1. objc方法调用的过程大致分为两步:
- 从objc_msgSend()开始,查找方法过程,俗称发消息
- 如果方法找不到,则进入消息转发机制
2. objc_msgSend()方法
2.1 这个方法其实有5个变体
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| objc_msgSend | 一般方法 |
| objc_msgSend_stret | 返回结构体类型数据 |
| objc_msgSend_fpret | 返回float类型数据 |
| objc_msgSendSuper | 父类方法调用 |
| objc_msgSendSuper_stret | 父类方法调用,同时返回结构体类型数据 |
参考:Apple 官方文档
When it encounters a method call, the compiler generates a call to one of the functions objc_msgSend, objc_msgSend_stret, objc_msgSendSuper, or objc_msgSendSuper_stret. Messages sent to an object’s superclass (using the super keyword) are sent using objc_msgSendSuper; other messages are sent using objc_msgSend. Methods that have data structures as return values are sent using objc_msgSendSuper_stret and objc_msgSend_stret.
2.2 配置runtime 源码可运行环境
看了一些博客及官方文档,觉得还是看源码这样更清晰,源码面前无秘密
- runtime开源代码可运行demo
- 参考:该如何阅读 Objective-C runtime源码?
2.3 消息发送过程,涉及两个方法_class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3和lookUpImpOrForward
- 配置oc运行代码如下:
#import "Test.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
Test *test = [Test new];
[test say];
}
return 0;
}
-
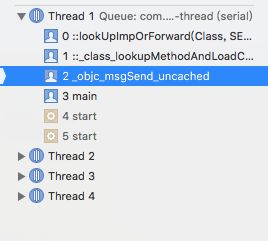
方法的调用堆栈截图如下:
可以看到
1>先走了_objc_msgSend_uncached方法,该方法是一个汇编方法,接下来调用了_class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3方法,指定不同的initialize,cache,resolver给lookUpImpOrForward方法,所以核心逻辑在lookUpImpOrForward方法里
(据我断点调试,当再次调用同一个方法时,不管是同一个对象或者新生成一个对象调用,都不会再执行上边过程,所以下述分析只针对方法第一次调用的情况)
IMP _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3(id obj, SEL sel, Class cls)
{
return lookUpImpOrForward(cls, sel, obj,
YES/*initialize*/, NO/*cache*/, YES/*resolver*/);
}
2>lookUpImpOrForward方法的作用就是查找和转发,由名字也可以看出;流程就是就是先找cache,找不到再从类对象、父类对象->元类->根元类中找,找到之后会cache;找到根元类还找不到,就开始消息转发流程
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
IMP imp = nil;
bool triedResolver = NO;
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
// Optimistic cache lookup
if (cache) { //判断是否已缓存,第一次不会走这里
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) return imp;
}
// runtimeLock is held during isRealized and isInitialized checking
// to prevent races against concurrent realization.
// runtimeLock is held during method search to make
// method-lookup + cache-fill atomic with respect to method addition.
// Otherwise, a category could be added but ignored indefinitely because
// the cache was re-filled with the old value after the cache flush on
// behalf of the category.
runtimeLock.read(); //使用了runtime读写锁
if (!cls->isRealized()) {
// Drop the read-lock and acquire the write-lock.
// realizeClass() checks isRealized() again to prevent
// a race while the lock is down.
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
runtimeLock.write();
realizeClass(cls); //if块中主要是该方法
runtimeLock.unlockWrite();
runtimeLock.read();
}
if (initialize && !cls->isInitialized()) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_initialize (_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst)); // 主要是该方法
runtimeLock.read();
// If sel == initialize, _class_initialize will send +initialize and
// then the messenger will send +initialize again after this
// procedure finishes. Of course, if this is not being called
// from the messenger then it won't happen. 2778172
}
retry:
runtimeLock.assertReading();
// Try this class's cache.
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel); //重新尝试cache,推测是因为加了锁的缘故,再次走到这里时,cache中可能已经有了,算是一个优化策略
if (imp) goto done;
// Try this class's method lists. //从类对象中获取找到method,找到之后缓存
{
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
// Try superclass caches and method lists. // 从父类中找,使用for循环不停向上遍历
{
unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();
for (Class curClass = cls->superclass;
curClass != nil;
curClass = curClass->superclass)
{
// Halt if there is a cycle in the superclass chain.
if (--attempts == 0) {
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
// Superclass cache.
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel); //跟上方逻辑基本一致,先找cache,再从类对象中找;
if (imp) {
if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
goto done;
}
else {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
}
// Superclass method list.
