FFmpeg —— FFmpeg常用结构体介绍
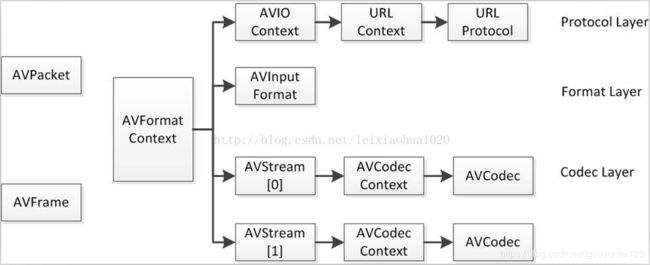
结构体之间的关系
FFMPEG中结构体很多。最关键的结构体可以分成以下几类:
a) 解协议(http,rtsp,rtmp,mms)
AVIOContext,URLProtocol,URLContext主要存储视音频使用的协议的类型以及状态。URLProtocol存储输入视音频使用的封装格式。每种协议都对应一个URLProtocol结构。(注意:FFMPEG中文件也被当做一种协议“file”)
b) 解封装(flv,avi,rmvb,mp4)
AVFormatContext主要存储视音频封装格式中包含的信息;AVInputFormat存储输入视音频使用的封装格式。每种视音频封装格式都对应一个AVInputFormat 结构。
c) 解码(h264,mpeg2,aac,mp3)
每个AVStream存储一个视频/音频流的相关数据;每个AVStream对应一个AVCodecContext,存储该视频/音频流使用解码方式的相关数据;每个AVCodecContext中对应一个AVCodec,包含该视频/音频对应的解码器。每种解码器都对应一个AVCodec结构。
d) 存数据
视频的话,每个结构一般是存一帧;音频可能有好几帧
解码前数据:AVPacket
解码后数据:AVFrame
AVIOContext:输入输出对应的结构体,用于输入输出(读写文件,RTMP协议等)。
AVFormatContext:统领全局的基本结构体。主要用于处理封装格式(FLV/MKV/RMVB等)。
AVStream,AVCodecContext:视音频流对应的结构体,用于视音频编解码。
AVFrame:存储非压缩的数据(视频对应RGB/YUV像素数据,音频对应PCM采样数据)
AVPacket:存储压缩数据(视频对应H.264等码流数据,音频对应AAC/MP3等码流数据)
结构体介绍
AVIOContext
AVIOContext是FFMPEG管理输入输出数据的结构体。
详细介绍参考:FFMPEG结构体分析:AVIOContext
首先看一下结构体的定义(位于avio.h):
/**
* Bytestream IO Context.
* New fields can be added to the end with minor version bumps.
* Removal, reordering and changes to existing fields require a major
* version bump.
* sizeof(AVIOContext) must not be used outside libav*.
*
* @note None of the function pointers in AVIOContext should be called
* directly, they should only be set by the client application
* when implementing custom I/O. Normally these are set to the
* function pointers specified in avio_alloc_context()
*/
typedef struct AVIOContext {
/**
* A class for private options.
*
* If this AVIOContext is created by avio_open2(), av_class is set and
* passes the options down to protocols.
*
* If this AVIOContext is manually allocated, then av_class may be set by
* the caller.
*
* warning -- this field can be NULL, be sure to not pass this AVIOContext
* to any av_opt_* functions in that case.
*/
const AVClass *av_class;
/*
* The following shows the relationship between buffer, buf_ptr,
* buf_ptr_max, buf_end, buf_size, and pos, when reading and when writing
* (since AVIOContext is used for both):
*
**********************************************************************************
* READING
**********************************************************************************
*
* | buffer_size |
* |---------------------------------------|
* | |
*
* buffer buf_ptr buf_end
* +---------------+-----------------------+
* |/ / / / / / / /|/ / / / / / /| |
* read buffer: |/ / consumed / | to be read /| |
* |/ / / / / / / /|/ / / / / / /| |
* +---------------+-----------------------+
*
* pos
* +-------------------------------------------+-----------------+
* input file: | | |
* +-------------------------------------------+-----------------+
*
*
**********************************************************************************
* WRITING
**********************************************************************************
*
* | buffer_size |
* |--------------------------------------|
* | |
*
* buf_ptr_max
* buffer (buf_ptr) buf_end
* +-----------------------+--------------+
* |/ / / / / / / / / / / /| |
* write buffer: | / / to be flushed / / | |
* |/ / / / / / / / / / / /| |
* +-----------------------+--------------+
* buf_ptr can be in this
* due to a backward seek
*
* pos
* +-------------+----------------------------------------------+
* output file: | | |
* +-------------+----------------------------------------------+
*
*/
unsigned char *buffer; /**< Start of the buffer. */
int buffer_size; /**< Maximum buffer size */
unsigned char *buf_ptr; /**< Current position in the buffer */
unsigned char *buf_end; /**< End of the data, may be less than
buffer+buffer_size if the read function returned
less data than requested, e.g. for streams where
no more data has been received yet. */
void *opaque; /**< A private pointer, passed to the read/write/seek/...
