【Mybatis源码阅读】mybatis中的设计模式
https://blog.csdn.net/worn_xiao/article/details/104235116 【Mybatis源码阅读】初始化过程
https://blog.csdn.net/worn_xiao/article/details/104462355 【Mybatis源码阅读】数据源与实现原理
https://blog.csdn.net/worn_xiao/article/details/104385339 【Mybatis源码阅读】mapper的执行流程
https://blog.csdn.net/worn_xiao/article/details/104362071 【Mybatis源码阅读】sqlSession的执行流程
https://blog.csdn.net/worn_xiao/article/details/78887831 【mybatis源码阅读】缓存与缓存原理
https://blog.csdn.net/worn_xiao/article/details/104403344 【mybatis源码阅读】插件与插件原理
https://blog.csdn.net/worn_xiao/article/details/104470343 【mybatis源码阅读】mybatis中的设计模式
涉及涉及模式:
Builder模式,例如SqlSessionFactoryBuilder、XMLConfigBuilder、XMLMapperBuilder、XMLStatementBuilder、CacheBuilder;
工厂模式,例如SqlSessionFactory、ObjectFactory、MapperProxyFactory;
抽象工厂模式,DataSource Transaction
单例模式,例如ErrorContext和LogFactory;
代理模式,Mybatis实现的核心,比如MapperProxy、ConnectionLogger,比如插件也是用的代理模式。用的jdk的动态代理;还有executor.loader包使用了cglib或者javassist达到延迟加载的效果;
组合模式,例如SqlNode和各个子类ChooseSqlNode等;
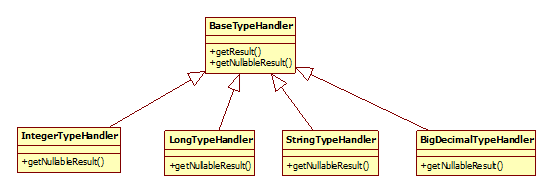
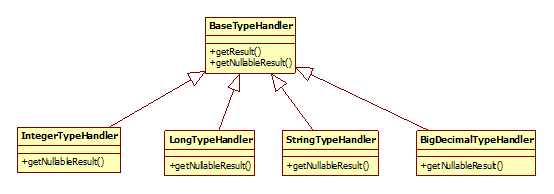
模板方法模式,例如BaseExecutor和SimpleExecutor,还有BaseTypeHandler和所有的子类例如IntegerTypeHandler;
适配器模式,例如Log的Mybatis接口和它对jdbc、log4j等各种日志框架的适配实现;
装饰者模式,例如Cache包中的cache.decorators子包中等各个装饰者的实现,比如CacheExcutor;
迭代器模式,例如迭代器模式PropertyTokenizer;
策略模式。比如Statement,Executor
如上先列出来放在这里,等我后面慢慢解析,会不断的更新此篇文章。
1.1工厂模式
1.1.1 Mybatis数据源
1.1.1.1 数据源使用
@Test
public void shouldRetrieveDataSourceFromJNDI() throws Exception {
createJndiDataSource();
JndiDataSourceFactory factory = new JndiDataSourceFactory();
factory.setProperties(new Properties() {
{
setProperty(JndiDataSourceFactory.ENV_PREFIX + Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, TEST_INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY);
setProperty(JndiDataSourceFactory.INITIAL_CONTEXT, TEST_INITIAL_CONTEXT);
setProperty(JndiDataSourceFactory.DATA_SOURCE, TEST_DATA_SOURCE);
}
});
DataSource actualDataSource = factory.getDataSource();
assertEquals(expectedDataSource, actualDataSource);
}
@Test
public void shouldNotRegisterTheSameDriverMultipleTimes() throws Exception {
UnpooledDataSource dataSource = null;
dataSource = new UnpooledDataSource("org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver", "jdbc:hsqldb:mem:multipledrivers", "sa", "");
dataSource.getConnection();
int before = countRegisteredDrivers();
dataSource = new UnpooledDataSource("org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver", "jdbc:hsqldb:mem:multipledrivers", "sa", "");
dataSource.getConnection();
assertEquals(before, countRegisteredDrivers());
}
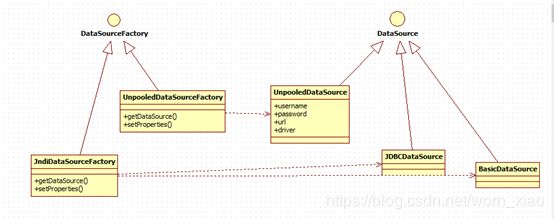
1.1.1.2 抽象工厂实践
在mybaties中比较典型的抽象工厂模式,数据源工厂,不同的数据源工厂创建不同的数据源。如上图抽象工厂模式的设计图。
工厂源代码:
public interface DataSourceFactory {
void setProperties(Properties props);
DataSource getDataSource();
}
public class UnpooledDataSourceFactory implements DataSourceFactory {
private static final String DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX = "driver.";
private static final int DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX_LENGTH = DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX.length();
protected DataSource dataSource;
public UnpooledDataSourceFactory() {
this.dataSource = new UnpooledDataSource();
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
Properties driverProperties = new Properties();
MetaObject metaDataSource = SystemMetaObject.forObject(dataSource);
for (Object key : properties.keySet()) {
String propertyName = (String) key;
if (propertyName.startsWith(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX)) {
String value = properties.getProperty(propertyName);
driverProperties.setProperty(propertyName.substring(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX_LENGTH), value);
} else if (metaDataSource.hasSetter(propertyName)) {
String value = (String) properties.get(propertyName);
Object convertedValue = convertValue(metaDataSource, propertyName, value);
metaDataSource.setValue(propertyName, convertedValue);
} else {
throw new DataSourceException("Unknown DataSource property: " + propertyName);
}
}
if (driverProperties.size() > 0) {
metaDataSource.setValue("driverProperties", driverProperties);
}
}
@Override
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return dataSource;
}
private Object convertValue(MetaObject metaDataSource, String propertyName, String value) {
Object convertedValue = value;
Class targetType = metaDataSource.getSetterType(propertyName);
if (targetType == Integer.class || targetType == int.class) {
convertedValue = Integer.valueOf(value);
} else if (targetType == Long.class || targetType == long.class) {
convertedValue = Long.valueOf(value);
} else if (targetType == Boolean.class || targetType == boolean.class) {
convertedValue = Boolean.valueOf(value);
}
return convertedValue;
}
}
public class JndiDataSourceFactory implements DataSourceFactory {
public static final String INITIAL_CONTEXT = "initial_context";
public static final String DATA_SOURCE = "data_source";
public static final String ENV_PREFIX = "env.";
private DataSource dataSource;
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
try {
InitialContext initCtx;
Properties env = getEnvProperties(properties);
if (env == null) {
initCtx = new InitialContext();
} else {
initCtx = new InitialContext(env);
}
if (properties.containsKey(INITIAL_CONTEXT)
&& properties.containsKey(DATA_SOURCE)) {
Context ctx = (Context) initCtx.lookup(properties.getProperty(INITIAL_CONTEXT));
dataSource = (DataSource) ctx.lookup(properties.getProperty(DATA_SOURCE));
} else if (properties.containsKey(DATA_SOURCE)) {
dataSource = (DataSource) initCtx.lookup(properties.getProperty(DATA_SOURCE));
}
} catch (NamingException e) {
throw new DataSourceException("There was an error configuring JndiDataSourceTransactionPool. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
@Override
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return dataSource;
}
private static Properties getEnvProperties(Properties allProps) {
final String PREFIX = ENV_PREFIX;
Properties contextProperties = null;
for (Entry entry : allProps.entrySet()) {
String key = (String) entry.getKey();
String value = (String) entry.getValue();
if (key.startsWith(PREFIX)) {
if (contextProperties == null) {
contextProperties = new Properties();
}
contextProperties.put(key.substring(PREFIX.length()), value);
}
}
return contextProperties;
}
}
public interface DataSource extends CommonDataSource, Wrapper {
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
Connection getConnection(String username, String password)
throws SQLException;
}
public class UnpooledDataSource implements DataSource {
private ClassLoader driverClassLoader;
private Properties driverProperties;
private static Map registeredDrivers = new ConcurrentHashMap();//可以加载多种驱动类型
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
private Boolean autoCommit;
private Integer defaultTransactionIsolationLevel;
static {
Enumeration drivers = DriverManager.getDrivers();
while (drivers.hasMoreElements()) {
Driver driver = drivers.nextElement();
registeredDrivers.put(driver.getClass().getName(), driver);
}
}
public UnpooledDataSource() {
}
public UnpooledDataSource(String driver, String url, String username, String password) {
this.driver = driver;
this.url = url;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public UnpooledDataSource(String driver, String url, Properties driverProperties) {
