{
get { return collection; }
set { collection = value; }
}
//IEnumerator<Book>的实现
public Book Current { get { return collection[index]; } }
//IEnumerator的实现
object IEnumerator.Current
{
get { return collection[index]; }
}
//向下一个位置
public bool MoveNext()
{
index++;
if (index >= collection.Count)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
//重设
public void Reset()
{
index = -1;
}
//实现IDisposabe
public void Dispose()
{
}
}
完整的我
好了,完整的我大致是这样:
展开
集合的使用
现在,你们可以使用我了。
通过foreach遍历:
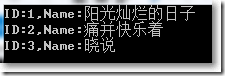
static void Main(string[] args)
{
BookCollection list = BookHelper.GetInitialCollection();
list.Add(new Book(){Id = "3",Name = "晓说"});
foreach (Book book in list)
{
Console.WriteLine(book.ToString());
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
或通过获取迭代器,移动迭代器指针的位置:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
BookCollection list = BookHelper.GetInitialCollection();
list.Add(new Book(){Id = "3",Name = "晓说"});
IEnumerator<Book> e = list.GetEnumerator();
while (e.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Current.ToString());
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
总结
最后,我想感谢哈希表,正是因为有了它,我才能把这么多的元素存放起来。也要感谢IEnumerable<T>和IEnumerator<T>,正是因为实现了这哥俩的接口方法,大家才可以遍历我的集合元素。