functions. */
int (*read_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size);
int (*write_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size);
int64_t (*seek)(void *opaque, int64_t offset, int whence);
int64_t pos; /**< position in the file of the current buffer */
int eof_reached; /**< true if was unable to read due to error or eof */
int write_flag; /**< true if open for writing */
int max_packet_size;
unsigned long checksum;
unsigned char *checksum_ptr;
unsigned long (*update_checksum)(unsigned long checksum, const uint8_t *buf, unsigned int size);
int error; /**< contains the error code or 0 if no error happened */
/**
* Pause or resume playback for network streaming protocols - e.g. MMS.
*/
int (*read_pause)(void *opaque, int pause);
/**
* Seek to a given timestamp in stream with the specified stream_index.
* Needed for some network streaming protocols which don't support seeking
* to byte position.
*/
int64_t (*read_seek)(void *opaque, int stream_index,
int64_t timestamp, int flags);
/**
* A combination of AVIO_SEEKABLE_ flags or 0 when the stream is not seekable.
*/
int seekable;
/**
* max filesize, used to limit allocations
* This field is internal to libavformat and access from outside is not allowed.
*/
int64_t maxsize;
/**
* avio_read and avio_write should if possible be satisfied directly
* instead of going through a buffer, and avio_seek will always
* call the underlying seek function directly.
*/
int direct;
/**
* Bytes read statistic
* This field is internal to libavformat and access from outside is not allowed.
*/
int64_t bytes_read;
/**
* seek statistic
* This field is internal to libavformat and access from outside is not allowed.
*/
int seek_count;
/**
* writeout statistic
* This field is internal to libavformat and access from outside is not allowed.
*/
int writeout_count;
/**
* Original buffer size
* used internally after probing and ensure seekback to reset the buffer size
* This field is internal to libavformat and access from outside is not allowed.
*/
int orig_buffer_size;
/**
* Threshold to favor readahead over seek.
* This is current internal only, do not use from outside.
*/
int short_seek_threshold;
/**
* ',' separated list of allowed protocols.
*/
const char *protocol_whitelist;
/**
* ',' separated list of disallowed protocols.
*/
const char *protocol_blacklist;
/**
* A callback that is used instead of write_packet.
*/
int (*write_data_type)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size,
enum AVIODataMarkerType type, int64_t time);
/**
* If set, don't call write_data_type separately for AVIO_DATA_MARKER_BOUNDARY_POINT,
* but ignore them and treat them as AVIO_DATA_MARKER_UNKNOWN (to avoid needlessly
* small chunks of data returned from the callback).
*/
int ignore_boundary_point;
/**
* Internal, not meant to be used from outside of AVIOContext.
*/
enum AVIODataMarkerType current_type;
int64_t last_time;
/**
* A callback that is used instead of short_seek_threshold.
* This is current internal only, do not use from outside.
*/
int (*short_seek_get)(void *opaque);
int64_t written;
/**
* Maximum reached position before a backward seek in the write buffer,
* used keeping track of already written data for a later flush.
*/
unsigned char *buf_ptr_max;
/**
* Try to buffer at least this amount of data before flushing it
*/
int min_packet_size;
} AVIOContext;
AVIOContext中有以下几个变量比较重要:
unsigned char *buffer:缓存开始位置
int buffer_size:缓存大小(默认32768)
unsigned char *buf_ptr:当前指针读取到的位置
unsigned char *buf_end:缓存结束的位置
void *opaque:URLContext结构体
在解码的情况下,buffer用于存储ffmpeg读入的数据。例如打开一个视频文件的时候,先把数据从硬盘读入buffer,然后在送给解码器用于解码。
其中opaque指向了URLContext。
AVFormatContext
在使用FFMPEG进行开发的时候,AVFormatContext是一个贯穿始终的数据结构,很多函数都要用到它作为参数。它是FFMPEG解封装(flv,mp4,rmvb,avi)功能的结构体。下面看几个主要变量的作用(在这里考虑解码的情况):
struct AVInputFormat *iformat:输入数据的封装格式
AVIOContext *pb:输入数据的缓存
unsigned int nb_streams:视音频流的个数
AVStream **streams:视音频流
char filename[1024]:文件名
int64_t duration:时长(单位:微秒us,转换为秒需要除以1000000)
int bit_rate:比特率(单位bps,转换为kbps需要除以1000)
AVDictionary *metadata:元数据
详细介绍参考:FFMPEG结构体分析:AVFormatContext
AVStream
AVStream是存储每一个视频/音频流信息的结构体。
AVStream重要的变量如下所示:
int index:标识该视频/音频流
AVCodecContext *codec:指向该视频/音频流的AVCodecContext(它们是一一对应的关系)
AVRational time_base:时基。通过该值可以把PTS,DTS转化为真正的时间。FFMPEG其他结构体中也有这个字段,但是根据我的经验,只有AVStream中的time_base是可用的。PTS*time_base=真正的时间
int64_t duration:该视频/音频流长度
AVDictionary *metadata:元数据信息
AVRational avg_frame_rate:帧率(注:对视频来说,这个挺重要的)
AVPacket attached_pic:附带的图片。比如说一些MP3,AAC音频文件附带的专辑封面。
详细介绍参考:FFMPEG结构体分析:AVStream
AVCodecContext
AVCodecContext中很多的参数是编码的时候使用的,而不是解码的时候使用的。
常用参数介绍:
enum AVMediaType codec_type:编解码器的类型(视频,音频...)
