Android:用 SQLite 实现 用户的登录查询功能(详解+效果图)
文章目录
- 前言:
- 什么是SQLite?
- 为什么要用 SQLite?
- 常见的应用场景:
- 实现功能:
- 实现效果:
- 代码部分:
- 总结:
前言:
在侃实现功能之前,先来侃侃什么是SQLite?SQLite的具体应用场合有哪些?(了解的大佬就可以跳过啦,嘻嘻,也可以复习一下哦)。
什么是SQLite?
SQLite是一个进程内的库,实现了自给自足的、无服务器的、零配置的、事务性的 SQL
数据库引擎。它是一个零配置的数据库,这意味着与其他数据库一样,您不需要在系统中配置。就像其他数据库,SQLite 引擎不是一个独立的进程,可以按应用程序需求进行静态或动态连接。SQLite 直接访问其存储文件。 --------- 菜鸟教程
为什么要用 SQLite?
不需要一个单独的服务器进程或操作的系统(无服务器的)。
SQLite 不需要配置,这意味着不需要安装或管理。
一个完整的 SQLite 数据库是存储在一个单一的跨平台的磁盘文件。
SQLite 是非常小的,是轻量级的,完全配置时小于 400KiB,省略可选功能配置时小于250KiB。
SQLite 是自给自足的,这意味着不需要任何外部的依赖。
SQLite 事务是完全兼容 ACID 的,允许从多个进程或线程安全访问。
SQLite 支持 SQL92(SQL2)标准的大多数查询语言的功能。
SQLite 使用 ANSI-C 编写的,并提供了简单和易于使用的 API。
SQLite 可在 UNIX(Linux, Mac OS-X, Android, iOS)和 Windows(Win32, WinCE,
WinRT)中运行。
常见的应用场景:
相信大家都用过像百词斩,有道词典等类似的背单词的软件,没有用过的小伙伴可以下载一下尝试尝试(无偿做广告),在用这些软件的时候那些单词是从哪里来的呢?想一下,如果我们每次打开软件的时候都需要去服务器进行下载相应的单词进行学习,一旦有成千上万的英语学习爱好者,那服务器就需要面临崩溃的危机,可能会有人说,升级服务器不就行了,of course。
但是, 百词斩只是一个内存不到 几百M 的软件,用一个超大的服务器显然不是一个优秀的选择。(以上经过 zyg teacher 讲解后自己的推敲)。
SQLite就可以很好的帮助处理这个问题: 它会将单词书下载到本地,然后我们每次看单词时就从本地进行读取。(而且看看上面SQLite的有点,是不是很适合呢?)
实现功能:
用SQLite制作本地登录功能
1、包含两个Actvity:LoginActivity、ListActivity,LoginActivity为启动Activity
2、启动LoginActivity初始化SQLite数据库
3、在LoginActivity录入用户名和密码时,在SQLite中进行校验,校验成功跳转到ListActivity,否则继续。
4、ListActivity显示登录成功!
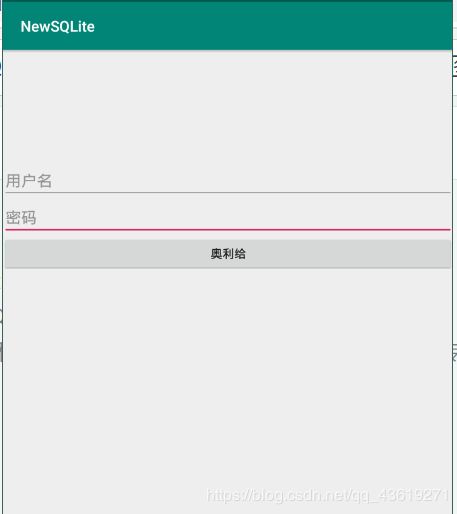
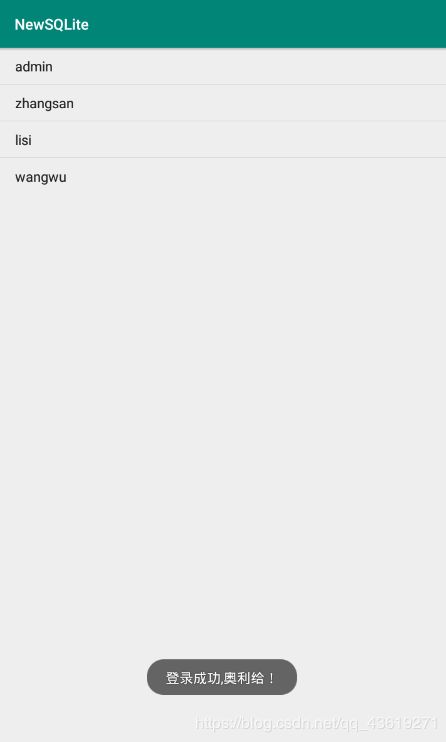
实现效果:
代码部分:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.newsqlite">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".SQLiteListActivity">activity>
<activity android:name=".SQLiteLoginActivity" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
intent-filter>
activity>
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
activity>
application>
manifest>
MainActivity.java
在本项目中用处不大。
package com.example.newsqlite;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}
SQLiteDBHelper.java:数据库帮助类:
package com.example.newsqlite;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
import android.util.Log;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
/**
* A helper class to manage database creation and version management.
