前言
上一篇【.Net Core微服务入门全纪录(二)——Consul-服务注册与发现(上)】已经成功将我们的服务注册到Consul中,接下来就该客户端通过Consul去做服务发现了。
服务发现
ServiceHelper.cs:
public class ServiceHelper : IServiceHelper
{
private readonly IConfiguration _configuration;
public ServiceHelper(IConfiguration configuration)
{
_configuration = configuration;
}
public async Task GetOrder()
{
//string[] serviceUrls = { "http://localhost:9060", "http://localhost:9061", "http://localhost:9062" };//订单服务的地址,可以放在配置文件或者数据库等等...
var consulClient = new ConsulClient(c =>
{
//consul地址
c.Address = new Uri(_configuration["ConsulSetting:ConsulAddress"]);
});
//consulClient.Catalog.Services().Result.Response;
//consulClient.Agent.Services().Result.Response;
var services = consulClient.Health.Service("OrderService", null, true, null).Result.Response;//健康的服务
string[] serviceUrls = services.Select(p => $"http://{p.Service.Address + ":" + p.Service.Port}").ToArray();//订单服务地址列表
if (!serviceUrls.Any())
{
return await Task.FromResult("【订单服务】服务列表为空");
}
//每次随机访问一个服务实例
var Client = new RestClient(serviceUrls[new Random().Next(0, serviceUrls.Length)]);
var request = new RestRequest("/orders", Method.GET);
var response = await Client.ExecuteAsync(request);
return response.Content;
}
public async Task GetProduct()
{
//string[] serviceUrls = { "http://localhost:9050", "http://localhost:9051", "http://localhost:9052" };//产品服务的地址,可以放在配置文件或者数据库等等...
