牛客网-剑指offer编程题解答。
牛客网-剑指offer编程题解答?
- 前言?
- 1. 二维数组中的查找
- 2. 构建乘积数组
- 3. 数组中重复的数字
- 4. 替换空格
- 5. 从尾到头打印链表
- 6. 重建二叉树
- 7. 用两个栈实现队列
- 8. 旋转数组的最小数字
- 9. 斐波那契数列
- 10. 跳台阶
- 11. 变态跳台阶
- 12.矩形覆盖
- 13. 二进制中1的个数
- 14. 数值的整数次方
- 15. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
- 16. 链表中倒数第K个节点
- 17. 反转链表
- 18. 合并两个排序的链表
前言?
牛客网-剑指offer大部分题目的解答,环境为牛客网的在线环境。不会详细解答思路,会在代码中尽量解释主要代码含义。以下按考点划分。
1. 二维数组中的查找
题目描述
在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
public class Solution {
public boolean Find(int target, int[][] array) {
// 判断数组是否为null、[]、[[]]
if ((array == null || array.length == 0) || (array.length == 1 && array[0].length == 0))
return false;
int col = array.length - 1;
int row = 0;
// 数组从array最左下角开始,值比target大就往上走,值比target小就往右走
while (col >= 0 && row < array[0].length) {
if (array[col][row] > target)
col--;
else if (array[col][row] < target)
row++;
else
return true;
}
// 没找到即返回false
return false;
}
}
2. 构建乘积数组
题目描述
给定一个数组A[0,1,…,n-1],请构建一个数组B[0,1,…,n-1],其中B中的元素B[i]=A[0]A[1]…*A[i-1]A[i+1]…*A[n-1]。不能使用除法。
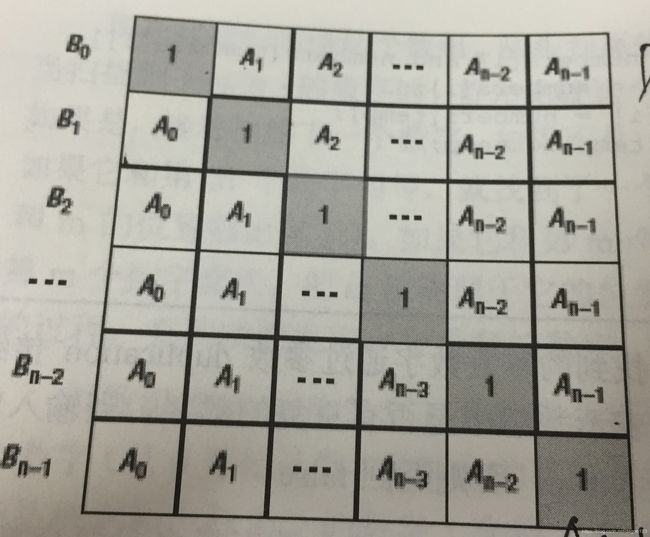
如图所示,所以可以拆成两部分,第一部分计算A[0]A[1]…A[i-1],第二部分计算A[i+1]…*A[n-1];
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public int[] multiply(int[] A) {
if (A.length == 0) {
return A;
}
int[] B = new int[A.length];
B[0] = 1;
// 第一部分,计算A[0]*A[1]*...*A[i-1]
for (int i = 1; i < A.length; i++)
B[i] = B[i - 1] * A[i - 1];
int tmp = 1;
// 第二部分,计算A[i+1]*...*A[n-1]
for (int i = A.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
tmp *= A[i + 1];
B[i] *= tmp;
}
return B;
}
}
3. 数组中重复的数字
题目描述
在一个长度为n的数组里的所有数字都在0到n-1的范围内。 数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字是重复的。也不知道每个数字重复几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。 例如,如果输入长度为7的数组{2,3,1,0,2,5,3},那么对应的输出是第一个重复的数字2。
解法一:通常解法,利用hashset(其实也可以用hashmap)
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Solution {
// Parameters:
// numbers: an array of integers
// length: the length of array numbers
// duplication: (Output) the duplicated number in the array number,length of
// duplication array is 1,so using duplication[0] = ? in implementation;
// Here duplication like pointor in C/C++, duplication[0] equal *duplication in
// C/C++
// 这里要特别注意~返回任意重复的一个,赋值duplication[0]
// Return value: true if the input is valid, and there are some duplications in
// the array number
// otherwise false
// 方法1
public boolean duplicate(int numbers[], int length, int[] duplication) {
if (length < 2 || numbers == null)
return false;
HashSet<Integer> result = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
if (!result.add(numbers[i])) {
duplication[0] = numbers[i];
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
解法二:不需要利用额外空间,题目里写了数组里数字的范围保证在0~n-1之间,所以可以利用现有数组设置标志,当一个数字被访问过后,可以设置对应位上的数+ n,之后再遇到相同的数时,会发现对应位上的数已经大于等于n了,那么直接返回这个数即可。
public class Solution {
public boolean duplicate2(int numbers[], int length, int[] duplication) {
if (length < 2 || numbers == null)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
// 取得numbers[i]的值
int index = numbers[i];
// 如果大于length,则需要减去length获得numbers[i]的值
if (index >= length)
index -= length;
// 若已经大于length,说明已经有过访问
if (numbers[index] >= length) {
duplication[0] = index;
return true;
}
// numbers[i]对应位置上的数字+length
numbers[index] = numbers[index] + length;
}
return false;
