分支定界法——旅行商(TSP)问题
问题描述
给定一个n顶点网络(有向或无向),找出一个包含n个顶点且具有最小耗费的换路。任何一个包含网络所有顶点的换路称为一个旅行。旅行商问题(Traveling Salesman Problem,TSP)是要寻找一条耗费最少的旅行。
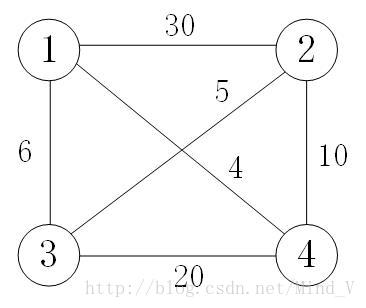
图1 四顶点网络
如图1是一个四顶点无向网络。这个网络的一些旅行:1,2,4,3,1;1,3,2,4,1和1,4,3,2,1。旅行1,2,4,3,1的耗费为66,;旅行1,3,2,4,1的耗费为25;旅行1,4,3,2,1的耗费为55.故1,3,2,4,1是网络中耗费最少的旅行。
算法设计
和回溯法解决TSP问题一样,首先确定问题的解空间是一个排列树,从顶点1出发最后回到顶点1,所以排列可以表示为[1,x2,…,xn,1]。和子集树一样,使用一个优先级队列求解。要求旅行的耗费最小,故使用小根堆储存活动节点,堆中每个活动节点的子树耗费所能取得的下界lowerCost 是优先级队列的优先级,即当前节点确定的途径下继续完成排列能取得最低耗费(并不一定保证能最终达到这个值)。
每个活动节点是小根堆的一个元素,元素结构包括:
lowerCost; //当前节点往后排列,整个回路所能取得的总耗费的下限
currentCost; //从根到当前节点的当前排列的耗费
restMinCost; //从当前节点到最后一个节点,每个节点的最小出边的耗费之和
s; //从根节点到当前节点的路径为[0:s]
currentTour[]; //从根节点到当前节点的路径(排列)
如何获得lowerCost:
对于每个活动节点,可知当前耗费currentCost,对于剩余的顶点,计算每个顶点的最小出边之和restMinCost即为剩余路径的最小耗费的下界,lowerCost=currentCost + restMinCost。
算法步骤
1、准备工作:建立小根堆,用于存储活动节点。计算每个顶点的最小出边,若存在某个顶点没有出边,则算法终止。初始化树根(顶点1)为第一个活动节点。
2、判断节点是否是叶结点的父节点:是的话,则检查是否一定有最低耗费,若是加入小根堆;
3、不是叶结点的父节点,则生成子节点,并判断子节点是否有可能取得最低耗费,若可能则加入小根堆;
4、取出下一个节点作为活动节点,若该节点已经是叶结点,返回当前最低耗费值,即为最优旅行。若不是叶结点则循环2、3步。
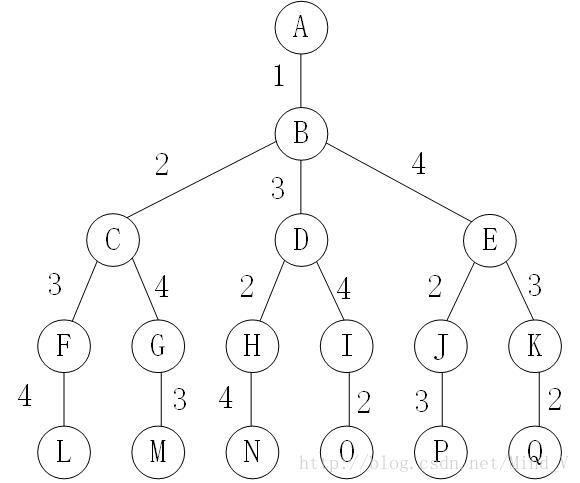
图2 四顶点网络的解空间树
小根堆中的元素变化:{}——>{C,D,E}——>{C,D,K,J}——>{C,K,J,H,I}——>{C,K,J,I,N}——>{C,K,I,N}——>{C,K,I}
最后取出活动节点N,但是N已经是叶结点,故返回最优值25,和最佳途径1->3->2->4->1,并终止算法。
事实上,检查节点J的子节点P时执行的是步骤2,也能得到最优值25,但是由于N已经加入小根堆,并且当前最优值已经是25,所以P没有加入小根堆,途径1->4->2->3->1也就被排除了。
需要注意的是,对于以下的C++程序,需要手动释放掉每个活动节点的数据成员currentTour数组的内寸,包括最后小根堆中剩余的节点。
C++实现
小根堆minHeap元素结构
#pragma once
struct heapNode
{
int lowerCost; //当前节点往后排列,整个回路所能取得的总耗费的下限
int currentCost; //从根到当前节点的当前排列的耗费
int restMinCost; //从当前节点到最后一个节点,每个节点的最小出边的耗费之和
int s; //从根节点到当前节点的路径为[0:s]
int *currentTour; //从根节点到当前节点的路径(排列)
