Python:SIFT特征提取与检索 - 计算机视觉
文章目录
- 一、SIFT原理
- 关键点(特征点)
- 尺度空间(scale space )
- 二、算法步骤
- 三、SIFT的缺点
- 四、代码
- 4.1. 特征点展示
- 4.2. 特征点匹配
- 4.3. 特征点检索算法
- 4.4. 地理标记图像匹配
- 五、分析与总结
一、SIFT原理
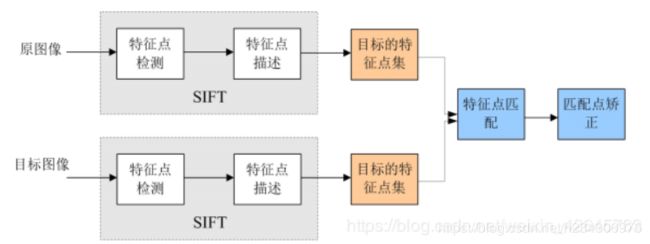
SIFT算法实现特征匹配主要有三个流程,
1、提取关键点;
2、对关键点附加 详细的信息(局部特征),即描述符;
3、通过特征点(附带上特征向量的关 键点)的两两比较找出相互匹配的若干对特征点,建立景物间的对应关系。
关键点(特征点)
这些点是一些十分突出的点不会因光照、尺度、旋转等因素的改变而消 失,比如角点、边缘点、暗区域的亮点以及亮区域的暗点。既然两幅图像中 有相同的景物,那么使用某种方法分别提取各自的稳定点,这些点之间会有 相互对应的匹配点。
尺度空间(scale space )
尺度空间理论最早于1962年提出,其主要思想是通过 对原始图像进行尺度变换,获得图像多尺度下的空间表示。 从而实现边缘、角点检测和不同分辨率上的特征提取,以 满足特征点的尺度不变性。
尺度空间中各尺度图像的 模糊程度逐渐变大,能够模拟 人在距离目标由近到远时目标 在视网膜上的形成过程。 尺度越大图像越模糊。
二、算法步骤
1、提取关键点:关键点是一些十分突出的不会因光照、尺度、旋转等因素而消失的点,比如角点、边缘点、暗区域的亮点以及亮区域的暗点。此步骤是搜索所有尺度空间上的图像位置。通过高斯微分函数来识别潜在的具有尺度和旋转不变的兴趣点。
2、定位关键点并确定特征方向:在每个候选的位置上,通过一个拟合精细的模型来确定位置和尺度。关键点的选择依据于它们的稳定程度。然后基于图像局部的梯度方向,分配给每个关键点位置一个或多个方向。所有后面的对图像数据的操作都相对于关键点的方向、尺度和位置进行变换,从而提供对于这些变换的不变性。
3、通过各关键点的特征向量,进行两两比较找出相互匹配的若干对特征点,建立景物间的对应关系
三、SIFT的缺点
SIFT在图像的不变特征提取方面拥有无与伦比的优势,但并不完美,仍然存在:
-
实时性不高。
-
有时特征点较少。
-
对边缘光滑的目标无法准确提取特征点。
四、代码
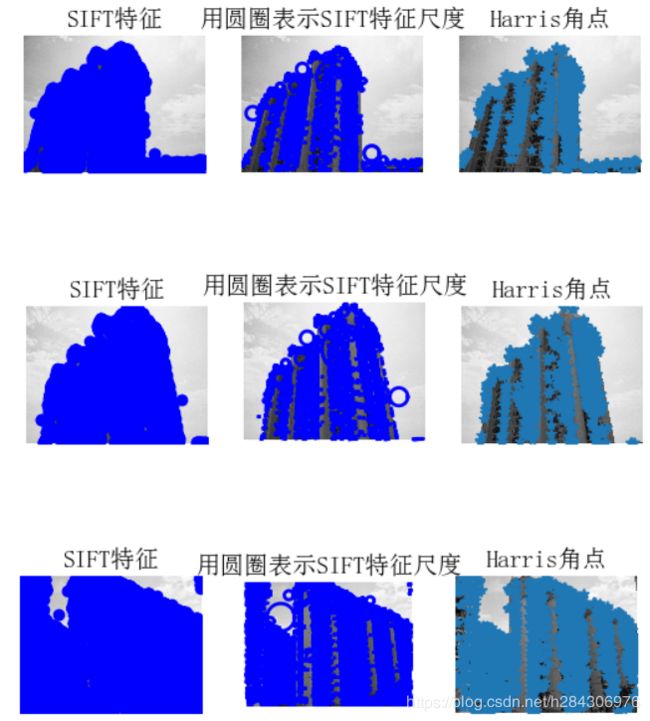
4.1. 特征点展示
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.localdescriptors import harris
# 添加中文字体支持
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\SimSun.ttc", size=14)
imname = 'D:/test/1.jpg'
im = array(Image.open(imname).convert('L'))
sift.process_image(imname, 'empire.sift')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('empire.sift')
figure()
gray()
subplot(131)
sift.plot_features(im, l1, circle=False)
title(u'SIFT特征',fontproperties=font)
subplot(132)
sift.plot_features(im, l1, circle=True)
title(u'用圆圈表示SIFT特征尺度',fontproperties=font)
# 检测harris角点
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im)
subplot(133)
filtered_coords = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, 6, 0.1)
imshow(im)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords], [p[0] for p in filtered_coords], '*')
axis('off')
title(u'Harris角点',fontproperties=font)
show()
4.2. 特征点匹配
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
import sys
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
if len(sys.argv) >= 3:
im1f, im2f = sys.argv[1], sys.argv[2]
else:
im1f = '../test/1.jpg'
im2f = '../test/2.jpg'
im1 = array(Image.open(im1f))
im2 = array(Image.open(im2f))
sift.process_image(im1f, 'out_sift_1.txt')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_1.txt')
figure()
gray()
subplot(121)
sift.plot_features(im1, l1, circle=False)
sift.process_image(im2f, 'out_sift_2.txt')
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_2.txt')
subplot(122)
sift.plot_features(im2, l2, circle=False)
#matches = sift.match(d1, d2)
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
print '{} matches'.format(len(matches.nonzero()[0]))
figure()
gray()
sift.plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, show_below=True)
show()
4.3. 特征点检索算法
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
im1f = 'D:/test/1.jpg'
im1 = array(Image.open(im1f))
