x264源代码简单分析:x264命令行工具(x264.exe)
=====================================================
H.264源代码分析文章列表:
【编码 - x264】
x264源代码简单分析:概述
x264源代码简单分析:x264命令行工具(x264.exe)
x264源代码简单分析:编码器主干部分-1
x264源代码简单分析:编码器主干部分-2
x264源代码简单分析:x264_slice_write()
x264源代码简单分析:滤波(Filter)部分
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
x264源代码简单分析:宏块编码(Encode)部分
x264源代码简单分析:熵编码(Entropy Encoding)部分
FFmpeg与libx264接口源代码简单分析
【解码 - libavcodec H.264 解码器】
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:概述
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解析器(Parser)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解码器主干部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:熵解码(EntropyDecoding)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:环路滤波(Loop Filter)部分
=====================================================
本文简单分析x264项目中的命令行工具(x264.exe)的源代码。该命令行工具可以调用libx264将YUV格式像素数据编码为H.264码流。
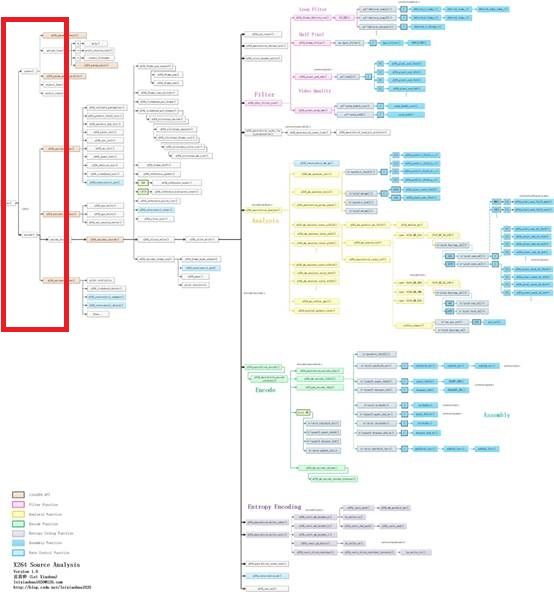
函数调用关系图
X264命令行工具的源代码在x264中的位置如下图所示。
X264命令行工具的源代码的调用关系如下图所示。
从图中可以看出,X264命令行工具调用了libx264的几个API完成了H.264编码工作。使用libx264的API进行编码可以参考《 最简单的视频编码器:基于libx264(编码YUV为H.264)》,这个流程中最关键的API包括:
x264_param_default():设置参数集结构体x264_param_t的缺省值。
x264_encoder_open():打开编码器。
x264_encoder_headers():输出SPS,PPS,SEI等信息。
x264_encoder_encode():编码输出一帧图像。
x264_encoder_close():关闭编码器。
在X264命令行工具中,main()首先调用parse()解析输入的命令行参数,然后调用encode()进行编码。parse()首先调用x264_param_default()为存储参数的结构体x264_param_t赋默认值;然后在一个大循环中调用getopt_long()逐个解析输入的参数,并作相应的处理;最后调用select_input()和select_output()解析输入文件格式(例如yuv,y4m…)和输出文件格式(例如raw,flv,MP4…)。encode()首先调用x264_encoder_open()打开H.264编码器,然后调用x264_encoder_headers()输出H.264码流的头信息(例如SPS、PPS、SEI),接着进入一个循环并且调用encode_frame()逐帧编码视频,最后调用x264_encoder_close()关闭解码器。其中encode_frame()中又调用了x264_encoder_encode()完成了具体的编码工作。下文将会对上述流程展开分析。
main()
main()是x264控制台程序的入口函数,定义如下所示。//主函数
int main( int argc, char **argv )
{
//参数集
x264_param_t param;
cli_opt_t opt = {0};
int ret = 0;
FAIL_IF_ERROR( x264_threading_init(), "unable to initialize threading\n" )
#ifdef _WIN32
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !get_argv_utf8( &argc, &argv ), "unable to convert command line to UTF-8\n" )
GetConsoleTitleW( org_console_title, CONSOLE_TITLE_SIZE );
_setmode( _fileno( stdin ), _O_BINARY );
_setmode( _fileno( stdout ), _O_BINARY );
_setmode( _fileno( stderr ), _O_BINARY );
#endif
/* Parse command line */
//解析命令行输入
if( parse( argc, argv, ¶m, &opt ) < 0 )
ret = -1;
#ifdef _WIN32
/* Restore title; it can be changed by input modules */
SetConsoleTitleW( org_console_title );
#endif
/* Control-C handler */
signal( SIGINT, sigint_handler );
//编码
if( !ret )
ret = encode( ¶m, &opt );
/* clean up handles */
if( filter.free )
filter.free( opt.hin );
else if( opt.hin )
cli_input.close_file( opt.hin );
if( opt.hout )
cli_output.close_file( opt.hout, 0, 0 );
if( opt.tcfile_out )
fclose( opt.tcfile_out );
if( opt.qpfile )
fclose( opt.qpfile );
#ifdef _WIN32
SetConsoleTitleW( org_console_title );
free( argv );
#endif
return ret;
}
可以看出main()的定义很简单,它主要调用了两个函数:parse()和encode()。main()首先调用parse()解析输入的命令行参数,然后调用encode()进行编码。下面分别分析这两个函数。
parse()
parse()用于解析命令行输入的参数(存储于argv[]中)。它的定义如下所示。//解析命令行输入
static int parse( int argc, char **argv, x264_param_t *param, cli_opt_t *opt )
{
char *input_filename = NULL;
const char *demuxer = demuxer_names[0];
char *output_filename = NULL;
const char *muxer = muxer_names[0];
char *tcfile_name = NULL;
x264_param_t defaults;
char *profile = NULL;
char *vid_filters = NULL;
int b_thread_input = 0;
int b_turbo = 1;
int b_user_ref = 0;
int b_user_fps = 0;
int b_user_interlaced = 0;
cli_input_opt_t input_opt;
cli_output_opt_t output_opt;
char *preset = NULL;
char *tune = NULL;
//初始化参数默认值
x264_param_default( &defaults );
cli_log_level = defaults.i_log_level;
memset( &input_opt, 0, sizeof(cli_input_opt_t) );
memset( &output_opt, 0, sizeof(cli_output_opt_t) );
input_opt.bit_depth = 8;
input_opt.input_range = input_opt.output_range = param->vui.b_fullrange = RANGE_AUTO;
int output_csp = defaults.i_csp;
opt->b_progress = 1;
/* Presets are applied before all other options. */
for( optind = 0;; )
{
int c = getopt_long( argc, argv, short_options, long_options, NULL );
if( c == -1 )
break;
if( c == OPT_PRESET )
preset = optarg;
if( c == OPT_TUNE )
tune = optarg;
else if( c == '?' )
return -1;
}
if( preset && !strcasecmp( preset, "placebo" ) )
b_turbo = 0;
//设置preset,tune
if( x264_param_default_preset( param, preset, tune ) < 0 )
return -1;
/* Parse command line options */
//解析命令行选项
for( optind = 0;; )
{
int b_error = 0;
int long_options_index = -1;
int c = getopt_long( argc, argv, short_options, long_options, &long_options_index );
if( c == -1 )
{
break;
}
//不同的选项做不同的处理
switch( c )
{
case 'h':
help( &defaults, 0 );//"-h"帮助菜单
exit(0);
case OPT_LONGHELP:
help( &defaults, 1 );
exit(0);
case OPT_FULLHELP:
help( &defaults, 2 );
exit(0);
case 'V':
print_version_info();//打印版本信息
exit(0);
case OPT_FRAMES:
param->i_frame_total = X264_MAX( atoi( optarg ), 0 );
break;
case OPT_SEEK:
opt->i_seek = X264_MAX( atoi( optarg ), 0 );
break;
case 'o':
output_filename = optarg;//输出文件路径
break;
case OPT_MUXER:
FAIL_IF_ERROR( parse_enum_name( optarg, muxer_names, &muxer ), "Unknown muxer `%s'\n", optarg )
break;
case OPT_DEMUXER:
FAIL_IF_ERROR( parse_enum_name( optarg, demuxer_names, &demuxer ), "Unknown demuxer `%s'\n", optarg )
break;
case OPT_INDEX:
input_opt.index_file = optarg;
break;
case OPT_QPFILE:
opt->qpfile = x264_fopen( optarg, "rb" );
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !opt->qpfile, "can't open qpfile `%s'\n", optarg )
if( !x264_is_regular_file( opt->qpfile ) )
{
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_ERROR, "qpfile incompatible with non-regular file `%s'\n", optarg );
fclose( opt->qpfile );
return -1;
}
break;
case OPT_THREAD_INPUT:
b_thread_input = 1;
break;
case OPT_QUIET:
cli_log_level = param->i_log_level = X264_LOG_NONE;//设置log级别
break;
case 'v':
cli_log_level = param->i_log_level = X264_LOG_DEBUG;//设置log级别
break;
case OPT_LOG_LEVEL:
if( !parse_enum_value( optarg, log_level_names, &cli_log_level ) )
cli_log_level += X264_LOG_NONE;
else
cli_log_level = atoi( optarg );
param->i_log_level = cli_log_level;//设置log级别
break;
case OPT_NOPROGRESS:
opt->b_progress = 0;
break;
case OPT_TUNE:
case OPT_PRESET:
break;
case OPT_PROFILE:
profile = optarg;
break;
case OPT_SLOWFIRSTPASS:
b_turbo = 0;
break;
case 'r':
b_user_ref = 1;
goto generic_option;
case OPT_FPS:
b_user_fps = 1;
param->b_vfr_input = 0;
goto generic_option;
case OPT_INTERLACED:
b_user_interlaced = 1;
goto generic_option;
case OPT_TCFILE_IN:
tcfile_name = optarg;
break;
case OPT_TCFILE_OUT:
opt->tcfile_out = x264_fopen( optarg, "wb" );
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !opt->tcfile_out, "can't open `%s'\n", optarg )
break;
case OPT_TIMEBASE:
input_opt.timebase = optarg;
break;
case OPT_PULLDOWN:
FAIL_IF_ERROR( parse_enum_value( optarg, pulldown_names, &opt->i_pulldown ), "Unknown pulldown `%s'\n", optarg )
break;
case OPT_VIDEO_FILTER:
vid_filters = optarg;
break;
case OPT_INPUT_FMT:
input_opt.format = optarg;//输入文件格式
break;
case OPT_INPUT_RES:
input_opt.resolution = optarg;//输入分辨率
break;
case OPT_INPUT_CSP:
input_opt.colorspace = optarg;//输入色域
break;
case OPT_INPUT_DEPTH:
input_opt.bit_depth = atoi( optarg );//输入颜色位深
break;
case OPT_DTS_COMPRESSION:
output_opt.use_dts_compress = 1;
break;
case OPT_OUTPUT_CSP:
FAIL_IF_ERROR( parse_enum_value( optarg, output_csp_names, &output_csp ), "Unknown output csp `%s'\n", optarg )
// correct the parsed value to the libx264 csp value
#if X264_CHROMA_FORMAT
static const uint8_t output_csp_fix[] = { X264_CHROMA_FORMAT, X264_CSP_RGB };
#else
static const uint8_t output_csp_fix[] = { X264_CSP_I420, X264_CSP_I422, X264_CSP_I444, X264_CSP_RGB };
#endif
param->i_csp = output_csp = output_csp_fix[output_csp];
break;
case OPT_INPUT_RANGE:
FAIL_IF_ERROR( parse_enum_value( optarg, range_names, &input_opt.input_range ), "Unknown input range `%s'\n", optarg )
input_opt.input_range += RANGE_AUTO;
break;
case OPT_RANGE:
FAIL_IF_ERROR( parse_enum_value( optarg, range_names, ¶m->vui.b_fullrange ), "Unknown range `%s'\n", optarg );
input_opt.output_range = param->vui.b_fullrange += RANGE_AUTO;
break;
default:
generic_option:
{
if( long_options_index < 0 )
{
for( int i = 0; long_options[i].name; i++ )
if( long_options[i].val == c )
{
long_options_index = i;
break;
}
if( long_options_index < 0 )
{
/* getopt_long already printed an error message */
return -1;
}
}
//解析以字符串方式输入的参数
//即选项名称和选项值都是字符串
b_error |= x264_param_parse( param, long_options[long_options_index].name, optarg );
}
}
if( b_error )
{
const char *name = long_options_index > 0 ? long_options[long_options_index].name : argv[optind-2];
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_ERROR, "invalid argument: %s = %s\n", name, optarg );
return -1;
}
}
/* If first pass mode is used, apply faster settings. */
if( b_turbo )
x264_param_apply_fastfirstpass( param );
/* Apply profile restrictions. */
//设置profile
if( x264_param_apply_profile( param, profile ) < 0 )
return -1;
/* Get the file name */
FAIL_IF_ERROR( optind > argc - 1 || !output_filename, "No %s file. Run x264 --help for a list of options.\n",
optind > argc - 1 ? "input" : "output" )
//根据文件名的后缀确定输出的文件格式(raw H264,flv,mp4...)
