无向图的连通分量和生成树
以下内容主要参考于严蔚敏版的数据结构教材。
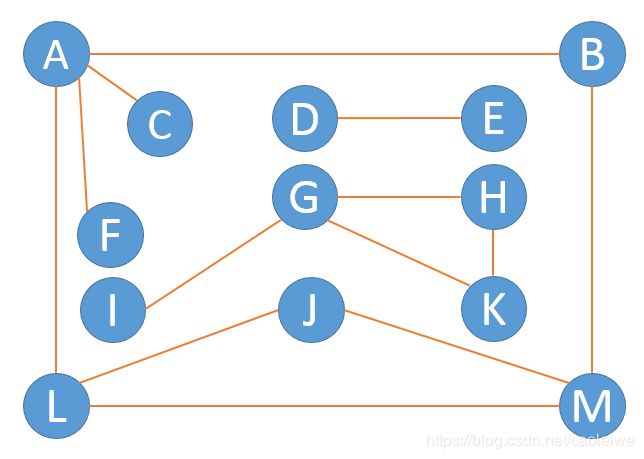
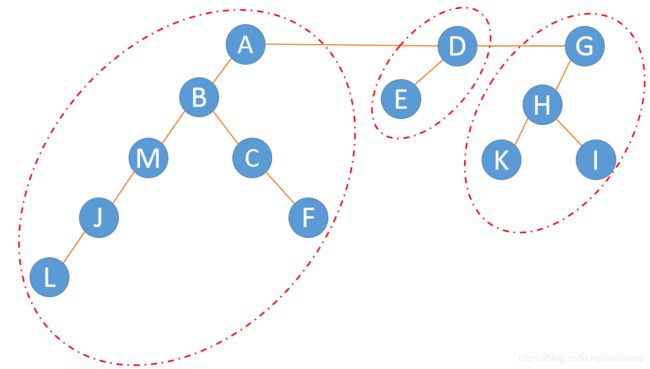
以下算法生成无向图的深度优先生成森林,图采用邻接表数据结构,生成森林才有左孩子右兄弟的存储结构。无向图的深度优先生成树或森林其实就是从图中某一个顶点V的深度优先遍历过程。将当前节点第一个邻接点作为其左孩子元素,第一个兄弟作为其右兄弟元素(如果当前节点为节点V且图不是连通图,则节点V的右兄弟元素为第二颗生成树的根节点,第二颗生成树的右兄弟元素为第三颗生成树的根节点,以此类推)。图1的非连通图的孩子兄弟节点结构的生成森林如图2所示。无向图的广度优先生成树与生成森林与此类似。
//图的邻接表表示
//弧节点
class GraphArcNode
{
private:
int weight;
int adjVertexIndex;
GraphArcNode* nextArcNode;
public:
GraphArcNode(int d = 0, int index = 0)
{
weight = d;
adjVertexIndex = index;
nextArcNode = nullptr;
}
void setNextArcNode(GraphArcNode* next)
{
nextArcNode = next;
}
int getWeight()
{
return weight;
}
int getAdjVertexIndex()
{
return adjVertexIndex;
}
GraphArcNode* getNextArcNode()
{
return nextArcNode;
}
};
//图节点
class GraphNode
{
private:
int data;
GraphArcNode* nextArcNode;
public:
GraphNode(int d = 0)
{
data = d;
nextArcNode = nullptr;
}
void setNextArcNode(GraphArcNode* next)
{
nextArcNode = next;
}
int getData()
{
return data;
}
GraphArcNode* getNextArcNode()
{
return nextArcNode;
}
};
//图的数据结构
class ALGraph
{
private:
vector<GraphNode> graphNodeSet;
int nodeNum;
public:
ALGraph(int num)
{
nodeNum = num;
}
void addGraphNode(int data)
{
graphNodeSet.push_back(GraphNode(data));
}
int getGraphNodeNum()
{
return nodeNum;
}
vector<GraphNode> getGraphNodeSet()
{
return graphNodeSet;
}
void setGraphNodeArc(int graphNodeIndex, int weight, int adjVertexIndex)
{
if (graphNodeSet[graphNodeIndex].getNextArcNode() == nullptr)
{
graphNodeSet[graphNodeIndex].setNextArcNode(new GraphArcNode(weight, adjVertexIndex));
}
else
{
GraphArcNode* currentArcNode = graphNodeSet[graphNodeIndex].getNextArcNode();
GraphArcNode* nextArcNode = graphNodeSet[graphNodeIndex].getNextArcNode()->getNextArcNode();
while (nextArcNode != nullptr)
{
currentArcNode = nextArcNode;
nextArcNode = nextArcNode->getNextArcNode();
}
currentArcNode->setNextArcNode(new GraphArcNode(weight, adjVertexIndex));
}
}
};
class CSNode
{
private:
int data;
CSNode* leftChild;
CSNode* rightBrother;
public:
CSNode(int d=0,CSNode* left = nullptr, CSNode* right=nullptr)
{
data = d;
leftChild = nullptr;
rightBrother = nullptr;
}
void setData(int value)
{
data = value;
}
void setLeft(CSNode* value)
{
leftChild = value;
}
void setRight(CSNode* value)
{
rightBrother = value;
}
int getData()
{
return data;
}
CSNode* getLeft()
{
return leftChild;
}
CSNode* getRight()
{
return rightBrother;
}
};
