【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】八,YOLOV2损失函数代码详解(region_layer.c)
想再说一下,这个系列的代码注释我放到https://github.com/GiantPandaCV/darknet 这里了,有需要的可以点star或者fork哦,还在持续更新中。
前言
昨天结合代码详细解析了YOLOV1的损失函数,今天AlexeyAB版DarkNet的YOLOV2损失函数代码解析也来了。之前我详细分析过YOLOv2的损失函数目标检测算法之YOLOv2损失函数详解,这一节就不再赘述损失函数本身的细节了,直接上源码注释来进一步理解这一损失函数。
YOLOV2损失函数
为了方便你理解,还是把YOLOV2损失函数叙述一下。
YOLOV2对每个预测box的[x,y],confidence进行逻辑回归,类别进行softmax回归;
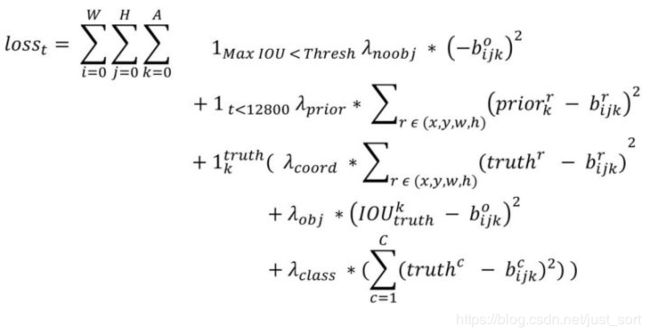
在Darknet中,损失函数可以用下图来进行表示:
可以看到这个损失函数是相当复杂的,损失函数的定义在Darknet/src/region_layer.c中。对于上面这一堆公式,我们先简单看一下,然后我们在源码中去找到对应部分。这里的 W W W和 H H H代表的是特征图的高宽,都为 13 13 13,而A指的是Anchor个数,YOLOv2中是5,各个 λ \lambda λ值是各个loss部分的权重系数。我们将损失函数分成3大部分来解释:
- 第一部分:
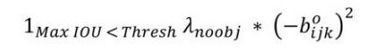
第一项需要好好解释一下,这个loss是计算background的置信度误差,这也是YOLO系列算法的特色,但是用哪些预测框来预测背景呢?这里需要计算各个预测框和所有的ground truth之间的IOU值,并且取最大值记作MaxIOU,如果该值小于一定的阈值,YOLOv2论文取了0.6,那么这个预测框就标记为background,需要计算 λ n o o b j \lambda_{noobj} λnoobj这么多倍的损失函数。为什么这个公式可以这样表达呢?因为我们有物体的话,那么 λ n o o b j = 0 \lambda_{noobj}=0 λnoobj=0,如果没有物体 λ n o o b j = 1 \lambda_{noobj}=1 λnoobj=1,我们把这个值带入到下面的公式就可以推出第一项啦!
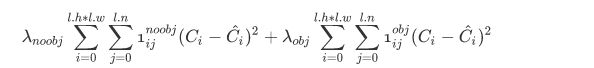
- 第二部分:
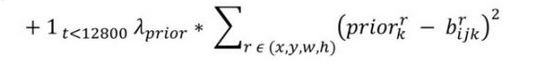
这一部分是计算Anchor boxes和预测框的坐标误差,但是只在前12800个iter计算,这一项应该是促进网络学习到Anchor的形状。 - 第三部分:
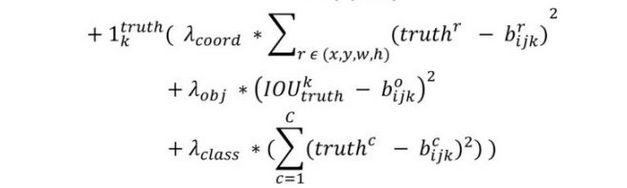
这一部分计算的是和ground truth匹配的预测框各部分的损失总和,包括坐标损失,置信度损失以及分类损失。
3.1 坐标损失 这里的匹配原则是指对于某个特定的ground truth,首先要计算其中心点落在哪个cell上,然后计算这个cell的5个先验框和grond truth的IOU值,计算IOU值的时候不考虑坐标只考虑形状,所以先将Anchor boxes和ground truth的中心都偏移到同一位置,然后计算出对应的IOU值,IOU值最大的先验框和ground truth匹配,对应的预测框用来预测这个ground truth。
3.2 置信度损失 在计算obj置信度时, 增加了一项 λ o b j \lambda_{obj} λobj权重系数,也被称为rescore参数,当其为1时,损失是预测框和ground truth的真实IOU值(darknet中采用了这种实现方式)。而对于没有和ground truth匹配的先验框,除去那些Max_IOU低于阈值的,其它就全部忽略。YOLOv2和SSD与RPN网络的处理方式有很大不同,因为它们可以将一个ground truth分配给多个先验框。
3.3 分类损失 这个和YOLOv1一致,没什么好说的了。
我看了一篇讲解YOLOv2损失函数非常好的文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/YiXiaoZhou/p/7429481.html 。里面还有一个关键点:
在计算boxes的 w w w和 h h h误差时,YOLOv1中采用的是平方根以降低boxes的大小对误差的影响,而YOLOv2是直接计算,但是根据ground truth的大小对权重系数进行修正:l.coord_scale * (2 - truth.w*truth.h)(这里 w w w和 h h h都归一化到(0,1)),这样对于尺度较小的 b o x e s boxes boxes其权重系数会更大一些,可以放大误差,起到和YOLOv1计算平方根相似的效果。
代码详解
#define DOABS 1
// 构建YOLOv2 region_layer层
// batch 一个batch中包含的图片数
// w 输入特征图的宽度
// h 输入特征图的高度
// n 一个cell预测多少个bbox
// classes 网络需要识别的物体类别数
// coord 一个bbox包含的[x,y,w,h]
region_layer make_region_layer(int batch, int w, int h, int n, int classes, int coords, int max_boxes)
{
region_layer l = { (LAYER_TYPE)0 };
l.type = REGION; //层类别
