PyTorch版YOLOv4训练自己的数据集---基于Google Colab
colab简介
Google Colaboratory是谷歌开放的一款研究工具,主要用于机器学习的开发和研究。
工具优势:Google Colab最大的好处是给广大的AI开发者提供了免费的GPU使用。你可以在上面轻松地跑例如:Keras、Tensorflow、Pytorch等框架;其次是入门相对简单,语法和cmd语句以及linux语句相似。目前colab平台GPU的状态信息如下图:

工具缺陷:对自身网络有一定要求,否则容易断联。但是目前本人使用过程中很少发生上述情况,除了电脑熄屏的时候导致断联。
因此这个工具对于自身电脑配置不高的开发者很是友好。
colab入门
官方教程:https://medium.com/deep-learning-turkey/google-colab-free-gpu-tutorial-e113627b9f5d
Deep-Learning-with-GoogleColab:https://github.com/hardik0/Deep-Learning-with-GoogleColab
这个github项目实现了在colab上使用yolov3,yolov4进行目标检测。
训练自己的数据集
准备自己的数据集(win10)
这是利用yolo系列算法训练自己数据集最为关键,也是最为繁琐的一步。所幸自己在github找到一个项目,此项目专门为yolo系列准备对应格式的数据。
voc2007_for_yolo_torch:https://github.com/ppr/voc2007_for_yolo_torch
大家只需要根据作者的指示,便可以轻松的得到可利用的数据。
注意事项
- 这个步骤本来可以统一在Google Colab实现,但是由于谷歌云端硬盘的空间有限,所以我在win10利用pycharm将这一步骤先进行实现,之后需要将对应结果的文件夹和文件上传到谷歌云盘就行。
- 由于自身的xml文件格式可能和作者的xml文件格式不一样,所以除了作者说的需要修改的地方,我们可能还需要对代码进行适当的修改。
- 比如我的xml文件就和作者xml文件不一样,我的xml文件中没有"size","difficult"等属性。所以需要对tools文件夹下的voc_lable.py文件进行修改。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
需要修改的地方:
1. sets中替换为自己的数据集
3. 将本文件放到VOC2007目录下
4. 直接开始运行
"""
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
from os import listdir
from os.path import join
import cv2
sets = [('2007', 'train'), ('2007', 'val'), ('2007', 'test')] #替换为自己的数据集
jpegimages_dir = r".\JPEGImages" #原本没有,自己添加,因为下面需要使用
def convert(size, box):
# 进行归一化
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def convert_annotation(year, image_id, classes):
in_file = open('Annotations/%s.xml' % (image_id), 'r', encoding='utf-8') #将数据集放于当前目录下
out_file = open('voc_labels/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
#因为我的xml文件中没有“size”,"difficult"标注,所以需要对源码进行修改
#size = root.find('size')
#w = int(size.find('width').text)
#h = int(size.find('height').text)
# for obj in root.iter('object'):
# difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
# cls = obj.find('name').text
# if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
# continue
# cls_id = classes.index(cls)
# xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
# b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text),
# float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
# bb = convert((w, h), b)
# out_file.write(
# str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
#在作者源码基础上,对其修改得到如下代码
img = cv2.imread(jpegimages_dir + "/" + image_id+'.jpg')
w = int(img.shape[1])
h = int(img.shape[0])
for obj in root.iter('object'):
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(
str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
def gen_voc_lable(classes):
for year, image_set in sets:
if not os.path.exists('voc_labels/'):
os.makedirs('voc_labels/')
image_ids = open('ImageSets/Main/%s.txt' %
(image_set)).readlines() #.strip()#.split()
# print(image_ids)
print('*' * 20)
list_file = open('%s_%s.txt' % (year, image_set),
'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
image_id = image_id[:-1]
print(image_id)
list_file.write('./data/images/%s2014/%s.jpg\n' % (image_set ,image_id))
convert_annotation(year, image_id, classes)
list_file.close()
上传结果文件夹
首先,我们需要打开,然后进入Google Colab
https://colab.research.google.com/
然后点击文件,新建笔记本。
接着运行如下语句:
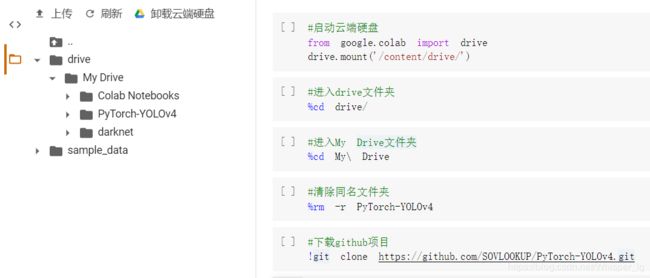 为了方便大家运行,将上述语句以代码块形式给出如下:
为了方便大家运行,将上述语句以代码块形式给出如下:
#启动云端硬盘
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive/')
#进入drive文件夹
%cd drive/
#进入My Drive文件夹
%cd My\ Drive
#清除同名文件夹
%rm -r PyTorch-YOLOv4
#下载github项目
!git clone https://github.com/SOVLOOKUP/PyTorch-YOLOv4.git
此处还参考了另一个github项目:PyTorch-YOLOv4
- 将images,labels文件夹放到PyTorch-YOLOv4里的data文件夹中。
由于images,labels文件夹较大,因此我们需要先将其压缩后上传,上传方式为将压缩文件直接拖入云盘网页 - 将2007_train.txt 2007_test.txt文件放到PyTorch-YOLOv4里的data文件夹
- 修改template.names, 里边就是classes内容,每行一个类
- 修改template.data,修改类别个数classes
2-4文件不大,可以直接通过云端硬盘上传,文件上传之后将他们都移至data文件夹,右击文件即可出现提示操作
配置相关环境
配置GPU