if( select_output( muxer, output_filename, param ) )
return -1;
FAIL_IF_ERROR( cli_output.open_file( output_filename, &opt->hout, &output_opt ), "could not open output file `%s'\n", output_filename )
//输入文件路径
input_filename = argv[optind++];
video_info_t info = {0};
char demuxername[5];
/* set info flags to be overwritten by demuxer as necessary. */
//设置info结构体
info.csp = param->i_csp;
info.fps_num = param->i_fps_num;
info.fps_den = param->i_fps_den;
info.fullrange = input_opt.input_range == RANGE_PC;
info.interlaced = param->b_interlaced;
if( param->vui.i_sar_width > 0 && param->vui.i_sar_height > 0 )
{
info.sar_width = param->vui.i_sar_width;
info.sar_height = param->vui.i_sar_height;
}
info.tff = param->b_tff;
info.vfr = param->b_vfr_input;
input_opt.seek = opt->i_seek;
input_opt.progress = opt->b_progress;
input_opt.output_csp = output_csp;
//设置输入文件的格式(yuv,y4m...)
if( select_input( demuxer, demuxername, input_filename, &opt->hin, &info, &input_opt ) )
return -1;
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !opt->hin && cli_input.open_file( input_filename, &opt->hin, &info, &input_opt ),
"could not open input file `%s'\n", input_filename )
x264_reduce_fraction( &info.sar_width, &info.sar_height );
x264_reduce_fraction( &info.fps_num, &info.fps_den );
x264_cli_log( demuxername, X264_LOG_INFO, "%dx%d%c %u:%u @ %u/%u fps (%cfr)\n", info.width,
info.height, info.interlaced ? 'i' : 'p', info.sar_width, info.sar_height,
info.fps_num, info.fps_den, info.vfr ? 'v' : 'c' );
if( tcfile_name )
{
FAIL_IF_ERROR( b_user_fps, "--fps + --tcfile-in is incompatible.\n" )
FAIL_IF_ERROR( timecode_input.open_file( tcfile_name, &opt->hin, &info, &input_opt ), "timecode input failed\n" )
cli_input = timecode_input;
}
else FAIL_IF_ERROR( !info.vfr && input_opt.timebase, "--timebase is incompatible with cfr input\n" )
/* init threaded input while the information about the input video is unaltered by filtering */
#if HAVE_THREAD
if( info.thread_safe && (b_thread_input || param->i_threads > 1
|| (param->i_threads == X264_THREADS_AUTO && x264_cpu_num_processors() > 1)) )
{
if( thread_input.open_file( NULL, &opt->hin, &info, NULL ) )
{
fprintf( stderr, "x264 [error]: threaded input failed\n" );
return -1;
}
cli_input = thread_input;
}
#endif
/* override detected values by those specified by the user */
if( param->vui.i_sar_width > 0 && param->vui.i_sar_height > 0 )
{
info.sar_width = param->vui.i_sar_width;
info.sar_height = param->vui.i_sar_height;
}
if( b_user_fps )
{
info.fps_num = param->i_fps_num;
info.fps_den = param->i_fps_den;
}
if( !info.vfr )
{
info.timebase_num = info.fps_den;
info.timebase_den = info.fps_num;
}
if( !tcfile_name && input_opt.timebase )
{
uint64_t i_user_timebase_num;
uint64_t i_user_timebase_den;
int ret = sscanf( input_opt.timebase, "%"SCNu64"/%"SCNu64, &i_user_timebase_num, &i_user_timebase_den );
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !ret, "invalid argument: timebase = %s\n", input_opt.timebase )
else if( ret == 1 )
{
i_user_timebase_num = info.timebase_num;
i_user_timebase_den = strtoul( input_opt.timebase, NULL, 10 );
}
FAIL_IF_ERROR( i_user_timebase_num > UINT32_MAX || i_user_timebase_den > UINT32_MAX,
"timebase you specified exceeds H.264 maximum\n" )
opt->timebase_convert_multiplier = ((double)i_user_timebase_den / info.timebase_den)
* ((double)info.timebase_num / i_user_timebase_num);
info.timebase_num = i_user_timebase_num;
info.timebase_den = i_user_timebase_den;
info.vfr = 1;
}
if( b_user_interlaced )
{
info.interlaced = param->b_interlaced;
info.tff = param->b_tff;
}
if( input_opt.input_range != RANGE_AUTO )
info.fullrange = input_opt.input_range;
//初始化滤镜filter
//filter可以认为是一种“扩展”了的输入源
if( init_vid_filters( vid_filters, &opt->hin, &info, param, output_csp ) )
return -1;
/* set param flags from the post-filtered video */
param->b_vfr_input = info.vfr;
param->i_fps_num = info.fps_num;
param->i_fps_den = info.fps_den;
param->i_timebase_num = info.timebase_num;
param->i_timebase_den = info.timebase_den;
param->vui.i_sar_width = info.sar_width;
param->vui.i_sar_height = info.sar_height;
info.num_frames = X264_MAX( info.num_frames - opt->i_seek, 0 );
if( (!info.num_frames || param->i_frame_total < info.num_frames)
&& param->i_frame_total > 0 )
info.num_frames = param->i_frame_total;
param->i_frame_total = info.num_frames;
if( !b_user_interlaced && info.interlaced )
{
#if HAVE_INTERLACED
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_WARNING, "input appears to be interlaced, enabling %cff interlaced mode.\n"
" If you want otherwise, use --no-interlaced or --%cff\n",
info.tff ? 't' : 'b', info.tff ? 'b' : 't' );
param->b_interlaced = 1;
param->b_tff = !!info.tff;
#else
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_WARNING, "input appears to be interlaced, but not compiled with interlaced support\n" );
#endif
}
/* if the user never specified the output range and the input is now rgb, default it to pc */
int csp = param->i_csp & X264_CSP_MASK;
if( csp >= X264_CSP_BGR && csp <= X264_CSP_RGB )
{
if( input_opt.output_range == RANGE_AUTO )
param->vui.b_fullrange = RANGE_PC;
/* otherwise fail if they specified tv */
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !param->vui.b_fullrange, "RGB must be PC range" )
}
/* Automatically reduce reference frame count to match the user's target level
* if the user didn't explicitly set a reference frame count. */
if( !b_user_ref )
{
int mbs = (((param->i_width)+15)>>4) * (((param->i_height)+15)>>4);
for( int i = 0; x264_levels[i].level_idc != 0; i++ )
if( param->i_level_idc == x264_levels[i].level_idc )
{
while( mbs * param->i_frame_reference > x264_levels[i].dpb && param->i_frame_reference > 1 )
param->i_frame_reference--;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
下面简单梳理parse()的流程:
(1)调用x264_param_default()为存储参数的结构体x264_param_t赋默认值
(2)调用x264_param_default_preset()为x264_param_t赋值
(3)在一个大循环中调用getopt_long()逐个解析输入的参数,并作相应的处理。举几个例子:a)“-h”:调用help()打开帮助菜单。b)“-V”调用print_version_info()打印版本信息。c)对于长选项,调用x264_param_parse()进行处理。(4)调用select_input()解析输出文件格式(例如raw,flv,MP4…)
(5)调用select_output()解析输入文件格式(例如yuv,y4m…)
下文按照顺序记录parse()中涉及到的函数:
x264_param_default()
x264_param_default_preset()
help()
print_version_info()
x264_param_parse()
select_input()
select_output()
x264_param_default()
x264_param_default()是一个x264的API。该函数用于设置x264中x264_param_t结构体的默认值。函数的声明如下所示。/* x264_param_default:
* fill x264_param_t with default values and do CPU detection */
void x264_param_default( x264_param_t * );/****************************************************************************
* x264_param_default:
****************************************************************************/
//初始化参数默认值
void x264_param_default( x264_param_t *param )
{
/* */
memset( param, 0, sizeof( x264_param_t ) );
/* CPU autodetect */
param->cpu = x264_cpu_detect();
param->i_threads = X264_THREADS_AUTO;
param->i_lookahead_threads = X264_THREADS_AUTO;
param->b_deterministic = 1;
param->i_sync_lookahead = X264_SYNC_LOOKAHEAD_AUTO;
/* Video properties */
param->i_csp = X264_CHROMA_FORMAT ? X264_CHROMA_FORMAT : X264_CSP_I420;
param->i_width = 0;
param->i_height = 0;
param->vui.i_sar_width = 0;
param->vui.i_sar_height= 0;
param->vui.i_overscan = 0; /* undef */
param->vui.i_vidformat = 5; /* undef */
param->vui.b_fullrange = -1; /* default depends on input */
param->vui.i_colorprim = 2; /* undef */
param->vui.i_transfer = 2; /* undef */
param->vui.i_colmatrix = -1; /* default depends on input */
param->vui.i_chroma_loc= 0; /* left center */
param->i_fps_num = 25;
param->i_fps_den = 1;
param->i_level_idc = -1;
param->i_slice_max_size = 0;
param->i_slice_max_mbs = 0;
param->i_slice_count = 0;
/* Encoder parameters */
//编码参数--最常见
param->i_frame_reference = 3;
param->i_keyint_max = 250;
param->i_keyint_min = X264_KEYINT_MIN_AUTO;
param->i_bframe = 3;
param->i_scenecut_threshold = 40;
param->i_bframe_adaptive = X264_B_ADAPT_FAST;
param->i_bframe_bias = 0;
param->i_bframe_pyramid = X264_B_PYRAMID_NORMAL;
param->b_interlaced = 0;
param->b_constrained_intra = 0;
param->b_deblocking_filter = 1;
param->i_deblocking_filter_alphac0 = 0;
param->i_deblocking_filter_beta = 0;
param->b_cabac = 1;
param->i_cabac_init_idc = 0;
//码率控制模块 Rate Control
param->rc.i_rc_method = X264_RC_CRF;
param->rc.i_bitrate = 0;
param->rc.f_rate_tolerance = 1.0;
param->rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate = 0;
param->rc.i_vbv_buffer_size = 0;
param->rc.f_vbv_buffer_init = 0.9;
param->rc.i_qp_constant = 23 + QP_BD_OFFSET;
param->rc.f_rf_constant = 23;
param->rc.i_qp_min = 0;
param->rc.i_qp_max = QP_MAX;
param->rc.i_qp_step = 4;
param->rc.f_ip_factor = 1.4;
param->rc.f_pb_factor = 1.3;
param->rc.i_aq_mode = X264_AQ_VARIANCE;
param->rc.f_aq_strength = 1.0;
param->rc.i_lookahead = 40;
param->rc.b_stat_write = 0;
param->rc.psz_stat_out = "x264_2pass.log";
param->rc.b_stat_read = 0;
param->rc.psz_stat_in = "x264_2pass.log";
param->rc.f_qcompress = 0.6;
param->rc.f_qblur = 0.5;
param->rc.f_complexity_blur = 20;
param->rc.i_zones = 0;
param->rc.b_mb_tree = 1;
/* Log */
//日志模块
param->pf_log = x264_log_default;
param->p_log_private = NULL;
param->i_log_level = X264_LOG_INFO;
/* */
//分析模块 Analysis
param->analyse.intra = X264_ANALYSE_I4x4 | X264_ANALYSE_I8x8;
param->analyse.inter = X264_ANALYSE_I4x4 | X264_ANALYSE_I8x8
| X264_ANALYSE_PSUB16x16 | X264_ANALYSE_BSUB16x16;
param->analyse.i_direct_mv_pred = X264_DIRECT_PRED_SPATIAL;
param->analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_HEX;
param->analyse.f_psy_rd = 1.0;
param->analyse.b_psy = 1;
param->analyse.f_psy_trellis = 0;
param->analyse.i_me_range = 16;
param->analyse.i_subpel_refine = 7;
param->analyse.b_mixed_references = 1;
param->analyse.b_chroma_me = 1;
param->analyse.i_mv_range_thread = -1;
param->analyse.i_mv_range = -1; // set from level_idc
param->analyse.i_chroma_qp_offset = 0;
param->analyse.b_fast_pskip = 1;
param->analyse.b_weighted_bipred = 1;
param->analyse.i_weighted_pred = X264_WEIGHTP_SMART;
param->analyse.b_dct_decimate = 1;
param->analyse.b_transform_8x8 = 1;
param->analyse.i_trellis = 1;
param->analyse.i_luma_deadzone[0] = 21;
param->analyse.i_luma_deadzone[1] = 11;
param->analyse.b_psnr = 0;
param->analyse.b_ssim = 0;
param->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_FLAT;
memset( param->cqm_4iy, 16, sizeof( param->cqm_4iy ) );
memset( param->cqm_4py, 16, sizeof( param->cqm_4py ) );
memset( param->cqm_4ic, 16, sizeof( param->cqm_4ic ) );
memset( param->cqm_4pc, 16, sizeof( param->cqm_4pc ) );
memset( param->cqm_8iy, 16, sizeof( param->cqm_8iy ) );
memset( param->cqm_8py, 16, sizeof( param->cqm_8py ) );
memset( param->cqm_8ic, 16, sizeof( param->cqm_8ic ) );
memset( param->cqm_8pc, 16, sizeof( param->cqm_8pc ) );
param->b_repeat_headers = 1;
param->b_annexb = 1;
param->b_aud = 0;
param->b_vfr_input = 1;
param->i_nal_hrd = X264_NAL_HRD_NONE;
param->b_tff = 1;
param->b_pic_struct = 0;
param->b_fake_interlaced = 0;
param->i_frame_packing = -1;
param->b_opencl = 0;
param->i_opencl_device = 0;
param->opencl_device_id = NULL;
param->psz_clbin_file = NULL;
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_param_default()对输入的存储参数的结构体x264_param_t的成员变量进行了赋值工作。
x264_param_default_preset()
x264_param_default_preset()是一个libx264的API,用于设置x264的preset和tune。该函数的声明如下所示。/* Multiple tunings can be used if separated by a delimiter in ",./-+",
* however multiple psy tunings cannot be used.
* film, animation, grain, stillimage, psnr, and ssim are psy tunings.