this.driver = driver;
this.url = url;
this.driverProperties = driverProperties;
}
public UnpooledDataSource(ClassLoader driverClassLoader, String driver, String url, String username, String password) {
this.driverClassLoader = driverClassLoader;
this.driver = driver;
this.url = url;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public UnpooledDataSource(ClassLoader driverClassLoader, String driver, String url, Properties driverProperties) {
this.driverClassLoader = driverClassLoader;
this.driver = driver;
this.url = url;
this.driverProperties = driverProperties;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return doGetConnection(username, password);
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return doGetConnection(username, password);
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int loginTimeout) throws SQLException {
DriverManager.setLoginTimeout(loginTimeout);
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getLoginTimeout();
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter logWriter) throws SQLException {
DriverManager.setLogWriter(logWriter);
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getLogWriter();
}
public ClassLoader getDriverClassLoader() {
return driverClassLoader;
}
public void setDriverClassLoader(ClassLoader driverClassLoader) {
this.driverClassLoader = driverClassLoader;
}
public Properties getDriverProperties() {
return driverProperties;
}
public void setDriverProperties(Properties driverProperties) {
this.driverProperties = driverProperties;
}
public String getDriver() {
return driver;
}
public synchronized void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Boolean isAutoCommit() {
return autoCommit;
}
public void setAutoCommit(Boolean autoCommit) {
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
public Integer getDefaultTransactionIsolationLevel() {
return defaultTransactionIsolationLevel;
}
public void setDefaultTransactionIsolationLevel(Integer defaultTransactionIsolationLevel) {
this.defaultTransactionIsolationLevel = defaultTransactionIsolationLevel;
}
private Connection doGetConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
Properties props = new Properties();
if (driverProperties != null) {
props.putAll(driverProperties);
}
if (username != null) {
props.setProperty("user", username);
}
if (password != null) {
props.setProperty("password", password);
}
return doGetConnection(props);
}
private Connection doGetConnection(Properties properties) throws SQLException {
initializeDriver();
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
configureConnection(connection);
return connection;
}
private synchronized void initializeDriver() throws SQLException {
if (!registeredDrivers.containsKey(driver)) {
Class driverType;
try {
if (driverClassLoader != null) {
driverType = Class.forName(driver, true, driverClassLoader);
} else {
driverType = Resources.classForName(driver);
}
// DriverManager requires the driver to be loaded via the system ClassLoader.
// http://www.kfu.com/~nsayer/Java/dyn-jdbc.html
Driver driverInstance = (Driver)driverType.newInstance();
DriverManager.registerDriver(new DriverProxy(driverInstance));
registeredDrivers.put(driver, driverInstance);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SQLException("Error setting driver on UnpooledDataSource. Cause: " + e);
}
}
}
private void configureConnection(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
if (autoCommit != null && autoCommit != conn.getAutoCommit()) {
conn.setAutoCommit(autoCommit);
}
if (defaultTransactionIsolationLevel != null) {
conn.setTransactionIsolation(defaultTransactionIsolationLevel);
}
}
private static class DriverProxy implements Driver {
private Driver driver;
DriverProxy(Driver d) {
this.driver = d;
}
@Override
public boolean acceptsURL(String u) throws SQLException {
return this.driver.acceptsURL(u);
}
@Override
public Connection connect(String u, Properties p) throws SQLException {
return this.driver.connect(u, p);
}
@Override
public int getMajorVersion() {
return this.driver.getMajorVersion();
}
@Override
public int getMinorVersion() {
return this.driver.getMinorVersion();
}
@Override
public DriverPropertyInfo[] getPropertyInfo(String u, Properties p) throws SQLException {
return this.driver.getPropertyInfo(u, p);
}
@Override
public boolean jdbcCompliant() {
return this.driver.jdbcCompliant();
}
// @Override only valid jdk7+
public Logger getParentLogger() {
return Logger.getLogger(Logger.GLOBAL_LOGGER_NAME);
}
}
@Override
public T unwrap(Class iface) throws SQLException {
throw new SQLException(getClass().getName() + " is not a wrapper.");
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
// @Override only valid jdk7+
public Logger getParentLogger() {
// requires JDK version 1.6
return Logger.getLogger(Logger.GLOBAL_LOGGER_NAME);
}
}
public class JDBCDataSource extends JDBCCommonDataSource implements DataSource, Serializable, Referenceable, Wrapper {
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (this.url == null) {
throw JDBCUtil.nullArgument("url");
} else if (this.connectionProps == null) {
if (this.user == null) {
throw JDBCUtil.invalidArgument("user");
} else if (this.password == null) {
throw JDBCUtil.invalidArgument("password");
} else {
return this.getConnection(this.user, this.password);
}
} else {
return this.getConnection(this.url, this.connectionProps);
}
}
public Connection getConnection(String var1, String var2) throws SQLException {
if (var1 == null) {
throw JDBCUtil.invalidArgument("user");
} else if (var2 == null) {
throw JDBCUtil.invalidArgument("password");
} else {
Properties var3 = new Properties();
var3.setProperty("user", var1);
var3.setProperty("password", var2);
var3.setProperty("loginTimeout", Integer.toString(this.loginTimeout));
return this.getConnection(this.url, var3);
}
}
private Connection getConnection(String var1, Properties var2) throws SQLException {
if (!var1.startsWith("jdbc:hsqldb:")) {
var1 = "jdbc:hsqldb:" + var1;
}
return JDBCDriver.getConnection(var1, var2);
}
public T unwrap(Class var1) throws SQLException {
if (this.isWrapperFor(var1)) {
return this;
} else {
throw JDBCUtil.invalidArgument("iface: " + var1);
}
}
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class var1) throws SQLException {
return var1 != null && var1.isAssignableFrom(this.getClass());
}
public Reference getReference() throws NamingException {
String var1 = "org.hsqldb.jdbc.JDBCDataSourceFactory";
Reference var2 = new Reference(this.getClass().getName(), var1, (String)null);
var2.add(new StringRefAddr("database", this.getDatabase()));
var2.add(new StringRefAddr("user", this.getUser()));
var2.add(new StringRefAddr("password", this.password));
var2.add(new StringRefAddr("loginTimeout", Integer.toString(this.loginTimeout)));
return var2;
}
public JDBCDataSource() {
}
}
1.1.2 Mybatis 事务
1.1.2.1 事务使用
@Test
public void shouldEnsureThatCallsToManagedTransactionAPIDoNotForwardToManagedConnections() throws Exception {
TransactionFactory tf = new ManagedTransactionFactory();
tf.setProperties(new Properties());
Transaction tx = tf.newTransaction(conn);
assertEquals(conn, tx.getConnection());
tx.commit();
tx.rollback();
tx.close();
verify(conn).close();
}
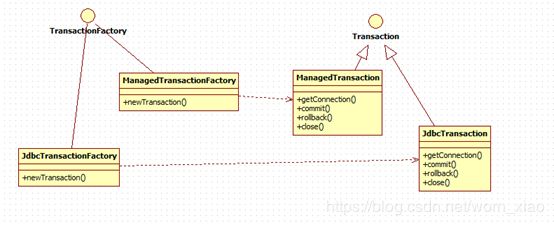
1.1.2.2 抽象工厂实践