// 这些变量都可以参考darknet.h中的注释
l.n = n; //一个cell中预测多少个box
l.batch = batch; //一个batch中包含的图片数
l.h = h; //输入图片的宽度
l.w = w; //输入图片的宽度
l.classes = classes; //网络需要识别的物体类数
l.coords = coords; //定位一个物体所需的参数个数(一般值为4,包括矩形中心点坐标x,y以及长宽w,h)
l.cost = (float*)xcalloc(1, sizeof(float)); //目标函数值,为单精度浮点型指针
l.biases = (float*)xcalloc(n * 2, sizeof(float));
l.bias_updates = (float*)xcalloc(n * 2, sizeof(float));
l.outputs = h*w*n*(classes + coords + 1); //一张训练图片经过region_layer层后得到的输出元素个数(等于网格数*每个网格预测的矩形框数*每个矩形框的参数个数)
l.inputs = l.outputs; //一张训练图片输入到reigon_layer层的元素个数(注意是一张图片,对于region_layer,输入和输出的元素个数相等)
//每张图片含有的真实矩形框参数的个数(max_boxes表示一张图片中最多有max_boxes个ground truth矩形框,每个真实矩形框有
//5个参数,包括x,y,w,h四个定位参数,以及物体类别),注意max_boxes是darknet程序内写死的,实际上每张图片可能
//并没有max_boxes个真实矩形框,也能没有这么多参数,但为了保持一致性,还是会留着这么大的存储空间,只是其中的
//值为空而已.
l.max_boxes = max_boxes;
// GT: max_boxes*(4+1) 存储max_boxes个bbox的信息,这里是假设图片中GT bbox的数量是
//小于max_boxes的,这里是写死的;此处与yolov1是不同的
l.truths = max_boxes*(5);
// region层误差项(包含整个batch的)
l.delta = (float*)xcalloc(batch * l.outputs, sizeof(float));
// region层所有输出(包含整个batch的)
//region_layer的输出维度是l.out_w*l.out_h,等于输出的维度,输出的通道数为l.out_c,也即是输入的通道数,具体为:n*(classes+coords+1)
//YOLO检测模型将图片分成S*S个网格,每个网格又预测B个矩形框,最后一层输出的就是这些网格中包含的所有矩形框的信息
l.output = (float*)xcalloc(batch * l.outputs, sizeof(float));
int i;
//存储bbox的Anchor box的[w,h]的初始化,在src/parse.c中parse_yolo函数会加载cfg中Anchor尺寸
for(i = 0; i < n*2; ++i){
l.biases[i] = .5;
}
l.forward = forward_region_layer;
l.backward = backward_region_layer;
#ifdef GPU
l.forward_gpu = forward_region_layer_gpu;
l.backward_gpu = backward_region_layer_gpu;
l.output_gpu = cuda_make_array(l.output, batch*l.outputs);
l.delta_gpu = cuda_make_array(l.delta, batch*l.outputs);
#endif
fprintf(stderr, "detection\n");
srand(time(0));
return l;
}
void resize_region_layer(layer *l, int w, int h)
{
#ifdef GPU
int old_w = l->w;
int old_h = l->h;
#endif
l->w = w;
l->h = h;
l->outputs = h*w*l->n*(l->classes + l->coords + 1);
l->inputs = l->outputs;
l->output = (float*)xrealloc(l->output, l->batch * l->outputs * sizeof(float));
l->delta = (float*)xrealloc(l->delta, l->batch * l->outputs * sizeof(float));
#ifdef GPU
if (old_w < w || old_h < h) {
cuda_free(l->delta_gpu);
cuda_free(l->output_gpu);
l->delta_gpu = cuda_make_array(l->delta, l->batch*l->outputs);
l->output_gpu = cuda_make_array(l->output, l->batch*l->outputs);
}
#endif
}
//获取某个矩形框的4个定位信息,即根据输入的矩形框索引从l.output中获取该矩形框的定位信息x,y,w,h
//x region_layer的输出,即l.output,包含所有batch预测得到的矩形框信息
//biases 表示Anchor框的长和宽
//index 矩形框的首地址(索引,矩形框中存储的首个参数x在l.output中的索引)