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
}
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
// 上边都找不到,就开始消息转发流程了
// 1.先进行消息解析,即runtime的两个resolve方法,解析成功的话,再走一遍查找流程
// 2.解析失败,再执行forward,forward又分两步
// 2.1 forwardingTargetForSelector交给其他对象去执行
// 2.2 forwardInvocation将@selector封装成一个NSInvocation对象,作为最后的执行机会
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
runtimeLock.read();
// Don't cache the result; we don't hold the lock so it may have
// changed already. Re-do the search from scratch instead.
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help.
// Use forwarding.
// 开始消息转发
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache; // 没有找到该方法的源码,要不然消息转发的调用过程我们也可以很清晰了
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
done:
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
return imp;
}
可以用伪代码帮助理解:
// 1. 判断是否要初始化对象
if(!cls->initialized()){
_class_initialize();
}
// 2. 开始查找
while(cls){
// 1. 查找缓存
imp = cache_getImp();
// 2. 缓存中没有,找方法列表
if(!imp){
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock();
if(Method){
return meth->imp;
}
cls = cls->superClass;
}
}
// 3. 方法没找到,先进行方法解析
Bool flag = _class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
// 4. 解析失败,转发消息
if(!flag){
_objc_msgForward_impcache();
}
3. 消息转发机制
由上述方法中可以看到_objc_msgForward_impcache这个IMP开启了消息转发过程,不过该IMP没有实现源码,怎么确定接下来过程呢?
有两个方案:
- 用instrumentObjcMessageSends(YES)来打印所有消息到文件中,参考:runtime 拾遗,我测试发现出现崩溃,输出的"/private/tmp/msgSends-进程id"文件是空的,与runtime锁机制有关,暂不知道解决办法,崩溃日志如下;
objc[4492]: lock 0x1008c53c0 (runtimeLock) acquired before 0x1008c5340 (objcMsgLogLock) with no defined lock order
- 重写自定义类的resolveClassMethod、forwardingTargetForSelector等方法,然后分别加断点,可以通过调用堆栈来确定流程
此处我采用第二种方式,得到的结果与第一种方式应该是一样的,重写的代码如下:
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel{
return NO;
}
-(id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
if([NSStringFromSelector(aSelector) isEqualToString:@"say"]){
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v@:"];
}else{
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation{ //该方法默认不执行,需要重写methodSignatureForSelector返回指定的方法签名才会进
[super forwardInvocation:anInvocation];
}
-
经过我断点调试,上边方法调用顺序如下:
resolveInstanceMethod->
forwardingTargetForSelector->
methodSignatureForSelector->
resolveInstanceMethod-> //此处会多一次方法解析,与lookUpImpOrForward里的逻辑有关
forwardInvocation->
崩溃
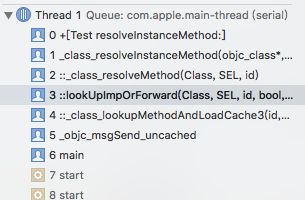
也就是注明的这张图
-
附一个resolveInstanceMethod方法第一次调用堆栈:
3. 消息转发一些理解:
- doesNotRecognizeSelector:会在控制台出现是因为当前类没有实现该方法,而基类NSObject forwardInvocation:方法实现中抛出了doesNotRecognizeSelector:异常,可以通过runtime的源码证明
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)invocation {
[self doesNotRecognizeSelector:(invocation ? [invocation selector] : 0)];
}
- (void)doesNotRecognizeSelector:(SEL)sel {
_objc_fatal("-[%s %s]: unrecognized selector sent to instance %p",
object_getClassName(self), sel_getName(sel), self);
}
- 防止unrecognized selector崩溃,可以有3种方式:
- 在resolveInstanceMethod方法中add一个方法实现
- 在forwardingTargetForSelector方法中转给其他对象实现
- 在forwardInvocation中转给其他对象实现
- 还可以重写doesNotRecognizeSelector来实现,原理是:参考上边一条注释,最终调用的当前类的doesNotRecognizeSelector实现,在该实现中不抛出异常就可以了,比如这样
- (void)doesNotRecognizeSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
NSString *selStr = NSStringFromSelector(aSelector);
NSLog(@"%@不存在",selStr);
}
参考这篇文章:iOS 消息转发机制Demo解析
- 利用消息转发可以实现类似多继承的效果,因为可以将消息转发给其他对象,就像是其他对象成了当前对象的基类一样。
参考:从源代码看 ObjC 中消息的发送