Android蓝牙4.0之玩爆智能穿戴、家具(一)
科技评论
目前的智能时代已经到来,智能穿戴,智能家居,一切都是智能的了,很幸运,我做的也是智能行业,所以发表点观点也是可以的,以我见到的,所谓智能穿戴,智能家居,无非都是用手机中的软件作为媒介,把手机和智能设备联系到了一起,那么联系到一起的方式就是我们很熟悉的蓝牙了,或者是无线网,但是大多数都使用的是蓝牙,包括很出色的Garmin智能手表,手环,也是通过蓝牙4.0让手机软件和手表硬件进行通信的,所以我们能够掌握蓝牙的技能显得格外重要,也并不是说他就是未来,谁也说不准,下一个替代者将会出现,但是目前好像还没有发现,在智能行业里,这就是必需品,但是据我估计,在未来5年内,不会有变动,蓝牙也在继续完善,传输效率更高了,总之优点还是很多的。智能让生活变得很神奇,虽然我身处在这个行业里,但是我也会感到很是神奇,列位,擦亮眼睛,让我们一起来完爆它吧
效果演示
扫盲
- 蓝牙有传统蓝牙(3.0以下)和低功耗蓝牙(ble,又称蓝牙4.0)之分
- android手机必须系统版本4.3及以上才支持BLE API。低功耗蓝牙较传统蓝牙, 传输速度更快,覆盖范围更广,安全性更高,延迟更短,耗电极低等等优点,这也是为什么近年来智能穿戴的东西越来越多,越来越火
- 传统蓝牙与低功耗蓝牙通信方式也有所不同,传统的一般通过socket方式,而低功耗蓝牙是通过Gatt协议来实现
- 低功耗蓝牙也叫BLE
蓝牙的组成
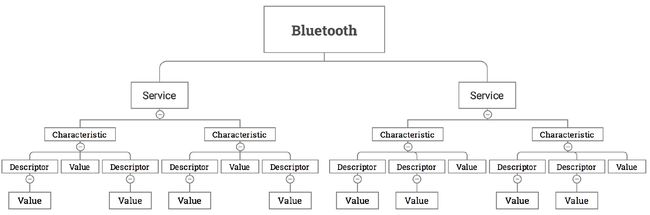
请先看一张图
解释:
BLE分为三个部分Service、Characteristic、Descriptor,每个部分都拥有不同的 UUID来标识。一个BLE设备可以拥有多个Service,一个Service可以包含多个Characteristic, 一个Characteristic包含一个Value和多个Descriptor,一个Descriptor包含一个Value。 通信数据一般存储在Characteristic内,目前一个Characteristic中存储的数据最大为20 byte。 与Characteristic相关的权限字段主要有READ、WRITE、WRITE_NO_RESPONSE、NOTIFY。 Characteristic具有的权限属性可以有一个或者多个。
介绍完了我们就开始看如何开发蓝牙4.0和开发流程
开发步骤
1. 检查该设备是否支持BLE设备
检查该设备是否支持BLE设备,谷歌在Android4.3才开始支持BLE设备
//第一步 检查设备时候支持BLE
if (!getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_BLUETOOTH_LE)) {
Toast.makeText(this, "请注意,您的手机不支持BLE", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}2. 拿到蓝牙管理器
一个Android系统只有一个BluetoothAdapter
//第二步 拿到蓝牙管理器
manager = (BluetoothManager) getSystemService(Context.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE);
bluetoothAdapter = manager.getAdapter();3. 打开蓝牙
//检查蓝牙是否已打开 如未打开 则打开蓝牙
if (!bluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) {
bluetoothAdapter.enable();
}4. 扫描蓝牙
注意:扫描蓝牙是比较耗资源的,所以扫描一段时间后应该及时关闭扫描
//10秒钟后停止扫描,扫描蓝牙设备是很费资源的
mhandler.postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mScanning = false;
bluetoothAdapter.stopLeScan(mLeScanCallback);
}
}, 10000);
mScanning = true;
//需要参数 BluetoothAdapter.LeScanCallback(返回的扫描结果)
bluetoothAdapter.startLeScan(mLeScanCallback);5. 实现扫描结果的回调
在第4步的时候在开始扫描的bluetoothAdapter.startLeScan(mLeScanCallback)中的mLeScanCallback,就是我们要实现的回调BluetoothAdapter.LeScanCallback,扫描的所有结果都会出现在回调里
/**
* 蓝牙扫面结果的回调
*/
private BluetoothAdapter.LeScanCallback mLeScanCallback = new BluetoothAdapter.LeScanCallback() {
@Override
public void onLeScan(BluetoothDevice bluetoothDevice, int i, byte[] bytes) {
if (bluetoothDevice != null && bluetoothDevice.getName() != null) {
mData.add(bluetoothDevice);
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//将扫描的到的bluetoothDevice添加到集合中 展示出来
ListAdapter = new MyAdapter(mData);