//i 第几行(region_layer维度为l.out_w*l.out_c)
//j 第几列
//w 特征图的宽度
//h 特征图的高度
box get_region_box(float *x, float *biases, int n, int index, int i, int j, int w, int h)
{
box b;
b.x = (i + logistic_activate(x[index + 0])) / w;
b.y = (j + logistic_activate(x[index + 1])) / h;
b.w = exp(x[index + 2]) * biases[2*n];
b.h = exp(x[index + 3]) * biases[2*n+1];
if(DOABS){
b.w = exp(x[index + 2]) * biases[2*n] / w;
b.h = exp(x[index + 3]) * biases[2*n+1] / h;
}
return b;
}
float delta_region_box(box truth, float *x, float *biases, int n, int index, int i, int j, int w, int h, float *delta, float scale)
{
// 获得第j*w+i个cell第n个bbox在当前特征图上位置和宽高
box pred = get_region_box(x, biases, n, index, i, j, w, h);
// 计算pred bbox 与 GT bbox的IOU【前12800GT boox为当前cell第n个bbox的Anchor】
float iou = box_iou(pred, truth);
// 计算GT bbox的tx,ty,tw,th
float tx = (truth.x*w - i);
float ty = (truth.y*h - j);
float tw = log(truth.w / biases[2*n]);
float th = log(truth.h / biases[2*n + 1]);
if(DOABS){
tw = log(truth.w*w / biases[2*n]);
th = log(truth.h*h / biases[2*n + 1]);
}
// 计算tx,ty,tw,th梯度
delta[index + 0] = scale * (tx - logistic_activate(x[index + 0])) * logistic_gradient(logistic_activate(x[index + 0]));
delta[index + 1] = scale * (ty - logistic_activate(x[index + 1])) * logistic_gradient(logistic_activate(x[index + 1]));
delta[index + 2] = scale * (tw - x[index + 2]);
delta[index + 3] = scale * (th - x[index + 3]);
return iou;
}
void delta_region_class(float *output, float *delta, int index, int class_id, int classes, tree *hier, float scale, float *avg_cat, int focal_loss)
{
int i, n;
if(hier){ // 在yolov2 中region层, 此部分不参与计算【这是在yolo9000才参与计算】
float pred = 1;
while(class_id >= 0){
pred *= output[index + class_id];
int g = hier->group[class_id];
int offset = hier->group_offset[g];
for(i = 0; i < hier->group_size[g]; ++i){
delta[index + offset + i] = scale * (0 - output[index + offset + i]);
}
delta[index + class_id] = scale * (1 - output[index + class_id]);
class_id = hier->parent[class_id];
}
*avg_cat += pred;
} else {
// Focal loss
if (focal_loss) { //如果使用focal loss
// Focal Loss
float alpha = 0.5; // 0.25 or 0.5
//float gamma = 2; // hardcoded in many places of the grad-formula
int ti = index + class_id;
float pt = output[ti] + 0.000000000000001F;
// http://fooplot.com/#W3sidHlwZSI6MCwiZXEiOiItKDEteCkqKDIqeCpsb2coeCkreC0xKSIsImNvbG9yIjoiIzAwMDAwMCJ9LHsidHlwZSI6MTAwMH1d
float grad = -(1 - pt) * (2 * pt*logf(pt) + pt - 1); // http://blog.csdn.net/linmingan/article/details/77885832
