RabbitMq的四种模式存储规则
RabbitMQ中,所有生产者提交的消息都由Exchange(交换机)来接受,然后Exchange按照特定的策略转发到Queue进行存储,RabbitMQ提供了四种Exchange:fanout、direct、topic、header,其中header模式在实际使用中较少,本文只对前三种模式进行比较。
性能方面比较:fanout > direct >> topic,比例大约为11:10:6
1、Fanout Exchange(发布订阅模式)
任何生产者发送到Fanout Exchange交换机的消息都被转发到与其绑定(binging)的所有的Queue队列中存储,并由监听该队列Queue的消费者所消费,整个过程一般情况下关系为:生产者与Fanout Exchange(交换机)为多对一,Exchange(交换机)与队列Queue为一对多,队列Queue与消费者为一对多;
(1)定义Queue队列、Fanout Exchange交换机,并将队列绑定在交换机上
package com.neo.rabbit;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FanoutRabbitConfig {
//定义三个Queue队列A、B、C
@Bean
public Queue AMessage() {
return new Queue("fanout.A");
}
@Bean
public Queue BMessage() {
return new Queue("fanout.B");
}
@Bean
public Queue CMessage() {
return new Queue("fanout.C");
}
//定义FanoutWxchange交换机
@Bean
FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange("fanoutExchange");
}
//将定义好Queue队列绑定在该交换机上
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeA(Queue AMessage,FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(AMessage).to(fanoutExchange);
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeB(Queue BMessage, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(BMessage).to(fanoutExchange);
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeC(Queue CMessage, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(CMessage).to(fanoutExchange);
}
}
(2)定义生产者,发布消息到具体的交换机上,再由交换机自动转发到绑定的所有队列Queue中存储
package com.neo.rabbit.fanout;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class FanoutSender {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send(int i) {
String context = "hi, fanout msg is " +i;
//指定名字为fanoutExchange的交换机,第二个参数为具体的Queue名,忽略不写
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fanoutExchange","", context);
}
}(3)定义消费者,实现MessageListener监听器接口,或SpringBoot中通过注解的方式根据具体的Queue队列名(RouteKey)进行实时的监听,从队列中获取消息
package com.neo.rabbit.fanout;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.A")
public class FanoutReceiverA {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message) {
System.out.println("fanout Receiver A : " + message);
}
}
注意:
- 该模式下生产者发布消息不需要指定RouteKey(指定了RouteKey也会被忽略)
- 该模式下需求提前将Exchange与Queue进行绑定,一个Exchange可以绑定多个Queue,一个Queue可以同多个Exchange进行绑定(按需求情况而定)
- 如果接受到消息的Exchange没有与任何Queue绑定,则消息会被抛弃。
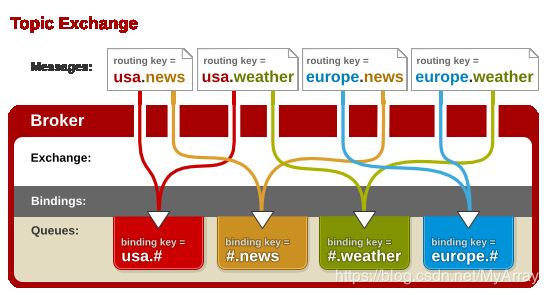
2、Topic Exchange(主题模式)
Topic Exchange 转发消息主要是根据通配符方式匹配Queue队列中的routing_key(即为队列名)。 在这种交换机下,队列和交换机的绑定会定义一种路由模式,那么,通配符就要在这种路由模式和路由键(routing_key)之间匹配后交换机才能转发消息。(任何发送到Topic Exchange的消息都会被转发到所有关心RouteKey中指定话题的Queue上)
在这种交换机模式下:(*:表示一个词,#:表示零个或多个词)
- 路由键必须是一串字符,用句号(.) 隔开,比如说 agreements.us,或者 agreements.eu.stockholm 等。
- 路由模式必须包含一个 星号(*),主要用于匹配路由键指定位置的一个单词,比如说,一个路由模式是这样子:agreements..b.*,那么就只能匹配路由键是这样子的:第一个单词是 agreements,第四个单词是 b。 井号(#)就表示相当于一个或者多个单词,例如一个匹配模式是 agreements.eu.berlin.#,那么,以agreements.eu.berlin 开头的路由键都是可以的。
定义的过程跟前面的 Fanout模式差不多,所不同的是:Queue队列绑定到交换机时,需要with带有某种规则的去绑定,即BindingBuilder.bind(queueMessages).to(exchange).with("topic.#"),topic.#为匹配规则,只要生产者发布消息时的路由键routing_key满足这一规则, 即可将消息转发到该Queue(queueMessages)队列中
package com.neo.rabbit;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class TopicRabbitConfig {
final static String message = "topic.message";
final static String messages = "topic.messages";
@Bean
public Queue queueMessage() {
return new Queue(TopicRabbitConfig.message);
}
@Bean
public Queue queueMessages() {
return new Queue(TopicRabbitConfig.messages);
}
@Bean
TopicExchange exchange() {
return new TopicExchange("topicExchange");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessage(Queue queueMessage, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueMessage).to(exchange).with("topic.message");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessages(Queue queueMessages, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueMessages).to(exchange).with("topic.#");
}
}
3、Direct Exchange(默认模式)
任何发送到Direct Exchange的消息都会被转发到RouteKey中指定的Queue,即无需定义交换机(Exchange),直接定义好队列(Queue)即可,生产者发布消息时,通过abbitMQ自带的交换机Exchange:”"(该Exchange的名字为空字符串,下文称其为default Exchange)转发到具体的RouteKey队列中存储,如果vhost中不存在RouteKey中指定的队列名,则该消息会被抛弃。
该模式为默认的、简单的一种,应用的方式为(都为在同一个队列中进行操作):
- 一对一发送:一个发送者,一 个接收者
- 一对多发送:一个发送者,N 个接收者
- 多对多发送:N个发送者,N 个接收者