var consulClient = new ConsulClient(c =>
{
//consul地址
c.Address = new Uri(_configuration["ConsulSetting:ConsulAddress"]);
});
//consulClient.Catalog.Services().Result.Response;
//consulClient.Agent.Services().Result.Response;
var services = consulClient.Health.Service("ProductService", null, true, null).Result.Response;//健康的服务
string[] serviceUrls = services.Select(p => $"http://{p.Service.Address + ":" + p.Service.Port}").ToArray();//产品服务地址列表
if (!serviceUrls.Any())
{
return await Task.FromResult("【产品服务】服务列表为空");
}
//每次随机访问一个服务实例
var Client = new RestClient(serviceUrls[new Random().Next(0, serviceUrls.Length)]);
var request = new RestRequest("/products", Method.GET);
var response = await Client.ExecuteAsync(request);
return response.Content;
}
}
appsettings.json:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConsulSetting": {
"ConsulAddress": "http://localhost:8500"
}
}
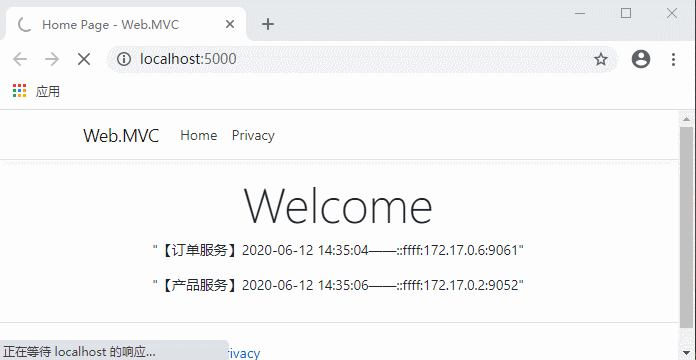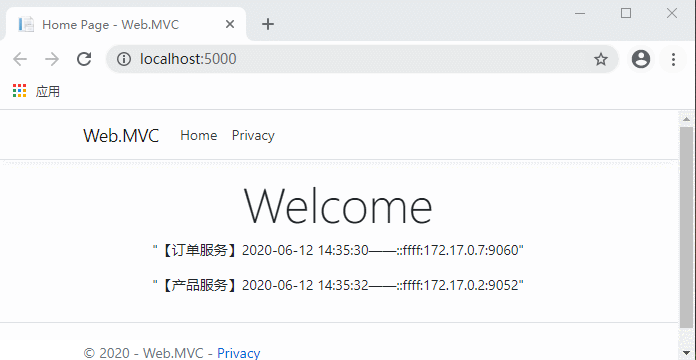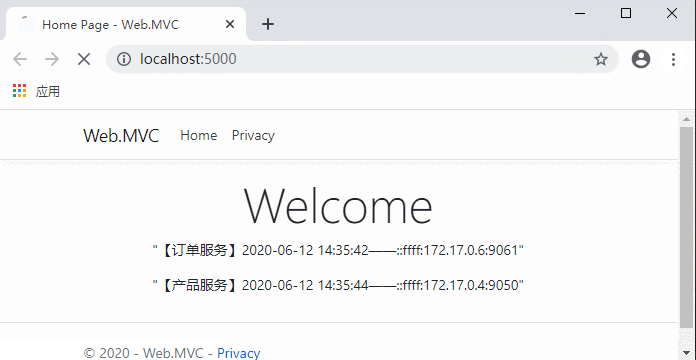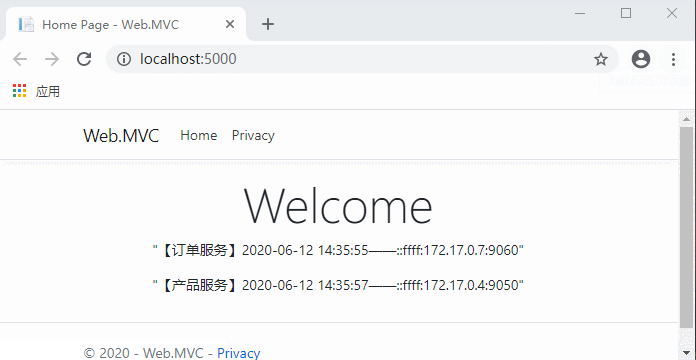
OK,以上代码就完成了服务列表的获取。
继续访问:
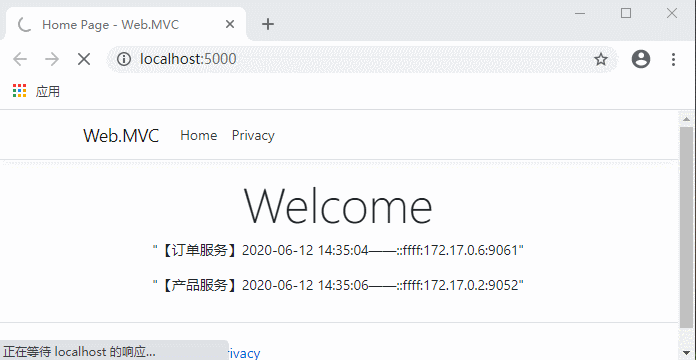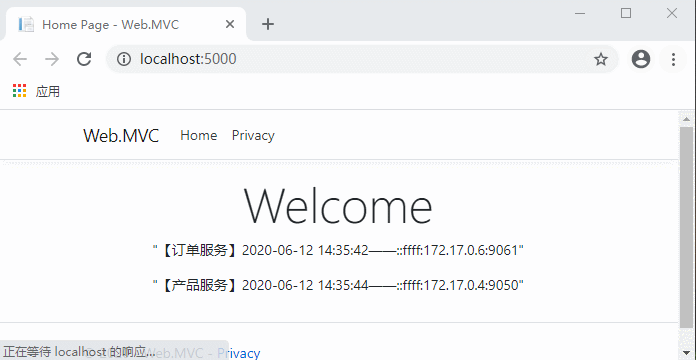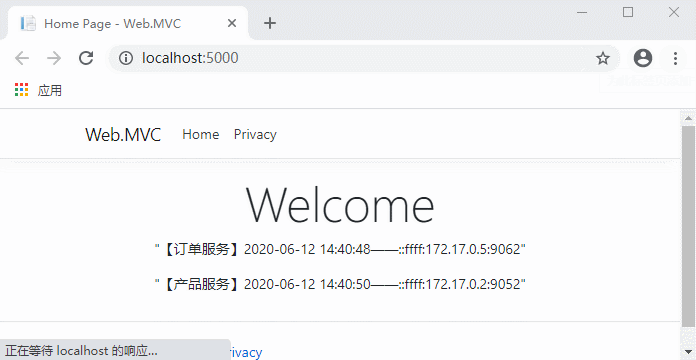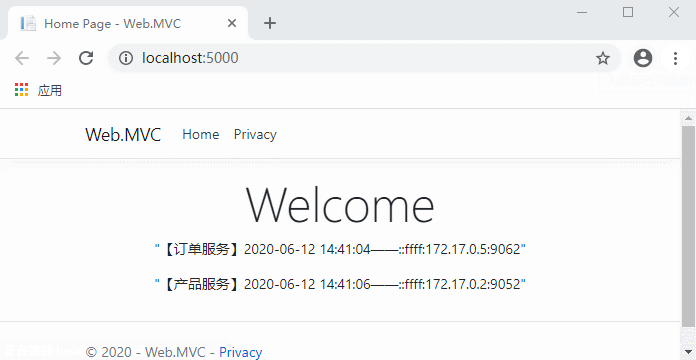
这时候停止的服务地址就获取不到了,客户端依然正常运行。
这时候解决了服务的发现,新的问题又来了...