int findNextAdjNodeIndex(ALGraph g, int currentNodeIndex, vector<bool>& visited)
{
if (currentNodeIndex >= 0)
{
GraphArcNode* currentArcNode = g.getGraphNodeSet()[currentNodeIndex].getNextArcNode();
while ((currentArcNode != nullptr) && (visited[currentArcNode->getAdjVertexIndex()]))
{
currentArcNode = currentArcNode->getNextArcNode();
}
if (currentArcNode != nullptr)
{
return currentArcNode->getAdjVertexIndex();
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
return -1;
}
void DFSTree(ALGraph g, int nodeIndex,CSNode*& root, vector<bool> &visited)
{
visited[nodeIndex] = true;
cout << "nodeIndex=" << nodeIndex << endl;
bool firstAdjVex = true;
CSNode* before = nullptr;
for (int adjVexIndex=findNextAdjNodeIndex(g, nodeIndex, visited);adjVexIndex>=0; adjVexIndex= findNextAdjNodeIndex(g, nodeIndex, visited))
{
if (!visited[adjVexIndex])
{
CSNode* p = new CSNode(g.getGraphNodeSet()[adjVexIndex].getData(), nullptr, nullptr);
if (firstAdjVex)
{
root->setLeft(p);
firstAdjVex = false;
}
else
{
cout << "right data=" << p->getData() << endl;
before->setRight(p);
}
before = p;
DFSTree(g, adjVexIndex, before, visited);
}
}
}
void DFSForest(ALGraph g, CSNode* &root)
{
vector<bool> visited(g.getGraphNodeNum(), false);
CSNode* before = nullptr;
for (int nodeIndex = 0; nodeIndex < g.getGraphNodeNum(); nodeIndex++)
{
if (!visited[nodeIndex])
{
cout << "//// Tree start ////"<< endl;
CSNode *p= new CSNode(g.getGraphNodeSet()[nodeIndex].getData(),nullptr,nullptr);
if (root == nullptr)
root = p;
else
before->setRight(p);
before = p;
DFSTree(g, nodeIndex, p, visited);
}
}
}
void printForest(CSNode* root)
{
if (root != nullptr)
{
cout << "visiting node " << root->getData() << endl;
printForest(root->getLeft());
printForest(root->getRight());
}
}
#define A 0
#define B 1
#define C 2
#define D 3
#define E 4
#define F 5
#define G 6
#define H 7
#define I 8
#define J 9
#define K 10
#define L 11
#define M 12
//测试程序
int main()
{
ALGraph g(13);
for (int nodeDataIndex = 0; nodeDataIndex < 13; nodeDataIndex++)
{
g.addGraphNode(nodeDataIndex);
}
g.setGraphNodeArc(A, 0, B);
g.setGraphNodeArc(A, 0, C);
g.setGraphNodeArc(A, 0, F);
g.setGraphNodeArc(A, 0, L);
g.setGraphNodeArc(B, 0, A);
g.setGraphNodeArc(B, 0, M);
g.setGraphNodeArc(C, 0, A);
g.setGraphNodeArc(D, 0, E);
g.setGraphNodeArc(E, 0, D);
g.setGraphNodeArc(F, 0, A);
g.setGraphNodeArc(G, 0, H);
g.setGraphNodeArc(G, 0, I);
g.setGraphNodeArc(G, 0, K);
g.setGraphNodeArc(H, 0, G);