//float grad = (1 - pt) * (2 * pt*logf(pt) + pt - 1); // https://github.com/unsky/focal-loss
for (n = 0; n < classes; ++n) {
// focal loss的梯度
delta[index + n] = scale * (((n == class_id) ? 1 : 0) - output[index + n]);
delta[index + n] *= alpha*grad;
if (n == class_id) *avg_cat += output[index + n];
}
}
else {
// default
for (n = 0; n < classes; ++n) {
// 计算类别损失的梯度, 反向传递到误差项l.delta中, 在yolo v2中scale=1
delta[index + n] = scale * (((n == class_id) ? 1 : 0) - output[index + n]);
if (n == class_id) *avg_cat += output[index + n];
}
}
}
}
float logit(float x)
{
return log(x/(1.-x));
}
float tisnan(float x)
{
return (x != x);
}
/**
* @brief 计算某个矩形框中某个参数在l.output中的索引。一个矩形框包含了x,y,w,h,c,C1,C2...,Cn信息,
* 前四个用于定位,第五个为矩形框含有物体的置信度信息c,即矩形框中存在物体的概率为多大,而C1到Cn
* 为矩形框中所包含的物体分别属于这n类物体的概率。本函数负责获取该矩形框首个定位信息也即x值在
* l.output中索引、获取该矩形框置信度信息c在l.output中的索引、获取该矩形框分类所属概率的首个
* 概率也即C1值的索引,具体是获取矩形框哪个参数的索引,取决于输入参数entry的值,这些在
* forward_region_layer()函数中都有用到,由于l.output的存储方式,当entry=0时,就是获取矩形框
* x参数在l.output中的索引;当entry=4时,就是获取矩形框置信度信息c在l.output中的索引;当
* entry=5时,就是获取矩形框首个所属概率C1在l.output中的索引,具体可以参考forward_region_layer()
* 中调用本函数时的注释.
* @param l 当前region_layer
* @param batch 当前照片是整个batch中的第几张,因为l.output中包含整个batch的输出,所以要定位某张训练图片
* 输出的众多网格中的某个矩形框,当然需要该参数.
* @param location 这个参数,说实话,感觉像个鸡肋参数,函数中用这个参数获取n和loc的值,这个n就是表示网格中
* 的第几个预测矩形框(比如每个网格预测5个矩形框,那么n取值范围就是从0~4,loc就是某个
* 通道上的元素偏移(region_layer输出的通道数为l.out_c = (classes + coords + 1),
* 这样说可能没有说明白,这都与l.output的存储结构相关,见下面详细注释以及其他说明。总之,
* 查看一下调用本函数的父函数forward_region_layer()就知道了,可以直接输入n和j*l.w+i的,
* 没有必要输入location,这样还得重新计算一次n和loc.
* @param entry 切入点偏移系数,关于这个参数,就又要扯到l.output的存储结构了,见下面详细注释以及其他说明.
* @details l.output这个参数的存储内容以及存储方式已经在多个地方说明了,再多的文字都不及图文说明,此处再
* 简要罗嗦几句,更为具体的参考图文说明。l.output中存储了整个batch的训练输出,每张训练图片都会输出
* l.out_w*l.out_h个网格,每个网格会预测l.n个矩形框,每个矩形框含有l.classes+l.coords+1个参数,
* 而最后一层的输出通道数为l.n*(l.classes+l.coords+1),可以想象下最终输出的三维张量是个什么样子的。
* 展成一维数组存储时,l.output可以首先分成batch个大段,每个大段存储了一张训练图片的所有输出;进一步细分,
* 取其中第一大段分析,该大段中存储了第一张训练图片所有输出网格预测的矩形框信息,每个网格预测了l.n个矩形框,
* 存储时,l.n个矩形框是分开存储的,也就是先存储所有网格中的第一个矩形框,而后存储所有网格中的第二个矩形框,
* 依次类推,如果每个网格中预测5个矩形框,则可以继续把这一大段分成5个中段。继续细分,5个中段中取第
* 一个中段来分析,这个中段中按行(有l.out_w*l.out_h个网格,按行存储)依次存储了这张训练图片所有输出网格中
* 的第一个矩形框信息,要注意的是,这个中段存储的顺序并不是挨个挨个存储每个矩形框的所有信息,
* 而是先存储所有矩形框的x,而后是所有的y,然后是所有的w,再是h,c,最后的的概率数组也是拆分进行存储,
* 并不是一下子存储完一个矩形框所有类的概率,而是先存储所有网格所属第一类的概率,再存储所属第二类的概率,
* 具体来说这一中段首先存储了l.out_w*l.out_h个x,然后是l.out_w*l.out_c个y,依次下去,
* 最后是l.out_w*l.out_h个C1(属于第一类的概率,用C1表示,下面类似),l.out_w*l.outh个C2,...,
* l.out_w*l.out_c*Cn(假设共有n类),所以可以继续将中段分成几个小段,依次为x,y,w,h,c,C1,C2,...Cn
* 小段,每小段的长度都为l.out_w*l.out_c.