- 客户端每次要调用服务,都先去Consul获取一下地址,这不仅浪费资源,还增加了请求的响应时间,这显然让人无法接受。
那么怎么保证不要每次请求都去Consul获取地址,同时又要拿到可用的地址列表呢?
Consul提供的解决方案:——Blocking Queries (阻塞的请求)。详情请见官网:https://www.consul.io/api-docs/features/blocking
Blocking Queries
这是什么意思呢,简单来说就是当客户端请求Consul获取地址列表时,需要携带一个版本号信息,Consul会比较这个客户端版本号是否和Consul服务端的版本号一致,如果一致,则Consul会阻塞这个请求,直到Consul中的服务列表发生变化,或者到达阻塞时间上限;如果版本号不一致,则立即返回。这个阻塞时间默认是5分钟,支持自定义。
那么我们另外启动一个线程去干这件事情,就不会影响每次的用户请求了。这样既保证了客户端服务列表的准确性,又节约了客户端请求服务列表的次数。
- 继续改造代码:
IServiceHelper增加一个获取服务列表的接口方法:
public interface IServiceHelper
{
///
/// 获取产品数据
///
/// GetProduct();
///
/// 获取订单数据
///
/// GetOrder();
///
/// 获取服务列表
///
void GetServices();
}
ServiceHelper实现接口:
public class ServiceHelper : IServiceHelper
{
private readonly IConfiguration _configuration;
private readonly ConsulClient _consulClient;
private ConcurrentBag _orderServiceUrls;
private ConcurrentBag _productServiceUrls;
public ServiceHelper(IConfiguration configuration)
{
_configuration = configuration;
_consulClient = new ConsulClient(c =>
{
//consul地址
c.Address = new Uri(_configuration["ConsulSetting:ConsulAddress"]);
});
}
public async Task GetOrder()
{
if (_productServiceUrls == null)
return await Task.FromResult("【订单服务】正在初始化服务列表...");
//每次随机访问一个服务实例
var Client = new RestClient(_orderServiceUrls.ElementAt(new Random().Next(0, _orderServiceUrls.Count())));
var request = new RestRequest("/orders", Method.GET);
var response = await Client.ExecuteAsync(request);
return response.Content;
}
public async Task GetProduct()
{
if(_productServiceUrls == null)
return await Task.FromResult("【产品服务】正在初始化服务列表...");
//每次随机访问一个服务实例
var Client = new RestClient(_productServiceUrls.ElementAt(new Random().Next(0, _productServiceUrls.Count())));