*
* returns 0 on success, negative on failure (e.g. invalid preset/tune name). */
int x264_param_default_preset( x264_param_t *, const char *preset, const char *tune );//设置preset,tune
int x264_param_default_preset( x264_param_t *param, const char *preset, const char *tune )
{
x264_param_default( param );
//设置preset
if( preset && x264_param_apply_preset( param, preset ) < 0 )
return -1;
//设置tune
if( tune && x264_param_apply_tune( param, tune ) < 0 )
return -1;
return 0;
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_param_default_preset()调用x264_param_apply_preset()设置preset,调用x264_param_apply_tune()设置tune。记录一下这两个函数。
x264_param_apply_preset()
x264_param_apply_preset()用于设置preset。该函数的定义如下所示。
//设置preset
static int x264_param_apply_preset( x264_param_t *param, const char *preset )
{
char *end;
int i = strtol( preset, &end, 10 );
if( *end == 0 && i >= 0 && i < sizeof(x264_preset_names)/sizeof(*x264_preset_names)-1 )
preset = x264_preset_names[i];
//几种不同的preset设置不同的参数
if( !strcasecmp( preset, "ultrafast" ) )
{
param->i_frame_reference = 1;
param->i_scenecut_threshold = 0;
param->b_deblocking_filter = 0;//不使用去块滤波
param->b_cabac = 0;//不使用CABAC
param->i_bframe = 0;//不使用B帧
param->analyse.intra = 0;
param->analyse.inter = 0;
param->analyse.b_transform_8x8 = 0;//不使用8x8DCT
param->analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_DIA;//运动搜索方法使用“Diamond”
param->analyse.i_subpel_refine = 0;
param->rc.i_aq_mode = 0;
param->analyse.b_mixed_references = 0;
param->analyse.i_trellis = 0;
param->i_bframe_adaptive = X264_B_ADAPT_NONE;
param->rc.b_mb_tree = 0;
param->analyse.i_weighted_pred = X264_WEIGHTP_NONE;//不使用加权
param->analyse.b_weighted_bipred = 0;
param->rc.i_lookahead = 0;
}
else if( !strcasecmp( preset, "superfast" ) )
{
param->analyse.inter = X264_ANALYSE_I8x8|X264_ANALYSE_I4x4;
param->analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_DIA;//钻石模板
param->analyse.i_subpel_refine = 1;//亚像素运动估计质量为1
param->i_frame_reference = 1;
param->analyse.b_mixed_references = 0;
param->analyse.i_trellis = 0;
param->rc.b_mb_tree = 0;
param->analyse.i_weighted_pred = X264_WEIGHTP_SIMPLE;
param->rc.i_lookahead = 0;
}
else if( !strcasecmp( preset, "veryfast" ) )
{
param->analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_HEX;//六边形模板
param->analyse.i_subpel_refine = 2;
param->i_frame_reference = 1;
param->analyse.b_mixed_references = 0;
param->analyse.i_trellis = 0;
param->analyse.i_weighted_pred = X264_WEIGHTP_SIMPLE;
param->rc.i_lookahead = 10;
}
else if( !strcasecmp( preset, "faster" ) )
{
param->analyse.b_mixed_references = 0;
param->i_frame_reference = 2;
param->analyse.i_subpel_refine = 4;
param->analyse.i_weighted_pred = X264_WEIGHTP_SIMPLE;
param->rc.i_lookahead = 20;
}
else if( !strcasecmp( preset, "fast" ) )
{
param->i_frame_reference = 2;
param->analyse.i_subpel_refine = 6;
param->analyse.i_weighted_pred = X264_WEIGHTP_SIMPLE;
param->rc.i_lookahead = 30;
}
else if( !strcasecmp( preset, "medium" ) )
{
/* Default is medium */
}
else if( !strcasecmp( preset, "slow" ) )
{
param->analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_UMH;//UMH相对复杂
param->analyse.i_subpel_refine = 8;//亚像素运动估计质量为8
param->i_frame_reference = 5;
param->i_bframe_adaptive = X264_B_ADAPT_TRELLIS;
param->analyse.i_direct_mv_pred = X264_DIRECT_PRED_AUTO;
param->rc.i_lookahead = 50;
}
else if( !strcasecmp( preset, "slower" ) )
{
param->analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_UMH;
param->analyse.i_subpel_refine = 9;
param->i_frame_reference = 8;
param->i_bframe_adaptive = X264_B_ADAPT_TRELLIS;
param->analyse.i_direct_mv_pred = X264_DIRECT_PRED_AUTO;
param->analyse.inter |= X264_ANALYSE_PSUB8x8;
param->analyse.i_trellis = 2;
param->rc.i_lookahead = 60;
}
else if( !strcasecmp( preset, "veryslow" ) )
{
param->analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_UMH;
param->analyse.i_subpel_refine = 10;
param->analyse.i_me_range = 24;
param->i_frame_reference = 16;
param->i_bframe_adaptive = X264_B_ADAPT_TRELLIS;
param->analyse.i_direct_mv_pred = X264_DIRECT_PRED_AUTO;
param->analyse.inter |= X264_ANALYSE_PSUB8x8;
param->analyse.i_trellis = 2;
param->i_bframe = 8;
param->rc.i_lookahead = 60;
}
else if( !strcasecmp( preset, "placebo" ) )
{
param->analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_TESA;//TESA很慢
param->analyse.i_subpel_refine = 11;
param->analyse.i_me_range = 24;
param->i_frame_reference = 16;
param->i_bframe_adaptive = X264_B_ADAPT_TRELLIS;
param->analyse.i_direct_mv_pred = X264_DIRECT_PRED_AUTO;
param->analyse.inter |= X264_ANALYSE_PSUB8x8;
param->analyse.b_fast_pskip = 0;
param->analyse.i_trellis = 2;
param->i_bframe = 16;
param->rc.i_lookahead = 60;
}
else
{
x264_log( NULL, X264_LOG_ERROR, "invalid preset '%s'\n", preset );
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
可以看出x264_param_apply_preset()通过strcasecmp()比较字符串的方法得到输入的preset类型;然后根据preset类型,设定 x264_param_t中相应的参数。
x264_param_apply_tune()
x264_param_apply_tune()用于设置tune。该函数的定义如下所示。
//设置tune
static int x264_param_apply_tune( x264_param_t *param, const char *tune )
{
char *tmp = x264_malloc( strlen( tune ) + 1 );
if( !tmp )
return -1;
tmp = strcpy( tmp, tune );
//分解一个字符串为一个字符串数组。第2个参数为分隔符
char *s = strtok( tmp, ",./-+" );
int psy_tuning_used = 0;
//设置
//这里是循环的,可以设置多次
while( s )
{
if( !strncasecmp( s, "film", 4 ) )
{
if( psy_tuning_used++ ) goto psy_failure;
param->i_deblocking_filter_alphac0 = -1;
param->i_deblocking_filter_beta = -1;
param->analyse.f_psy_trellis = 0.15;
}
else if( !strncasecmp( s, "animation", 9 ) )
{
if( psy_tuning_used++ ) goto psy_failure;
param->i_frame_reference = param->i_frame_reference > 1 ? param->i_frame_reference*2 : 1;
param->i_deblocking_filter_alphac0 = 1;
param->i_deblocking_filter_beta = 1;
param->analyse.f_psy_rd = 0.4;
param->rc.f_aq_strength = 0.6;
param->i_bframe += 2;
}
else if( !strncasecmp( s, "grain", 5 ) )
{
if( psy_tuning_used++ ) goto psy_failure;
param->i_deblocking_filter_alphac0 = -2;
param->i_deblocking_filter_beta = -2;
param->analyse.f_psy_trellis = 0.25;
param->analyse.b_dct_decimate = 0;
param->rc.f_pb_factor = 1.1;
param->rc.f_ip_factor = 1.1;
param->rc.f_aq_strength = 0.5;
param->analyse.i_luma_deadzone[0] = 6;
param->analyse.i_luma_deadzone[1] = 6;
param->rc.f_qcompress = 0.8;
}
else if( !strncasecmp( s, "stillimage", 10 ) )
{
if( psy_tuning_used++ ) goto psy_failure;
param->i_deblocking_filter_alphac0 = -3;
param->i_deblocking_filter_beta = -3;
param->analyse.f_psy_rd = 2.0;
param->analyse.f_psy_trellis = 0.7;
param->rc.f_aq_strength = 1.2;
}
else if( !strncasecmp( s, "psnr", 4 ) )
{
if( psy_tuning_used++ ) goto psy_failure;
param->rc.i_aq_mode = X264_AQ_NONE;
param->analyse.b_psy = 0;
}
else if( !strncasecmp( s, "ssim", 4 ) )
{
if( psy_tuning_used++ ) goto psy_failure;
param->rc.i_aq_mode = X264_AQ_AUTOVARIANCE;
param->analyse.b_psy = 0;
}
else if( !strncasecmp( s, "fastdecode", 10 ) )
{
param->b_deblocking_filter = 0;
param->b_cabac = 0;
param->analyse.b_weighted_bipred = 0;
param->analyse.i_weighted_pred = X264_WEIGHTP_NONE;
}
else if( !strncasecmp( s, "zerolatency", 11 ) )
{
//zerolatency速度快
param->rc.i_lookahead = 0;
param->i_sync_lookahead = 0;
param->i_bframe = 0;//不使用B帧
param->b_sliced_threads = 1;
param->b_vfr_input = 0;
param->rc.b_mb_tree = 0;
}
else if( !strncasecmp( s, "touhou", 6 ) )
{
if( psy_tuning_used++ ) goto psy_failure;
param->i_frame_reference = param->i_frame_reference > 1 ? param->i_frame_reference*2 : 1;
param->i_deblocking_filter_alphac0 = -1;
param->i_deblocking_filter_beta = -1;
param->analyse.f_psy_trellis = 0.2;
param->rc.f_aq_strength = 1.3;
if( param->analyse.inter & X264_ANALYSE_PSUB16x16 )
param->analyse.inter |= X264_ANALYSE_PSUB8x8;
}
else
{
x264_log( NULL, X264_LOG_ERROR, "invalid tune '%s'\n", s );
x264_free( tmp );
return -1;
}
if( 0 )
{
psy_failure:
x264_log( NULL, X264_LOG_WARNING, "only 1 psy tuning can be used: ignoring tune %s\n", s );
}
s = strtok( NULL, ",./-+" );
}
x264_free( tmp );
return 0;
}
可以看出x264_param_apply_tune()首先通过strtok()得到存储tune[]数组;然后通过strncasecmp()比较字符串的方法判断当前的tune类型;最后根据tune类型,设定 x264_param_t中相应的参数。
help()
help()用于打印帮助菜单。在x264命令行程序中添加“-h”参数后会调用该函数。该函数的定义如下所示。//帮助菜单
//longhelp标识是否展开更长的帮助菜单
static void help( x264_param_t *defaults, int longhelp )
{
char buf[50];
//H0(),H1(),H2()都是printf()
//H1(),H2()只有“长帮助菜单”的情况下才会调用printf()
#define H0 printf
#define H1 if(longhelp>=1) printf
#define H2 if(longhelp==2) printf
H0( "x264 core:%d%s\n"
"Syntax: x264 [options] -o outfile infile\n"
"\n"
"Infile can be raw (in which case resolution is required),\n"
" or YUV4MPEG (*.y4m),\n"
" or Avisynth if compiled with support (%s).\n"
" or libav* formats if compiled with lavf support (%s) or ffms support (%s).\n"
"Outfile type is selected by filename:\n"
" .264 -> Raw bytestream\n"
" .mkv -> Matroska\n"
" .flv -> Flash Video\n"
" .mp4 -> MP4 if compiled with GPAC or L-SMASH support (%s)\n"
"Output bit depth: %d (configured at compile time)\n"
"\n"
"Options:\n"
"\n"
" -h, --help List basic options\n"
" --longhelp List more options\n"
" --fullhelp List all options\n"
"\n",
X264_BUILD, X264_VERSION,
#if HAVE_AVS
"yes",
#else
"no",
#endif
#if HAVE_LAVF
"yes",
#else
"no",
#endif
#if HAVE_FFMS
"yes",
#else
"no",
#endif
#if HAVE_GPAC
"gpac",
#elif HAVE_LSMASH
"lsmash",
#else
"no",
#endif
x264_bit_depth
);
H0( "Example usage:\n" );
H0( "\n" );
H0( " Constant quality mode:\n" );
H0( " x264 --crf 24 -o help()中主要有3个宏定义:H0(),H1()和H2()。这三个宏定义实质上都是printf()。它们之间的区别在于:H0()无论如何都会调用print();H1()在longhelp大于等于1的时候才会调用print();而H2()在longhelp等于2时候才会调用print()。
print_version_info()
print_version_info()用于打印x264的版本信息。在x264命令行程序中添加“-V”参数后会调用该函数。该函数的定义如下所示。//打印版本信息
static void print_version_info( void )
{
#ifdef X264_POINTVER
printf( "x264 "X264_POINTVER"\n" );
#else
printf( "x264 0.%d.X\n", X264_BUILD );
#endif
#if HAVE_SWSCALE
printf( "(libswscale %d.%d.%d)\n", LIBSWSCALE_VERSION_MAJOR, LIBSWSCALE_VERSION_MINOR, LIBSWSCALE_VERSION_MICRO );
#endif
#if HAVE_LAVF
printf( "(libavformat %d.%d.%d)\n", LIBAVFORMAT_VERSION_MAJOR, LIBAVFORMAT_VERSION_MINOR, LIBAVFORMAT_VERSION_MICRO );
#endif
#if HAVE_FFMS
printf( "(ffmpegsource %d.%d.%d.%d)\n", FFMS_VERSION >> 24, (FFMS_VERSION & 0xff0000) >> 16, (FFMS_VERSION & 0xff00) >> 8, FFMS_VERSION & 0xff );
#endif
printf( "built on " __DATE__ ", " );
#ifdef __INTEL_COMPILER
printf( "intel: %.2f (%d)\n", __INTEL_COMPILER / 100.f, __INTEL_COMPILER_BUILD_DATE );
#elif defined(__GNUC__)
printf( "gcc: " __VERSION__ "\n" );
#elif defined(_MSC_FULL_VER)
printf( "msvc: %.2f (%u)\n", _MSC_VER / 100.f, _MSC_FULL_VER );
#else
printf( "using an unknown compiler\n" );
#endif
printf( "configuration: --bit-depth=%d --chroma-format=%s\n", x264_bit_depth, X264_CHROMA_FORMAT ? (output_csp_names[0]+1) : "all" );
printf( "x264 license: " );
#if HAVE_GPL
printf( "GPL version 2 or later\n" );
#else
printf( "Non-GPL commercial\n" );
#endif
#if HAVE_SWSCALE
const char *license = swscale_license();
printf( "libswscale%s%s license: %s\n", HAVE_LAVF ? "/libavformat" : "", HAVE_FFMS ? "/ffmpegsource" : "" , license );
if( !strcmp( license, "nonfree and unredistributable" ) ||
(!HAVE_GPL && (!strcmp( license, "GPL version 2 or later" )
|| !strcmp( license, "GPL version 3 or later" ))))
printf( "WARNING: This binary is unredistributable!\n" );
#endif
}
该函数定义比较浅显易懂,不再详细记录。
x264_param_parse()
x264_param_parse()是一个x264的API。该函数以字符串键值对的方式设置x264_param_t结构体的一个成员变量。该函数的声明如下所示。/* x264_param_parse:
* set one parameter by name.