//算术运算时的类型转换
operator int() { return lowerCost; }
//重载大于号运算符,用于小根堆比较
bool operator>(const heapNode &right)
{
return lowerCost > right.lowerCost;
}
};小根堆minHeap 部分源码
#pragma once
#include::minHeap(int initialCapacity)
{// Constructor.
if (initialCapacity < 1)
{
cout << "Initial capacity = " << initialCapacity << " Must be > 0";
exit(1);
}
arrayLength = initialCapacity + 1;
heap = new T[arrayLength];
heapSize = 0;
}
template<class T>
void minHeap::push(const T& theElement)
{// Add theElement to heap.
// increase array length if necessary
if (heapSize == arrayLength - 1)
{// double array length
changeLength1D(heap, arrayLength, 2 * arrayLength);
arrayLength *= 2;
}
// find place for theElement
// currentNode starts at new leaf and moves up tree
int currentNode = ++heapSize;
while (currentNode != 1 && heap[currentNode / 2] > theElement)
{
// cannot put theElement in heap[currentNode]
heap[currentNode] = heap[currentNode / 2]; // move element down
currentNode /= 2; // move to parent
}
heap[currentNode] = theElement;
}
template<class T>
void minHeap::pop()
{// Remove max element.
// if heap is empty return null
if (heapSize == 0) // heap empty
{
cout << "heap is empty!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
// Delete min element
heap[1].~T();
// Remove last element and reheapify
T lastElement = heap[heapSize--];
// find place for lastElement starting at root
int currentNode = 1,
child = 2; // child of currentNode
while (child <= heapSize)
{
// heap[child] should be smaller child of currentNode
if (child < heapSize && heap[child] > heap[child + 1])
child++;
// can we put lastElement in heap[currentNode]?
