多线程并发编程--AQS阻塞队列、Condition.await()/signal()源码分析、生产-消费者案例分享 -上
一、前言:
复习一下之前学习的知识点,之前咱们学习了synchronized、wait、notify相关功能,synchronized实现锁,有隐形的可重入功能(同一个线程,可以重复进入一把锁);
wait/notify实现线程间的异步通信;wait会释放锁,进入等待队列(线程状态:WAITING) ,需要依赖别的线程notify唤醒;其中wait(long time) 超时等待(线程状态:TIMED_WAITING),时间到,自动转入就绪队列,竞争锁。
二、今天重点:AQS阻塞队列、Condition,咱们依旧以生产消费者模型为例:
package com.jason.thread;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
/**
* @program: JasonSpringMybatis
* @description
* @author: 大龄程序猿
* @create: 2020-05-28 23:44
**/
public class Productor implements Runnable{
private List deque;
private int maxSize;
private Lock lock;
private Condition condition;
public Productor(List deque, int maxSize, Lock lock, Condition condition) {
this.deque = deque;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.lock = lock;
this.condition = condition;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i=0;
while(true)
{
lock.lock();
try{
if(deque.size()>=maxSize)
{
try {
condition.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("生产者->生产消息:"+(++i));
deque.add("i="+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
condition.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
package com.jason.thread;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
/**
* @program: JasonSpringMybatis
* @description
* @author: 大龄程序猿
* @create: 2020-05-28 23:45
**/
public class Consumer implements Runnable {
private List deque;
private int maxSize;
private Lock lock;
private Condition condition;
public Consumer(List deque, int maxSize, Lock lock, Condition condition) {
this.deque = deque;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.lock = lock;
this.condition = condition;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i=0;
while(true)
{
lock.lock();
try{
if(deque.size()>0)
{
System.out.println("消费者->消费消息:"+deque.get(0));
deque.remove(0);
try {
condition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else
{
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
condition.await();
long t2=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("consumer 被唤醒重新加入就绪队列,耗时="+(t2-t1));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
package com.jason.thread;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @program: JasonSpringMybatis
* @description
* @author: 大龄程序猿
* @create: 2020-05-29 00:00
**/
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list= new LinkedList();
int maxSize=5;
Lock lock=new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition=lock.newCondition();
Condition condition1=lock.newCondition();
System.out.println(condition+" -------- "+condition1);
Thread product=new Thread(new Productor(list,maxSize,lock,condition),"product");
Thread consumer=new Thread(new Consumer(list,maxSize,lock,condition),"consumer");
product.start();
consumer.start();
}
}
运行结果:
生产者->生产消息:1
生产者->生产消息:2
生产者->生产消息:3
consumer 被唤醒重新加入就绪队列,耗时=3004
消费者->消费消息:i=1
消费者->消费消息:i=2
消费者->消费消息:i=3
生产者->生产消息:4
生产者->生产消息:5
生产者->生产消息:6
consumer 被唤醒重新加入就绪队列,耗时=3000
消费者->消费消息:i=4
消费者->消费消息:i=5
消费者->消费消息:i=6
生产者->生产消息:7
生产者->生产消息:8
生产者->生产消息:9
生产者->生产消息:10
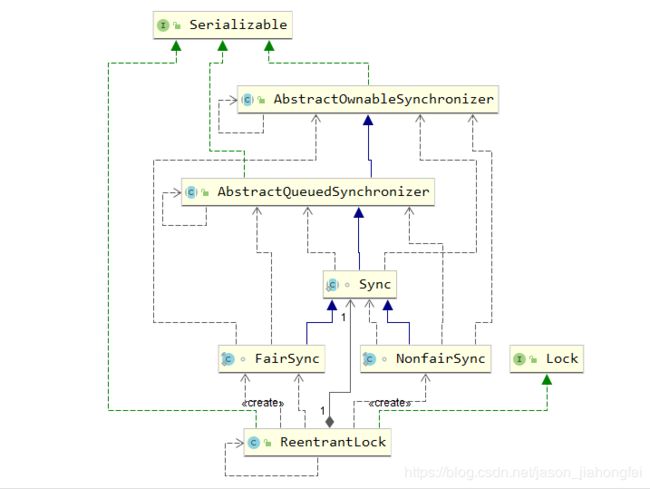
生产者->生产消息:113、AQS异步队列工作机制分析:
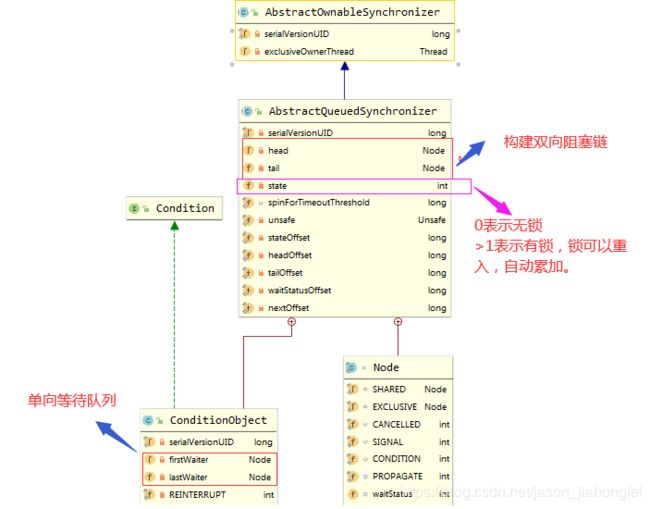
1)数据模型:
2)AQS双向队列阻塞队列&等待队列,数据模型:
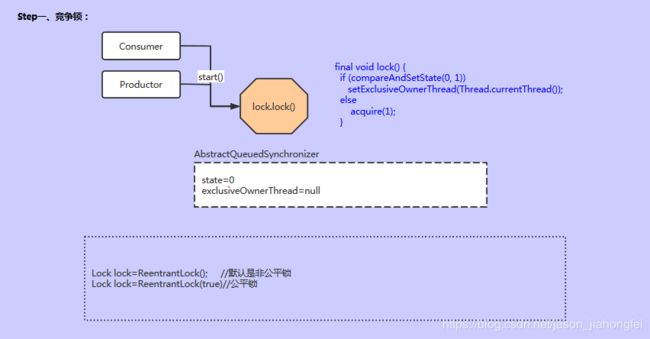
3)场景分析:
Step一:竞争锁,依据锁的互斥性,判断AQS中state的状态,如果不为初始值0,则会通过底层的CAPS操作 native方法.