sift.process_image(im1f, 'out_sift_1.txt')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_1.txt')
arr=[]
arrHash = {}
for i in range(2,7):
im2f = (r'C:/Users/47098/Desktop/1/'+str(i)+'.jpg')
im2 = array(Image.open(im2f))
sift.process_image(im2f, 'out_sift_2.txt')
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_2.txt')
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
length=len(matches.nonzero()[0])
length=int(length)
arr.append(length)
arrHash[length]=im2f
arr.sort()
arr=arr[::-1]
arr=arr[:5]
i=0
plt.figure(figsize=(5,12))
for item in arr:
if(arrHash.get(item)!=None):
img=arrHash.get(item)
im1 = array(Image.open(img))
ax=plt.subplot(511 + i)
ax.set_title('{} matches'.format(item))
plt.axis('off')
imshow(im1)
i = i + 1
plt.show()
4.4. 地理标记图像匹配
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
import pydot
""" This is the example graph illustration of matching images from Figure 2-10.
To download the images, see ch2_download_panoramio.py."""
#download_path = "panoimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
#path = "/FULLPATH/panoimages/" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
download_path = "F:/dropbox/Dropbox/translation/pcv-notebook/data/panoimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
path = "F:/dropbox/Dropbox/translation/pcv-notebook/data/panoimages/" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
# list of downloaded filenames
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
# extract features
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print 'comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j]
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print 'number of matches = ', nbr_matches
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
print "The match scores is: \n", matchscores
# copy values
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
#可视化
threshold = 2 # min number of matches needed to create link
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # don't want the default directed graph
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images):
if matchscores[i, j] > threshold:
# first image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[i])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(i) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
# second image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[j])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(j) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j)))
g.write_png('whitehouse.png')
运行结果
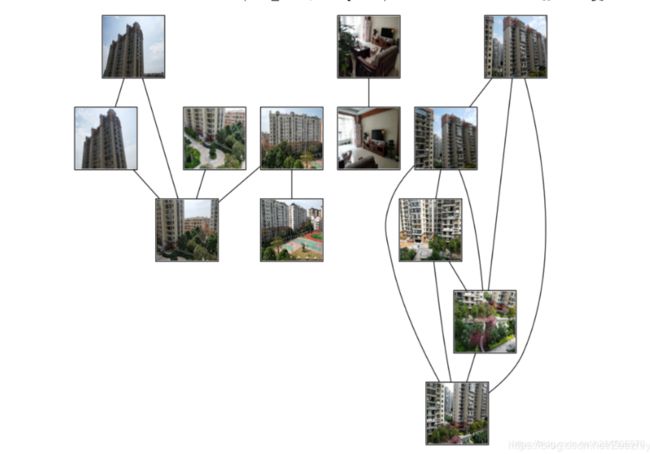
小结
1、将数据集中图片匹配结果可视化,将相同物体存在的图片进行连接,数据集图片分类情况清晰明确,结果一目了然
2、可以将图像之间的匹配数进行输出,也可根据可视化连接进行图像之间匹配数的查询,使结果更具体
3、数据集共有4种不同物品的15张图片,通过本次实验可以快速进行图片分类与关系表示,简洁明了;算法整体运行速度快,无论角度、尺度、光照变化,关系连线都非常准确,进一步说明了SIFT算法的优越性
五、分析与总结
- SIFT特征是图像的局部特征,其对旋转、尺度缩放、亮度变化保持不变性。
- 对视角变化、仿射变换、噪声也保持一定程度的稳定性。
- 信息量丰富,适用于在海量特征数据库中进行快速、准确的匹配。
- 匹配速度快。
- 在图片像素过大时,容易发生不必要的报错;可调整图片的大小,这样程序的运行速度可加快,但会降低匹配值。