var request = new RestRequest("/products", Method.GET);
var response = await Client.ExecuteAsync(request);
return response.Content;
}
public void GetServices()
{
var serviceNames = new string[] { "OrderService", "ProductService" };
Array.ForEach(serviceNames, p =>
{
Task.Run(() =>
{
//WaitTime默认为5分钟
var queryOptions = new QueryOptions { WaitTime = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(10) };
while (true)
{
GetServices(queryOptions, p);
}
});
});
}
private void GetServices(QueryOptions queryOptions, string serviceName)
{
var res = _consulClient.Health.Service(serviceName, null, true, queryOptions).Result;
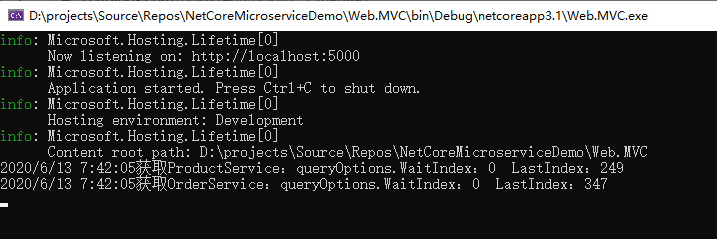
//控制台打印一下获取服务列表的响应时间等信息
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now}获取{serviceName}:queryOptions.WaitIndex:{queryOptions.WaitIndex} LastIndex:{res.LastIndex}");
//版本号不一致 说明服务列表发生了变化
if (queryOptions.WaitIndex != res.LastIndex)
{
queryOptions.WaitIndex = res.LastIndex;
//服务地址列表
var serviceUrls = res.Response.Select(p => $"http://{p.Service.Address + ":" + p.Service.Port}").ToArray();
if (serviceName == "OrderService")
_orderServiceUrls = new ConcurrentBag(serviceUrls);
else if (serviceName == "ProductService")
_productServiceUrls = new ConcurrentBag(serviceUrls);
}
}
}
Startup的Configure方法中调用一下获取服务列表:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env, IServiceHelper serviceHelper)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
}
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
//程序启动时 获取服务列表
serviceHelper.GetServices();
}
代码完成,运行测试:
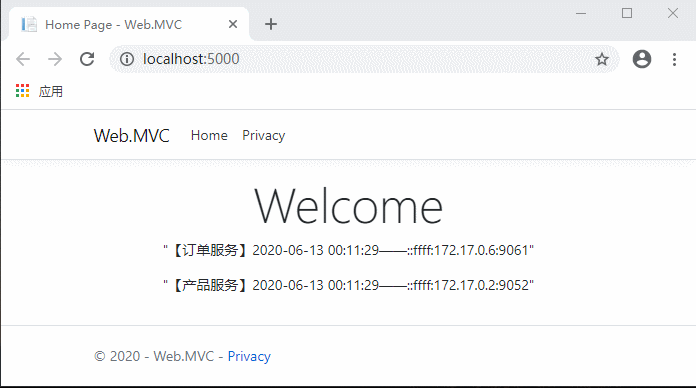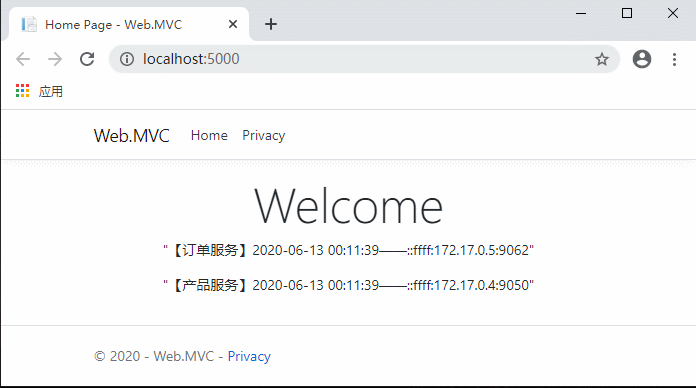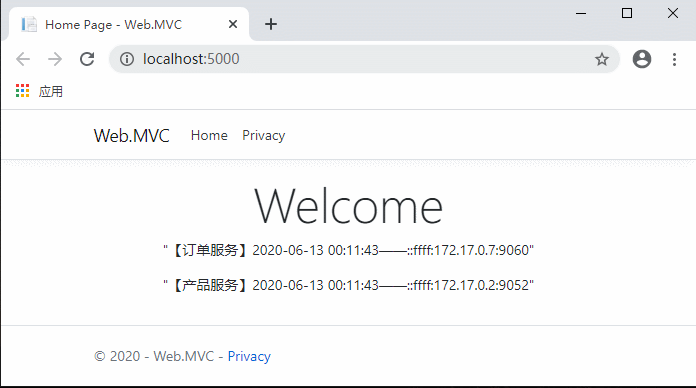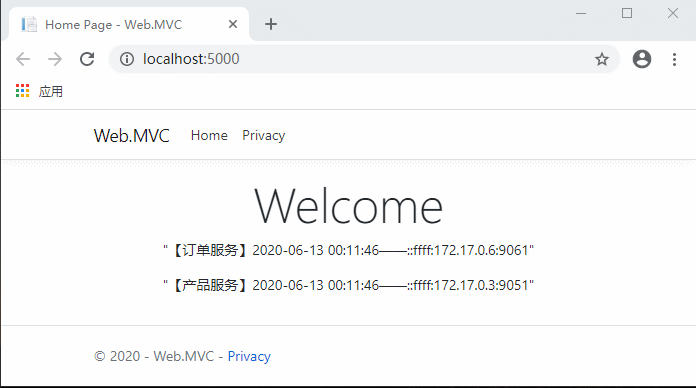
现在不用每次先请求服务列表了,是不是流畅多了?