g.setGraphNodeArc(H, 0, K);
g.setGraphNodeArc(I, 0, G);
g.setGraphNodeArc(J, 0, L);
g.setGraphNodeArc(J, 0, M);
g.setGraphNodeArc(K, 0, G);
g.setGraphNodeArc(K, 0, H);
g.setGraphNodeArc(L, 0, A);
g.setGraphNodeArc(L, 0, J);
g.setGraphNodeArc(L, 0, M);
g.setGraphNodeArc(M, 0, B);
g.setGraphNodeArc(M, 0, J);
g.setGraphNodeArc(M, 0, L);
CSNode* root = nullptr;
DFSForest(g, root);
printForest(root);
}
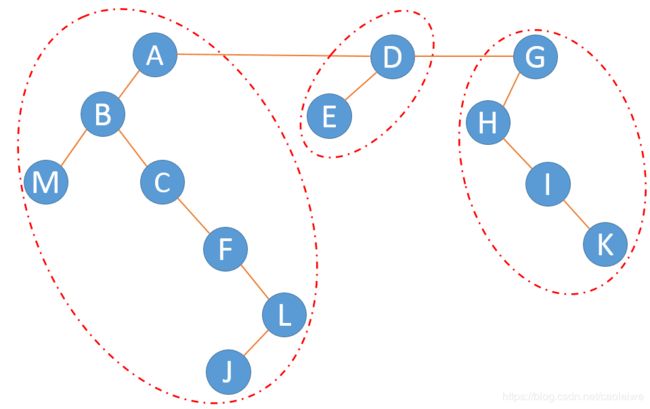
图1的广度优先生成树如图3所示。
void findBeforeNode(CSNode* root,int nodeData, CSNode* &beforeNode)
{
CSNode* left = root->getLeft();
CSNode* right = root->getRight();
if ((root!=nullptr)&&(root->getData() == nodeData))
{
beforeNode= root;
}
if (left != nullptr)
{
findBeforeNode(left, nodeData, beforeNode);
}
if (right != nullptr)
{
findBeforeNode(right, nodeData, beforeNode);
}
}
void BFSForest(ALGraph g,CSNode*& root)
{
vector<bool> visited(g.getGraphNodeNum(), false);
queue<int> adjNode;
CSNode* beforeTree = nullptr;
int queueHead = 0;
int nextAdjNodeIndex = 0;
bool firstAdjNode = false;
CSNode* beforeNode = nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < g.getGraphNodeNum(); i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
cout << "//// Tree start ////" << endl;
CSNode* p1 = new CSNode(g.getGraphNodeSet()[i].getData(), nullptr, nullptr);
cout << "root=" << p1 ->getData()<<endl;
if (root == nullptr)
root = p1;
else
beforeTree->setRight(p1);
beforeTree = p1;
visited[i] = true;
adjNode.push(i);
printForest(root);
while (!adjNode.empty())
{
queueHead = adjNode.front();
cout<<"queueHead = "<<queueHead<<endl;
adjNode.pop();
findBeforeNode(root, queueHead, beforeNode);
cout << "beforeNode->getData=" << beforeNode->getData() << endl;
firstAdjNode = true;
//依次访问以前访问过的一个节点的所有邻接点
for (GraphArcNode* nextAdjNode = g.getGraphNodeSet()[queueHead].getNextArcNode(); nextAdjNode != nullptr; nextAdjNode = nextAdjNode->getNextArcNode())
{
nextAdjNodeIndex = nextAdjNode->getAdjVertexIndex();
if (!visited[nextAdjNodeIndex])
{
visited[nextAdjNodeIndex] = true;
CSNode* p2 = new CSNode(g.getGraphNodeSet()[nextAdjNodeIndex].getData(), nullptr, nullptr);
cout << "Adj data=" << g.getGraphNodeSet()[nextAdjNodeIndex].getData() << endl;
if (firstAdjNode)
{
cout << "beforeNode->setLeft(p2);" << endl;
beforeNode->setLeft(p2);
firstAdjNode = false;
}
else
{
beforeNode->setRight(p2);
cout << "beforeNode->setRight(p2);" << endl;
}
beforeNode = p2;
adjNode.push(nextAdjNodeIndex);
}
}
}
}
}
return;
}