Android-自定义相机Camera
博主声明:
转载请在开头附加本文链接及作者信息,并标记为转载。本文由博主 小口锅 原创,请多支持与指教。
本文首发于此 博主:小口锅 | 博客主页:https://blog.csdn.net/gb702250823
前言
由于最近一个项目需要自定义相机这块,踩了很多坑,在这里做个记录,以防忘记。
Android Camera 相关API可以说是Android 生态碎片化最严重的一块
目前有两套Camera Api 以android 5.0为分界线,5.0以下的是Camera ,5.0以上的是Camera2,然而Camera2 各个产商支持的各不相同,这就导致我们在相机开发中要花很大的精力去处理兼容性问题。
相机开发的流程
自定义相机开发流程大概可以分为5步
- 1、检测并访问相机资源,检查手机是否存在相机资源,如果存在则请求访问相机资源。
- 2、创建预览界面,将预览画面与设计好的用户界面控件融合在一起,实时显示相机的预览图像。
- 3、设置拍照监听,给用户界面控件绑定监听器,使其能响应用户操作, 开始拍照过程。
- 4、拍照并保存文件,将拍摄获得的图像转换成位图文件,最终输出保存成各种常用格式的图片。
- 5、释放相机资源,相机是一个共享资源,当相机使用完毕后,必须正确地将其释放,以免其它程序访问使用时发生冲突。
Camera相关API了解
Camera Api中主要涉及以下几个关键类
- Camera:操作和管理相机资源,支持相机资源切换,设置预览和拍摄尺寸,设置光圈、曝光等相关参数。
- SurfaceView:用于绘制相机预览图像,提供实时预览的图像。
- SurfaceHolder:用于控制Surface的一个抽象接口,它可以控制Surface的尺寸、格式与像素等,并可以监视Surface的变化。
- SurfaceHolder.Callback:用于监听Surface状态变化的接口。
1、Camera
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| open(int cameraId) | 获取Camera实例 cameraId 的值有两个,一个是CameraInfo.CAMERA_FACING_BACK,CameraInfo.CAMERA_FACING_FRONT 前置摄像头和后置摄像头 |
| setPreviewDisplay | 绑定绘制预览图像的surface。 |
| setPrameters | 设置相机参数,包括前后摄像头,闪光灯模式、聚焦模式、预览和拍照尺寸等 |
| startPreview() | 开始预览,将camera底层硬件传来的预览帧数据显示在绑定的surface上 |
| stopPreview() | 停止预览,关闭camra底层的帧数据传递以及surface上的绘制。 |
| release() | 释放Camera实例 |
| takePicture(ShutterCallback shutter, PictureCallback raw,PictureCallback jpeg) | 这个是实现相机拍照的主要方法,包含了三个回调参数。shutter是快门按下时的回调,raw是获取拍照原始数据的回调,jpeg是获取经过压缩成jpg格式的图像数据的回调。 |
更多API 可以查看这篇博客
2、SurfaceHolder.Callback
| 接口 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) | 在surface第一次创建的时候调用。 |
| surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int width, int height) | 在surface的format或size等发生变化时调用。 |
| surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) | 在surface销毁的时候被调用。 |
Camera2相关API了解
- Android Camera2 官方视频
- Android Camera2 官方文档
- Android Camera2 官方用例
1、Camera2
- CameraManager:摄像头管理器,用于打开和关闭系统摄像头
- CameraCharacteristics:描述摄像头的各种特性,我们可以通过CameraManager的getCameraCharacteristics(@NonNull String cameraId)方法来获取。
- CameraDevice:描述系统摄像头,类似于早期的Camera。
- CameraCaptureSession:Session类,当需要拍照、预览等功能时,需要先创建该类的实例,然后通过该实例里的方法进行控制(例如:拍照 capture())。
- CaptureRequest:描述了一次操作请求,拍照、预览等操作都需要先传入
- CaptureRequest参数,具体的参数控制也是通过CameraRequest的成员变量来设置。
- CaptureResult:描述拍照完成后的结果
关于SurfaceView/TextureView
SurfaceView是一个有自己Surface的View。界面渲染可以放在单独线程而不是主线程中。它更像是一个Window,自身不能做变形和动画。
TextureView同样也有自己的Surface。但是它只能在拥有硬件加速层层的Window中绘制,它更像是一个普通View,可以做变形和动画。
更多关于SurfaceView与TextureView区别的内容可以参考这篇文章Android 5.0(Lollipop)中的SurfaceTexture,TextureView, SurfaceView和GLSurfaceView.