struct AVCodec *codec:采用的解码器AVCodec(H.264,MPEG2...)
int bit_rate:平均比特率
uint8_t *extradata; int extradata_size:针对特定编码器包含的附加信息(例如对于H.264解码器来说,存储SPS,PPS等)
AVRational time_base:根据该参数,可以把PTS转化为实际的时间(单位为秒s)
int width, height:如果是视频的话,代表宽和高
int refs:运动估计参考帧的个数(H.264的话会有多帧,MPEG2这类的一般就没有了)
int sample_rate:采样率(音频)
int channels:声道数(音频)
enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt:采样格式
int profile:型(H.264里面就有,其他编码标准应该也有)
int level:级(和profile差不太多)
详细介绍参考:FFMPEG结构体分析:AVCodecContext
AVCodec
AVCodec是存储编解码器信息的结构体。
常用参数介绍:
const char *name:编解码器的名字,比较短
const char *long_name:编解码器的名字,全称,比较长
enum AVMediaType type:指明了类型,是视频,音频,还是字幕
enum AVCodecID id:ID,不重复
const AVRational *supported_framerates:支持的帧率(仅视频)
const enum AVPixelFormat *pix_fmts:支持的像素格式(仅视频)
const int *supported_samplerates:支持的采样率(仅音频)
const enum AVSampleFormat *sample_fmts:支持的采样格式(仅音频)
const uint64_t *channel_layouts:支持的声道数(仅音频)
int priv_data_size:私有数据的大小
详细介绍参考:FFMPEG结构体分析:AVCodec
AVPacket
AVPacket是存储压缩编码数据相关信息的结构体。
常用参数介绍:
uint8_t *data:压缩编码的数据。
例如对于H.264来说。1个AVPacket的data通常对应一个NAL。
注意:在这里只是对应,而不是一模一样。他们之间有微小的差别:使用FFMPEG类库分离出多媒体文件中的H.264码流
因此在使用FFMPEG进行视音频处理的时候,常常可以将得到的AVPacket的data数据直接写成文件,从而得到视音频的码流文件。
int size:data的大小
int64_t pts:显示时间戳
int64_t dts:解码时间戳
int stream_index:标识该AVPacket所属的视频/音频流。
详细介绍参考:FFMPEG结构体分析:AVPacket
AVFrame
AVFrame结构体一般用于存储原始数据(即非压缩数据,例如对视频来说是YUV,RGB,对音频来说是PCM),此外还包含了一些相关的信息。比如说,解码的时候存储了宏块类型表,QP表,运动矢量表等数据。编码的时候也存储了相关的数据。因此在使用FFMPEG进行码流分析的时候,AVFrame是一个很重要的结构体。
常用参数介绍:
uint8_t *data[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]:解码后原始数据(对视频来说是YUV,RGB,对音频来说是PCM)
int linesize[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]:data中“一行”数据的大小。注意:未必等于图像的宽,一般大于图像的宽。
int width, height:视频帧宽和高(1920x1080,1280x720...)
int nb_samples:音频的一个AVFrame中可能包含多个音频帧,在此标记包含了几个
int format:解码后原始数据类型(YUV420,YUV422,RGB24...)
int key_frame:是否是关键帧
enum AVPictureType pict_type:帧类型(I,B,P...)
AVRational sample_aspect_ratio:宽高比(16:9,4:3...)
int64_t pts:显示时间戳
int coded_picture_number:编码帧序号
int display_picture_number:显示帧序号
int8_t *qscale_table:QP表
uint8_t *mbskip_table:跳过宏块表
int16_t (*motion_val[2])[2]:运动矢量表
uint32_t *mb_type:宏块类型表
short *dct_coeff:DCT系数,这个没有提取过
int8_t *ref_index[2]:运动估计参考帧列表(貌似H.264这种比较新的标准才会涉及到多参考帧)
int interlaced_frame:是否是隔行扫描
uint8_t motion_subsample_log2:一个宏块中的运动矢量采样个数,取log的
详细介绍参考:FFMPEG结构体分析:AVFrame