由于上图也是一个抽象工厂的设计模式图,可以看到都是抽象的事务工厂,创建具体的事务的。其实事务是对数据源的封装,当事务调用getConnnet()方法的时候,无非就是调用配置文件里的数据库连接地址,创建数据库连接,至于数据源怎么创建mysql的连接,这个就要求我们去简单的回顾一下java的jdbc了。然而为什么事务类呢。其实是因为所有的事务都是从创建数据库连接来的。只要能拿到数据库连接,就可以对数据库的操作,进行手动提交,回滚,设置数据库隔离级别等等的。
public interface TransactionFactory {
void setProperties(Properties props);
Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn);
Transaction newTransaction(DataSource dataSource, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit);
}
public class ManagedTransactionFactory implements TransactionFactory {
private boolean closeConnection = true;
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties props) {
if (props != null) {
String closeConnectionProperty = props.getProperty("closeConnection");
if (closeConnectionProperty != null) {
closeConnection = Boolean.valueOf(closeConnectionProperty);
}
}
}
@Override
public Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn) {
return new ManagedTransaction(conn, closeConnection);
}
@Override
public Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
return new ManagedTransaction(ds, level, closeConnection);
}
}
public class JdbcTransactionFactory implements TransactionFactory {
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties props) {
}
@Override
public Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn) {
return new JdbcTransaction(conn);
}
@Override
public Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
return new JdbcTransaction(ds, level, autoCommit);
}
}
public interface Transaction {
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
void commit() throws SQLException;
void rollback() throws SQLException;
void close() throws SQLException;
Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException;
}
public class JdbcTransaction implements Transaction {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(JdbcTransaction.class);
protected Connection connection;
protected DataSource dataSource;
protected TransactionIsolationLevel level;
protected boolean autoCommmit;
public JdbcTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel desiredLevel, boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
dataSource = ds;
level = desiredLevel;
autoCommmit = desiredAutoCommit;
}
public JdbcTransaction(Connection connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return connection;
}
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.commit();
}
}
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.rollback();
}
}
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null) {
resetAutoCommit();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.close();
}
}
protected void setDesiredAutoCommit(boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
try {
if (connection.getAutoCommit() != desiredAutoCommit) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Setting autocommit to " + desiredAutoCommit + " on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.setAutoCommit(desiredAutoCommit);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TransactionException("Error configuring AutoCommit. "
+ "Your driver may not support getAutoCommit() or setAutoCommit(). "
+ "Requested setting: " + desiredAutoCommit + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
protected void resetAutoCommit() {
try {
if (!connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.setAutoCommit(true);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Error resetting autocommit to true "
+ "before closing the connection. Cause: " + e);
}
}
}
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
if (level != null) {
connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());
}
setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommmit);
}
@Override
public Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
}
public class ManagedTransaction implements Transaction {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(ManagedTransaction.class);
private DataSource dataSource;
private TransactionIsolationLevel level;
private Connection connection;
private final boolean closeConnection;
public ManagedTransaction(Connection connection, boolean closeConnection) {
this.connection = connection;
this.closeConnection = closeConnection;
}
public ManagedTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean closeConnection) {
this.dataSource = ds;
this.level = level;
this.closeConnection = closeConnection;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (this.connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return this.connection;
}
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {}
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {}
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (this.closeConnection && this.connection != null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "]");
}
this.connection.close();
}
}
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
this.connection = this.dataSource.getConnection();
if (this.level != null) {
this.connection.setTransactionIsolation(this.level.getLevel());
}}
@Override
public Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
}
1.1.3 mybatis mapper
1.1.3.1 mapper 使用
@Test
public void shouldRollbackInsertedAuthor() throws Exception {
try {
manager.startManagedSession();
AuthorMapper mapper = manager.getMapper(AuthorMapper.class);
Author expected = new Author(501, "lmeadors", "******", "[email protected]", "Something...", null);
mapper.insertAuthor(expected);
manager.rollback();
Author actual = mapper.selectAuthor(501);
assertNull(actual);
} finally {
manager.close();
}
}
如上所示是调用代码,我们可以从manager.gerMapper(AuthorMapper.class)入手看看,这个代码的底层是怎么实现的。
1.1.3.2 工厂模式实践
public class MapperRegistry {
private final Configuration config;
private final Map, MapperProxyFactory> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public boolean hasMapper(Class type) {
return knownMappers.containsKey(type);
}
public void addMapper(Class type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
/**
* @since 3.2.2
*/
public Collection> getMappers() {
return Collections.unmodifiableCollection(knownMappers.keySet());
}
/**
* @since 3.2.2
*/
public void addMappers(String packageName, Class superType) {
ResolverUtil> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
Set>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for (Class mapperClass : mapperSet) {
addMapper(mapperClass);
}
}
/**
* @since 3.2.2
*/
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
addMappers(packageName, Object.class);
}
}
如上图所示 MapperProxyFactory看名字就可以猜出来这是一个创建Mapper代理的一个工厂类。核心方法大概就是newInstance(sqlSession),目的就是创建一个MapperProxy。
/**
* @author Lasse Voss
*/
public class MapperProxyFactory {
private final Class mapperInterface;
private final Map methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
如上所示通过MapperProxyFactory创建一个T的Proxy就是工厂模式,通过这个newInstance就可以创建不通的Proxy,这里用了一个巧妙的就是泛化T,这个T刚好就不用每个代理都弄一个工厂方法,而是一个工厂方法创建多个代理。
1.2 装饰者模式
1.2.1 Mybatis缓存
1.2.1.1 缓存使用
@Test
public void shouldDemonstrate5LevelSuperCacheHandlesLotsOfEntriesWithoutCrashing() {
final int N = 100000;
Cache cache = new PerpetualCache("default");
cache = new LruCache(cache);
cache = new FifoCache(cache);
cache = new SoftCache(cache);
cache = new WeakCache(cache);
cache = new ScheduledCache(cache);
cache = new SerializedCache(cache);
cache = new SynchronizedCache(cache);
cache = new TransactionalCache(cache);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cache.putObject(i, i);