封装
API大概熟悉了,那么重点来了。那该如何封装呢?其实我们封装相机无非就是需要以下功能
- 打开相机
- 开启预览
- 拍照
- 开关闪关灯
- 聚焦
- 等等
- 关闭预览
- 关闭相机
那么如何封装呢,官方的开源库cameraview给出了方案

查看源码,大概的就是这几个类。
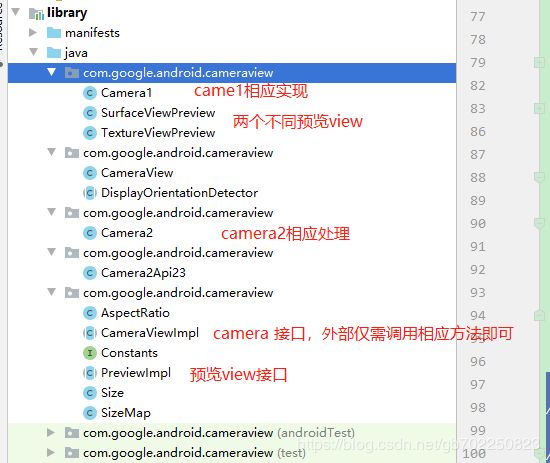
类不多,大致使用的设计模式是抽象工厂模式。这里也只是简单的拍照功能。
如果你不是重度的去定制相机的话,大概也只会用到预览界面,保存图片,以及闪光灯,聚焦这几个,这几个中最容易出现适配问题的就是预览界面失真以及保存图片的方向问题。保存图片方向的问题其实也可以在最后输出结果时进行转向,这样的话又要多一步操作,能够一步到位的事情,坚决不多一步。
那么接下来根据分析一下预览界面失真问题。
public class CameraView extends FrameLayout {
public CameraView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CameraView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
@SuppressWarnings("WrongConstant")
public CameraView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
....
依据不同版本实例化不同的camera
// Internal setup
final PreviewImpl preview = createPreviewImpl(context);
mCallbacks = new CallbackBridge();
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < 21) {
mImpl = new Camera1(mCallbacks, preview);
} else if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < 23) {
mImpl = new Camera2(mCallbacks, preview, context);
} else {
mImpl = new Camera2Api23(mCallbacks, preview, context);
}
.....
}
//获取相应的预览界面
@NonNull
private PreviewImpl createPreviewImpl(Context context) {
PreviewImpl preview;
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 23) {
preview = new SurfaceViewPreview(context, this);
} else {
preview = new TextureViewPreview(context, this);
}
return preview;
}
//根据设计稿设计的预览界面尺寸去获取相应的
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (isInEditMode()) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
return;
}
// Handle android:adjustViewBounds
//需要调整预览界面。这个设计和UI设计的预览会有点不同,可能过高或者过矮。如果底部按钮会相应的适配可采用此方式
if (mAdjustViewBounds) {
if (!isCameraOpened()) {
mCallbacks.reserveRequestLayoutOnOpen();
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
return;
}
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && heightMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
final AspectRatio ratio = getAspectRatio();
assert ratio != null;
int height = (int) (MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) * ratio.toFloat());
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
height = Math.min(height, MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec));
}
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec,
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
} else if (widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
final AspectRatio ratio = getAspectRatio();
assert ratio != null;
int width = (int) (MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec) * ratio.toFloat());
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
width = Math.min(width, MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec));
}
super.onMeasure(MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY),
heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
} else {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
// Measure the TextureView
int width = getMeasuredWidth();
int height = getMeasuredHeight();
//获取当前设置的比例,当前设置的比例也是通过预览尺寸计算出来的
AspectRatio ratio = getAspectRatio();
if (mDisplayOrientationDetector.getLastKnownDisplayOrientation() % 180 == 0) {
ratio = ratio.inverse();
}
assert ratio != null;
//根据当前的比例计算预览View相应的宽高。同比例放大或缩小。保证preview不会出现图形压扁或者拉伸的情况
if (height < width * ratio.getY() / ratio.getX()) {
mImpl.getView().measure(
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY),
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(width * ratio.getY() / ratio.getX(),
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
} else {
mImpl.getView().measure(
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height * ratio.getX() / ratio.getY(),
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY),
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
}
}
}
class Camera1 extends CameraViewImpl {
.....