* returns 0 on success, or returns one of the following errors.
* note: BAD_VALUE occurs only if it can't even parse the value,
* numerical range is not checked until x264_encoder_open() or
* x264_encoder_reconfig().
* value=NULL means "true" for boolean options, but is a BAD_VALUE for non-booleans. */
int x264_param_parse( x264_param_t *, const char *name, const char *value );//解析以字符串方式输入的参数
//即选项名称和选项值都是字符串
//实质就是通过strcmp()方法
int x264_param_parse( x264_param_t *p, const char *name, const char *value )
{
char *name_buf = NULL;
int b_error = 0;
int name_was_bool;
int value_was_null = !value;
int i;
if( !name )
return X264_PARAM_BAD_NAME;
if( !value )
value = "true";
if( value[0] == '=' )
value++;
if( strchr( name, '_' ) ) // s/_/-/g
{
char *c;
name_buf = strdup(name);
while( (c = strchr( name_buf, '_' )) )
*c = '-';
name = name_buf;
}
if( (!strncmp( name, "no-", 3 ) && (i = 3)) ||
(!strncmp( name, "no", 2 ) && (i = 2)) )
{
name += i;
value = atobool(value) ? "false" : "true";
}
name_was_bool = 0;
#define OPT(STR) else if( !strcmp( name, STR ) )
#define OPT2(STR0, STR1) else if( !strcmp( name, STR0 ) || !strcmp( name, STR1 ) )
if(0);
//OPT()实际上就是strcmp()
OPT("asm")
{
p->cpu = isdigit(value[0]) ? atoi(value) :
!strcasecmp(value, "auto") || atobool(value) ? x264_cpu_detect() : 0;
if( b_error )
{
char *buf = strdup(value);
char *tok, UNUSED *saveptr=NULL, *init;
b_error = 0;
p->cpu = 0;
for( init=buf; (tok=strtok_r(init, ",", &saveptr)); init=NULL )
{
for( i=0; x264_cpu_names[i].flags && strcasecmp(tok, x264_cpu_names[i].name); i++ );
p->cpu |= x264_cpu_names[i].flags;
if( !x264_cpu_names[i].flags )
b_error = 1;
}
free( buf );
if( (p->cpu&X264_CPU_SSSE3) && !(p->cpu&X264_CPU_SSE2_IS_SLOW) )
p->cpu |= X264_CPU_SSE2_IS_FAST;
}
}
OPT("threads")
{
if( !strcasecmp(value, "auto") )
p->i_threads = X264_THREADS_AUTO;
else
p->i_threads = atoi(value);
}
OPT("lookahead-threads")
{
if( !strcasecmp(value, "auto") )
p->i_lookahead_threads = X264_THREADS_AUTO;
else
p->i_lookahead_threads = atoi(value);
}
OPT("sliced-threads")
p->b_sliced_threads = atobool(value);
OPT("sync-lookahead")
{
if( !strcasecmp(value, "auto") )
p->i_sync_lookahead = X264_SYNC_LOOKAHEAD_AUTO;
else
p->i_sync_lookahead = atoi(value);
}
OPT2("deterministic", "n-deterministic")
p->b_deterministic = atobool(value);
OPT("cpu-independent")
p->b_cpu_independent = atobool(value);
OPT2("level", "level-idc")
{
if( !strcmp(value, "1b") )
p->i_level_idc = 9;
else if( atof(value) < 6 )
p->i_level_idc = (int)(10*atof(value)+.5);
else
p->i_level_idc = atoi(value);
}
OPT("bluray-compat")
p->b_bluray_compat = atobool(value);
OPT("avcintra-class")
p->i_avcintra_class = atoi(value);
OPT("sar")
{
b_error = ( 2 != sscanf( value, "%d:%d", &p->vui.i_sar_width, &p->vui.i_sar_height ) &&
2 != sscanf( value, "%d/%d", &p->vui.i_sar_width, &p->vui.i_sar_height ) );
}
OPT("overscan")
b_error |= parse_enum( value, x264_overscan_names, &p->vui.i_overscan );
OPT("videoformat")
b_error |= parse_enum( value, x264_vidformat_names, &p->vui.i_vidformat );
OPT("fullrange")
b_error |= parse_enum( value, x264_fullrange_names, &p->vui.b_fullrange );
OPT("colorprim")
b_error |= parse_enum( value, x264_colorprim_names, &p->vui.i_colorprim );
OPT("transfer")
b_error |= parse_enum( value, x264_transfer_names, &p->vui.i_transfer );
OPT("colormatrix")
b_error |= parse_enum( value, x264_colmatrix_names, &p->vui.i_colmatrix );
OPT("chromaloc")
{
p->vui.i_chroma_loc = atoi(value);
b_error = ( p->vui.i_chroma_loc < 0 || p->vui.i_chroma_loc > 5 );
}
OPT("fps")
{
if( sscanf( value, "%u/%u", &p->i_fps_num, &p->i_fps_den ) == 2 )
;
else
{
float fps = atof(value);
if( fps > 0 && fps <= INT_MAX/1000 )
{
p->i_fps_num = (int)(fps * 1000 + .5);
p->i_fps_den = 1000;
}
else
{
p->i_fps_num = atoi(value);
p->i_fps_den = 1;
}
}
}
OPT2("ref", "frameref")
p->i_frame_reference = atoi(value);
OPT("dpb-size")
p->i_dpb_size = atoi(value);
OPT("keyint")
{
if( strstr( value, "infinite" ) )
p->i_keyint_max = X264_KEYINT_MAX_INFINITE;
else
p->i_keyint_max = atoi(value);
}
OPT2("min-keyint", "keyint-min")
{
p->i_keyint_min = atoi(value);
if( p->i_keyint_max < p->i_keyint_min )
p->i_keyint_max = p->i_keyint_min;
}
OPT("scenecut")
{
p->i_scenecut_threshold = atobool(value);
if( b_error || p->i_scenecut_threshold )
{
b_error = 0;
p->i_scenecut_threshold = atoi(value);
}
}
OPT("intra-refresh")
p->b_intra_refresh = atobool(value);
OPT("bframes")
p->i_bframe = atoi(value);
OPT("b-adapt")
{
p->i_bframe_adaptive = atobool(value);
if( b_error )
{
b_error = 0;
p->i_bframe_adaptive = atoi(value);
}
}
OPT("b-bias")
p->i_bframe_bias = atoi(value);
OPT("b-pyramid")
{
b_error |= parse_enum( value, x264_b_pyramid_names, &p->i_bframe_pyramid );
if( b_error )
{
b_error = 0;
p->i_bframe_pyramid = atoi(value);
}
}
OPT("open-gop")
p->b_open_gop = atobool(value);
OPT("nf")
p->b_deblocking_filter = !atobool(value);
OPT2("filter", "deblock")
{
if( 2 == sscanf( value, "%d:%d", &p->i_deblocking_filter_alphac0, &p->i_deblocking_filter_beta ) ||
2 == sscanf( value, "%d,%d", &p->i_deblocking_filter_alphac0, &p->i_deblocking_filter_beta ) )
{
p->b_deblocking_filter = 1;
}
else if( sscanf( value, "%d", &p->i_deblocking_filter_alphac0 ) )
{
p->b_deblocking_filter = 1;
p->i_deblocking_filter_beta = p->i_deblocking_filter_alphac0;
}
else
p->b_deblocking_filter = atobool(value);
}
OPT("slice-max-size")
p->i_slice_max_size = atoi(value);
OPT("slice-max-mbs")
p->i_slice_max_mbs = atoi(value);
OPT("slice-min-mbs")
p->i_slice_min_mbs = atoi(value);
OPT("slices")
p->i_slice_count = atoi(value);
OPT("slices-max")
p->i_slice_count_max = atoi(value);
OPT("cabac")
p->b_cabac = atobool(value);
OPT("cabac-idc")
p->i_cabac_init_idc = atoi(value);
OPT("interlaced")
p->b_interlaced = atobool(value);
OPT("tff")
p->b_interlaced = p->b_tff = atobool(value);
OPT("bff")
{
p->b_interlaced = atobool(value);
p->b_tff = !p->b_interlaced;
}
OPT("constrained-intra")
p->b_constrained_intra = atobool(value);
OPT("cqm")
{
if( strstr( value, "flat" ) )
p->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_FLAT;
else if( strstr( value, "jvt" ) )
p->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_JVT;
else
p->psz_cqm_file = strdup(value);
}
OPT("cqmfile")
p->psz_cqm_file = strdup(value);
OPT("cqm4")
{
p->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_CUSTOM;
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_4iy, 16 );
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_4py, 16 );
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_4ic, 16 );
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_4pc, 16 );
}
OPT("cqm8")
{
p->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_CUSTOM;
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_8iy, 64 );
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_8py, 64 );
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_8ic, 64 );
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_8pc, 64 );
}
OPT("cqm4i")
{
p->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_CUSTOM;
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_4iy, 16 );
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_4ic, 16 );
}
OPT("cqm4p")
{
p->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_CUSTOM;
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_4py, 16 );
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_4pc, 16 );
}
OPT("cqm4iy")
{
p->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_CUSTOM;
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_4iy, 16 );
}
OPT("cqm4ic")
{
p->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_CUSTOM;
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_4ic, 16 );
}
OPT("cqm4py")
{
p->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_CUSTOM;
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_4py, 16 );
}
OPT("cqm4pc")
{
p->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_CUSTOM;
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_4pc, 16 );
}
OPT("cqm8i")
{
p->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_CUSTOM;
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_8iy, 64 );
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_8ic, 64 );
}
OPT("cqm8p")
{
p->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_CUSTOM;
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_8py, 64 );
b_error |= parse_cqm( value, p->cqm_8pc, 64 );
}
OPT("log")
p->i_log_level = atoi(value);
OPT("dump-yuv")
p->psz_dump_yuv = strdup(value);
OPT2("analyse", "partitions")
{
p->analyse.inter = 0;
if( strstr( value, "none" ) ) p->analyse.inter = 0;
if( strstr( value, "all" ) ) p->analyse.inter = ~0;
if( strstr( value, "i4x4" ) ) p->analyse.inter |= X264_ANALYSE_I4x4;
if( strstr( value, "i8x8" ) ) p->analyse.inter |= X264_ANALYSE_I8x8;
if( strstr( value, "p8x8" ) ) p->analyse.inter |= X264_ANALYSE_PSUB16x16;
if( strstr( value, "p4x4" ) ) p->analyse.inter |= X264_ANALYSE_PSUB8x8;
if( strstr( value, "b8x8" ) ) p->analyse.inter |= X264_ANALYSE_BSUB16x16;
}
OPT("8x8dct")
p->analyse.b_transform_8x8 = atobool(value);
OPT2("weightb", "weight-b")
p->analyse.b_weighted_bipred = atobool(value);
OPT("weightp")
p->analyse.i_weighted_pred = atoi(value);
OPT2("direct", "direct-pred")
b_error |= parse_enum( value, x264_direct_pred_names, &p->analyse.i_direct_mv_pred );
OPT("chroma-qp-offset")
p->analyse.i_chroma_qp_offset = atoi(value);
OPT("me")
b_error |= parse_enum( value, x264_motion_est_names, &p->analyse.i_me_method );
OPT2("merange", "me-range")
p->analyse.i_me_range = atoi(value);
OPT2("mvrange", "mv-range")
p->analyse.i_mv_range = atoi(value);