}
}
举个例子,数组{1,2,3,2,3}
当i=0时,index=numbers[i]=1, 小于length,index=1
numbers[index]=2 小于length,说明第一次访问
此时标记访问记录,numbers[index]=2+length; 即numbers[1]=2+length;
当i=1时,index=numbers[i]=2+length,大于ength,需要取得真实值,减去length,index=2
numbers[index]=3 小于length,说明第一次访问
此时标记访问记录,numbers[index]=3+length; 即numbers[2]=3+length;
当i=2时,index=numers[i]=3+length,大于length,需要取得真实值,减去length,index=3
numbers[index]=2 小于length,说明第一次访问
此时标记访问记录,numbers[index]=2+length;即numbers[3]=2+length;
当i=3时,index=numbers[i]=2+length,大于length,需要取得真实值,减去length,index=2
numbers[index]=3+length 大于length,说明第二次访问
此时返回index的值
4. 替换空格
题目描述
请实现一个函数,将一个字符串中的每个空格替换成“%20”。例如,当字符串为We Are Happy.则经过替换之后的字符串为We%20Are%20Happy。
public class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) {
String str1 = str.toString();
char[] str2 = str1.toCharArray();
StringBuilder str3 = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < str2.length; i++) {
if (str2[i] == ' ') {
str3.append("%20");
} else {
str3.append(str2[i]);
}
}
return str3.toString();
}
}
5. 从尾到头打印链表
题目描述
输入一个链表,按链表值从尾到头的顺序返回一个ArrayList。
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// 利用栈先进后出的思想
while (listNode != null) {
stack.push(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
result.add(stack.pop());
}
return result;
}
}
6. 重建二叉树
题目描述
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回。
采用递归的思想,根据前序遍历和中序遍历,先构建根节点,再构建根节点的左右子树。然后将左右子树分别看成独立的一棵树,再构建根节点与左右子树,如此下去。
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int[] pre, int[] in) {
TreeNode root = reConstructBinaryTree(pre, 0, pre.length - 1, in, 0, in.length - 1);
return root;
}
private TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int[] pre, int sPre, int ePre, int[] in, int sIn, int eIn) {
if (sPre > ePre || sIn > eIn)
return null;
// 此部分的根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[sPre]);
for (int i = sIn; i <= eIn; i++) {
// 根据中序遍历获取左右子树
if (in[i] == pre[sPre]) {
// i-sIn为左右子树的节点个数
root.left = reConstructBinaryTree(pre, sPre + 1, sPre + i - sIn, in, sIn, i - 1);
root.right = reConstructBinaryTree(pre, sPre + i - sIn + 1, ePre, in, i + 1, eIn);
}
}
return root;
}
}
7. 用两个栈实现队列
题目描述
用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作。 队列中的元素为int类型。
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
// 如果stack2为空,则需从stack1中读取
public int pop() {
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
8. 旋转数组的最小数字
题目描述
把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。 输入一个非减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。 例如数组{3,4,5,1,2}为{1,2,3,4,5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。 NOTE:给出的所有元素都大于0,若数组大小为0,请返回0。
最简单的方法,因为是非减排序数组,直接遍历。
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
// 直接遍历法
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int[] array) {
if (array.length == 0)
return 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
if (array[i] > array[i + 1])
return array[i + 1];
}
return array[0];
}
}
稍微优化一下,采用二分查找法
需要考虑三种情况:
(1)array[mid] > array[high]:
出现这种情况的array类似[3,4,5,6,0,1,2],此时最小数字一定在mid的右边。
low = mid + 1
(2)array[mid] == array[high]:
出现这种情况的array类似 [1,0,1,1,1] 或者[1,1,1,0,1],此时最小数字不好判断在mid左边
还是右边,这时只好一个一个试 ,
high = high - 1
(3)array[mid] < array[high]:
出现这种情况的array类似[2,2,3,4,5,6,6],此时最小数字一定就是array[mid]或者在mid的左
边。因为右边必然都是递增的。
high = mid