void adjustCameraParameters() {
SortedSet<Size> sizes = mPreviewSizes.sizes(mAspectRatio);
if (sizes == null) { // Not supported
mAspectRatio = chooseAspectRatio();
sizes = mPreviewSizes.sizes(mAspectRatio);
}
Size size = chooseOptimalSize(sizes);
// Always re-apply camera parameters
// Largest picture size in this ratio
final Size pictureSize = mPictureSizes.sizes(mAspectRatio).last();
if (mShowingPreview) {
mCamera.stopPreview();
}
mCameraParameters.setPreviewSize(size.getWidth(), size.getHeight());
mCameraParameters.setPictureSize(pictureSize.getWidth(), pictureSize.getHeight());
mCameraParameters.setRotation(calcCameraRotation(mDisplayOrientation));
setAutoFocusInternal(mAutoFocus);
setFlashInternal(mFlash);
mCamera.setParameters(mCameraParameters);
if (mShowingPreview) {
mCamera.startPreview();
}
}
//获取最佳预览尺寸。
@SuppressWarnings("SuspiciousNameCombination")
private Size chooseOptimalSize(SortedSet<Size> sizes) {
//如果预览界面的尺寸是0,0 那么就随便取一个尺寸。
if (!mPreview.isReady()) { // Not yet laid out
return sizes.first(); // Return the smallest size
}
//等到View的绘制完成(onMeasure())后拿到预览界面的view宽高去获取相近的预览宽高。
int desiredWidth;
int desiredHeight;
final int surfaceWidth = mPreview.getWidth();
final int surfaceHeight = mPreview.getHeight();
if (isLandscape(mDisplayOrientation)) {
desiredWidth = surfaceHeight;
desiredHeight = surfaceWidth;
} else {
desiredWidth = surfaceWidth;
desiredHeight = surfaceHeight;
}
Size result = null;
for (Size size : sizes) { // Iterate from small to large
if (desiredWidth <= size.getWidth() && desiredHeight <= size.getHeight()) {
return size;
}
result = size;
}
return result;
}
.....
}
上面大概分析的是根据当前设置的比例去计算camera预览界面宽高,然后根据预览界面的宽高去获取相近的预览尺寸,这样可以保证预览时显示的图像不会出现失真。
网上比较多的方案是以下这个方法,这个方式其实是这个根据这个项目open camera进行修改的。是根据surfaceview的宽高比去获取相camera对应相近的预览尺寸,但是这个有一个缺点,就是如果 SurfaceView的宽高比和camera对应预览尺寸的宽高比不一致,有一点点的误差,就会出现一点点失真,而官方的开源库cameraview 宽高比是根据预览尺寸计算出来的,因此官方开源那种方式百分百不会出现失真,当然如果这个SurfaceView的宽高比和相机提供的预览尺寸中的宽高比一致的话,那么也不会失真。因此下面这个方式宽高要设置好。
/**
* 获取最佳预览大小
*
* @param sizes 所有支持的预览大小
* @param w SurfaceView宽
* @param h SurfaceView高
*/
private Camera.Size getOptimalPreviewSize(List<Camera.Size> sizes, int w, int h) {
final double ASPECT_TOLERANCE = 0.1;
double targetRatio = (double) w / h;
if (sizes == null)
return null;
Camera.Size optimalSize = null;
double minDiff = Double.MAX_VALUE;
int targetHeight = h;
// Try to find an size match aspect ratio and size
for (Camera.Size size : sizes) {
double ratio = (double) size.width / size.height;
if (Math.abs(ratio - targetRatio) > ASPECT_TOLERANCE)
continue;
if (Math.abs(size.height - targetHeight) < minDiff) {
optimalSize = size;
minDiff = Math.abs(size.height - targetHeight);
}
}
// Cannot find the one match the aspect ratio, ignore the requirement
if (optimalSize == null) {
minDiff = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for (Camera.Size size : sizes) {
if (Math.abs(size.height - targetHeight) < minDiff) {
optimalSize = size;
minDiff = Math.abs(size.height - targetHeight);
}
}
}
return optimalSize;
}
照片保存方向的问题相对简单一点,只需要给camera设置
setDisplayOrientation()就可以了。以下两种方式均可以。
这个是官方的开源库cameraview 提供的方式
private int calcDisplayOrientation(int screenOrientationDegrees) {
if (mCameraInfo.facing == Camera.CameraInfo.CAMERA_FACING_FRONT) {
return (360 - (mCameraInfo.orientation + screenOrientationDegrees) % 360) % 360;
} else { // back-facing
return (mCameraInfo.orientation - screenOrientationDegrees + 360) % 360;
}
}
这个是根据open camera进行相应修改后的方式。
/**
* 照片方向
*/
public static void onOrientationChanged(Activity activity, Camera.Parameters parameters, int cameraId) {
Camera.CameraInfo info = new Camera.CameraInfo();
Camera.getCameraInfo(cameraId, info);
int camera_orientation = info.orientation;
int result;
int device_orientation = getDeviceDefaultOrientation(activity);
if (device_orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT) {
// should be equivalent to onOrientationChanged(0)
result = camera_orientation;
} else {
// should be equivalent to onOrientationChanged(90)
if ((info.facing == Camera.CameraInfo.CAMERA_FACING_FRONT)) {
result = (camera_orientation + 270) % 360;
} else {
result = (camera_orientation + 90) % 360;
}
}
parameters.setRotation(result);
}
关于Camera2 这个由于项目时间问题,目前没有采用Camera2 相应的API,官方开源库这块也是有点小问题的,在修改对应的预览比例也会出现失真,除了4:3的情况,因此本文没有去分析camera2相应的源码。如果想要使用Camera2新特性的功能,那么建议可以去研究一下Jetpack 新出的CameraX
具体内容请查看官方文档 和 代码示例。