OPT2("mvrange-thread", "mv-range-thread")
p->analyse.i_mv_range_thread = atoi(value);
OPT2("subme", "subq")
p->analyse.i_subpel_refine = atoi(value);
OPT("psy-rd")
{
if( 2 == sscanf( value, "%f:%f", &p->analyse.f_psy_rd, &p->analyse.f_psy_trellis ) ||
2 == sscanf( value, "%f,%f", &p->analyse.f_psy_rd, &p->analyse.f_psy_trellis ) ||
2 == sscanf( value, "%f|%f", &p->analyse.f_psy_rd, &p->analyse.f_psy_trellis ))
{ }
else if( sscanf( value, "%f", &p->analyse.f_psy_rd ) )
{
p->analyse.f_psy_trellis = 0;
}
else
{
p->analyse.f_psy_rd = 0;
p->analyse.f_psy_trellis = 0;
}
}
OPT("psy")
p->analyse.b_psy = atobool(value);
OPT("chroma-me")
p->analyse.b_chroma_me = atobool(value);
OPT("mixed-refs")
p->analyse.b_mixed_references = atobool(value);
OPT("trellis")
p->analyse.i_trellis = atoi(value);
OPT("fast-pskip")
p->analyse.b_fast_pskip = atobool(value);
OPT("dct-decimate")
p->analyse.b_dct_decimate = atobool(value);
OPT("deadzone-inter")
p->analyse.i_luma_deadzone[0] = atoi(value);
OPT("deadzone-intra")
p->analyse.i_luma_deadzone[1] = atoi(value);
OPT("nr")
p->analyse.i_noise_reduction = atoi(value);
OPT("bitrate")
{
p->rc.i_bitrate = atoi(value);
p->rc.i_rc_method = X264_RC_ABR;
}
OPT2("qp", "qp_constant")
{
p->rc.i_qp_constant = atoi(value);
p->rc.i_rc_method = X264_RC_CQP;
}
OPT("crf")
{
p->rc.f_rf_constant = atof(value);
p->rc.i_rc_method = X264_RC_CRF;
}
OPT("crf-max")
p->rc.f_rf_constant_max = atof(value);
OPT("rc-lookahead")
p->rc.i_lookahead = atoi(value);
OPT2("qpmin", "qp-min")
p->rc.i_qp_min = atoi(value);
OPT2("qpmax", "qp-max")
p->rc.i_qp_max = atoi(value);
OPT2("qpstep", "qp-step")
p->rc.i_qp_step = atoi(value);
OPT("ratetol")
p->rc.f_rate_tolerance = !strncmp("inf", value, 3) ? 1e9 : atof(value);
OPT("vbv-maxrate")
p->rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate = atoi(value);
OPT("vbv-bufsize")
p->rc.i_vbv_buffer_size = atoi(value);
OPT("vbv-init")
p->rc.f_vbv_buffer_init = atof(value);
OPT2("ipratio", "ip-factor")
p->rc.f_ip_factor = atof(value);
OPT2("pbratio", "pb-factor")
p->rc.f_pb_factor = atof(value);
OPT("aq-mode")
p->rc.i_aq_mode = atoi(value);
OPT("aq-strength")
p->rc.f_aq_strength = atof(value);
OPT("pass")
{
int pass = x264_clip3( atoi(value), 0, 3 );
p->rc.b_stat_write = pass & 1;
p->rc.b_stat_read = pass & 2;
}
OPT("stats")
{
p->rc.psz_stat_in = strdup(value);
p->rc.psz_stat_out = strdup(value);
}
OPT("qcomp")
p->rc.f_qcompress = atof(value);
OPT("mbtree")
p->rc.b_mb_tree = atobool(value);
OPT("qblur")
p->rc.f_qblur = atof(value);
OPT2("cplxblur", "cplx-blur")
p->rc.f_complexity_blur = atof(value);
OPT("zones")
p->rc.psz_zones = strdup(value);
OPT("crop-rect")
b_error |= sscanf( value, "%u,%u,%u,%u", &p->crop_rect.i_left, &p->crop_rect.i_top,
&p->crop_rect.i_right, &p->crop_rect.i_bottom ) != 4;
OPT("psnr")
p->analyse.b_psnr = atobool(value);
OPT("ssim")
p->analyse.b_ssim = atobool(value);
OPT("aud")
p->b_aud = atobool(value);
OPT("sps-id")
p->i_sps_id = atoi(value);
OPT("global-header")
p->b_repeat_headers = !atobool(value);
OPT("repeat-headers")
p->b_repeat_headers = atobool(value);
OPT("annexb")
p->b_annexb = atobool(value);
OPT("force-cfr")
p->b_vfr_input = !atobool(value);
OPT("nal-hrd")
b_error |= parse_enum( value, x264_nal_hrd_names, &p->i_nal_hrd );
OPT("filler")
p->rc.b_filler = atobool(value);
OPT("pic-struct")
p->b_pic_struct = atobool(value);
OPT("fake-interlaced")
p->b_fake_interlaced = atobool(value);
OPT("frame-packing")
p->i_frame_packing = atoi(value);
OPT("stitchable")
p->b_stitchable = atobool(value);
OPT("opencl")
p->b_opencl = atobool( value );
OPT("opencl-clbin")
p->psz_clbin_file = strdup( value );
OPT("opencl-device")
p->i_opencl_device = atoi( value );
else
return X264_PARAM_BAD_NAME;
#undef OPT
#undef OPT2
#undef atobool
#undef atoi
#undef atof
if( name_buf )
free( name_buf );
b_error |= value_was_null && !name_was_bool;
return b_error ? X264_PARAM_BAD_VALUE : 0;
}
x264_param_parse()中判断参数的宏OPT()和OPT2()实质上就是strcmp()。由此可见该函数的流程首先是调用strcmp()判断当前输入参数的名称name,然后再调用atoi(),atof(),或者atobool()等将当前输入参数值value转换成相应类型的值并赋值给对应的参数。
x264_param_apply_profile()
x264_param_apply_profile()是一个x264的API。该函数用于设置x264的profile,它的声明如下所示。/* (can be NULL, in which case the function will do nothing)
*
* Does NOT guarantee that the given profile will be used: if the restrictions
* of "High" are applied to settings that are already Baseline-compatible, the
* stream will remain baseline. In short, it does not increase settings, only
* decrease them.
*
* returns 0 on success, negative on failure (e.g. invalid profile name). */
int x264_param_apply_profile( x264_param_t *, const char *profile );//设置profile
int x264_param_apply_profile( x264_param_t *param, const char *profile )
{
if( !profile )
return 0;
//字符串到整型
int p = profile_string_to_int( profile );
//检查profile设置是否正确
if( p < 0 )
{
x264_log( NULL, X264_LOG_ERROR, "invalid profile: %s\n", profile );
return -1;
}
if( p < PROFILE_HIGH444_PREDICTIVE && ((param->rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CQP && param->rc.i_qp_constant <= 0) ||
(param->rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CRF && (int)(param->rc.f_rf_constant + QP_BD_OFFSET) <= 0)) )
{
x264_log( NULL, X264_LOG_ERROR, "%s profile doesn't support lossless\n", profile );
return -1;
}
if( p < PROFILE_HIGH444_PREDICTIVE && (param->i_csp & X264_CSP_MASK) >= X264_CSP_I444 )
{
x264_log( NULL, X264_LOG_ERROR, "%s profile doesn't support 4:4:4\n", profile );
return -1;
}
if( p < PROFILE_HIGH422 && (param->i_csp & X264_CSP_MASK) >= X264_CSP_I422 )
{
x264_log( NULL, X264_LOG_ERROR, "%s profile doesn't support 4:2:2\n", profile );
return -1;
}
if( p < PROFILE_HIGH10 && BIT_DEPTH > 8 )
{
x264_log( NULL, X264_LOG_ERROR, "%s profile doesn't support a bit depth of %d\n", profile, BIT_DEPTH );
return -1;
}
//根据不同的Profile做设置
//Baseline基本型
if( p == PROFILE_BASELINE )
{
//不支持DCT8x8
param->analyse.b_transform_8x8 = 0;
//不使用CABAC
param->b_cabac = 0;
param->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_FLAT;
param->psz_cqm_file = NULL;
//没有B帧
param->i_bframe = 0;
//没有加权
param->analyse.i_weighted_pred = X264_WEIGHTP_NONE;
//不支持隔行扫描
if( param->b_interlaced )
{
x264_log( NULL, X264_LOG_ERROR, "baseline profile doesn't support interlacing\n" );
return -1;
}
if( param->b_fake_interlaced )
{
x264_log( NULL, X264_LOG_ERROR, "baseline profile doesn't support fake interlacing\n" );
return -1;
}
}
//Main主型
else if( p == PROFILE_MAIN )
{
//不支持DCT8x8
param->analyse.b_transform_8x8 = 0;
param->i_cqm_preset = X264_CQM_FLAT;
param->psz_cqm_file = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
从定义可以看出,x264_param_apply_profile()首先调用了一个函数profile_string_to_int()将输入的profile字符串转换为int类型的profile;然后会检查该profile的设置是否合理;最后会根据profile对x264_param_t中的参数进行相应的设置。
该函数中调用的profile_string_to_int()的定义如下。
static int profile_string_to_int( const char *str )
{
if( !strcasecmp( str, "baseline" ) )
return PROFILE_BASELINE;
if( !strcasecmp( str, "main" ) )
return PROFILE_MAIN;
if( !strcasecmp( str, "high" ) )
return PROFILE_HIGH;
if( !strcasecmp( str, "high10" ) )
return PROFILE_HIGH10;
if( !strcasecmp( str, "high422" ) )
return PROFILE_HIGH422;
if( !strcasecmp( str, "high444" ) )
return PROFILE_HIGH444_PREDICTIVE;
return -1;
}select_output()
select_output()用于设定输出的文件格式。该函数的定义如下所示。//根据文件名的后缀确定输出的文件格式(raw H264,flv,mp4...)
static int select_output( const char *muxer, char *filename, x264_param_t *param )
{
//从文件路径字符串中解析出扩展名,存入ext
//解析的方式就是反向搜索字符“.”
const char *ext = get_filename_extension( filename );
//strcasecmp(char *s1, char *s2)用于忽略大小写比较字符串.
//参数s1和s2字符串相等则返回0。s1大于s2则返回大于0 的值,s1 小于s2 则返回小于0的值。
if( !strcmp( filename, "-" ) || strcasecmp( muxer, "auto" ) )
ext = muxer;
//后缀为“mp4”
if( !strcasecmp( ext, "mp4" ) )
{
#if HAVE_GPAC || HAVE_LSMASH
cli_output = mp4_output;
param->b_annexb = 0;
param->b_repeat_headers = 0;
if( param->i_nal_hrd == X264_NAL_HRD_CBR )
{
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_WARNING, "cbr nal-hrd is not compatible with mp4\n" );
param->i_nal_hrd = X264_NAL_HRD_VBR;
}
#else
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_ERROR, "not compiled with MP4 output support\n" );
return -1;
#endif
}
else if( !strcasecmp( ext, "mkv" ) )
{
//设定cli_output_t
cli_output = mkv_output;
//不加起始码0x00000001
param->b_annexb = 0;
//不再每个Keyframe前面加SPS和PPS
param->b_repeat_headers = 0;
}
else if( !strcasecmp( ext, "flv" ) )
{
cli_output = flv_output;
param->b_annexb = 0;
param->b_repeat_headers = 0;
}
else
cli_output = raw_output;//不符合上述后缀,则输出裸流
return 0;
}
从函数定义可以看出,select_output()首先调用get_filename_extension()从输入文件路径的字符串中提取出了扩展名,然后根据不同的扩展名设定不同的输出格式。其中get_filename_extension()是一个提取扩展名的函数,定义如下所示。
//根据“.”确定文件后缀
static inline char *get_filename_extension( char *filename )
{
char *ext = filename + strlen( filename );
while( *ext != '.' && ext > filename )
ext--;
ext += *ext == '.';
return ext;
}select_input()
select_input()用于设定输入的文件格式。该函数的定义如下所示。//设置输入文件的格式(yuv,y4m...)
static int select_input( const char *demuxer, char *used_demuxer, char *filename,
hnd_t *p_handle, video_info_t *info, cli_input_opt_t *opt )
{
int b_auto = !strcasecmp( demuxer, "auto" );
//从文件路径字符串中解析出扩展名,存入ext
//解析的方式就是反向搜索字符“.”
const char *ext = b_auto ? get_filename_extension( filename ) : "";
int b_regular = strcmp( filename, "-" );
if( !b_regular && b_auto )
ext = "raw";
b_regular = b_regular && x264_is_regular_file_path( filename );
if( b_regular )
{
FILE *f = x264_fopen( filename, "r" );
if( f )
{
b_regular = x264_is_regular_file( f );
fclose( f );
}
}
const char *module = b_auto ? ext : demuxer;
//strcasecmp(char *s1, char *s2)用于忽略大小写比较字符串.
