萌新做点小玩意儿DAY-3 运用递归和分治的棋盘覆盖算法
今天复习了一下很久很久前学过的分治和递归算法思想。
分治顾名思义分而治之,当面对一个规模比较大的问题时,暴力解决问题则会面临庞大的计算量,因此并不妥当,我们可以把一个大的问题转换为规模相同的子问题,通过调用解决子问题的算法来解决整个问题。
在我看来递归并不是一种算法而是解决问题的一种思想,最常见的递归计算就是计算n!和斐波那契数列,递归的特点就是代码实现起来比较快捷,短短的几行代码就可以计算解决斐波那契数列问题。而非递归的方式则要实现一个很复杂很复杂的函数。
int Fibonacci(int n){
if(n <= 1)
return 1;
return Fibonacci(n-1)+Fibonacci(n-2);
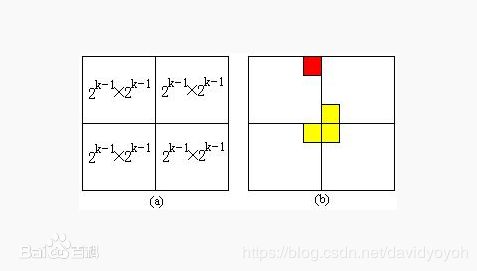
}今天解决的问题就是棋盘覆盖问题。问题描述:在一个2^k*2^k的方格组成的一个棋盘上,恰有一个方格与其他方格不同,称之为特殊方格,显然特殊方格出现的概率有4^种情况,图例中的(a)是k=2中的一种情况,棋盘覆盖问题要求用(b)中的四种L型骨牌覆盖满给定棋盘上除特殊方格以外的所有方格,且要求任何两个骨牌不能重叠覆盖。
(本图源自百度百科)
运用分治策略时,可以将棋盘分为4个2^k-1*2^k-1个子棋盘,特殊方格一定在子棋盘其中之一,其余三个棋盘中无特殊方格,可以进一步在这三个子棋盘的汇合处添加一个L骨牌将这三个子棋盘转换为规模相同的有一个特殊方格的子棋盘,再进行递归的分割,直至棋盘为1*1为止。
(图片源自百度百科)
用C++实现代码如下
#include
using namespace std;
const int max = 100;
int title = 1;
int Board[max][max];
int X,Y,SIZE;
//tx:Line number of the upper left corner of the checkerboard
//ty:Column number of the upper left corner of the checkerboard
//x:The line number of the special square
//y:The column number of the special square
//size:The size of the chessboard
void Chessboard(int tx, int ty, int x, int y, int size){
if (size == 1)
return;
int t = title++; //The type of L
int s = size/2; //Divide the board in half
if (x < tx+s && y < ty+s) //If the special square is in the upper left corner of the checkerboard
Chessboard(tx,ty,x,y,s); //Divide again
else {
Board[tx+s-1][ty+s-1] = t; //Cover the lower right corner
Chessboard(tx,ty,tx+s-1,ty+s-1,s); //Overlaying board
}
if (x < tx+s && y >= ty+s) //If the special square is in the top right corner of the checkerboard
Chessboard(tx,ty+s,x,y,s);
else {
Board[tx+s-1][ty+s] = t;
Chessboard(tx,ty+s,tx+s-1,ty+s,s);
}
if (x >= tx+s && y < ty+s) //If the special square is in the lower left corner of the checkerboard
Chessboard(tx+s,ty,x,y,s);
else {
Board[tx+s][ty+s-1] = t;
Chessboard(tx+s,ty,tx+s,ty+s-1,s);
}
if (x >= tx+s && y >= ty+s) //If the special square is in the lower left corner of the checkerboard
Chessboard(tx+s,ty+s,x,y,s);
else {
Board[tx+s][ty+s] = t;
Chessboard(tx+s,ty+s,tx+s,ty+s,s);
}
}
int main(){
cout <<"请输入特殊方格坐标和棋盘规格"<< endl;
cin >>X>>Y>>SIZE;
Chessboard(0,0,X,Y,SIZE);
for(int i = 0; i < SIZE; i ++){
for(int j = 0; j < SIZE; j ++){
cout < 代码测试效果图:
整个算法的时间复杂度也是显而易见的,
T(K)=1 (K=0)
T(K)=4T(K-1)
可得T(K)=O(4^K)。
总而言之,棋盘覆盖算法属于比较简单而且比较经典的递归分治算法,比较适用于刚接触这种算法思想的人去写一写尝试一下。而递归分治更多的用在排序问题上,比如快排和合并排序,能够在一定程度上优化问题解决的时间复杂度。