*
* 既然父类是一个帮助类,子类至少也是一个帮助类,而且更加强大
*
* */
public class SQLiteDBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
// 创建数据库
static final String CREATE_SQL[] = {
"CREATE TABLE news (" +
"_id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT," +
"title varchar," +
"content varchar," +
"keyword varchar," +
"category varchar," +
"author INTEGER," +
"publish_time varchar" +
")",
"CREATE TABLE user (" +
"_id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT," +
"name varchar," +
"password varchar," +
"email varchar," +
"phone varchar," +
"address varcher" +
")",
"INSERT INTO user VALUES (1,'admin',123,'[email protected]',123,'洛阳')",
"INSERT INTO user VALUES (2,'zhangsan',123,'[email protected]',123,'北京')",
"INSERT INTO user VALUES (3,'lisi',123,'[email protected]',123,'上海')",
"INSERT INTO user VALUES (4,'wangwu',123,'[email protected]',123,'深圳')"
};
// 调用父类的构造方法(便于之后进行初始化赋值)
public SQLiteDBHelper(@Nullable Context context, @Nullable String name, int version) {
super(context, name, null, version);
}
/**
* Called when the database is created for the first time. This is where the
* creation of tables and the initial population of the tables should happen.
*
* @param db The database.
*/
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
// 创建数据库
Log.i("sqlite_____", "create Database");
// 执行 SQL 语句
for (int i = 0; i < CREATE_SQL.length; i++) {
db.execSQL(CREATE_SQL[i]);
}
// 完成数据库的创建
Log.i("sqlite_____", "Finished Database");
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
}
}
SQLiteLoginActivity: 登录
package com.example.newsqlite;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.example.newsqlite.R;
import com.example.newsqlite.SQLiteDBHelper;
import com.example.newsqlite.SQLiteListActivity;
/**
* 用户登录校验:
* 1、登录成功则跳转到 SQLiteListActivity。
* 2、登录失败则重新登录。
*
* */
public class SQLiteLoginActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
SQLiteDBHelper dbHelper;
EditText etUsername;
EditText etPassword;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_sqlite_login);
// 创建 SQLiteDBHelper 对象,利用构造方法进行初始化赋值
dbHelper = new SQLiteDBHelper(this,"sqlite.db",1);
// 通过 id 找到 布局管理器中的 相关属性
etUsername = findViewById(R.id.etUsername);
etPassword = findViewById(R.id.etPassword);
}
// 当用户点击提交按钮时,就会到这里(单击事件)
public void onClick(View view) {
// 获取用户的用户名和密码进行验证
String username = etUsername.getText().toString();
String password = etPassword.getText().toString();
/**
* Create and/or open a database.
* */
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getReadableDatabase();
/**
*
* 查询用户信息,放回值是一个游标(结果集,遍历结果集)
*
* */
Cursor cursor = db.query("user",new String[]{"name","password"}, "name=?",new String[]{username},null,null,null,"0,1");
// 游标移动进行校验
if(cursor.moveToNext()) {
// 从数据库获取密码进行校验
String dbPassword = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("password"));
// 关闭游标
cursor.close();
if(password.equals(dbPassword)) {
// 校验成功则跳转到 SQLiteListActivity
Intent intent = new Intent(this, SQLiteListActivity.class);
// 启动
startActivity(intent);
return;
}
}
// 跳转失败也要进行关闭
cursor.close();
// 跳转失败就提示用户相关的错误信息
Toast.makeText(this,"奥利给不足,输入信息有误!",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
dbHelper.close();
}
}
SQLiteListActivity: 登录成功跳转页面
package com.example.newsqlite;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.media.session.MediaSession;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class SQLiteListActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
ListView listView01;
SQLiteDBHelper dbHelper;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_sqlite_list);
// 提示信息
Toast.makeText(this,"登录成功,奥利给!",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
listView01 = findViewById(R.id.listView01);
// 创建 SQLiteDBHelper 对象,利用构造方法进行初始化赋值
dbHelper = new SQLiteDBHelper(this,"sqlite.db",1);
// 通过 id 找到 布局管理器中的 相关属性
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.query("user",new String[]{"_id","name"},null,null,null,null,null,null);
// 适配器,利用适配器进行填充信息,相对于数组来说更加灵活,动态化(为这种设计点赞)
SimpleCursorAdapter adapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(
this,
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,
cursor,
new String[]{"_id","name"},
new int[]{android.R.id.text1,android.R.id.text1},
0
);
listView01.setAdapter(adapter);
}
/**
* 关闭 dbHelper.
* */
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
dbHelper.close();
}
}
activity_sqlite_list.xml
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".SQLiteListActivity">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listView01"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
tools:ignore="MissingConstraints">
ListView>
androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
activity_sqlite_login.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".SQLiteLoginActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="150dp">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/etUsername"
android:hint="用户名"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/etPassword"
android:hint="密码"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textPassword"/>
<Button
android:text="奥利给"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="onClick"/>
LinearLayout>
RelativeLayout>
总结:
嘻嘻,到此一个简单的登录+查询的小功能就是实现了,再也不用担心 Teacher 抽作业啦。
如果你 JavaWeb 学的不错的话,可以类比一下,布局管理器相当于是 html 文件,中间的
Activity 类比成 Servlet 进行跳转,数据库当然就是我们的 Dao 层了。
如果对您有帮助的,别忘了来个三连哦,感激感激。
如果上述的代码不够清晰,可以私聊我。
溜了溜了,交作业咯!