这时候如果服务列表没有发生变化的话,获取服务列表的请求会一直阻塞到我们设置的10分钟。
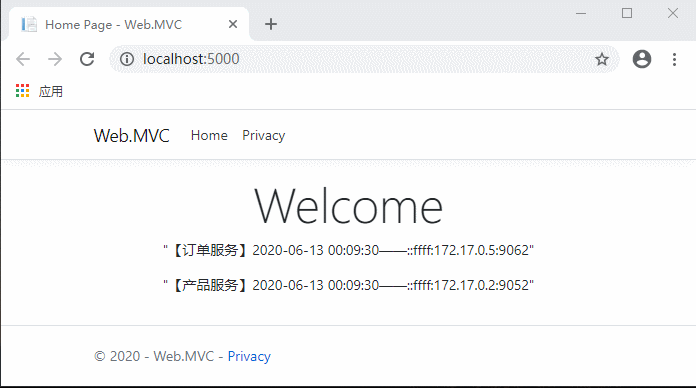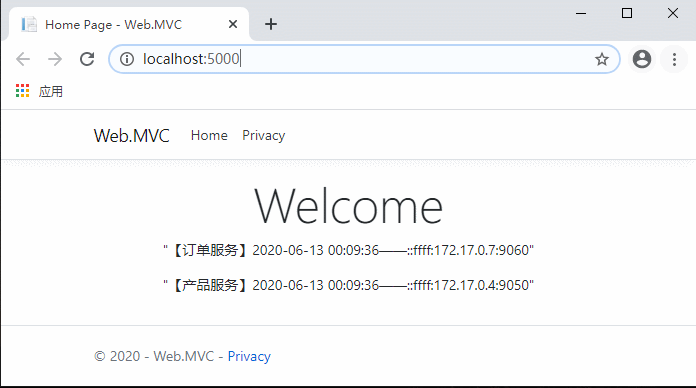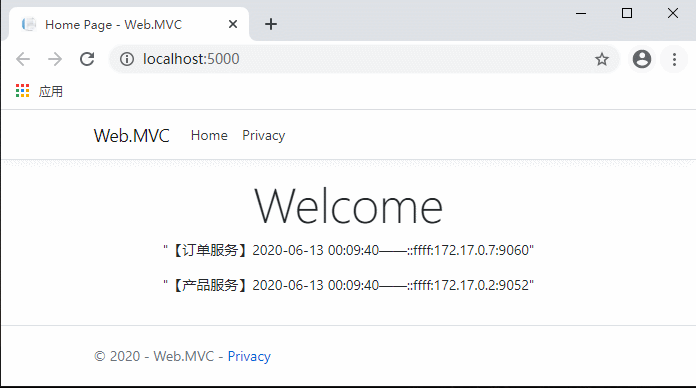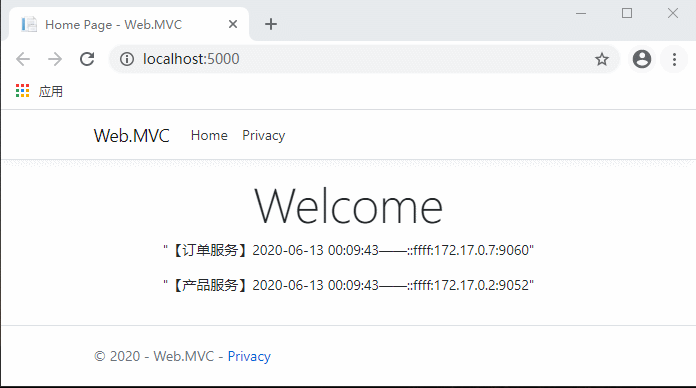
继续访问客户端网站,同样流畅。
(gif图传的有点问题。。。)
至此,我们就通过Consul完成了服务的注册与发现。
接下来又引发新的思考。。。
- 每个客户端系统都去维护这一堆服务地址,合理吗?
- 服务的ip端口直接暴露给所有客户端,安全吗?
- 这种模式下怎么做到客户端的统一管理呢?
...
代码放在:https://github.com/xiajingren/NetCoreMicroserviceDemo
未完待续...