ion orphaned memory
- Introduction
- ion orphaned memory
- How did it happen
- How to debug
- Graphicbuffer passed between processes
- Summary
Introduction
ION是google在Android4.0 ICS为了解决内存碎片管理而引入的通用内存管理器,用来支持不同的内存分配机制,如kmalloc, vmalloc …
用户空间和内核空间都可以使用ION,ION有几个重要的概念:
- ion_client: 用struct ion_client表示, ION的使用者。用户空间和内核控件要使用ION,必须先创建一个ion_client。
- ion_handle: 用struct ion_handle表示,将buffer抽象出来,可以认为ION用handle来管理buffer,用户直接拿到的是handle,而不是buffer。
- ion_heap:用struct ion_heap 表示,代表分配内存的类型,可以是物理连续、不连续的或提前reserved.
- ion_buffer: 用struct ion_buffer表示,代表一块内存
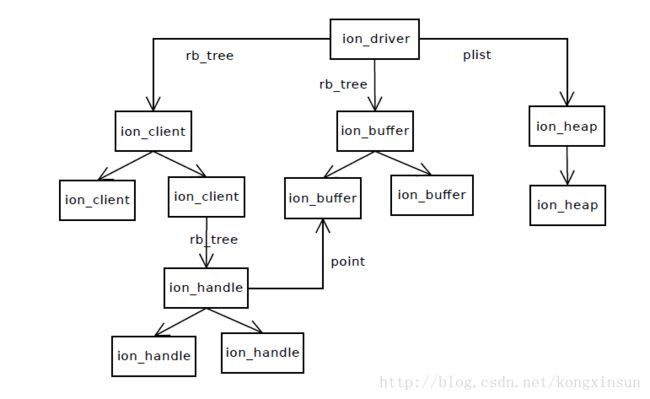
它们之间的关系图如下:
ion_client 和ion_buffer 以红黑树的形式组织在 ion_driver上 。不同的ion_heap以plist的形式组织到ion_driver上。 ion_handle也是以红黑树的形式组织到ion_client上,ion_client有指向ion_driver的指针。同样ion_handle有指向ion_client的指针,和指向它所对应的ion_buffer的指针。
ION是通过handle而非buffer地址来实现驱动间共享内存,用户空间共享内存也是利用同样原理。当ion client分配buffer时,相应的一个唯一的handle也会被指定。Handle有指向client和buffer的指针。
handle用ref表示指向它的client计数 ;buffer用ref 表示使用这块buffer的计数,用handle_count表示指向它的handle计数。
分配时buffer ref会加1, 释放时 buffer ref会减1
此外,shared/map时, buffer ref 也会加1 。
ion orphaned memory
ion orphaned memory: 这种类型的内存是指handle_count 为0,但是ref 大于0 的ion_buffer。
ion orphaned 的内存相当于泄漏的内存。可以在ion debugfs heap 节点中查看到:
cat /d/ion/heaps/carveout_ion
cat /d/ion/heaps/vmalloc_ion
cat /d/ion/heaps/cma_ionHow did it happen
用户空间如果想使用ION,必须先要创建ion_client。通过IOCTL来分配内存的,cmd为ION_IOC_ALLOC。分配好了buffer之后,如果用户空间想使用buffer,先需要mmap。ION是通过调用IOCTL中的ION_IOC_SHARE/ION_IOC_MAP来得到可以mmap的fd。
然后,你也可以将此fd传给另一个进程,如通过binder传递。
那么问题来了,如果,这个传到其它进程的fd,在使用完后,没有close;而buffer已经调用过ion_free,就会造成ion orphaned 的内存。
比如以下代码段:
ion_client = ion_open();
ion_alloc(ion_client, 4096, 0, ION_HEAP_SYSTEM_MASK, ion_flags, &ion_hnd);
ion_share(ion_client, ion_hnd, &shared_fd);
ion_free(ion_client, ion_hnd);当然用户空间一般不会这么操作,用户空间使用ion通常都是gralloc申请GraphicBuffer,由Gralloc HAL完成。
How to debug
通常使用ion的是gralloc,而gralloc是由surfaceflinger使用的。所以看到占用ion内存的是surfaceflinger。上层和ion buffer相对应的是graphicbuffer对象(C++层的)。这个graphicbuffer对象隶属于GraphicbufferProducer对象。
但是所有的graphicbuffer都是通过单例graphicbufferAlloctor对象来分配的。由于是单例,所以可以用来追踪graphicbuffer。
surfaceflinger在dequeue buffer时,会通过graphicbufferAlloctor调用gralloc模块分配ion buffer。在这个过程中:
- ion driver 返回到gralloc的是一个ion_handle. 这个ion_handle在driver里与ion buffer对应。此时,ion buffer的ion_handle值(指向它的ion_handle数)为1, ref的值也为1。
- gralloc 除了做ion_alloc动作外,还会做ion_share。ion share driver会返回一个fd,这个fd 是一个dma buffer,保存在handle的shared_fd中。
- 经过ion_alloc和ion_share后,ion driver里这个ion buffer的ion_handle值为1, ref值为2。ref为2是因为,ion alloc时+1;ion share时+1。
Surfaceflinger分配得到了graphicbuffer对象,graphicbuffer对象里有个handle,是private_handle_t类型(继承native_handle)。这个handle里有两个fd,一个指向dmabuf,也就是通过ion_shared得到的,另一个指ashmem。
假如surfaceflinger 将这个graphicbuffer可以通过binder传递给进程A,这时进程A得到一个graphicbuffer,其中有一个fd,指向这个dmabuf。当surfaceflinger调用ion_free, 释放ion_handle后;但是进程A使用后,如果没有释放。就会产生ion orphaned buffer。
Graphicbuffer passed between processes
Graphicbuffer 的传递是通过binder进行的,传递时parcel里会调graphicBuffer的flatten,它的fd会通过writeDupFileDescriptor把这个fd传递给其它的进程。
frameworks/native/libs/binder/Parcel.cpp
status_t Parcel::write(const FlattenableHelperInterface& val)
{
status_t err;
...