如上图所示点击代码执行程序,点击更改运行时类型,便可选择GPU
安装相关的库
%cd PyTorch-YOLOv4/
!pip3 install -r requirements.txt
下载权重文件
 运行上面两行语句,但是发现并不能执行成功,出现错误提示如下:
运行上面两行语句,但是发现并不能执行成功,出现错误提示如下:

经过分析发现wights文件下的download_weights.sh文件部分信息错误:
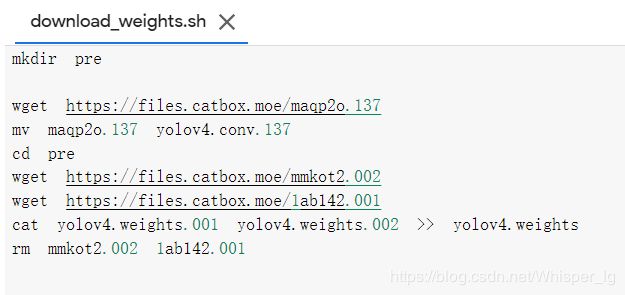
需将cat yolov4.weights.001 yolov4.weights.002 >> yolov4.weights改为cat 1ab142.001 mmkot2.002 >> yolov4.weights
修改后文件如下:

创建自己的模型配置
 其中最后一行运行语句中的数字为自己需要识别的类别个数。
其中最后一行运行语句中的数字为自己需要识别的类别个数。
对应的代码块语句如下:
%cd ..
%cd config
!bash create_custom_model.sh 5#数字修改为自己识别个数
解压上传的images和labels压缩文件
运行语句训练模型
%cd ..
#第一个参数为自己模型配置的路径,第二个参数为自己数据集文件路径
!python3 train.py --model_def config/yolov4-custom.cfg --data_config data/template.data --pretrained_weights weights/pre/yolov4.conv.137
仔细观察运行结果,我们发现并没有运行成功,所以项目作者的源代码存在一些错误。
错误1:
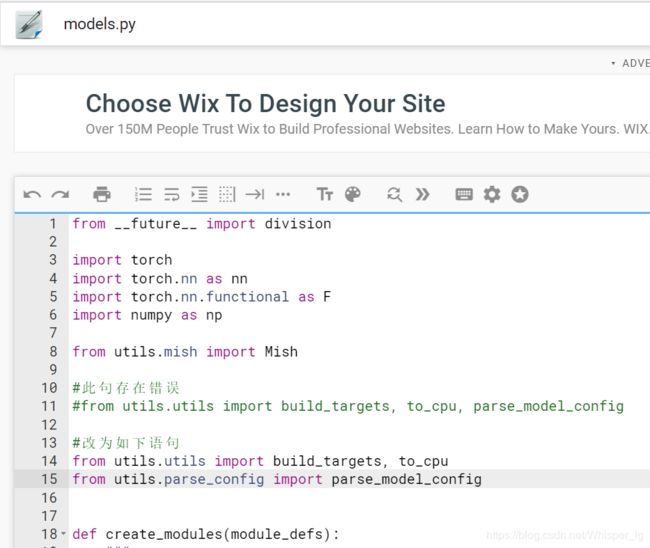
经分析我们得出导入parse_model_config模块时出错,原因是parse_model_config在utils.parse_model中,而不是utils.utils。
因此我们找到出错的model.py文件,对相应内容修改即可,如上图所示。
修改的代码块为:
#此句存在错误
#from utils.utils import build_targets, to_cpu, parse_model_config
#改为如下语句
from utils.utils import build_targets, to_cpu
from utils.parse_config import parse_model_config
错误2:
修改错误1之后我们继续运行!python3 train.py --model_def config/yolov4-custom.cfg --data_config data/template.data --pretrained_weights weights/pre/yolov4.conv.137
但是我们发现它又出现了错误2提示:
 根据提示,我们知道是路径出现了问题,多了一个"\"
根据提示,我们知道是路径出现了问题,多了一个"\"