((TransactionalCache) cache).commit();
Object o = cache.getObject(i);
assertTrue(o == null || i == ((Integer) o));
}
assertTrue(cache.getSize() < N);
}
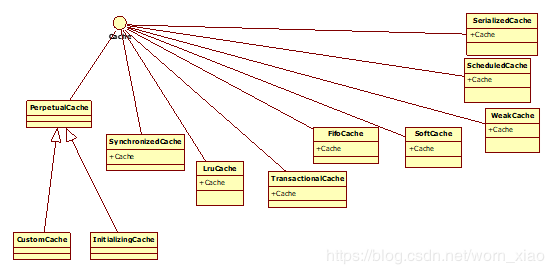
1.2.1.2 装饰模式实践
public class CacheBuilder {
private final String id;
private Class implementation;
private final List> decorators;
private Integer size;
private Long clearInterval;
private boolean readWrite;
private Properties properties;
private boolean blocking;
public CacheBuilder(String id) {
this.id = id;
this.decorators = new ArrayList>();
}
public CacheBuilder implementation(Class implementation) {
this.implementation = implementation;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder addDecorator(Class decorator) {
if (decorator != null) {
this.decorators.add(decorator);
}
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder size(Integer size) {
this.size = size;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder clearInterval(Long clearInterval) {
this.clearInterval = clearInterval;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder readWrite(boolean readWrite) {
this.readWrite = readWrite;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder blocking(boolean blocking) {
this.blocking = blocking;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder properties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
return this;
}
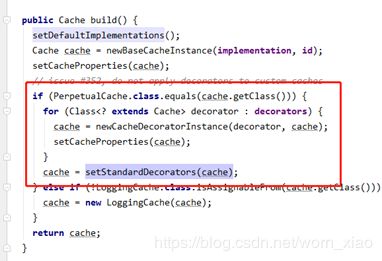
public Cache build() {
setDefaultImplementations();
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
setCacheProperties(cache);
// issue #352, do not apply decorators to custom caches
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) {
for (Class decorator : decorators) {
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
setCacheProperties(cache);
}
cache = setStandardDecorators(cache);
} else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) {
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
}
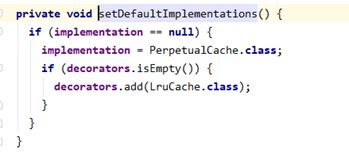
private void setDefaultImplementations() {
if (implementation == null) {
implementation = PerpetualCache.class;
if (decorators.isEmpty()) {
decorators.add(LruCache.class);
}
}
}
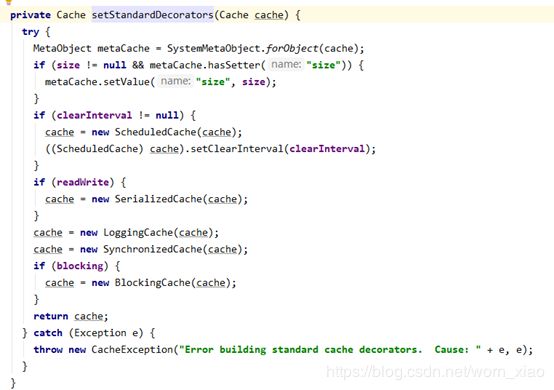
private Cache setStandardDecorators(Cache cache) {
try {
MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache);
if (size != null && metaCache.hasSetter("size")) {
metaCache.setValue("size", size);
}
if (clearInterval != null) {
cache = new ScheduledCache(cache);
((ScheduledCache) cache).setClearInterval(clearInterval);
}
if (readWrite) {
cache = new SerializedCache(cache);
}
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
cache = new SynchronizedCache(cache);
if (blocking) {
cache = new BlockingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Error building standard cache decorators. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private void setCacheProperties(Cache cache) {
if (properties != null) {
MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache);
for (Map.Entry entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String name = (String) entry.getKey();
String value = (String) entry.getValue();
if (metaCache.hasSetter(name)) {
Class type = metaCache.getSetterType(name);
if (String.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, value);
} else if (int.class == type
|| Integer.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Integer.valueOf(value));
} else if (long.class == type
|| Long.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Long.valueOf(value));
} else if (short.class == type
|| Short.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Short.valueOf(value));
} else if (byte.class == type
|| Byte.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Byte.valueOf(value));
} else if (float.class == type
|| Float.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Float.valueOf(value));
} else if (boolean.class == type
|| Boolean.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Boolean.valueOf(value));
} else if (double.class == type
|| Double.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Double.valueOf(value));
} else {
throw new CacheException("Unsupported property type for cache: '" + name + "' of type " + type);
}
}
}
}
if (InitializingObject.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())){
try {
((InitializingObject) cache).initialize();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Failed cache initialization for '" +
cache.getId() + "' on '" + cache.getClass().getName() + "'", e);
}
}
}
private Cache newBaseCacheInstance(Class cacheClass, String id) {
Constructor cacheConstructor = getBaseCacheConstructor(cacheClass);
try {
return cacheConstructor.newInstance(id);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Could not instantiate cache implementation (" + cacheClass + "). Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private Constructor getBaseCacheConstructor(Class cacheClass) {
try {
return cacheClass.getConstructor(String.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Invalid base cache implementation (" + cacheClass + "). " +
"Base cache implementations must have a constructor that takes a String id as a parameter. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private Cache newCacheDecoratorInstance(Class cacheClass, Cache base) {
Constructor cacheConstructor = getCacheDecoratorConstructor(cacheClass);
try {
return cacheConstructor.newInstance(base);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Could not instantiate cache decorator (" + cacheClass + "). Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private Constructor getCacheDecoratorConstructor(Class cacheClass) {
try {
return cacheClass.getConstructor(Cache.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Invalid cache decorator (" + cacheClass + "). " +
"Cache decorators must have a constructor that takes a Cache instance as a parameter. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
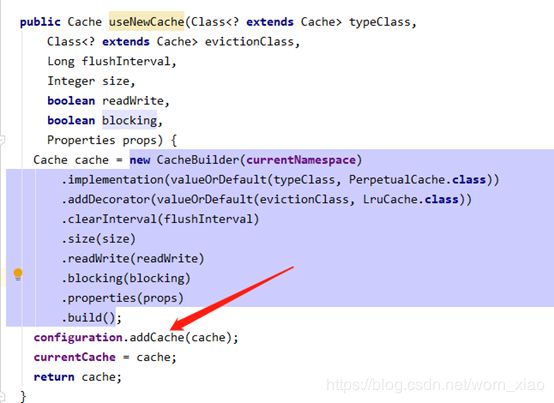
public Cache useNewCache(Class typeClass,
Class evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
configuration.addCache(cache);
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class CacheBuilder {
private final String id;
private Class implementation;
private final List> decorators;
private Integer size;
private Long clearInterval;
private boolean readWrite;
private Properties properties;
private boolean blocking;
public CacheBuilder(String id) {
this.id = id;
this.decorators = new ArrayList>();
}
public CacheBuilder implementation(Class implementation) {
this.implementation = implementation;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder addDecorator(Class decorator) {
if (decorator != null) {
this.decorators.add(decorator);
}
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder size(Integer size) {
this.size = size;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder clearInterval(Long clearInterval) {
this.clearInterval = clearInterval;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder readWrite(boolean readWrite) {
this.readWrite = readWrite;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder blocking(boolean blocking) {
this.blocking = blocking;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder properties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
return this;
}
public Cache build() {
setDefaultImplementations();