注意这里有个坑:如果待查询的范围最后只剩两个数,那么mid 一定会指向下标靠前的数字
比如 array = [1,0,1]
array[low] = 1 ;array[mid] =0 ; array[high] = 1 ;
如果high = mid - 1,就会产生错误,return array[low] 此时的low=0;
但情形(1)中low = mid + 1就不会错误
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
// 二分查找法
public int minNumberInRotateArray2(int[] array) {
if (array.length == 0)
return 0;
int low = 0;
int high = array.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;// 防止溢出
if (array[mid] > array[high]) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (array[mid] == array[high]) {
high = high - 1;
} else {
high = mid;
}
}
return array[low];
}
}
9. 斐波那契数列
题目描述
大家都知道斐波那契数列,现在要求输入一个整数n,请你输出斐波那契数列的第n项(从0开始,第0项为0)。
n<=39
递归
public class Solution {
// 递归
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
return 1;
else
return Fibonacci(n - 1) + Fibonacci(n - 2);
}
}
非递归,打表的方式
public class Solution {
// 非递归 打表
public int Fibonacci2(int n) {
int[] result = new int[40];
result[1] = 1;
result[2] = 1;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
result[i] = result[i - 2] + result[i - 1];
return result[n];
}
}
10. 跳台阶
题目描述
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法(先后次序不同算不同的结果)。
这种题目是斐波那契数列的变形题目。跳第n层台阶可以看作 第n-1层台阶的方法次数(最后一步条1层台阶)+第n-2层台阶的方法次数(最后一步跳2层台阶)
递归
public class Solution {
// 递归
public int JumpFloor(int target) {
if (target < 3)
return target;
else
return JumpFloor(target - 1) + JumpFloor(target - 2);
}
}
非递归,打表的方式
public class Solution {
// 非递归
public int JumpFloor2(int target) {
if (target < 3)
return target;
int[] result = new int[target + 1];
result[1] = 1;
result[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= target; i++) {
result[i] = result[i - 1] + result[i - 2];
}
return result[target];
}
}
11. 变态跳台阶
题目描述
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级……它也可以跳上n级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
这种题目是斐波那契数列的变形题目。跳第n层台阶可以看作 = 第n-1层台阶的方法次数 + 第n-2层台阶的方法次数……第1层台阶的方法次数 + 一步跳到第n层台阶。
递归
public class Solution {
// 递归
public int JumpFloor(int target) {
if (target < 3)
return target;
else {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < target; i++) {
result += JumpFloorII(i);
}
return result + 1;
}
}
}
非递归
public class Solution {
// 非递归
public int JumpFloor2(int target) {
if (target < 3)
return target;
int[] result = new int[target + 1];
result[1] = 1;
result[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= target; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
result[i] += result[j];
}
result[i] += 1;
}
return result[target];
}
}
12.矩形覆盖
题目描述
我们可以用21的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。请问用n个21的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2*n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
依旧是斐波那契数列
2n的大矩形,和n个21的小矩形
其中target*2为大矩阵的大小
有以下几种情形:
1、target = 0 大矩形为<= 2 * 0,直接return 0;
2、target = 1大矩形为2 * 1,只有一种摆放方法,return 1;
3、target = 2 大矩形为2 * 2,有两种摆放方法,return 2;
4、target = n 分为两步考虑:
第一次摆放一块 2 * 1 的小矩阵,则摆放方法总共为f(target - 1)
| ✔ | |||||||
| ✔ |
第一次摆放一块 1 * 2 的小矩阵,则摆放方法总共为f(target - 2)
因为,摆放了一块12的小矩阵(用✔ ✔ 表示),对应下方的12(用 ✖ ✖表示)摆放方法就确定了,所以为f(targte-2)
| ✔ | ✔ | ||||||
| ✖ | ✖ |
递归
public class Solution {
// 递归
public int RectCover(int target) {
if (target < 3)
return target;
else
return RectCover(target - 2) + RectCover(target - 1);
}
}
非递归,打表的方式
public class Solution {