listview.setAdapter(ListAdapter);
}
});
} else {
ToastUtil.showToast("没有获取到设备信息",MainActivity.this);
}
}
};6. 连接蓝牙
连接时应关闭扫描,连接是通过获取到设备的mac地址进行连接的
//停止扫描
if (mScanning) {
bluetoothAdapter.stopLeScan(mLeScanCallback);
mScanning = false;
}
//通过蓝牙设备地址 获取远程设备 开始连接
BluetoothDevice device = bluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(mData.get(i).getAddress());
//第二个参数 是否要自动连接
mBluetoothGatt = device.connectGatt(MainActivity.this, false, mBluetoothGattCallback);7. 实现连接成功或者失败状态的回调
点击要连接的设备之后都会调用用BluetoothGattCallback回调,在这里我定义的是mBluetoothGattCallback,然后在实现回调里的onConnectionStateChange方法,系统会自动调用此方法
private BluetoothGattCallback mBluetoothGattCallback = new BluetoothGattCallback() {
/**
* 蓝牙连接状态改变后调用 此回调 (断开,连接)
* @param gatt
* @param status
* @param newState
*/
@Override
public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status, int newState) {
LogUtil.fussenLog().d("10086" + "===newState===" + newState);
if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED) {//连接成功
Message message = new Message();
message.what = CONNECT_SUCCESS;
mhandler.sendMessage(message);
//连接成功后去发现该连接的设备的服务
mBluetoothGatt.discoverServices();
} else if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED) {//连接失败 或者连接断开都会调用此方法
Message message = new Message();
message.what = CONNECT_FIAL;
mhandler.sendMessage(message);
}
}
}8. 连接成功后发现设备的所有服务
连接成功后紧接着就得去发现连接设备中的所有服务Service,为什么要发现服务?看下前面的第一张图你就明白了,继续实现BluetoothGattCallback中的onServicesDiscovered方法,因为系统会自动调用此方法
/**
* 连接成功后发现设备服务后调用此方法
* @param gatt
* @param status
*/
@Override
public void onServicesDiscovered(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status) {
LogUtil.fussenLog().d("10086" + "===搜到服务===");
if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) {//发现该设备的服务
//拿到该服务 1,通过UUID拿到指定的服务 2,可以拿到该设备上所有服务的集合
List serviceList = mBluetoothGatt.getServices();
//可以遍历获得该设备上的服务集合,通过服务可以拿到该服务的UUID,和该服务里的所有属性Characteristic
for (int x = 0; x < serviceList.size(); x++) {
services.add(serviceList.get(x));
}
Message message = new Message();
message.what = FIND_SERVICE;
mhandler.sendMessage(message);
} else {//未发现该设备的服务
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ToastUtil.showToast("未发现服务", MainActivity.this);
}
});
}
} 9. 向蓝牙设备发送数据
连接成功之后,我们总不能什么都不做吧,要做的就是和设备通信啊,也就是向设备发送数据喽,一般数据都会写在蓝牙设备的某个服务中的一个特征中,然后发送出去,当然这还得具体看厂家的蓝牙协议
//1.准备数据
byte[] data = new byte[6];
data[0] = 0x55;
data[1] = (byte) 0xAA;
data[2] = 0x00;
data[3] = 0x03;
data[4] = 0x02;
data[5] = (byte) 0xFB;
//2.通过指定的UUID拿到设备中的服务也可使用在发现服务回调中保存的服务