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
setCacheProperties(cache);
// issue #352, do not apply decorators to custom caches
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) {
for (Class decorator : decorators) {
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
setCacheProperties(cache);
}
cache = setStandardDecorators(cache);
} else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) {
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
}
private void setDefaultImplementations() {
if (implementation == null) {
implementation = PerpetualCache.class;
if (decorators.isEmpty()) {
decorators.add(LruCache.class);
}
}
}
private Cache setStandardDecorators(Cache cache) {
try {
MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache);
if (size != null && metaCache.hasSetter("size")) {
metaCache.setValue("size", size);
}
if (clearInterval != null) {
cache = new ScheduledCache(cache);
((ScheduledCache) cache).setClearInterval(clearInterval);
}
if (readWrite) {
cache = new SerializedCache(cache);
}
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
cache = new SynchronizedCache(cache);
if (blocking) {
cache = new BlockingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Error building standard cache decorators. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private void setCacheProperties(Cache cache) {
if (properties != null) {
MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache);
for (Map.Entry entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String name = (String) entry.getKey();
String value = (String) entry.getValue();
if (metaCache.hasSetter(name)) {
Class type = metaCache.getSetterType(name);
if (String.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, value);
} else if (int.class == type
|| Integer.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Integer.valueOf(value));
} else if (long.class == type
|| Long.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Long.valueOf(value));
} else if (short.class == type
|| Short.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Short.valueOf(value));
} else if (byte.class == type
|| Byte.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Byte.valueOf(value));
} else if (float.class == type
|| Float.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Float.valueOf(value));
} else if (boolean.class == type
|| Boolean.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Boolean.valueOf(value));
} else if (double.class == type
|| Double.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Double.valueOf(value));
} else {
throw new CacheException("Unsupported property type for cache: '" + name + "' of type " + type);
}
}
}
}
if (InitializingObject.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())){
try {
((InitializingObject) cache).initialize();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Failed cache initialization for '" +
cache.getId() + "' on '" + cache.getClass().getName() + "'", e);
}
}
}
private Cache newBaseCacheInstance(Class cacheClass, String id) {
Constructor cacheConstructor = getBaseCacheConstructor(cacheClass);
try {
return cacheConstructor.newInstance(id);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Could not instantiate cache implementation (" + cacheClass + "). Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private Constructor getBaseCacheConstructor(Class cacheClass) {
try {
return cacheClass.getConstructor(String.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Invalid base cache implementation (" + cacheClass + "). " +
"Base cache implementations must have a constructor that takes a String id as a parameter. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private Cache newCacheDecoratorInstance(Class cacheClass, Cache base) {
Constructor cacheConstructor = getCacheDecoratorConstructor(cacheClass);
try {
return cacheConstructor.newInstance(base);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Could not instantiate cache decorator (" + cacheClass + "). Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private Constructor getCacheDecoratorConstructor(Class cacheClass) {
try {
return cacheClass.getConstructor(Cache.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CacheException("Invalid cache decorator (" + cacheClass + "). " +
"Cache decorators must have a constructor that takes a Cache instance as a parameter. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
如上代码段所示,最重要的就是build()方法了,首先是为Cache设置一个默认的实现
也就是我们所说的被装饰者,然而实际上PerpetualCache的底层也是HashMap。这个是一个默认的被装饰者,然而build()的装饰
主要是这一段,一个是newCacheDecorator一个是setStandardDecorators
如上代码片段所示就是装饰者模式的掉用地方。通过不断的在构造函数中传入缓存参数。不断的装饰。当然还没完。我们也要看看它用在哪里了。
我们可以看到他是构建了一个缓存,添加到了Configuration配置类中了。
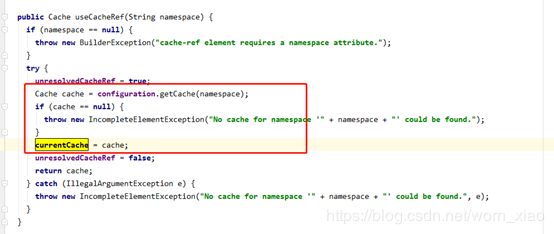
接下来我们看当开启缓存引用的时候,从configuration中获取到装饰好的cache,然后
然后把构建好的缓存添加到mapperStatement中去,
在框架执行查询的时候把装饰好的缓存拿出来。
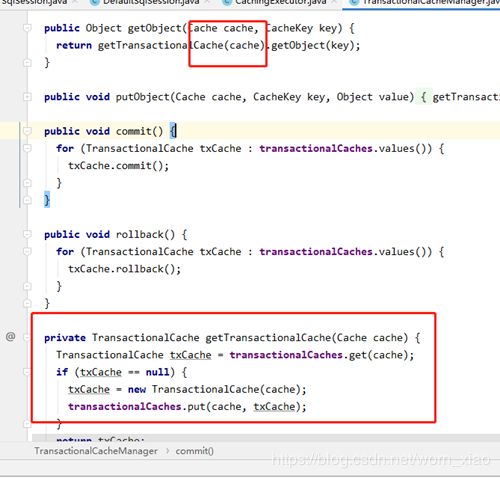
再做一次装饰,包装成事务缓存。之所以用事务缓存是为了保证缓存数据跟数据库数据的一致性问题。这就是mybaties缓存的地方。大量引用了设计模式的装饰者模式。
1.2.2 Mybatis执行器
1.2.2.1 执行器使用
@Test
public void shouldInsertNewAuthorWithBeforeAutoKey() throws Exception {
Executor executor = new SimpleExecutor(config,transaction);
try {
Author author = new Author(-1, "someone", "******", "[email protected]", null, Section.NEWS);
MappedStatement insertStatement = ExecutorTestHelper.prepareInsertAuthorMappedStatementWithBeforeAutoKey(config);
MappedStatement selectStatement = ExecutorTestHelper.prepareSelectOneAuthorMappedStatement(config);
int rows = executor.update(insertStatement, author);
assertTrue(rows > 0 || rows == BatchExecutor.BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE);
if (rows == BatchExecutor.BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE) {
executor.flushStatements();
}
assertEquals(123456, author.getId());
if (author.getId() != BatchExecutor.BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE) {
List authors = executor.query(selectStatement, author.getId(), RowBounds.DEFAULT, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
executor.rollback(true);
assertEquals(1, authors.size());
assertEquals(author.toString(), authors.get(0).toString());
assertTrue(author.getId() >= 10000);
}
} finally {
executor.rollback(true);
executor.close(false);
}
}
如上图是Excutor的使用例子。通过Excuctor就可以绕过Mapper与SqlSession执行,也就是说mapper和Sqlsession主要就是封装了Executor进行执行的。
1.2.2.2 装饰者模式实践
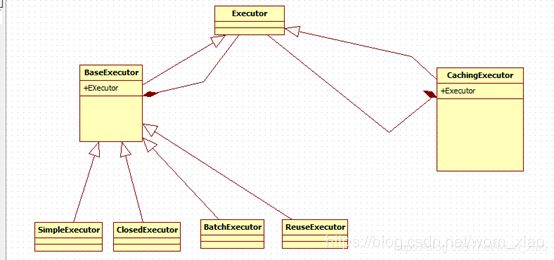
如上是装饰者模式的一个实践图,也就是在执行这些个基本的Executor的时候,都会加上一层缓存层来对所有的普通的Excutor做装饰。
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
首先可以看到如上代码片段所示,创建一个DefaultSqlSession对象,实际上是组合了一个Excutor,那么我们接着看装饰者模式是怎么提现出来的。
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//这里在Seting文件中开启了缓存就可以在执行器的时候增加一个缓存的包装
if (cacheEnabled) {//用户装饰者模式,基本的执行器加上了缓存的执行器 所以在这里如果开启了缓存的化就会用装饰者模式开启缓存
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
如上代码可以看到,如果开启了缓存的时候,就执行CachingExecutor对原Executor进行装饰。
* @author Clinton Begin
* @author Eduardo Macarron
*/
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {
private final Executor delegate;
private final TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();
public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this);
}
@Override
public Transaction getTransaction() {
return delegate.getTransaction();
}
@Override
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
//issues #499, #524 and #573
if (forceRollback) {
tcm.rollback();
} else {
tcm.commit();
}
} finally {