最终我发现在train.py文件中出现了错误,于是我们对其进行如下修改:

修改的代码块如下:
#此句存在错误
#rootdir = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) + '\\'
#修改如下,将'\\'改为'/'
rootdir = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) + '/'
错误3:
修改完错误二后,再次运行`!python3 train.py --model_def config/yolov4-custom.cfg --data_config data/template.data --pretrained_weights weights/pre/yolov4.conv.137
我们又重新得到了一个错误3,错误提示如图所示:
 经分析发现是传入参数错误,我们应该将运行语句改为:
经分析发现是传入参数错误,我们应该将运行语句改为:
!python3 train.py --model_def config/yolov4-custom.cfg --data_config data/template.data --pretrained_weights weights/yolov4.conv.137
错误4:
当我们执行上述语句时,则出现了错误4:
RuntimeError: shape ‘[256]’ is invalid for input of size 0
了解到的初步原因是:预训练模型yolov4.conv.137要求的图片大小是自身图片数据大小不一致
我的解决方案是:直接用最初始的权重文件yolov4.weights训练
即执行下面代码块:
!python3 train.py --model_def config/yolov4-custom.cfg --data_config data/template.data --pretrained_weights weights/pre/yolov4.weights
错误5:
当运行完一个Epoch之后,新的问题又出现了。错误提示:

rootdir没有作为参数传入
于是我对如下地方进行了修改:
1.
 我在test.py中的23和28行传入参数rootdir
我在test.py中的23和28行传入参数rootdir
2.

我在train.py中164行处传入参数rootdir
错误6:
 这个错误原因为:
这个错误原因为:
1. 路径存在/./
2. images文件夹不存在test2014
分析可知是由于一开始准备数据时出错。
我的解决方式是:
- 修改之前准备数据集项目文件夹voc2007_for_yolo_torch-master中tools中的voc_label.py文件,如图所示:
 2. 将images文件夹中的val2014文件夹改为test2014文件夹,修改之后文件格式如下:
2. 将images文件夹中的val2014文件夹改为test2014文件夹,修改之后文件格式如下:

错误7:
接着我们又遇到这个错误:
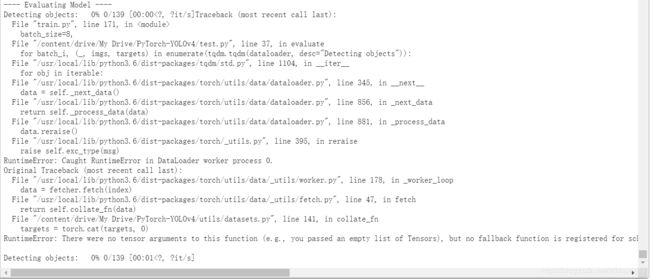 错误提示为:RuntimeError: There were no tensor arguments to this function (e.g., you passed an empty list of Tensors), but no fallback function is registered for schema aten::_cat. This usually means that this function requires a non-empty list of Tensors. Available functions are [CPUTensorId, CUDATensorId, QuantizedCPUTensorId, VariableTensorId]
错误提示为:RuntimeError: There were no tensor arguments to this function (e.g., you passed an empty list of Tensors), but no fallback function is registered for schema aten::_cat. This usually means that this function requires a non-empty list of Tensors. Available functions are [CPUTensorId, CUDATensorId, QuantizedCPUTensorId, VariableTensorId]
起初,我通过查阅资料得到:只要通过增加batch-size便可将问题解决
于是我将batch-size由默认的8改为16,12,10,9的时候都提示cuda is out of the memory;此外我还试验了4和6,但是提示的错误和起初8的错误是一样的。
后来我仔细读错误提示,发现是由于验证数据集时没有传入图片数据,判定为路径出错。于是我将lables文件夹中的val2014也改为了test2014,这样就确保了验证模型时有数据导入。
错误8:
继续运行代码,我发现已经检测完模型,正当我高兴的时候出现错误8:

错误提示:ap_table += [[c, class_names[c], “%.5f” % AP[i]]] IndexError: list index out of range
查阅资料发现是由于template.names文件输入待检测类别名称是最后一行未输入空格,在最后一行加入空格即可将问题解决。
输出训练好之后的模型
至此,所有在运行过程中的bug已经全部被排清,于是得到了训练完的模型文件,如图所示:
 模型输出在checkpoints文件夹中,大家训练完后可自行查看。
模型输出在checkpoints文件夹中,大家训练完后可自行查看。
一些细节
- 由于电脑网络,电量等原因不能长时间训练模型,所以可以修改将模型迭代训练,从而达到实时保存的目的。实例代码块如下:
!python3 train.py --model_def config/yolov4-custom.cfg --data_config data/template.data --pretrained_weights weights/pre/yolov4.weights --epoch 1 --checkpoint_interval 1
其中一些参数说明如下:
–model_def config:自己构建的模型配置
–data_config:数据集文件
–pretrained_weights:训练的模型权重
–epoch:训练的批次数(代数)
–checkpoint_interval:保存模型的间隔数
- 通过后来在colab上对准备自己的数据集复现(文档之前介绍的是在win10)的尝试,我发现其实在win10环境下实现会方便很多。因为准备数据集是一个繁琐的过程,很容易出现错误,所以需要对错误的数据集进行删除。colab移除后的数据集仍然存储在回收站中,因此需要在回收站对其进行进一步删除,但是如果数据量很多的时候,这是一个很痛苦的操作,但是在win10就只需要删除一次便可以全部删除。而且关键是如果没有对回收站内容进行删除时,你后来通过程序得到的数据集超出原本15G存储范围时,将会自动被删除。综上所述,如果不能确保数据集一次性正确的时候,还是在win10将自己数据集准备好在上传比较方便。
模型预测(检测)
模型训练好之后,便可以利用训练好的模型对我们需要预测的图片进行预测。
#预测数据集
!python3 detect.py --model_def config/yolov4-custom.cfg --weights_path checkpoints/yolov4_ckpt_51.pth --image_folder data/test --class_path data/template.names
其中的一些参数说明如下:
–weights_path:训练完毕的的模型权重文件
–image_folder:待预测的图片文件
–class_path:训练种类文件
以下是部分预测完成的结果:

 为了体现yolov3和yolov4的精度区别,附上之前yolov3的预测结果:
为了体现yolov3和yolov4的精度区别,附上之前yolov3的预测结果:


通过对比我们可以发现,在原图像均未进行处理之前,yolov4的精度的确是比yolov3精度高一些的!
图像处理
由于水下环境复杂,所以很多图片都存在许多如光照不足,生物保护色,图像模糊等问题。于是我们需要对图像进行处理。具体的处理过程,可以参考团队成员的另一篇博客:



