c语言库函数总结----stdlib.h库
思维导图大纲
前言
stdlib .h 头文件定义了四个变量类型、一些宏和各种通用工具函数。
- double atof(const char *str)
函数原型 double atof(const char *str)
函数功能: 把参数 str 所指向的字符串转换为一个浮点数(类型为 double 型)。
//时间:2019年11月18日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境:VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 double atof(const char *str)
//函数功能: 把参数 str 所指向的字符串转换为一个浮点数(类型为 double 型)。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include - int atoi(const char *str)
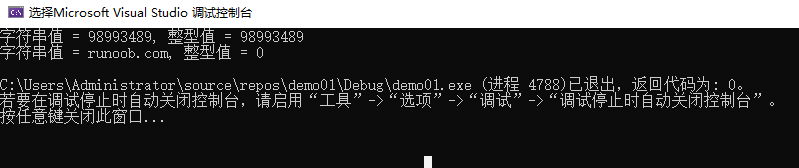
函数原型 int atoi(const char *str)
函数功能: 把参数 str 所指向的字符串转换为一个整数(类型为 int 型)。
//时间:2019年11月18日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境:VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 int atoi(const char *str)
//函数功能: 把参数 str 所指向的字符串转换为一个整数(类型为 int 型)。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include - long int atol(const char *str)
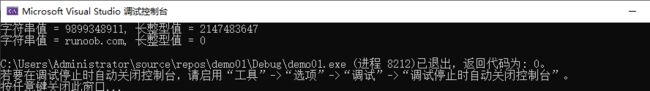
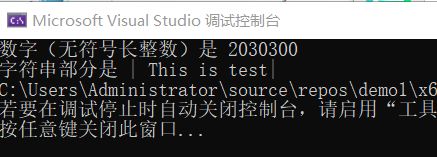
函数原型 long int atol(const char *str)
函数功能: 把参数 str 所指向的字符串转换为一个长整数(类型为 long int 型)
//时间:2019年11月18日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境:VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 long int atol(const char *str)
//函数功能: 把参数 str 所指向的字符串转换为一个长整数(类型为 long int 型)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
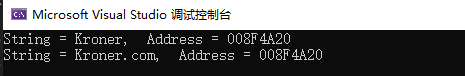
#include - double strtod(const char *str, char **endptr)
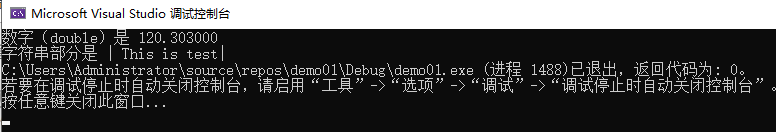
函数原型 double strtod(const char *str, char *endptr)
函数功能: 把参数 str 所指向的字符串转换为一个浮点数(类型为 double 型),
str – 要转换为双精度浮点数的字符串。
endptr – 对类型为 char 的对象的引用,其值由函数设置为 str 中数值后的下一个字符。
这个当第二个参数为空时和 double atof(const char *str)是相同,但是当而第二形参引用后,第二个指针会指向存储字符串位置的地址。
//时间:2019年11月18日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境:VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 double strtod(const char *str, char **endptr)
//函数功能: 把参数 str 所指向的字符串转换为一个浮点数(类型为 double 型)。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include - long int strtol(const char *str, char **endptr, int base)
函数原型 long int strtol(const char *str, char *endptr, int base)
函数功能: 把参数 str 所指向的字符串转换为一个长整数(类型为 long int 型)。
str – 要转换为长整数的字符串。
endptr – 对类型为 char 的对象的引用,其值由函数设置为 str 中数值后的下一个字符。
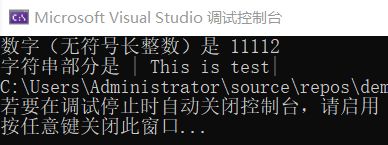
base – 基数,必须介于 2 和 36(包含)之间,或者是特殊值 0。这个基数就表示这个多少数字就多少进制
如果下列代码改为ret = strtol(str, &ptr, 8);就表示11112是八进制的数
//时间:2019年11月18日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境:VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 long int strtol(const char *str, char **endptr, int base)
//函数功能: 把参数 str 所指向的字符串转换为一个长整数(类型为 long int 型)。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include - unsigned long int strtoul(const char *str, char **endptr, int base)
函数原型 unsigned long int strtoul(const char *str, char **endptr, int base)
函数功能: 把参数 str 所指向的字符串转换为一个无符号长整数(类型为 unsigned long int 型)。
//时间:2019年11月19日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境:VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 unsigned long int strtoul(const char *str, char **endptr, int base)
//函数功能: 把参数 str 所指向的字符串转换为一个无符号长整数(类型为 unsigned long int 型)。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include - void *calloc(size_t nitems, size_t size)
函数原型 void *calloc(size_t nitems, size_t size)
函数功能: 分配所需的内存空间,并返回一个指向它的指针。
malloc 和 calloc 之间的不同点是,malloc 不会设置内存为零,
//时间: 2019年11月19日
//作者: Kroner
//编译环境: VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 void *calloc(size_t nitems, size_t size)
//函数功能: 释放之前调用 calloc、malloc 或 realloc 所分配的内存空间。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include - void free(void *ptr)
函数原型 void free(void *ptr)
函数功能: 分配所需的内存空间,该函数不返回任何值。
//时间:2019年11月19日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境:VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 void free(void *ptr)
//函数功能: 分配所需的内存空间,并返回一个指向它的指针。
// malloc 和 calloc 之间的不同点是,malloc 不会设置内存为零,而 calloc 会设置分配的内存为零。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include - void *malloc(size_t size)
函数原型 void *malloc(size_t size)
函数功能: 分配所需的内存空间,并返回一个指向它的指针。
该函数返回一个指针 ,指向已分配大小的内存。如果请求失败,则返回 NULL。
//时间:2019年11月15日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境:VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 void *malloc(size_t size)
//函数功能: 分配所需的内存空间,并返回一个指向它的指针。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
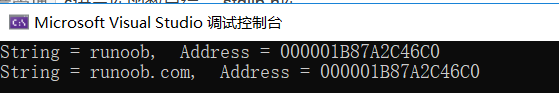
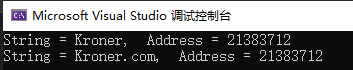
#include - void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t size)
函数原型 void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t size)
函数功能: 尝试重新调整之前调用 malloc 或 calloc 所分配的 ptr 所指向的内存块的大小。
该函数返回一个指针 ,指向重新分配大小的内存。如果请求失败,则返回 NULL。
//时间:2019年11月15日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境:VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t size)
//函数功能: 尝试重新调整之前调用 malloc 或 calloc 所分配的 ptr 所指向的内存块的大小。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include - void abort(void)
函数原型 void abort(void)
函数功能: 使一个异常程序终止。
//时间:2019年11月15日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境:VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 void abort(void)
//函数功能: 使一个异常程序终止。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include 测试结果:
由于我们没有创建nofile.txt,所以是无法使用fopen()打开文件的,所以就会有弹出这样的异常界面
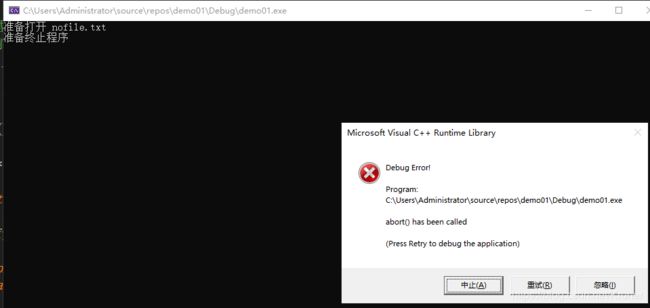
- int atexit(void (*func)(void))
函数原型 int atexit(void (*func)(void))
函数功能: 当程序正常终止时,调用指定的函数 func。
//时间:2019年11月15日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境: VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 int atexit(void (*func)(void))
//函数功能: 当程序正常终止时,调用指定的函数 func。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include - void exit(int status)
函数原型 void exit(int status)
函数功能: 使程序正常终止。
//时间:2019年11月15日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境:VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 void exit(int status)
//函数功能: 使程序正常终止。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
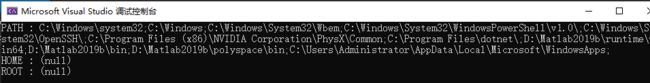
#include - char *getenv(const char *name)
函数原型 char *getenv(const char *name)
函数功能: 搜索 name 所指向的环境字符串,并返回相关的值给字符串。
//时间:2019年11月15日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境:VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 char *getenv(const char *name)
//函数功能: 搜索 name 所指向的环境字符串,并返回相关的值给字符串。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include - int system(const char *string)
函数原型 int system(const char *string)
/函数功能: 由 string 指定的命令传给要被命令处理器执行的主机环境。
//时间:2019年11月15日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境: VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 int system(const char *string)