delegate.close(forceRollback);
}
}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() {
return delegate.isClosed();
}
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
@Override
public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public Cursor queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
return delegate.queryCursor(ms, parameter, rowBounds);
}
@Override
public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List list = (List) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate. query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate. query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public List flushStatements() throws SQLException {
return delegate.flushStatements();
}
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
delegate.commit(required);
tcm.commit();
}
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
try {
delegate.rollback(required);
} finally {
if (required) {
tcm.rollback();
}
}
}
private void ensureNoOutParams(MappedStatement ms, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.IN) {
throw new ExecutorException("Caching stored procedures with OUT params is not supported. Please configure useCache=false in " + ms.getId() + " statement.");
}
}
}
}
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
return delegate.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
}
@Override
public boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key) {
return delegate.isCached(ms, key);
}
@Override
public void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class targetType) {
delegate.deferLoad(ms, resultObject, property, key, targetType);
}
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
delegate.clearLocalCache();
}
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
@Override
public void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This method should not be called");
}
}
可以看到在执行指定方法的时候,都会对缓存进行操作。实际上这里的缓存就是我们上文讲的装饰者模式缓存。
1.3 代理模式
1.3.1 mybatis mapper
1.3.1.1 mapper 使用
@Test
public void shouldRollbackInsertedAuthor() throws Exception {
try {
manager.startManagedSession();
AuthorMapper mapper = manager.getMapper(AuthorMapper.class);
Author expected = new Author(501, "lmeadors", "******", "[email protected]", "Something...", null);
mapper.insertAuthor(expected);
manager.rollback();
Author actual = mapper.selectAuthor(501);
assertNull(actual);
} finally {
manager.close();
}
}
如上所示是调用代码,我们可以从manager.gerMapper(AuthorMapper.class)入手看看,这个代码的底层是怎么实现的。
1.3.1.2 代理模式实践
@Override
public T getMapper(Class type) {
return getConfiguration().getMapper(type, this);
}
接下来我们看看getMapper(type,this)这个Configuration做了什么。
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
再往下看。
public class MapperRegistry {
private final Configuration config;
private final Map, MapperProxyFactory> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public boolean hasMapper(Class type) {
return knownMappers.containsKey(type);
}
public void addMapper(Class type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory(type));
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
public Collection> getMappers() {
return Collections.unmodifiableCollection(knownMappers.keySet());
}
public void addMappers(String packageName, Class superType) {
ResolverUtil> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
Set>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for (Class mapperClass : mapperSet) {
addMapper(mapperClass);
}
}
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
addMappers(packageName, Object.class);
}
}
如上代码段我们可以看到mapper的代理。其实这里还杂糅了一个mapperProxyFactory的工厂模式,就是用来创建mapperProxy的工厂
/**
* @author Lasse Voss
*/
public class MapperProxyFactory {
private final Class mapperInterface;
private final Map methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
MapperProxyFactory 代理工厂做了什么?其实就是通过jdk的动态代理, 从哪里可以看出是jdk的动态代理呢,其实这里大家可以看到是使用了接口的,有接口的代理我们就可以判断是jdk的动态代理了。那么我们看看代理创建的MapperProxy是什么?
public class MapperProxy implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class mapperInterface;
private final Map methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class mapperInterface, Map methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
@UsesJava7
private Object invokeDefaultMethod(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
final Constructor constructor = MethodHandles.Lookup.class
.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class);
if (!constructor.isAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
}
final Class declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
return constructor
.newInstance(declaringClass,
MethodHandles.Lookup.PRIVATE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PROTECTED
| MethodHandles.Lookup.PACKAGE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PUBLIC)
.unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass).bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args);
}
private boolean isDefaultMethod(Method method) {
return (method.getModifiers()
& (Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.STATIC)) == Modifier.PUBLIC
&& method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface();
}
}
从代码可以看出,实际上mapperProxy就是用sqlSession来代替自己执行的。所以本质上Mapper执行,底层是SqlSession在执行的。
1.3.2 mybatis插件
1.3.2.1 插件使用
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Map.class, method = "get", args = {Object.class})})
public static class AlwaysMapPlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
return "Always";
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
}
1.3.2.2 代理模式实践
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//这里在Seting文件中开启了缓存就可以在执行器的时候增加一个缓存的包装
if (cacheEnabled) {//用户装饰者模式,基本的执行器加上了缓存的执行器 所以在这里如果开启了缓存的化就会用装饰者模式开启缓存
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
如上代码片段是Mybatis构建执行器的代码片段,那么interceptorChain这个是什么呢我们来看一下
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class InterceptorChain {
private final List interceptors = new ArrayList();
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public List getInterceptors() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
}
}
实际上这里是一组Interceptor也就是我们所说的Mybaties插件必须实现的类
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
通过这行代码,把executor,resultSetHandler等用interceptor的plugin(target)方法装饰起来。如上那么plugin就是代理实现的核心了。代理模式讲的是在executor执行指定方法之前对其进行拦截去执行其他的方法。那么我们来看一个这里的实现。
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
这里调用了Plugin.wrap(target,this)这个方法。那么这里面做了什么呢,我们继续往里面看。
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
private final Object target;
private final Interceptor interceptor;
private final Map, Set> signatureMap;
private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map, Set> signatureMap) {
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
}
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
Map, Set> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class type = target.getClass();
Class[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
Set methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
private static Map, Set> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) {
Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class);
// issue #251
if (interceptsAnnotation == null) {
throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value();
Map, Set> signatureMap = new HashMap, Set>();
for (Signature sig : sigs) {
Set methods = signatureMap.get(sig.type());