//参数s1和s2字符串相等则返回0。s1大于s2则返回大于0 的值,s1 小于s2 则返回小于0的值。
if( !strcasecmp( module, "avs" ) || !strcasecmp( ext, "d2v" ) || !strcasecmp( ext, "dga" ) )
{
#if HAVE_AVS
cli_input = avs_input;
module = "avs";
#else
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_ERROR, "not compiled with AVS input support\n" );
return -1;
#endif
}
else if( !strcasecmp( module, "y4m" ) )
cli_input = y4m_input;
else if( !strcasecmp( module, "raw" ) || !strcasecmp( ext, "yuv" ) )
cli_input = raw_input;
else
{
#if HAVE_FFMS
if( b_regular && (b_auto || !strcasecmp( demuxer, "ffms" )) &&
!ffms_input.open_file( filename, p_handle, info, opt ) )
{
module = "ffms";
b_auto = 0;
cli_input = ffms_input;
}
#endif
#if HAVE_LAVF
if( (b_auto || !strcasecmp( demuxer, "lavf" )) &&
!lavf_input.open_file( filename, p_handle, info, opt ) )
{
module = "lavf";
b_auto = 0;
cli_input = lavf_input;
}
#endif
#if HAVE_AVS
if( b_regular && (b_auto || !strcasecmp( demuxer, "avs" )) &&
!avs_input.open_file( filename, p_handle, info, opt ) )
{
module = "avs";
b_auto = 0;
cli_input = avs_input;
}
#endif
if( b_auto && !raw_input.open_file( filename, p_handle, info, opt ) )
{
module = "raw";
b_auto = 0;
cli_input = raw_input;
}
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !(*p_handle), "could not open input file `%s' via any method!\n", filename )
}
strcpy( used_demuxer, module );
return 0;
}
从源代码中可以看出,select_input()首先调用get_filename_extension()获取输入文件名的扩展名;然后根据扩展名设置不同的输入格式。
至此x264命令行程序main()函数调用的parse()函数就分析完毕了。下面分析main()函数调用的另一个函数encode()。
encode()
encode()编码YUV为H.264码流,该函数的定义如下所示。//编码(在内部有一个循环用于一帧一帧编码)
static int encode( x264_param_t *param, cli_opt_t *opt )
{
x264_t *h = NULL;
x264_picture_t pic;
cli_pic_t cli_pic;
const cli_pulldown_t *pulldown = NULL; // shut up gcc
int i_frame = 0;
int i_frame_output = 0;
int64_t i_end, i_previous = 0, i_start = 0;
int64_t i_file = 0;
int i_frame_size;
int64_t last_dts = 0;
int64_t prev_dts = 0;
int64_t first_dts = 0;
# define MAX_PTS_WARNING 3 /* arbitrary */
int pts_warning_cnt = 0;
int64_t largest_pts = -1;
int64_t second_largest_pts = -1;
int64_t ticks_per_frame;
double duration;
double pulldown_pts = 0;
int retval = 0;
opt->b_progress &= param->i_log_level < X264_LOG_DEBUG;
/* set up pulldown */
if( opt->i_pulldown && !param->b_vfr_input )
{
param->b_pulldown = 1;
param->b_pic_struct = 1;
pulldown = &pulldown_values[opt->i_pulldown];
param->i_timebase_num = param->i_fps_den;
FAIL_IF_ERROR2( fmod( param->i_fps_num * pulldown->fps_factor, 1 ),
"unsupported framerate for chosen pulldown\n" )
param->i_timebase_den = param->i_fps_num * pulldown->fps_factor;
}
//打开编码器
h = x264_encoder_open( param );
FAIL_IF_ERROR2( !h, "x264_encoder_open failed\n" );
//获得参数
x264_encoder_parameters( h, param );
//一些不是裸流的封转格式(FLV,MP4等)需要一些参数,例如宽高等等
//cli_output_t是代表输出媒体文件的结构体
FAIL_IF_ERROR2( cli_output.set_param( opt->hout, param ), "can't set outfile param\n" );
//计时
i_start = x264_mdate();
/* ticks/frame = ticks/second / frames/second */
ticks_per_frame = (int64_t)param->i_timebase_den * param->i_fps_den / param->i_timebase_num / param->i_fps_num;
FAIL_IF_ERROR2( ticks_per_frame < 1 && !param->b_vfr_input, "ticks_per_frame invalid: %"PRId64"\n", ticks_per_frame )
ticks_per_frame = X264_MAX( ticks_per_frame, 1 );
//如果不是在每个keyframe前面都增加SPS/PPS/SEI的话,就在整个码流前面加SPS/PPS/SEI
//Header指的就是SPS/PPS/SEI
if( !param->b_repeat_headers )
{
// Write SPS/PPS/SEI
x264_nal_t *headers;
int i_nal;
//获得文件头(SPS、PPS、SEI)
FAIL_IF_ERROR2( x264_encoder_headers( h, &headers, &i_nal ) < 0, "x264_encoder_headers failed\n" )
//把文件头写入输出文件
FAIL_IF_ERROR2( (i_file = cli_output.write_headers( opt->hout, headers )) < 0, "error writing headers to output file\n" );
}
if( opt->tcfile_out )
fprintf( opt->tcfile_out, "# timecode format v2\n" );
/* Encode frames */
//循环进行编码
for( ; !b_ctrl_c && (i_frame < param->i_frame_total || !param->i_frame_total); i_frame++ )
{
//从输入源中获取1帧YUV数据,存于cli_pic
//cli_vid_filter_t可以认为是x264一种“扩展”后的输入源,可以在像素域对图像进行拉伸裁剪等工作。
//原本代表输入源的结构体是cli_input_t
if( filter.get_frame( opt->hin, &cli_pic, i_frame + opt->i_seek ) )
break;
//初始化x264_picture_t结构体pic
x264_picture_init( &pic );
//cli_pic到pic
convert_cli_to_lib_pic( &pic, &cli_pic );
if( !param->b_vfr_input )
pic.i_pts = i_frame;
if( opt->i_pulldown && !param->b_vfr_input )
{
pic.i_pic_struct = pulldown->pattern[ i_frame % pulldown->mod ];
pic.i_pts = (int64_t)( pulldown_pts + 0.5 );
pulldown_pts += pulldown_frame_duration[pic.i_pic_struct];
}
else if( opt->timebase_convert_multiplier )
pic.i_pts = (int64_t)( pic.i_pts * opt->timebase_convert_multiplier + 0.5 );
if( pic.i_pts <= largest_pts )
{
if( cli_log_level >= X264_LOG_DEBUG || pts_warning_cnt < MAX_PTS_WARNING )
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_WARNING, "non-strictly-monotonic pts at frame %d (%"PRId64" <= %"PRId64")\n",
i_frame, pic.i_pts, largest_pts );
else if( pts_warning_cnt == MAX_PTS_WARNING )
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_WARNING, "too many nonmonotonic pts warnings, suppressing further ones\n" );
pts_warning_cnt++;
pic.i_pts = largest_pts + ticks_per_frame;
}
second_largest_pts = largest_pts;
largest_pts = pic.i_pts;
if( opt->tcfile_out )
fprintf( opt->tcfile_out, "%.6f\n", pic.i_pts * ((double)param->i_timebase_num / param->i_timebase_den) * 1e3 );
if( opt->qpfile )
parse_qpfile( opt, &pic, i_frame + opt->i_seek );
prev_dts = last_dts;
//编码pic中存储的1帧YUV数据
i_frame_size = encode_frame( h, opt->hout, &pic, &last_dts );
if( i_frame_size < 0 )
{
b_ctrl_c = 1; /* lie to exit the loop */
retval = -1;
}
else if( i_frame_size )
{
i_file += i_frame_size;
i_frame_output++;
if( i_frame_output == 1 )
first_dts = prev_dts = last_dts;
}
//释放处理完的YUV数据
if( filter.release_frame( opt->hin, &cli_pic, i_frame + opt->i_seek ) )
break;
/* update status line (up to 1000 times per input file) */
if( opt->b_progress && i_frame_output )
i_previous = print_status( i_start, i_previous, i_frame_output, param->i_frame_total, i_file, param, 2 * last_dts - prev_dts - first_dts );
}
/* Flush delayed frames */
//输出编码器中剩余的帧
//x264_encoder_delayed_frames()返回剩余的帧的个数
while( !b_ctrl_c && x264_encoder_delayed_frames( h ) )
{
prev_dts = last_dts;
//编码
//注意第3个参数为NULL
i_frame_size = encode_frame( h, opt->hout, NULL, &last_dts );
if( i_frame_size < 0 )
{
b_ctrl_c = 1; /* lie to exit the loop */
retval = -1;
}
else if( i_frame_size )
{
i_file += i_frame_size;
i_frame_output++;
if( i_frame_output == 1 )
first_dts = prev_dts = last_dts;
}
//输出一些统计信息
if( opt->b_progress && i_frame_output )
i_previous = print_status( i_start, i_previous, i_frame_output, param->i_frame_total, i_file, param, 2 * last_dts - prev_dts - first_dts );
}
fail:
if( pts_warning_cnt >= MAX_PTS_WARNING && cli_log_level < X264_LOG_DEBUG )
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_WARNING, "%d suppressed nonmonotonic pts warnings\n", pts_warning_cnt-MAX_PTS_WARNING );
/* duration algorithm fails when only 1 frame is output */
if( i_frame_output == 1 )
duration = (double)param->i_fps_den / param->i_fps_num;
else if( b_ctrl_c )
duration = (double)(2 * last_dts - prev_dts - first_dts) * param->i_timebase_num / param->i_timebase_den;
else
duration = (double)(2 * largest_pts - second_largest_pts) * param->i_timebase_num / param->i_timebase_den;
//计时
i_end = x264_mdate();
/* Erase progress indicator before printing encoding stats. */
if( opt->b_progress )
fprintf( stderr, " \r" );
//关闭编码器
if( h )
x264_encoder_close( h );
fprintf( stderr, "\n" );
if( b_ctrl_c )
fprintf( stderr, "aborted at input frame %d, output frame %d\n", opt->i_seek + i_frame, i_frame_output );
//关闭输出文件
cli_output.close_file( opt->hout, largest_pts, second_largest_pts );
opt->hout = NULL;
if( i_frame_output > 0 )
{
double fps = (double)i_frame_output * (double)1000000 /
(double)( i_end - i_start );
fprintf( stderr, "encoded %d frames, %.2f fps, %.2f kb/s\n", i_frame_output, fps,
(double) i_file * 8 / ( 1000 * duration ) );
}
return retval;
}
从源代码可以梳理出来encode()的流程:
(1)调用x264_encoder_open()打开H.264编码器。
(2)调用x264_encoder_parameters()获得当前的参数集x264_param_t,用于后续步骤中的一些配置。
(3)调用输出格式(H.264裸流、FLV、mp4等)对应cli_output_t结构体的set_param()方法,为输出格式的封装器设定参数。其中参数源自于上一步骤得到的x264_param_t。
(4)如果不是在每个keyframe前面都增加SPS/PPS/SEI的话,就调用x264_encoder_headers()在整个码流前面加SPS/PPS/SEI。
(5)进入一个循环中进行一帧一帧的将YUV编码为H.264:a)调用输入格式(YUV、Y4M等)对应的cli_vid_filter_t结构体get_frame()方法,获取一帧YUV数据。b)调用encode_frame()编码该帧YUV数据为H.264数据,并且输出出来。该函数内部调用x264_encoder_encode()完成编码工作,调用输出格式对应cli_output_t结构体的write_frame()完成了输出工作。c)调用输入格式(YUV、Y4M等)对应的cli_vid_filter_t结构体release_frame()方法,释放刚才获取的YUV数据。d)调用print_status()输出一些统计信息。(6)编码即将结束的时候,进入另一个循环,输出编码器中缓存的视频帧:a)不再传递新的YUV数据,直接调用encode_frame(),将编码器中缓存的剩余几帧数据编码输出出来。b)调用print_status()输出一些统计信息。(7)调用x264_encoder_close()关闭H.264编码器。
encode()的流程中涉及到libx264的几个关键的API,在这里暂时不做详细分析(后续文章中再进行补充):
x264_encoder_open():打开H.264编码器。
x264_encoder_headers():输出SPS/PPS/SEI。
x264_encoder_encode():编码一帧数据。
x264_encoder_close():关闭H.264编码器。
此外上述流程中涉及到两个比较简单的函数:encode_frame()和print_status()。其中encode_frame()用于编码一帧数据,而print_status()用于输出一帧数据编码后的统计信息。下文记录一下这两个函数的定义。
encode_frame()
encode_frame()的定义如下。//编码1帧
static int encode_frame( x264_t *h, hnd_t hout, x264_picture_t *pic, int64_t *last_dts )
{
x264_picture_t pic_out;
x264_nal_t *nal;
int i_nal;
int i_frame_size = 0;
//编码API
//编码x264_picture_t为x264_nal_t
i_frame_size = x264_encoder_encode( h, &nal, &i_nal, pic, &pic_out );
FAIL_IF_ERROR( i_frame_size < 0, "x264_encoder_encode failed\n" );
if( i_frame_size )
{
//通过cli_output_t中的方法输出
//输出raw H.264流的话,等同于直接fwrite()
//其他封装格式,则还需进行一定的封装
i_frame_size = cli_output.write_frame( hout, nal[0].p_payload, i_frame_size, &pic_out );
*last_dts = pic_out.i_dts;
}
return i_frame_size;
}
从源代码可以看出,encode_frame()内部调用x264_encoder_encode()完成编码工作,调用输出格式对应cli_output_t结构体的write_frame()完成了输出工作。其中有关cli_output_t结构体的知识将在后文中记录。
print_status()
print_status()的定义如下。//打印一些和时间有关的统计信息
static int64_t print_status( int64_t i_start, int64_t i_previous, int i_frame, int i_frame_total, int64_t i_file, x264_param_t *param, int64_t last_ts )
{
char buf[200];
int64_t i_time = x264_mdate();
if( i_previous && i_time - i_previous < UPDATE_INTERVAL )
return i_previous;
int64_t i_elapsed = i_time - i_start;
double fps = i_elapsed > 0 ? i_frame * 1000000. / i_elapsed : 0;
double bitrate;
if( last_ts )
bitrate = (double) i_file * 8 / ( (double) last_ts * 1000 * param->i_timebase_num / param->i_timebase_den );
else
bitrate = (double) i_file * 8 / ( (double) 1000 * param->i_fps_den / param->i_fps_num );
if( i_frame_total )
{
//形成输出的字符串
int eta = i_elapsed * (i_frame_total - i_frame) / ((int64_t)i_frame * 1000000);
sprintf( buf, "x264 [%.1f%%] %d/%d frames, %.2f fps, %.2f kb/s, eta %d:%02d:%02d",
100. * i_frame / i_frame_total, i_frame, i_frame_total, fps, bitrate,
eta/3600, (eta/60)%60, eta%60 );
}
else
sprintf( buf, "x264 %d frames: %.2f fps, %.2f kb/s", i_frame, fps, bitrate );
//输出到stderr
fprintf( stderr, "%s \r", buf+5 );
//设置到标题栏?