//函数功能: 由 string 指定的命令传给要被命令处理器执行的主机环境。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include 测试结果:在windows 系统中显示的结果,相当于win+r运行cmd后再输入栏中输入dir的结果
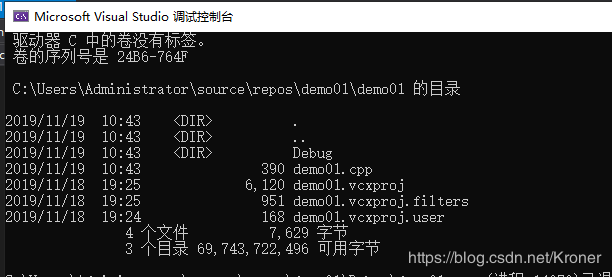
- void *bsearch(const void *key, const void *base, size_t nitems,
size_t size, int (*compar)(const void *, const void *))
函数原型 void *bsearch(const void *key, const void *base, size_t nitems, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void , const void ))
key – 指向要查找的元素的指针,类型转换为 void 。
base – 指向进行查找的数组的第一个对象的指针,类型转换为 void 。
nitems – base 所指向的数组中元素的个数。
size – 数组中每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
compar – 用来比较两个元素的函数。
函数功能: 执行二分查找。
//时间:2019年11月15日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境: VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 void *bsearch(const void *key, const void *base, size_t nitems, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void *, const void *))
// key -- 指向要查找的元素的指针,类型转换为 void* 。
// base -- 指向进行查找的数组的第一个对象的指针,类型转换为 void* 。
// nitems -- base 所指向的数组中元素的个数。
// size -- 数组中每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
// compar -- 用来比较两个元素的函数。
//函数功能: 执行二分查找。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include 测试结果:这个相当于C语言封装的一个二分算法。后缀讲解算法题目的时候在讲解。
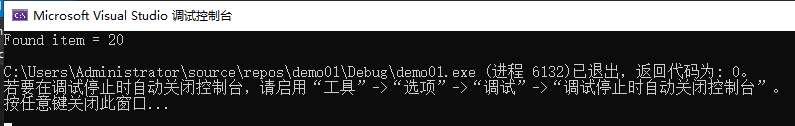
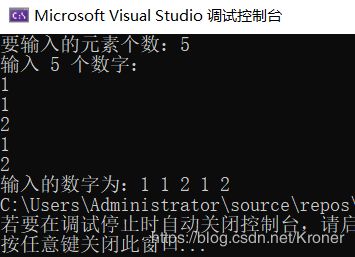
- void qsort(void *base, size_t nitems, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void , const void))
函数原型 void qsort(void *base, size_t nitems, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void , const void))
base – 指向要排序的数组的第一个元素的指针。
nitems – 由 base 指向的数组中元素的个数。
size – 数组中每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
compar – 用来比较两个元素的函数。
函数功能: 数组排序
//时间:2019年11月15日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境: VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 void qsort(void *base, size_t nitems, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void *, const void*))
// base -- 指向要排序的数组的第一个元素的指针。
// nitems -- 由 base 指向的数组中元素的个数。
//size -- 数组中每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
//compar -- 用来比较两个元素的函数。
//函数功能: 数组排序
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include 测试结果:若是要从大到小排列只需要cmpfunc的返回值前加个一个符号就可以。
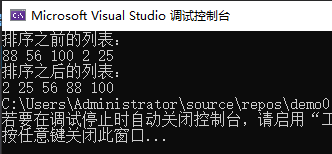
- int abs(int x)
函数原型 int abs(int x)
函数功能: 返回 x 的绝对值。
//时间:2019年11月15日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境: VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型 int abs(int x)
//函数功能: 返回 x 的绝对值。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
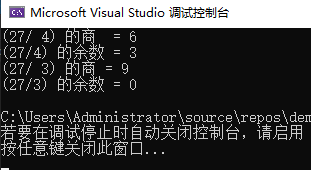
#include - div_t div(int numer, int denom)
函数原型 div_t div(int numer, int denom)
函数功能: 分子除以分母。
//时间:2019年11月15日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境: VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型: div_t div(int numer, int denom)
//函数功能: 分子除以分母。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include - int rand(void)
- void srand(unsigned int seed)
函数原型: int rand(void)
函数原型: void srand(unsigned int seed)
函数功能: 返回一个范围在 0 到 RAND_MAX 之间的伪随机数。
函数功能: 该函数播种由函数 rand 使用的随机数发生器。
//时间:2019年11月15日
//作者:Kroner
//编译环境: VS 2019
//库函数 stdlib.h
//函数原型: int rand(void)
//函数原型 void srand(unsigned int seed)
//函数功能: 返回一个范围在 0 到 RAND_MAX 之间的伪随机数。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include