//ReentrantLock方法:
final void lock() {
//判断AQS中的state是否为0,如果是0,则将状态改为1
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
//成功将状态改为1,同时设置AQS中的当前工作线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
//状态不是0,处于锁的状态,可能是别人锁了,也可能是自己锁了(重入锁)
acquire(1);
}
//大家刚开始可能会比较困惑AQS到底是啥,老铁们可以看一下我上面贴出来的数据模型图,当在构建Lock对象时,ReentrantLock有个Sync内部成员
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
创建Lock对象时,可以根据构造方法传参 选择是否公平锁(默认无参是非公平锁)
例如:Lock lock=new ReentrantLock(true)//创建了公平锁FIFO,非公平锁,可以直接插队。
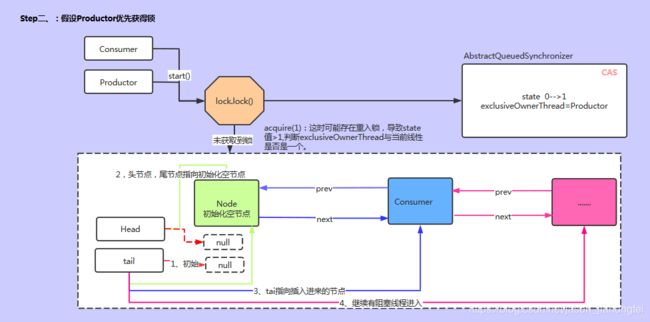
//这段代码,包含了三个方法:tryAcquire addWaiter acquireQueued
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
//tryAcquire 重试获取锁
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {//如果状态为0,可以获取锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}//如果状态不为0,但是AQS中的独占线程是自己,说明是重入,累加状态值,更新。
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
//addWaiter 将未获得锁的线程,加入到队列
//AQS中双向链表初始化:
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);//初始化head,tail节点
return node;
}
//初始化head,tail 节点
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
//acquireQueued
入参:新节点插入等待队列后,返回当前位置,
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();//取前一个节点
//如果前一个节点是头节点,则再尝试获取一次锁
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
//获取前一个节点:
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
Node p = prev;
if (p == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
else
return p;
}
//获取
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
//节点状态值,大于0表示,当前节点是取消,需要重当前队列中剔除掉。
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
//节点挂起:
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
//节点状态值:
/**
* Status field, taking on only the values:
* SIGNAL: The successor of this node is (or will soon be)
* blocked (via park), so the current node must
* unpark its successor when it releases or
* cancels. To avoid races, acquire methods must
* first indicate they need a signal,
* then retry the atomic acquire, and then,
* on failure, block.
* CANCELLED: This node is cancelled due to timeout or interrupt.
* Nodes never leave this state. In particular,
* a thread with cancelled node never again blocks.
* CONDITION: This node is currently on a condition queue.
* It will not be used as a sync queue node
* until transferred, at which time the status
* will be set to 0. (Use of this value here has
* nothing to do with the other uses of the
* field, but simplifies mechanics.)
* PROPAGATE: A releaseShared should be propagated to other
* nodes. This is set (for head node only) in
* doReleaseShared to ensure propagation
* continues, even if other operations have
* since intervened.
* 0: None of the above
*
* The values are arranged numerically to simplify use.
* Non-negative values mean that a node doesn't need to
* signal. So, most code doesn't need to check for particular
* values, just for sign.
*
* The field is initialized to 0 for normal sync nodes, and
* CONDITION for condition nodes. It is modified using CAS
* (or when possible, unconditional volatile writes).
*/
volatile int waitStatus;