x264_cli_set_console_title( buf );
fflush( stderr ); // needed in windows
return i_time;
}
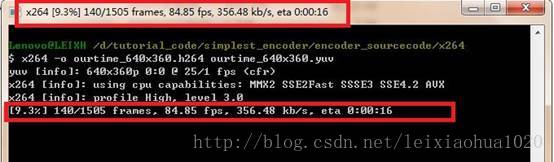
print_status()的代码不再详细记录,它的输出效果如下图中红框中的文字。
X264控制台程序中和输入输出相关的结构体
在x264控制台程序中有3个和输入输出相关的结构体:cli_output_t:输出格式对应的结构体。输出格式一般为H.264裸流、FLV、MP4等。在x264的编码过程中,调用cli_vid_filter_t结构体的get_frame()读取YUV数据,调用cli_output_t的write_frame()写入数据。下面简单分析一下它们之间的关系。
cli_input_t:输入格式对应的结构体。输入格式一般为纯YUV像素数据,Y4M格式数据等。
cli_vid_filter_t:输入格式滤镜结构体。滤镜可以对输入数据做一些简单的处理,例如拉伸、裁剪等等(当然滤镜也可以不作任何处理,直接读取输入数据)。
cli_output_t
x264项目中和cli_output_t结构体相关的源代码都位于根目录的output文件夹下。cli_output_t的定义位于output\output.h,如下所示。typedef struct
{
int (*open_file)( char *psz_filename, hnd_t *p_handle, cli_output_opt_t *opt );
int (*set_param)( hnd_t handle, x264_param_t *p_param );
int (*write_headers)( hnd_t handle, x264_nal_t *p_nal );
int (*write_frame)( hnd_t handle, uint8_t *p_nal, int i_size, x264_picture_t *p_picture );
int (*close_file)( hnd_t handle, int64_t largest_pts, int64_t second_largest_pts );
} cli_output_t;
extern const cli_output_t raw_output;
extern const cli_output_t mkv_output;
extern const cli_output_t mp4_output;
extern const cli_output_t flv_output;
从源代码中可以看出,cli_output_t中一共包含了open_file(),set_param(),write_headers(),write_frame(),close_file()五个接口。在x264中有raw_output,mkv_output,mp4_output,flv_output这几个cli_output_t结构体,分别对应H.264裸流,MKV,MP4,FLV格式。下面举例看两个结构体:raw_output和flv_output。
raw_output(H.264裸流的cli_output_t结构体)
raw_output的定义位于output\raw.c,该文件内容如下所示。
#include "output.h"
static int open_file( char *psz_filename, hnd_t *p_handle, cli_output_opt_t *opt )
{
if( !strcmp( psz_filename, "-" ) )
*p_handle = stdout;
else if( !(*p_handle = x264_fopen( psz_filename, "w+b" )) )
return -1;
return 0;
}
static int set_param( hnd_t handle, x264_param_t *p_param )
{
return 0;
}
static int write_headers( hnd_t handle, x264_nal_t *p_nal )
{
int size = p_nal[0].i_payload + p_nal[1].i_payload + p_nal[2].i_payload;
if( fwrite( p_nal[0].p_payload, size, 1, (FILE*)handle ) )
return size;
return -1;
}
static int write_frame( hnd_t handle, uint8_t *p_nalu, int i_size, x264_picture_t *p_picture )
{
if( fwrite( p_nalu, i_size, 1, (FILE*)handle ) )
return i_size;
return -1;
}
static int close_file( hnd_t handle, int64_t largest_pts, int64_t second_largest_pts )
{
if( !handle || handle == stdout )
return 0;
return fclose( (FILE*)handle );
}
const cli_output_t raw_output = { open_file, set_param, write_headers, write_frame, close_file };
可以看出raw_output中的函数定义都比较简单,只是封装了fwrite(),fclose()等函数。
flv_output(FLV格式的cli_output_t结构体)
flv_output的定义位于output\flv.c,如下所示。
const cli_output_t flv_output = { open_file, set_param, write_headers, write_frame, close_file };open_file()
flv_output 中的open_file()的定义如下所示。
static int write_header( flv_buffer *c )
{
flv_put_tag( c, "FLV" ); // Signature
flv_put_byte( c, 1 ); // Version
flv_put_byte( c, 1 ); // Video Only
flv_put_be32( c, 9 ); // DataOffset
flv_put_be32( c, 0 ); // PreviousTagSize0
return flv_flush_data( c );
}
static int open_file( char *psz_filename, hnd_t *p_handle, cli_output_opt_t *opt )
{
*p_handle = NULL;
flv_hnd_t *p_flv = calloc( 1, sizeof(flv_hnd_t) );
if( !p_flv )
return -1;
p_flv->b_dts_compress = opt->use_dts_compress;
p_flv->c = flv_create_writer( psz_filename );
if( !p_flv->c )
return -1;
CHECK( write_header( p_flv->c ) );
*p_handle = p_flv;
return 0;
}write_frame()
flv_output 中的write_frame()的定义如下所示。
static int write_frame( hnd_t handle, uint8_t *p_nalu, int i_size, x264_picture_t *p_picture )
{
flv_hnd_t *p_flv = handle;
flv_buffer *c = p_flv->c;
#define convert_timebase_ms( timestamp, timebase ) (int64_t)((timestamp) * (timebase) * 1000 + 0.5)
if( !p_flv->i_framenum )
{
p_flv->i_delay_time = p_picture->i_dts * -1;
if( !p_flv->b_dts_compress && p_flv->i_delay_time )
x264_cli_log( "flv", X264_LOG_INFO, "initial delay %"PRId64" ms\n",
convert_timebase_ms( p_picture->i_pts + p_flv->i_delay_time, p_flv->d_timebase ) );
}
int64_t dts;
int64_t cts;
int64_t offset;
if( p_flv->b_dts_compress )
{
if( p_flv->i_framenum == 1 )
p_flv->i_init_delta = convert_timebase_ms( p_picture->i_dts + p_flv->i_delay_time, p_flv->d_timebase );
dts = p_flv->i_framenum > p_flv->i_delay_frames
? convert_timebase_ms( p_picture->i_dts, p_flv->d_timebase )
: p_flv->i_framenum * p_flv->i_init_delta / (p_flv->i_delay_frames + 1);
cts = convert_timebase_ms( p_picture->i_pts, p_flv->d_timebase );
}
else
{
dts = convert_timebase_ms( p_picture->i_dts + p_flv->i_delay_time, p_flv->d_timebase );
cts = convert_timebase_ms( p_picture->i_pts + p_flv->i_delay_time, p_flv->d_timebase );
}
offset = cts - dts;
if( p_flv->i_framenum )
{
if( p_flv->i_prev_dts == dts )
x264_cli_log( "flv", X264_LOG_WARNING, "duplicate DTS %"PRId64" generated by rounding\n"
" decoding framerate cannot exceed 1000fps\n", dts );
if( p_flv->i_prev_cts == cts )
x264_cli_log( "flv", X264_LOG_WARNING, "duplicate CTS %"PRId64" generated by rounding\n"
" composition framerate cannot exceed 1000fps\n", cts );
}
p_flv->i_prev_dts = dts;
p_flv->i_prev_cts = cts;
// A new frame - write packet header
flv_put_byte( c, FLV_TAG_TYPE_VIDEO );
flv_put_be24( c, 0 ); // calculated later
flv_put_be24( c, dts );
flv_put_byte( c, dts >> 24 );
flv_put_be24( c, 0 );
p_flv->start = c->d_cur;
flv_put_byte( c, p_picture->b_keyframe ? FLV_FRAME_KEY : FLV_FRAME_INTER );
flv_put_byte( c, 1 ); // AVC NALU
flv_put_be24( c, offset );
if( p_flv->sei )
{
flv_append_data( c, p_flv->sei, p_flv->sei_len );
free( p_flv->sei );
p_flv->sei = NULL;
}
flv_append_data( c, p_nalu, i_size );
unsigned length = c->d_cur - p_flv->start;
flv_rewrite_amf_be24( c, length, p_flv->start - 10 );
flv_put_be32( c, 11 + length ); // Last tag size
CHECK( flv_flush_data( c ) );
p_flv->i_framenum++;
return i_size;
}
flv_output 中的可以看出write_frame()中完成了FLV封装格式中一个Tag单元的创建。
cli_input_t
x264项目中和cli_input_t结构体相关的源代码都位于根目录的input文件夹下。cli_input_t的定义位于input\input.h,如下所示。typedef struct
{
int (*open_file)( char *psz_filename, hnd_t *p_handle, video_info_t *info, cli_input_opt_t *opt );
int (*picture_alloc)( cli_pic_t *pic, int csp, int width, int height );
int (*read_frame)( cli_pic_t *pic, hnd_t handle, int i_frame );
int (*release_frame)( cli_pic_t *pic, hnd_t handle );
void (*picture_clean)( cli_pic_t *pic );
int (*close_file)( hnd_t handle );
} cli_input_t;
extern const cli_input_t raw_input;
extern const cli_input_t y4m_input;
extern const cli_input_t avs_input;
extern const cli_input_t lavf_input;
extern const cli_input_t ffms_input;
从源代码中可以看出,cli_input_t中一共包含了open_file(),picture_alloc(),read_frame(),release_frame(),picture_clean(),close_file()六个接口。在x264中有raw_input,y4m_input,avs_input,lavf_input,ffms_input这几个cli_output_t结构体,分别对应H.264裸流,Y4M,AVS,LAVF,FFMS格式(后几种没有接触过)。下面举例看两个结构体:raw_input和y4m_input。
raw_input(纯YUV像素数据的cli_input_t结构体)
raw_input的定义位于input\raw.c,该文件内容如下所示。
#include "input.h"
#define FAIL_IF_ERROR( cond, ... ) FAIL_IF_ERR( cond, "raw", __VA_ARGS__ )
typedef struct
{
FILE *fh;
int next_frame;
uint64_t plane_size[4];
uint64_t frame_size;
int bit_depth;
} raw_hnd_t;
//打开raw YUV格式文件
static int open_file( char *psz_filename, hnd_t *p_handle, video_info_t *info, cli_input_opt_t *opt )
{
raw_hnd_t *h = calloc( 1, sizeof(raw_hnd_t) );
if( !h )
return -1;
if( !opt->resolution )
{
//如果没有设置分辨率
//尝试从文件名中解析分辨率
/* try to parse the file name */
for( char *p = psz_filename; *p; p++ )
if( *p >= '0' && *p <= '9' && sscanf( p, "%dx%d", &info->width, &info->height ) == 2 )
break;
}
else
sscanf( opt->resolution, "%dx%d", &info->width, &info->height );
//没有分辨率信息的话,会弹出错误信息
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !info->width || !info->height, "raw input requires a resolution.\n" )
//设置颜色空间
if( opt->colorspace )
{
for( info->csp = X264_CSP_CLI_MAX-1; info->csp > X264_CSP_NONE; info->csp-- )
{
if( x264_cli_csps[info->csp].name && !strcasecmp( x264_cli_csps[info->csp].name, opt->colorspace ) )
break;
}
FAIL_IF_ERROR( info->csp == X264_CSP_NONE, "unsupported colorspace `%s'\n", opt->colorspace );
}
else /* default */
info->csp = X264_CSP_I420;//默认为YUV420P
//颜色位深
h->bit_depth = opt->bit_depth;
FAIL_IF_ERROR( h->bit_depth < 8 || h->bit_depth > 16, "unsupported bit depth `%d'\n", h->bit_depth );
if( h->bit_depth > 8 )
info->csp |= X264_CSP_HIGH_DEPTH;
if( !strcmp( psz_filename, "-" ) )
h->fh = stdin; //从管道输入
else
h->fh = x264_fopen( psz_filename, "rb" ); //打开文件
if( h->fh == NULL )
return -1;
info->thread_safe = 1;
info->num_frames = 0;
info->vfr = 0;
const x264_cli_csp_t *csp = x264_cli_get_csp( info->csp );
for( int i = 0; i < csp->planes; i++ )
{
h->plane_size[i] = x264_cli_pic_plane_size( info->csp, info->width, info->height, i );
h->frame_size += h->plane_size[i];
/* x264_cli_pic_plane_size returns the size in bytes, we need the value in pixels from here on */
h->plane_size[i] /= x264_cli_csp_depth_factor( info->csp );
}
if( x264_is_regular_file( h->fh ) )
{
fseek( h->fh, 0, SEEK_END );
uint64_t size = ftell( h->fh );
fseek( h->fh, 0, SEEK_SET );
info->num_frames = size / h->frame_size;
}
*p_handle = h;
return 0;
}
//读取一帧数据-内部
static int read_frame_internal( cli_pic_t *pic, raw_hnd_t *h, int bit_depth_uc )
{
int error = 0;
int pixel_depth = x264_cli_csp_depth_factor( pic->img.csp );
//一个分量一个分量读
for( int i = 0; i < pic->img.planes && !error; i++ )
{
//fread()读取
error |= fread( pic->img.plane[i], pixel_depth, h->plane_size[i], h->fh ) != h->plane_size[i];
if( bit_depth_uc )
{
/* upconvert non 16bit high depth planes to 16bit using the same
* algorithm as used in the depth filter. */
uint16_t *plane = (uint16_t*)pic->img.plane[i];
uint64_t pixel_count = h->plane_size[i];
int lshift = 16 - h->bit_depth;
for( uint64_t j = 0; j < pixel_count; j++ )
plane[j] = plane[j] << lshift;
}
}
return error;
}
//读取一帧数据
static int read_frame( cli_pic_t *pic, hnd_t handle, int i_frame )
{
raw_hnd_t *h = handle;
if( i_frame > h->next_frame )
{
if( x264_is_regular_file( h->fh ) )