* 现在回过来看本函数的输入参数,batch就是大段的偏移数(从第几个大段开始,对应是第几张训练图片),
* 由location计算得到的n就是中段的偏移数(从第几个中段开始,对应是第几个矩形框),
* entry就是小段的偏移数(从几个小段开始,对应具体是那种参数,x,c还是C1),而loc则是最后的定位,
* 前面确定好第几大段中的第几中段中的第几小段的首地址,loc就是从该首地址往后数loc个元素,得到最终定位
* 某个具体参数(x或c或C1)的索引值,比如l.output中存储的数据如下所示(这里假设只存了一张训练图片的输出,
* 因此batch只能为0;并假设l.out_w=l.out_h=2,l.classes=2):
* xxxxyyyywwwwhhhhccccC1C1C1C1C2C2C2C2-#-xxxxyyyywwwwhhhhccccC1C1C1C1C2C2C2C2,
* n=0则定位到-#-左边的首地址(表示每个网格预测的第一个矩形框),n=1则定位到-#-右边的首地址(表示每个网格预测的第二个矩形框)
* entry=0,loc=0获取的是x的索引,且获取的是第一个x也即l.out_w*l.out_h个网格中第一个网格中第一个矩形框x参数的索引;
* entry=4,loc=1获取的是c的索引,且获取的是第二个c也即l.out_w*l.out_h个网格中第二个网格中第一个矩形框c参数的索引;
* entry=5,loc=2获取的是C1的索引,且获取的是第三个C1也即l.out_w*l.out_h个网格中第三个网格中第一个矩形框C1参数的索引;
* 如果要获取第一个网格中第一个矩形框w参数的索引呢?如果已经获取了其x值的索引,显然用x的索引加上3*l.out_w*l.out_h即可获取到,
* 这正是delta_region_box()函数的做法;
* 如果要获取第三个网格中第一个矩形框C2参数的索引呢?如果已经获取了其C1值的索引,显然用C1的索引加上l.out_w*l.out_h即可获取到,
* 这正是delta_region_class()函数中的做法;
* 由上可知,entry=0时,即偏移0个小段,是获取x的索引;entry=4,是获取自信度信息c的索引;entry=5,是获取C1的索引.
* l.output的存储方式大致就是这样,个人觉得说的已经很清楚了,但可视化效果终究不如图文说明~
*/
static int entry_index(layer l, int batch, int location, int entry)
{
int n = location / (l.w*l.h);
int loc = location % (l.w*l.h);
return batch*l.outputs + n*l.w*l.h*(l.coords + l.classes + 1) + entry*l.w*l.h + loc;
}
void softmax_tree(float *input, int batch, int inputs, float temp, tree *hierarchy, float *output);
//本函数多次调用了entry_index()函数,且使用的参数不尽相同,尤其是最后一个参数,通过最后一个参数,
//可以确定出region_layer输出l.output的数据存储方式。为方便叙述,假设本层输出参数l.w = 2, l.h= 3,
//l.n = 2, l.classes = 2, l.coords = 4, l.c = l.n * (l.coords + l.classes + 1) = 21,
//l.output中存储了所有矩形框的信息参数,每个矩形框包括4条定位信息参数x,y,w,h,一条置信度(confidience)
//参数c,以及所有类别的概率C1,C2(本例中,假设就只有两个类别,l.classes=2),那么一张样本图片最终会有
//l.w*l.h*l.n个矩形框(l.w*l.h即为最终图像划分层网格的个数,每个网格预测l.n个矩形框),那么
//l.output中存储的元素个数共有l.w*l.h*l.n*(l.coords + 1 + l.classes),这些元素全部拉伸成一维数组
//的形式存储在l.output中,存储的顺序为:
//xxxxxx-yyyyyy-wwwwww-hhhhhh-cccccc-C1C1C1C1C1C1C2C2C2C2C2C2-##-xxxxxx-yyyyyy-wwwwww-hhhhhh-cccccc-C1C2C1C2C1C2C1C2C1C2C1C2
//文字说明如下:-##-隔开分成两段,左右分别是代表所有网格的第1个box和第2个box(因为l.n=2,表示每个网格预测两个box)
//总共有l.w*l.h个网格,且存储时,把所有网格的x,y,w,h,c信息聚到一起再拼接起来,因此xxxxxx及其他信息都有l.w*l.h=6个,
//因为每个有l.classes个物体类别,而且也是和xywh一样,每一类都集中存储,先存储l.w*l.h=6个C1类,而后存储6个C2类,
//置信度参数c表示的是该矩形框内存在物体的概率,而C1,C2分别表示矩形框内存在物体时属于物体1和物体2的概率,
//因此c*C1即得矩形框内存在物体1的概率,c*C2即得矩形框内存在物体2的概率
void forward_region_layer(const region_layer l, network_state state)
{
int i,j,b,t,n;
int size = l.coords + l.classes + 1;
//内存拷贝, l.output = state.input
memcpy(l.output, state.input, l.outputs*l.batch*sizeof(float));
//这个#ifndef预编译指令没有必要用的,因为forward_region_layer()函数本身就对应没有定义gpu版的,所以肯定会执行其中的语句
#ifndef GPU
flatten(l.output, l.w*l.h, size*l.n, l.batch, 1);
#endif
for (b = 0; b < l.batch; ++b){
for(i = 0; i < l.h*l.w*l.n; ++i){
int index = size*i + b*l.outputs;
// 对confidence进行逻辑回归
l.output[index + 4] = logistic_activate(l.output[index + 4]);
}
}
#ifndef GPU