if (lastElement <= heap[child])
break; // yes
// no
heap[currentNode] = heap[child]; // move child up
currentNode = child; // move down a level
child *= 2;
}
heap[currentNode] = lastElement;
} TSP算法程序
#include liveNodeMinHeap;
//costOfMinOutEdge[i]表示顶点i的最小出边
int *minCostOutEdge = new int[n + 1];
int sumOfMinCostOutEdges = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
int minCost = -1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
if (cost[i][j] != -1 && (minCost == -1 || minCost > cost[i][j]))
minCost = cost[i][j];
if (minCost == -1)
return -1;
minCostOutEdge[i] = minCost;
sumOfMinCostOutEdges += minCost;
}
//初始E-节点的根
heapNode eNode;
eNode.lowerCost = sumOfMinCostOutEdges;
eNode.currentCost = 0;
eNode.restMinCost = sumOfMinCostOutEdges;
eNode.s = 0;
eNode.currentTour = new int[n];
//初始化排列为[1,2,3,...,n,1]
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
eNode.currentTour[i] = i + 1;
int bestCostSoFar = -1; //当前最佳旅行耗费
int *currentTour = eNode.currentTour;
//搜索排列树
while (eNode.s < n - 1)
{
currentTour = eNode.currentTour;
if (eNode.s == n - 2)
{//叶结点的父节点
//检查是否为当前最优旅行
if (cost[currentTour[n - 2]][currentTour[n - 1]] != -1 &&
cost[currentTour[n - 1]][1] != -1 &&
(bestCostSoFar == -1 || eNode.currentCost +
cost[currentTour[n - 2]][currentTour[n - 1]] +
cost[currentTour[n - 1]][1] < bestCostSoFar))
{//发现最优旅行,加入小根堆
bestCostSoFar = eNode.currentCost +
cost[currentTour[n - 2]][currentTour[n - 1]] +
cost[currentTour[n - 1]][1];
eNode.currentCost = bestCostSoFar;
eNode.lowerCost = bestCostSoFar;
eNode.s++;
liveNodeMinHeap.push(eNode);
}
else
{
delete[] eNode.currentTour; //舍弃非最优的叶结点的父节点,释放内存
eNode.currentTour = nullptr;
}
}
else
{//生成子节点
for(int i = eNode.s + 1; i < n; ++i)
if (cost[currentTour[eNode.s]][currentTour[i]] != -1)
{//子节点可行
int currentCost = eNode.currentCost +
cost[currentTour[eNode.s]][currentTour[i]];
int restMinCost = eNode.restMinCost -
minCostOutEdge[currentTour[eNode.s]];
int leastCostPossible = currentCost + restMinCost;
if (bestCostSoFar == -1 ||
leastCostPossible < bestCostSoFar)
{//子树可能有更优的叶结点,把当前子树的根放入小根堆
heapNode hNode;
hNode.lowerCost = leastCostPossible;
hNode.currentCost = currentCost;
hNode.restMinCost = restMinCost;
hNode.s = eNode.s + 1;
hNode.currentTour = new int[n];
copy(currentTour, currentTour + n, hNode.currentTour);
swap(hNode.currentTour[hNode.s], hNode.currentTour[i]);
liveNodeMinHeap.push(hNode);
}
}
//完成节点扩展,释放内存
delete[] eNode.currentTour;
eNode.currentTour = nullptr;
}
if (liveNodeMinHeap.empty())
break;
//取下一个E-节点
eNode = liveNodeMinHeap.top();
liveNodeMinHeap.pop();
}
if (bestCostSoFar == -1)
return -1;
//复制到bestTour
copy(eNode.currentTour, eNode.currentTour + n, bestTour + 1);
//释放小根堆中剩余元素的currentTour数组内存***虽然小根堆析构,
//但是currentTour是new的内存,依然存在,故必须手动释放
while (true)
{
delete[] eNode.currentTour;
if (liveNodeMinHeap.empty())
break;
//取下一个E-节点
eNode = liveNodeMinHeap.top();
liveNodeMinHeap.pop();
}
return bestCostSoFar;
}
void init()
{
cost[1][1] = -1;
cost[1][2] = 30;
cost[1][3] = 6;
cost[1][4] = 4;
cost[2][1] = 30;
cost[2][2] = -1;
cost[2][3] = 5;
cost[2][4] = 10;
cost[3][1] = 6;
cost[3][2] = 5;
cost[3][3] = -1;
cost[3][4] = 20;
cost[4][1] = 4;
cost[4][2] = 10;
cost[4][3] = 20;
cost[4][4] = -1;
}
void main()
{
init();
int bestCost = TSP(bestTour); //起点定为1,从第二层开始
cout << "最少的运费为:" << bestCost << endl;
cout << "最佳路径为: ";
copy(bestTour + 1, bestTour + n + 1, ostream_iterator<int>(cout, "->"));
cout << bestTour[1] << endl;
} 测试结果
最少的运费为:25
最佳路径为: 1->3->2->4->1
请按任意键继续. . .