fseek( h->fh, i_frame * h->frame_size, SEEK_SET ); //fseek()。偏移量=帧序号*帧大小。
else
while( i_frame > h->next_frame )
{
//读取一帧数据-内部
if( read_frame_internal( pic, h, 0 ) )
return -1;
h->next_frame++;
}
}
if( read_frame_internal( pic, h, h->bit_depth & 7 ) )
return -1;
h->next_frame = i_frame+1;
return 0;
}
//关闭文件
static int close_file( hnd_t handle )
{
raw_hnd_t *h = handle;
if( !h || !h->fh )
return 0;
//fclose()关闭文件
fclose( h->fh );
free( h );
return 0;
}
//raw格式对应的数组
const cli_input_t raw_input = { open_file, x264_cli_pic_alloc, read_frame, NULL, x264_cli_pic_clean, close_file };
从源代码中可以看出,raw_input 中的open_file()函数在打开YUV像素数据的时候,会首先判断是否设置了宽和高(YUV是纯像素数据,没有宽和高信息),如果没有设置,则会尝试从文件路径中解析宽和高信息。如果成功完成上述步骤,open_file()就会调用x264_fopen()打开输入文件。其他的函数在源代码中都写了注释,就不再重复记录了。
y4m_input的定义位于input\y4m.c,如下所示。
const cli_input_t y4m_input = { open_file, x264_cli_pic_alloc, read_frame, NULL, x264_cli_pic_clean, close_file };typedef struct
{
FILE *fh;
int next_frame;
int seq_header_len;
int frame_header_len;
uint64_t frame_size;
uint64_t plane_size[3];
int bit_depth;
} y4m_hnd_t;
#define Y4M_MAGIC "YUV4MPEG2"
#define MAX_YUV4_HEADER 80
#define Y4M_FRAME_MAGIC "FRAME"
#define MAX_FRAME_HEADER 80
static int parse_csp_and_depth( char *csp_name, int *bit_depth )
{
int csp = X264_CSP_MAX;
/* Set colorspace from known variants */
if( !strncmp( "420", csp_name, 3 ) )
csp = X264_CSP_I420;
else if( !strncmp( "422", csp_name, 3 ) )
csp = X264_CSP_I422;
else if( !strncmp( "444", csp_name, 3 ) && strncmp( "444alpha", csp_name, 8 ) ) // only accept alphaless 4:4:4
csp = X264_CSP_I444;
/* Set high bit depth from known extensions */
if( sscanf( csp_name, "%*d%*[pP]%d", bit_depth ) != 1 )
*bit_depth = 8;
return csp;
}
static int open_file( char *psz_filename, hnd_t *p_handle, video_info_t *info, cli_input_opt_t *opt )
{
y4m_hnd_t *h = malloc( sizeof(y4m_hnd_t) );
int i;
uint32_t n, d;
char header[MAX_YUV4_HEADER+10];
char *tokend, *header_end;
int colorspace = X264_CSP_NONE;
int alt_colorspace = X264_CSP_NONE;
int alt_bit_depth = 8;
if( !h )
return -1;
h->next_frame = 0;
info->vfr = 0;
if( !strcmp( psz_filename, "-" ) )
h->fh = stdin;
else
h->fh = x264_fopen(psz_filename, "rb");
if( h->fh == NULL )
return -1;
h->frame_header_len = strlen( Y4M_FRAME_MAGIC )+1;
/* Read header */
//解析Y4M格式的文件头
for( i = 0; i < MAX_YUV4_HEADER; i++ )
{
header[i] = fgetc( h->fh );
if( header[i] == '\n' )
{
/* Add a space after last option. Makes parsing "444" vs
"444alpha" easier. */
header[i+1] = 0x20;
header[i+2] = 0;
break;
}
}
if( i == MAX_YUV4_HEADER || strncmp( header, Y4M_MAGIC, strlen( Y4M_MAGIC ) ) )
return -1;
/* Scan properties */
header_end = &header[i+1]; /* Include space */
h->seq_header_len = i+1;
for( char *tokstart = &header[strlen( Y4M_MAGIC )+1]; tokstart < header_end; tokstart++ )
{
if( *tokstart == 0x20 )
continue;
switch( *tokstart++ )
{
case 'W': /* Width. Required. */
info->width = strtol( tokstart, &tokend, 10 );
tokstart=tokend;
break;
case 'H': /* Height. Required. */
info->height = strtol( tokstart, &tokend, 10 );
tokstart=tokend;
break;
case 'C': /* Color space */
colorspace = parse_csp_and_depth( tokstart, &h->bit_depth );
tokstart = strchr( tokstart, 0x20 );
break;
case 'I': /* Interlace type */
switch( *tokstart++ )
{
case 't':
info->interlaced = 1;
info->tff = 1;
break;
case 'b':
info->interlaced = 1;
info->tff = 0;
break;
case 'm':
info->interlaced = 1;
break;
//case '?':
//case 'p':
default:
break;
}
break;
case 'F': /* Frame rate - 0:0 if unknown */
if( sscanf( tokstart, "%u:%u", &n, &d ) == 2 && n && d )
{
x264_reduce_fraction( &n, &d );
info->fps_num = n;
info->fps_den = d;
}
tokstart = strchr( tokstart, 0x20 );
break;
case 'A': /* Pixel aspect - 0:0 if unknown */
/* Don't override the aspect ratio if sar has been explicitly set on the commandline. */
if( sscanf( tokstart, "%u:%u", &n, &d ) == 2 && n && d )
{
x264_reduce_fraction( &n, &d );
info->sar_width = n;
info->sar_height = d;
}
tokstart = strchr( tokstart, 0x20 );
break;
case 'X': /* Vendor extensions */
if( !strncmp( "YSCSS=", tokstart, 6 ) )
{
/* Older nonstandard pixel format representation */
tokstart += 6;
alt_colorspace = parse_csp_and_depth( tokstart, &alt_bit_depth );
}
tokstart = strchr( tokstart, 0x20 );
break;
}
}
if( colorspace == X264_CSP_NONE )
{
colorspace = alt_colorspace;
h->bit_depth = alt_bit_depth;
}
// default to 8bit 4:2:0 if nothing is specified
if( colorspace == X264_CSP_NONE )
{
colorspace = X264_CSP_I420;
h->bit_depth = 8;
}
FAIL_IF_ERROR( colorspace <= X264_CSP_NONE || colorspace >= X264_CSP_MAX, "colorspace unhandled\n" )
FAIL_IF_ERROR( h->bit_depth < 8 || h->bit_depth > 16, "unsupported bit depth `%d'\n", h->bit_depth );
info->thread_safe = 1;
info->num_frames = 0;
info->csp = colorspace;
h->frame_size = h->frame_header_len;
if( h->bit_depth > 8 )
info->csp |= X264_CSP_HIGH_DEPTH;
const x264_cli_csp_t *csp = x264_cli_get_csp( info->csp );
for( i = 0; i < csp->planes; i++ )
{
h->plane_size[i] = x264_cli_pic_plane_size( info->csp, info->width, info->height, i );
h->frame_size += h->plane_size[i];
/* x264_cli_pic_plane_size returns the size in bytes, we need the value in pixels from here on */
h->plane_size[i] /= x264_cli_csp_depth_factor( info->csp );
}
/* Most common case: frame_header = "FRAME" */
if( x264_is_regular_file( h->fh ) )
{
uint64_t init_pos = ftell( h->fh );
fseek( h->fh, 0, SEEK_END );
uint64_t i_size = ftell( h->fh );
fseek( h->fh, init_pos, SEEK_SET );
info->num_frames = (i_size - h->seq_header_len) / h->frame_size;
}
*p_handle = h;
return 0;
}
从源代码可以看出,y4m_input中的open_file()完成了Y4M文件的打开和文件头解析的功能。
cli_vid_filter_t
x264项目中和cli_vid_filter_t结构体相关的源代码都位于根目录的filters文件夹下。cli_vid_filter_t的定义位于filters\video\video.h,如下所示。struct cli_vid_filter_t
{
/* name of the filter */
const char *name;
/* help: a short message on what the filter does and how to use it.
* this should only be implemented by filters directly accessible by the user */
void (*help)( int longhelp );
/* init: initializes the filter given the input clip properties and parameter to adjust them as necessary
* with the given options provided by the user.
* returns 0 on success, nonzero on error. */
int (*init)( hnd_t *handle, cli_vid_filter_t *filter, video_info_t *info, x264_param_t *param, char *opt_string );
/* get_frame: given the storage for the output frame and desired frame number, generate the frame accordingly.
* the image data returned by get_frame should be treated as const and not be altered.
* returns 0 on success, nonzero on error. */
int (*get_frame)( hnd_t handle, cli_pic_t *output, int frame );
/* release_frame: frame is done being used and is signaled for cleanup.
* returns 0 on succeess, nonzero on error. */
int (*release_frame)( hnd_t handle, cli_pic_t *pic, int frame );
/* free: run filter cleanup procedures. */
void (*free)( hnd_t handle );
/* next registered filter, unused by filters themselves */
cli_vid_filter_t *next;
};
从源代码中可以看出,cli_vid_filter_t中一共包含了help(),init(),get_frame(),release_frame(),free()几个接口。下面举例看两个Filter结构体:
source_filter:不作任何处理。
resize_filter:拉伸。
source_filter(没有功能的cli_vid_filter_t结构体)
source_filter的定义位于filters\video\source.c,该文件内容如下所示。
#include "video.h"
/* This filter converts the demuxer API into the filtering API for video frames.
* Backseeking is prohibited here as not all demuxers are capable of doing so. */
typedef struct
{
cli_pic_t pic;
hnd_t hin;
int cur_frame;
} source_hnd_t;
cli_vid_filter_t source_filter;
static int init( hnd_t *handle, cli_vid_filter_t *filter, video_info_t *info, x264_param_t *param, char *opt_string )
{
source_hnd_t *h = calloc( 1, sizeof(source_hnd_t) );
if( !h )
return -1;
h->cur_frame = -1;
if( cli_input.picture_alloc( &h->pic, info->csp, info->width, info->height ) )
return -1;
h->hin = *handle;
*handle = h;
*filter = source_filter;
return 0;
}
static int get_frame( hnd_t handle, cli_pic_t *output, int frame )
{
source_hnd_t *h = handle;
/* do not allow requesting of frames from before the current position */
if( frame <= h->cur_frame || cli_input.read_frame( &h->pic, h->hin, frame ) )
return -1;
h->cur_frame = frame;
*output = h->pic;
return 0;
}
static int release_frame( hnd_t handle, cli_pic_t *pic, int frame )
{
source_hnd_t *h = handle;
if( cli_input.release_frame && cli_input.release_frame( &h->pic, h->hin ) )
return -1;
return 0;
}
static void free_filter( hnd_t handle )
{
source_hnd_t *h = handle;
cli_input.picture_clean( &h->pic );
cli_input.close_file( h->hin );
free( h );
}
cli_vid_filter_t source_filter = { "source", NULL, init, get_frame, release_frame, free_filter, NULL };
从源代码中可以看出,source_filter的get_frame()直接调用了cli_input_t的read_frame();而它的release_frame()也是直接调用了cli_input_t的release_frame()。简而言之,source_filter相当于是一个cli_input_t。
resize_filter(拉伸功能对应的cli_vid_filter_t结构体)
resize_filter的定义位于filters\video\resize.c,该结构体定义如下。
cli_vid_filter_t resize_filter = { NAME, help, init, get_frame, release_frame, free_filter, NULL };static int get_frame( hnd_t handle, cli_pic_t *output, int frame )
{
resizer_hnd_t *h = handle;
if( h->prev_filter.get_frame( h->prev_hnd, output, frame ) )
return -1;
if( h->variable_input && check_resizer( h, output ) )
return -1;
h->working = 1;
if( h->pre_swap_chroma )
XCHG( uint8_t*, output->img.plane[1], output->img.plane[2] );
if( h->ctx )
{
sws_scale( h->ctx, (const uint8_t* const*)output->img.plane, output->img.stride,
0, output->img.height, h->buffer.img.plane, h->buffer.img.stride );
output->img = h->buffer.img; /* copy img data */
}
else
output->img.csp = h->dst_csp;
if( h->post_swap_chroma )
XCHG( uint8_t*, output->img.plane[1], output->img.plane[2] );
return 0;
}
可以看出resize_filter中调用了libswscale类库中的sws_scale()对图像完成了拉伸工作。
注:拉伸滤镜需要libswscale类库的支持。
至此cli_output_t,cli_input_t,cli_vid_filter_t这3个在x264中与输入输出有关的结构体的源代码就分析完毕了。有关x264命令行工具的源代码分析工作也就做完了。下一篇文章开始对libx264内部的源代码进行分析。
雷霄骅
[email protected]
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020