if (l.softmax_tree){
for (b = 0; b < l.batch; ++b){
for(i = 0; i < l.h*l.w*l.n; ++i){
int index = size*i + b*l.outputs;
softmax_tree(l.output + index + 5, 1, 0, 1, l.softmax_tree, l.output + index + 5);
}
}
} else if (l.softmax){
for (b = 0; b < l.batch; ++b){
for(i = 0; i < l.h*l.w*l.n; ++i){
int index = size*i + b*l.outputs;
// l.softmax 对class进行softmax回归
softmax(l.output + index + 5, l.classes, 1, l.output + index + 5, 1);
}
}
}
#endif
// inference阶段,则到此结束
if(!state.train) return;
// 将reorg层的误差项进行初始化(包含整个batch的)
memset(l.delta, 0, l.outputs * l.batch * sizeof(float));
float avg_iou = 0; //平均IoU(Intersection over Union)
float recall = 0; //召回率
float avg_cat = 0;
float avg_obj = 0;
float avg_anyobj = 0; //一张训练图片所有预测矩形框的平均置信度(矩形框中含有物体的概率),该参数没有实际用处,仅用于输出打印
int count = 0;
int class_count = 0;
// region层的总损失初始化为0
*(l.cost) = 0;
// 遍历batch中每一张图片
for (b = 0; b < l.batch; ++b) {
if(l.softmax_tree){ //【这是在yolo9000才参与计算】
int onlyclass_id = 0;
// 循环max_boxes次,每张图片固定处理max_boxes个矩形框
for(t = 0; t < l.max_boxes; ++t){
// 通过移位来获取每一个真实矩形框的信息,net.truth存储了网络吞入的所有图片的真实矩形框信息(一次吞入一个batch的训练图片),
// net.truth作为这一个大数组的首地址,l.truths参数是每一张图片含有的真实值参数个数(可参考layer.h中的truths参数中的注释),
// b是batch中已经处理完图片的图片的张数,5是每个真实矩形框需要5个参数值(也即每条矩形框真值有5个参数),t是本张图片已经处理
// 过的矩形框的个数(每张图片最多处理max_boxes个矩形框),明白了上面的参数之后对于下面的移位获取对应矩形框真实值的代码就不难了
box truth = float_to_box(state.truth + t*5 + b*l.truths);
// 这个if语句是用来判断一下是否有读到真实矩形框值(每个矩形框有5个参数,float_to_box只读取其中的4个定位参数,
// 只要验证x的值不为0,那肯定是4个参数值都读取到了,要么全部读取到了,要么一个也没有),另外,因为程序中写死了每张图片处理max_boxes个矩形框,
// 那么有些图片没有这么多矩形框,就会出现没有读到的情况。
if(!truth.x) break; // continue;
//float_to_box()中没有读取矩形框中包含的物体类别编号的信息,就在此处获取。(darknet中,物体类别标签值为编号,
//每一个类别都有一个编号值,这些物体具体的字符名称存储在一个文件中,如data/*.names文件,其所在行数就是其编号值)
int class_id = state.truth[t*5 + b*l.truths + 4];
float maxp = 0;
int maxi = 0;
if(truth.x > 100000 && truth.y > 100000){
for(n = 0; n < l.n*l.w*l.h; ++n){
int index = size*n + b*l.outputs + 5;
float scale = l.output[index-1];
float p = scale*get_hierarchy_probability(l.output + index, l.softmax_tree, class_id);
if(p > maxp){
maxp = p;
maxi = n;
}
}
int index = size*maxi + b*l.outputs + 5;
delta_region_class(l.output, l.delta, index, class_id, l.classes, l.softmax_tree, l.class_scale, &avg_cat, l.focal_loss);
++class_count;
onlyclass_id = 1;
break;
}
}
if(onlyclass_id) continue;
}
for (j = 0; j < l.h; ++j) {
for (i = 0; i < l.w; ++i) { // 遍历每个cell, 当前cell编号为[j, i]
for (n = 0; n < l.n; ++n) { // 遍历每个bbox,当前bbox编号为[n]
//根据i,j,n计算该矩形框的索引,实际是矩形框中存储的x参数在l.output中的索引,矩形框中包含多个参数,
//x是其存储的首个参数,所以也可以说是获取该矩形框的首地址。
int index = size*(j*l.w*l.n + i*l.n + n) + b*l.outputs;
// 根据矩形框的索引,获取矩形框的定位信息
box pred = get_region_box(l.output, l.biases, n, index, i, j, l.w, l.h);
// 最高IoU,赋初值0
float best_iou = 0;
int best_class_id = -1;
// 遍历每一个GT bbox
for(t = 0; t < l.max_boxes; ++t){
//将第t个bbox由float数组转bbox结构体,方便计算IOU
box truth = float_to_box(state.truth + t*5 + b*l.truths);