err = val.flatten(buf, len, fds, fd_count);
for (size_t i=0 ; iwriteDupFileDescriptor( fds[i] );
}
if (fd_count) {
delete [] fds;
}
return err;
} binder driver里,会通过这个fd找到对应的struct file,然后在target process里申请一个fd,和这个file关联上。fget会增加file的ref值,fput会减小这个ref值。
drivers/staging/android/binder.c
static int binder_translate_fd(int fd,
struct binder_transaction *t,
struct binder_thread *thread,
struct binder_transaction *in_reply_to)
{
struct binder_proc *proc = thread->proc;
struct binder_proc *target_proc = t->to_proc;
int target_fd;
struct file *file;
int ret;
bool target_allows_fd;
if (in_reply_to)
target_allows_fd = !!(in_reply_to->flags & TF_ACCEPT_FDS);
else
target_allows_fd = t->buffer->target_node->accept_fds;
if (!target_allows_fd) {
binder_user_error("%d:%d got %s with fd, %d, but target does not allow fds\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
in_reply_to ? "reply" : "transaction",
fd);
ret = -EPERM;
goto err_fd_not_accepted;
}
file = fget(fd);
if (!file) {
binder_user_error("%d:%d got transaction with invalid fd, %d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, fd);
ret = -EBADF;
goto err_fget;
}
ret = security_binder_transfer_file(proc->tsk, target_proc->tsk, file);
if (ret < 0) {
ret = -EPERM;
goto err_security;
}
target_fd = task_get_unused_fd_flags(target_proc, O_CLOEXEC);
if (target_fd < 0) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err_get_unused_fd;
}
task_fd_install(target_proc, target_fd, file);
trace_binder_transaction_fd(t, fd, target_fd);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_TRANSACTION, " fd %d -> %d\n",
fd, target_fd);
return target_fd;
err_get_unused_fd:
err_security:
fput(file);
err_fget:
err_fd_not_accepted:
return ret;
}所以当Graphicbuffer通过binder传递到其它进程时,相关的fd也会传递。在这个过程中ion driver不会参与。相应struct file上的ref记数会加1。所以对应的ion binder的ref还会是2。
假如这个时候,surfacelinger调用ion_free把ion_handle释放掉。此时,ion_buffer的handle_count会为0,ref为1,就是orphaned状态。只有dmabuff对应的struct file上的ref全为0时,才会释放。也就是这个dmabuff上的fd全部关掉。
但是如果在传递过程中,fd已经传递完成,Graphicbuffer在unflatten时,出错,fd没有close的话,就会导致 ion orphaned buffer的出现。如下面这段代码
frameworks/native/libs/ui/GraphicBuffer.cpp (7.1)
status_t GraphicBuffer::unflatten(
void const*& buffer, size_t& size, int const*& fds, size_t& count) {
...
if (handle != 0) {
status_t err = mBufferMapper.registerBuffer(this);
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
width = height = stride = format = usage = 0;
handle = NULL;
ALOGE("unflatten: registerBuffer failed: %s (%d)",
strerror(-err), err);
return err;
}
}
...
}
如果,registerBuffer出错,handle会被赋值NULL。但是这是fd已经传递完成。会导致这个fd没有close。从而出现ion orphaned的内存。好在AOSP 8.0上已经fix了。
Summary
从驱动的角度看,ion orphaned的内存是上层进程没有关掉指向dmabuf的fd。上层进程有graphicBuffer对象没有释放。
由于graphicbuffer对象可以通过binder在进程间传递,所以比较难追踪。当出现ion orphaned的内存时,要确认是哪个模块hold住了。可以kill进程,然后看是否会释放。比如kill mediaserver后,发现释放了,这个锅就是mediaserver去背了