if (methods == null) {
methods = new HashSet();
signatureMap.put(sig.type(), methods);
}
try {
Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args());
methods.add(method);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
return signatureMap;
}
private static Class[] getAllInterfaces(Class type, Map, Set> signatureMap) {
Set> interfaces = new HashSet>();
while (type != null) {
for (Class c : type.getInterfaces()) {
if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) {//如果
interfaces.add(c);
}
}
type = type.getSuperclass();
}
return interfaces.toArray(new Class[interfaces.size()]);
}
}
实际上大家看到InvocationHandler的时候,已经很清楚了,实际上就是用了代理模式,通过查找事项了Interceptor接口,然后有Signature签名的类,这姓Interceptor的interceptor方法。那么如果我们就可以通过这里在Excutor执行节后通过插件来对数据做一个变更什么的。这就是插件中用到的代理模式。
1.3.2.3 日志代理
public final class StatementLogger extends BaseJdbcLogger implements InvocationHandler {
private final Statement statement;
private StatementLogger(Statement stmt, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
super(statementLog, queryStack);
this.statement = stmt;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] params) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, params);
}
if (EXECUTE_METHODS.contains(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
debug(" Executing: " + removeBreakingWhitespace((String) params[0]), true);
}
if ("executeQuery".equals(method.getName())) {
ResultSet rs = (ResultSet) method.invoke(statement, params);
return rs == null ? null : ResultSetLogger.newInstance(rs, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return method.invoke(statement, params);
}
} else if ("getResultSet".equals(method.getName())) {
ResultSet rs = (ResultSet) method.invoke(statement, params);
return rs == null ? null : ResultSetLogger.newInstance(rs, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return method.invoke(statement, params);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
public static Statement newInstance(Statement stmt, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
InvocationHandler handler = new StatementLogger(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
ClassLoader cl = Statement.class.getClassLoader();
return (Statement) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cl, new Class[]{Statement.class}, handler);
}
public Statement getStatement() {
return statement;
}
}
这个类用来为statement执行jdbc连接语句做代理,通过代理statementhandler执行数据库的操作,在操作数据库前后添加相应的日志。
1.4 组合模式
1.4.1 mybatis动态sql
1.4.1.1 动态sql使用
1.4.1.2 组合模式实践
@Test
public void shouldPerformStrictMatchOnForEachVariableSubstitution() throws Exception {
final Map param = new HashMap();
final Map uuu = new HashMap();
uuu.put("u", "xyz");
List uuuu = new ArrayList();
uuuu.add(new Bean("bean id"));
param.put("uuu", uuu);
param.put("uuuu", uuuu);
SqlNode sqlnodes[]={
new TextSqlNode("INSERT INTO BLOG (ID, NAME, NOTE, COMMENT) VALUES"),
new ForEachSqlNode(
new Configuration(),mixedContents(
new TextSqlNode("#{uuu.u}, #{u.id}, " +
"#{ u,typeHandler=org.apache.ibatis.type.StringTypeHandler},"
+ " #{u:VARCHAR,typeHandler=org.apache.ibatis.type.StringTypeHandler}")),
"uuuu", "uu", "u", "(", ")",
",")
};
createBlogDataSource();
final String resource = "org/apache/ibatis/builder/MapperConfig.xml";
final Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlMapper = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
Configuration configuration = sqlMapper.getConfiguration();
MixedSqlNode sqlNode = new MixedSqlNode(Arrays.asList(sqlnodes));
DynamicSqlSource source=new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, sqlNode);
BoundSql boundSql = source.getBoundSql(param);
assertEquals(4, boundSql.getParameterMappings().size());
assertEquals("uuu.u", boundSql.getParameterMappings().get(0).getProperty());
assertEquals("__frch_u_0.id", boundSql.getParameterMappings().get(1).getProperty());
assertEquals("__frch_u_0", boundSql.getParameterMappings().get(2).getProperty());
assertEquals("__frch_u_0", boundSql.getParameterMappings().get(3).getProperty());
}
可以看到如上的动态sql片段,实际上是通过xml配置文件,动态的构建一棵Sql树,然后统一的调用apply()接口的方法,
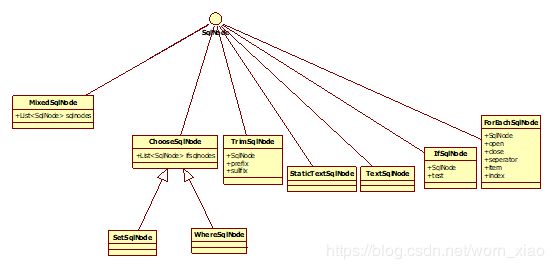
实际上SqlNode就是用了我们设计模式中的组合模式,可以看到SqlNode中每一个组件都与整个SqlNode产生了整体与部分的关系。通过把各种树形结构的SqlNode进行组合,合并成一个MixedSqlNode,执行相同的行为apply()。那么接下来我们看看细节SqlNode
public interface SqlNode {
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}
public class MixedSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final List contents;
public MixedSqlNode(List contents) {
this.contents = contents;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
for (SqlNode sqlNode : contents) {
sqlNode.apply(context);
}
return true;
}
}
public class IfSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final ExpressionEvaluator evaluator;
private final String test;
private final SqlNode contents;
public IfSqlNode(SqlNode contents, String test) {
this.test = test;
this.contents = contents;
this.evaluator = new ExpressionEvaluator();
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) {
contents.apply(context);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
以上就是sqlNode的基本代码,差不多都类型吧。其实我们从上面的代码可以看出Mybatis无非就是加载xml转换封装成一个mixSqlNode。然后通过解析这些个SqlNode解析出来,成一个sql,再封装到BoundSql里面。
1.5 模板方法模式
1.5.1 mybatis执行器
1.5.1.1 执行器使用
@Test
public void shouldDeleteAuthor() throws Exception {
Executor executor = createExecutor(new JdbcTransaction(ds, null, false));
try {
Author author = new Author(101, null, null, null, null, null);
MappedStatement deleteStatement = ExecutorTestHelper.prepareDeleteAuthorMappedStatement(config);
MappedStatement selectStatement = ExecutorTestHelper.prepareSelectOneAuthorMappedStatement(config);
int rows = executor.update(deleteStatement, author);
List authors = executor.query(selectStatement, 101, RowBounds.DEFAULT, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
executor.flushStatements();
executor.rollback(true);
assertEquals(0, authors.size());
assertTrue(1 == rows || BatchExecutor.BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE == rows);
} finally {
executor.rollback(true);
executor.close(false);
}
}
如上是执行器使用的代码片段。通过执行器执行从MappedStatement语句。
1.5.1.2 模板方法模式实践
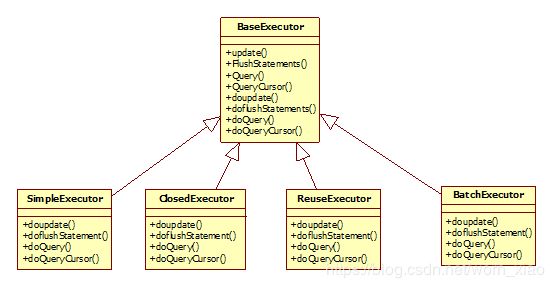
接下来我们看看模板方法的代码
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(BaseExecutor.class);
protected Transaction transaction;
protected Executor wrapper;
protected ConcurrentLinkedQueue deferredLoads;
protected PerpetualCache localCache;
protected PerpetualCache localOutputParameterCache;
protected Configuration configuration;
protected int queryStack;
private boolean closed;
protected BaseExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
this.transaction = transaction;
this.deferredLoads = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
this.localCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalCache");
this.localOutputParameterCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalOutputParameterCache");
this.closed = false;
this.configuration = configuration;
this.wrapper = this;
}
@Override
public Transaction getTransaction() {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
return transaction;
}
@Override
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
try {
rollback(forceRollback);
} finally {
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.close();
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// Ignore. There's nothing that can be done at this point.