//获取第t个bbox的物体类别
int class_id = state.truth[t * 5 + b*l.truths + 4];
if (class_id >= l.classes) continue; // if label contains class_id more than number of classes in the cfg-file
if(!truth.x) break; // continue;
// 计算pred与第t个GT之间的IOU
float iou = box_iou(pred, truth);
if (iou > best_iou) {
best_class_id = state.truth[t*5 + b*l.truths + 4];
best_iou = iou; // 最大IOU更新
}
}
// 统计有目标的概率
avg_anyobj += l.output[index + 4];
// 与yolov1相似, 先将所有pred bbox都当做noobject,计算其confidence损失梯度
l.delta[index + 4] = l.noobject_scale * ((0 - l.output[index + 4]) * logistic_gradient(l.output[index + 4]));
// 在yolov2中并没有执行
if(l.classfix == -1) l.delta[index + 4] = l.noobject_scale * ((best_iou - l.output[index + 4]) * logistic_gradient(l.output[index + 4]));
else{
// best_iou大于阈值则说明有object, 在yolo v2中阈值为0.6
if (best_iou > l.thresh) {
l.delta[index + 4] = 0;
if(l.classfix > 0){
delta_region_class(l.output, l.delta, index + 5, best_class_id, l.classes, l.softmax_tree, l.class_scale*(l.classfix == 2 ? l.output[index + 4] : 1), &avg_cat, l.focal_loss);
++class_count;
}
}
}
// net.seen 保存当前是训练第多少张图片
if(*(state.net.seen) < 12800){
// 对于训练阶段的前12800张图片,GT bbox 直接用了anchor box
box truth = {0}; // 计算第[j, i]cell, 第n个bbox的anchor bbox
truth.x = (i + .5)/l.w; // +0.5是因为x位于几何中心, 然后计算x相对整张特征图的位置
truth.y = (j + .5)/l.h;
truth.w = l.biases[2*n];
truth.h = l.biases[2*n+1];
if(DOABS){
truth.w = l.biases[2*n]/l.w;
truth.h = l.biases[2*n+1]/l.h;
}
// 将pred bbox的tx,ty,tw,th和上面的truth box的差值反向传递到l.detla
delta_region_box(truth, l.output, l.biases, n, index, i, j, l.w, l.h, l.delta, .01);
}
}
}
}
// 遍历每一个GT bbox
for(t = 0; t < l.max_boxes; ++t){
// 将第t个bbox由float数组转bbox结构体,方便计算IOU
box truth = float_to_box(state.truth + t*5 + b*l.truths);
int class_id = state.truth[t * 5 + b*l.truths + 4];
if (class_id >= l.classes) {
printf(" Warning: in txt-labels class_id=%d >= classes=%d in cfg-file. In txt-labels class_id should be [from 0 to %d] \n", class_id, l.classes, l.classes-1);
getchar();
continue; // if label contains class_id more than number of classes in the cfg-file
}
// 如果x坐标为0则取消, 因为yolov2这里定义了30 bbox, 可能实际上没有bbox
if(!truth.x) break; // continue;
float best_iou = 0; // 保存最大IOU
int best_index = 0;// 保存最大IOU的bbox index
int best_n = 0;
i = (truth.x * l.w); // 获得当前第t个GT bbox所在cell
j = (truth.y * l.h);
//printf("%d %f %d %f\n", i, truth.x*l.w, j, truth.y*l.h);
box truth_shift = truth; // 将truth_shift的box移动到0,0
truth_shift.x = 0;
truth_shift.y = 0;
//printf("index %d %d\n",i, j);
for(n = 0; n < l.n; ++n){ // 遍历cell[j,i]所在的n个预测bbox
// 获得第j*w+i个cell第n个bbox的index
int index = size*(j*l.w*l.n + i*l.n + n) + b*l.outputs;
// 获得第j*w+i个cell第n个bbox在当前特征图上位置和宽高
box pred = get_region_box(l.output, l.biases, n, index, i, j, l.w, l.h);
if(l.bias_match){// yolov2 reorg层 bias_match = 1
pred.w = l.biases[2*n];
pred.h = l.biases[2*n+1];
if(DOABS){