// 非递归
public int RectCover2(int target) {
if (target < 3)
return target;
int[] result = new int[target + 1];
result[1] = 1;
result[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= target; i++) {
result[i] = result[i - 1] + result[i - 2];
}
return result[target];
}
}
13. 二进制中1的个数
题目描述
输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。其中负数用补码表示。
思想:用1(1自身左移运算,其实后来就不是1了)和n的每位进行位与,来判断1的个数
public class Solution {
// 思想:用1(1自身左移运算,其实后来就不是1了)和n的每位进行位与,来判断1的个数
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int result = 0;
int index = 1;
while (index != 0) {
if ((n & index) != 0) {
result++;
}
index = index << 1;
}
return result;
}
}
最优解:
public class Solution {
// 最优解
public int NumberOf12(int n) {
int count = 0;
while (n != 0) {
count++;
n = (n - 1) & n;
}
return count;
}
}
分析:如果一个整数不为0,那么这个整数至少有一位是1。如果我们把这个整数减1,那么原来处在整数最右边的1就会变为0,原来在1后面的所有的0都会变成1(如果最右边的1后面还有0的话)。其余所有位将不会受到影响。
举个例子:一个二进制数1100,从右边数起第三位是处于最右边的一个1。减去1后,第三位变成0,它后面的两位0变成了1,而前面的1保持不变,因此得到的结果是1011.我们发现减1的结果是把最右边的一个1开始的所有位都取反了。这个时候如果我们再把原来的整数和减去1之后的结果做与运算,从原来整数最右边一个1那一位开始所有位都会变成0。如1100&1011=1000.也就是说,把一个整数减去1,再和原整数做与运算,会把该整数最右边一个1变成0.那么一个整数的二进制有多少个1,就可以进行多少次这样的操作。
14. 数值的整数次方
题目描述
给定一个double类型的浮点数base和int类型的整数exponent。求base的exponent次方。
分三种情况:
1、指数 > 0
2、指数 = 0
3、指数 < 0 (第一种情况的倒数)
public class Solution {
public double Power(double base, int exponent) {
double result = 1.0;
if (exponent > 0) {
for (int i = 1; i <= exponent; ++i) {
result *= base;
}
} else if (exponent == 0) {
return result;
} else {
if (base == 0)
throw new RuntimeException("分母不能为零");
for (int i = 1; i <= -exponent; ++i) {
result *= base;
}
result = 1 / result;
}
return result;
}
}
15. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
题目描述
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
找到奇数时,将奇数放到最前面的偶数位置,并且将所有偶数后移。
public class Solution {
public void reOrderArray(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] % 2 != 0) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (array[j] % 2 == 0) {
array[i] ^= array[j];
array[j] ^= array[i];
array[i] ^= array[j];
}
}
}
}
}
}
16. 链表中倒数第K个节点
题目描述
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
当p抵达链表末端(即null时),p与q之间的节点数为k-1个,所以q当前的节点即为倒数第k个节点。
如果p抵达链表末端时,计数器还小于k,说明k大于链表长度,返回null。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode p, q;
p = q = head;
int i = 0;
for (; p != null; i++) {
if (i >= k)
q = q.next;
p = p.next;
}
return i < k ? null : q;
}
}
17. 反转链表
题目描述
输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
"->“表示next,”-"表示当前值
1、 1->2->3->4->5
pre-null cur-1 tmp-2
2、 2->3->4->5 1->null
pre-null cur-1 tmp-2
3、 2->3->4->5 1->null
pre-1 cur-2 tmp-3
4、 3->4->5 2->1->null
pre-2 cur-2 tmp-3
5、 3->4->5 2->1->null
pre-2 cur-3 tmp-4
……
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur, pre;
cur = head;
pre = null;
while (cur.next != null) {
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
cur.next = pre;
return cur;
}
}
18. 合并两个排序的链表
题目描述
输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null) {
return list2;
} else if (list2 == null) {
return list1;
}
ListNode mergeNode = null;
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
mergeNode = list1;
mergeNode.next = Merge(list1.next, list2);
} else {
mergeNode = list2;
mergeNode.next = Merge(list1, list2.next);
}
return mergeNode;
}
}