log.warn("Unexpected exception on closing transaction. Cause: " + e);
} finally {
transaction = null;
deferredLoads = null;
localCache = null;
localOutputParameterCache = null;
closed = true;
}
}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() {
return closed;
}
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
clearLocalCache();
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
@Override
public List flushStatements() throws SQLException {
return flushStatements(false);
}
public List flushStatements(boolean isRollBack) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
return doFlushStatements(isRollBack);
}
@Override
public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
@Override
public Cursor queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
return doQueryCursor(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
}
@Override
public void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class targetType) {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
DeferredLoad deferredLoad = new DeferredLoad(resultObject, property, key, localCache, configuration, targetType);
if (deferredLoad.canLoad()) {
deferredLoad.load();
} else {
deferredLoads.add(new DeferredLoad(resultObject, property, key, localCache, configuration, targetType));
}
}
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
List parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// mimic DefaultParameterHandler logic
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
cacheKey.update(value);
}
}
if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
// issue #176
cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
}
return cacheKey;
}
@Override
public boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key) {
return localCache.getObject(key) != null;
}
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Cannot commit, transaction is already closed");
}
clearLocalCache();
flushStatements();
if (required) {
transaction.commit();
}
}
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (!closed) {
try {
clearLocalCache();
flushStatements(true);
} finally {
if (required) {
transaction.rollback();
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
if (!closed) {
localCache.clear();
localOutputParameterCache.clear();
}
}
protected abstract int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract List doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract List doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract Cursor doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException;
protected void closeStatement(Statement statement) {
if (statement != null) {
try {
if (!statement.isClosed()) {
statement.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// ignore
}
}
}
protected void applyTransactionTimeout(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
StatementUtil.applyTransactionTimeout(statement, statement.getQueryTimeout(), transaction.getTimeout());
}
private void handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key, Object parameter, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
final Object cachedParameter = localOutputParameterCache.getObject(key);
if (cachedParameter != null && parameter != null) {
final MetaObject metaCachedParameter = configuration.newMetaObject(cachedParameter);
final MetaObject metaParameter = configuration.newMetaObject(parameter);
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.IN) {
final String parameterName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
final Object cachedValue = metaCachedParameter.getValue(parameterName);
metaParameter.setValue(parameterName, cachedValue);
}
}
}
}
}
private List queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = transaction.getConnection();
if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return connection;
}
}
@Override
public void setExecutorWrapper(Executor wrapper) {
this.wrapper = wrapper;
}
private static class DeferredLoad {
private final MetaObject resultObject;
private final String property;
private final Class targetType;
private final CacheKey key;
private final PerpetualCache localCache;
private final ObjectFactory objectFactory;
private final ResultExtractor resultExtractor;
// issue #781
public DeferredLoad(MetaObject resultObject,
String property,
CacheKey key,
PerpetualCache localCache,
Configuration configuration,
Class targetType) {
this.resultObject = resultObject;
this.property = property;
this.key = key;
this.localCache = localCache;
this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory();
this.resultExtractor = new ResultExtractor(configuration, objectFactory);
this.targetType = targetType;
}
public boolean canLoad() {
return localCache.getObject(key) != null && localCache.getObject(key) != EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER;
}
public void load() {
@SuppressWarnings( "unchecked" )
// we suppose we get back a List
List 结合我画的设计模式结构图,可以看到如上所示的那几个BaseExcutor里面的方法,调用了相同的模板的实现,用了抽象方法,交给子类进行实现。
protected abstract int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract List doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract List doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract Cursor doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException;
这里我们不多看太多的子类。大家慢慢去看就好,这里只黏贴出一个子类来。
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
super(configuration, transaction);
}
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
public List doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
protected Cursor doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, null, boundSql);
Statement stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.queryCursor(stmt);
}
@Override
public List doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
}
如上代码片段,集成抽象的Executor实现了对应的方法。
1.5.2 mybatis类型映射器
如上图所示是Mybatis类型映射的设计框架,如上可能还有很多子类型。我这里只是列举了四个子类型。
1.5.2.1 类型映射器的使用
private static final TypeHandler TYPE_HANDLER = new StringTypeHandler();
@Override
@Test
public void shouldGetResultFromCallableStatement() throws Exception {
when(cs.getString(1)).thenReturn("Hello");
when(cs.wasNull()).thenReturn(false);
assertEquals("Hello", TYPE_HANDLER.getResult(cs, 1));
}
这里实际上getResult就是获取指定的那一列的数据库值,再经过指定的类型转换器,转换成对应的类型。比如
public class DateTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler
@Override
public Date getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex)
throws SQLException {
Timestamp sqlTimestamp = cs.getTimestamp(columnIndex);
if (sqlTimestamp != null) {
return new Date(sqlTimestamp.getTime());
}
return null;
}
如上可以看出从结果集中拿出timestamp出来以后,再通过Date()做了一次实践的转。
1.5.2.2 模板方法模式实践
public abstract class BaseTypeHandler extends TypeReference implements TypeHandler {
protected Configuration configuration;
public void setConfiguration(Configuration c) {
this.configuration = c;
}
@Override
public void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
if (parameter == null) {
if (jdbcType == null) {
throw new TypeException("JDBC requires that the JdbcType must be specified for all nullable parameters.");
}
try {
ps.setNull(i, jdbcType.TYPE_CODE);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Error setting null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . " +
"Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different jdbcTypeForNull configuration property. " +
"Cause: " + e, e);
}
} else {
try {
setNonNullParameter(ps, i, parameter, jdbcType);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new TypeException("Error setting non null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . " +
"Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different configuration property. " +
"Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
@Override
public T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
T result;
try {
result = getNullableResult(rs, columnName);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column '" + columnName + "' from result set. Cause: " + e, e);
}
if (rs.wasNull()) {
return null;
} else {
return result;
}
}
@Override
public T getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
T result;
try {
result = getNullableResult(rs, columnIndex);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column #" + columnIndex+ " from result set. Cause: " + e, e);
}
if (rs.wasNull()) {
return null;
} else {
return result;
}
}
@Override
public T getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
T result;
try {
result = getNullableResult(cs, columnIndex);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column #" + columnIndex+ " from callable statement. Cause: " + e, e);
}
if (cs.wasNull()) {
return null;
} else {
return result;
}
}
public abstract void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException;
public abstract T getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException;
public abstract T getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
public abstract T getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
}
如上所示是我们所说的模板方法
public class DateTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler {
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, Date parameter, JdbcType jdbcType)
throws SQLException {
ps.setTimestamp(i, new Timestamp(parameter.getTime()));
}
@Override
public Date getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName)
throws SQLException {
Timestamp sqlTimestamp = rs.getTimestamp(columnName);
if (sqlTimestamp != null) {
return new Date(sqlTimestamp.getTime());
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Date getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex)
throws SQLException {
Timestamp sqlTimestamp = rs.getTimestamp(columnIndex);
if (sqlTimestamp != null) {
return new Date(sqlTimestamp.getTime());
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Date getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex)
throws SQLException {
Timestamp sqlTimestamp = cs.getTimestamp(columnIndex);
if (sqlTimestamp != null) {
return new Date(sqlTimestamp.getTime());
}
return null;
}
}
如上所示是模板方法的具体实现类,可以看到它实现了抽象类中的日期时间转化。