pred.w = l.biases[2*n]/l.w; // 然后计算pred box的w相对整张特征图的位置
pred.h = l.biases[2*n+1]/l.h; // 然后计算pred box的h相对整张特征图的位置
}
}
//printf("pred: (%f, %f) %f x %f\n", pred.x, pred.y, pred.w, pred.h);
pred.x = 0; // 将预测的bbox移动到0,0
pred.y = 0;
float iou = box_iou(pred, truth_shift); // 计算GT box truth_shift 与 预测bbox pred 二者之间的IOU
if (iou > best_iou){
best_index = index; // 记录best_iou对应bbox的index
best_iou = iou; // 记录IOU最大的IOU
best_n = n; // 以及记录该bbox的编号n
}
}
//printf("%d %f (%f, %f) %f x %f\n", best_n, best_iou, truth.x, truth.y, truth.w, truth.h);
// 计算获得best_iou的pred bbox 与 GT bbox之间的真实iou, 之前best_iou是方便计算,以及加速,
// 同时完成坐标损失的反向传递
float iou = delta_region_box(truth, l.output, l.biases, best_n, best_index, i, j, l.w, l.h, l.delta, l.coord_scale);
// 如果iou大于0.5, recall ++;
if(iou > .5) recall += 1;
avg_iou += iou;
//l.delta[best_index + 4] = iou - l.output[best_index + 4];
// 统计有目标的概率
avg_obj += l.output[best_index + 4];
// 与yolov1相似, 该pred bbox中是有object,计算其confidence损失梯度; object_scale = 5
l.delta[best_index + 4] = l.object_scale * (1 - l.output[best_index + 4]) * logistic_gradient(l.output[best_index + 4]);
if (l.rescore) { // yolov2 reorg层中rescore = 1, 参于计算
//定义了rescore表示同时对confidence score进行回归
// 该pred bbox中是有object,计算其confidence损失梯度的方法发生变化; object_scale = 5,
l.delta[best_index + 4] = l.object_scale * (iou - l.output[best_index + 4]) * logistic_gradient(l.output[best_index + 4]);
}
// yolov2 reorg层中map = 0, 不参与计算 【这是在yolo9000才参与计算】
if (l.map) class_id = l.map[class_id];
// 与yolov1相似, 该pred bbox中是有object,计算其class损失梯度; class_scale = 1
delta_region_class(l.output, l.delta, best_index + 5, class_id, l.classes, l.softmax_tree, l.class_scale, &avg_cat, l.focal_loss);
++count;// 正样本个数+1
++class_count;
}
}
//printf("\n");
#ifndef GPU
flatten(l.delta, l.w*l.h, size*l.n, l.batch, 0);
#endif
*(l.cost) = pow(mag_array(l.delta, l.outputs * l.batch), 2);
printf("Region Avg IOU: %f, Class: %f, Obj: %f, No Obj: %f, Avg Recall: %f, count: %d\n", avg_iou/count, avg_cat/class_count, avg_obj/count, avg_anyobj/(l.w*l.h*l.n*l.batch), recall/count, count);
}
后记
详细的代码注释结合上面的公式就大概能完整的对应上YOLOV2的损失函数了。当然可能还有一些小细节我有解释的失误,欢迎一起交流讨论。
参考
- https://github.com/hgpvision/darknet
- https://blog.csdn.net/caicaiatnbu/article/details/102923953
同期文章
- 【翻译】手把手教你用AlexeyAB版Darknet
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】一,框架总览
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】二,数据结构解析
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】三,加载数据进行训练
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】四,网络的前向传播和反向传播介绍以及layer的详细解析
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】五,卷积层的前向传播解析
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】六,卷积层的反向传播解析
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】七,YOLOV1损失函数代码详解(detection_layer.c)
欢迎关注GiantPandaCV, 在这里你将看到独家的深度学习分享,坚持原创,每天分享我们学习到的新鲜知识。( • ̀ω•́ )✧
有对文章相关的问题,或者想要加入交流群,欢迎添加BBuf微信:
![]()