BluetoothGattService bluetoothGattService = services.get(0);
//3.通过指定的UUID拿到设备中的服务中的characteristic,也可以使用在发现服务回调中通过遍历服务中信息保存的Characteristic
BluetoothGattCharacteristic gattCharacteristic = bluetoothGattService.getCharacteristic(UUID1);
//4.将byte数据设置到特征Characteristic中去
gattCharacteristic.setValue(data);
//5.将设置好的特征发送出去
mBluetoothGatt.writeCharacteristic(gattCharacteristic); 一般硬件里读出写入的数据为二进制类型,所以要熟悉整型,字符串,二进制,十六进制等它们之间的转换,这些我会在蓝牙进阶里再展开,还有如何不停的写数据和读取数据,一并会在蓝牙进阶中给出最佳方案
10. 发送数据后的回调
蓝牙采用的是一应一答的模式,就是说,你给他发送了一个数据,不管你是发送失败还是成功,蓝牙都会给你应答一下,我们暂且这样理解,我们肯定也是希望我们自己能够监视自己到底有没有把数据发送出去,那么此时就应该重写BluetoothGattCallback中的onCharacteristicWrite方法
/**
* Characteristic数据发送后调用此方法
* @param gatt
* @param characteristic
* @param status
*/
@Override
public void onCharacteristicWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) {
if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) {//写入成功
Message message = new Message();
message.what = SEND_DATA_SUCCESS;
mhandler.sendMessage(message);
} else if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_FAILURE) {//写入失败
Message message = new Message();
message.what = SEND_DATA_FAIL;
mhandler.sendMessage(message);
} else if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_WRITE_NOT_PERMITTED) {// 没有写入的权限
}
}需要注意的是,蓝牙采用的是一应一答模式,也就是说,只要你对他做了操作之后,那么蓝牙设备都会响应你,就拿写入数据来说,只有当第一条数据写入完毕之后,才能写入第二条数据,换句话说,只有当这个回调中的onCharacteristicWrite方法执行完之后,才能继续写入数据,具体我们如何知道蓝牙什么时候响应和在什么地方响应,那么此时BluetoothGattCallback就显得尤为重要,蓝牙设备的所有响应都会在BluetoothGattCallback回调,并且执行相应的方法,下面我们就给出BluetoothGattCallback的解释和说明
11. BluetoothGattCallback
BluetoothGattCallback一共有9个方法,那么只有当你调用或者和连接的设备发生互动的时候,他的与之对应的方法才会回调,下面就是方法的对应
notification对应onCharacteristicChanged;
gatt.setCharacteristicNotification(characteristic, true);readCharacteristic对应onCharacteristicRead;
gatt.readCharacteristic(characteristic);writeCharacteristic对应onCharacteristicWrite;
gatt.wirteCharacteristic(mCurrentcharacteristic);连接蓝牙或者断开蓝牙 对应 onConnectionStateChange;
readDescriptor对应onDescriptorRead;
writeDescriptor对应onDescriptorWrite;
gatt.writeDescriptor(descriptor);readRemoteRssi对应onReadRemoteRssi;
gatt.readRemoteRssi()executeReliableWrite对应onReliableWriteCompleted;
discoverServices对应onServicesDiscovered。
gatt.discoverServices()
结尾
- 完成了以上的10步,那么就算对蓝牙什么都不知道,那么你也能做出一个蓝牙的Demo,其中更详细的代码可以参照Demo中的源码
- 这只是蓝牙的初级阶段,但是已经很厉害了好么
- 当然你要是和蓝牙进行通信的话,这些东西还不止,你还需要掌握更多的知识,才能完全的玩转蓝牙4.0
- 以后我会把蓝牙的完整解决方案都会展示出来,为大家作为参考
遗留的问题
- 如何读取蓝牙给我们返回的数据,在什么地方读取?什么时候读取?
- 如何将很多条数据同时发给蓝牙设备?
- 如何解析蓝牙返回的数据,在什么地方解析?什么时候解析?
- 如何能将蓝牙的部分形成一个完整的方案,直接拿来用,而不是还要我自己去搭建!
- 列位,让我们一起期待蓝牙4.0的进阶篇吧