机器学习 -- 支持向量机SVM(Ⅳ sklearn中的SVM)
使用SVM算法和使用kNN一样,要做数据标准化处理(涉及距离,需要统一量纲)。
(1)导入所需的模块和包
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets(2)加载并提取部分数据集
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
X = X[y < 2, :2]
y = y[y < 2](3)绘制出提取的数据集的点
plt.scatter(X[y == 0, 0], X[y == 0, 1], color='r')
plt.scatter(X[y == 1, 0], X[y == 1, 1], color='b')
plt.show()(4)数据集的归一化处理
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
standardScaler = StandardScaler()
standardScaler.fit(X)
X_standard = standardScaler.transform(X)(5)导入linearSVC线性分类支持向量机
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC(6)绘制决策边界的函数
def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis):
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)),
np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100))
)
x_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
y_predict = model.predict(x_new).reshape(x0.shape)
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A', '#FFF59D', '#90CAF9'])
plt.contourf(x0,x1,y_predict, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap)(7)实例化linearSVC线性分类支持向量机对象并绘制图像
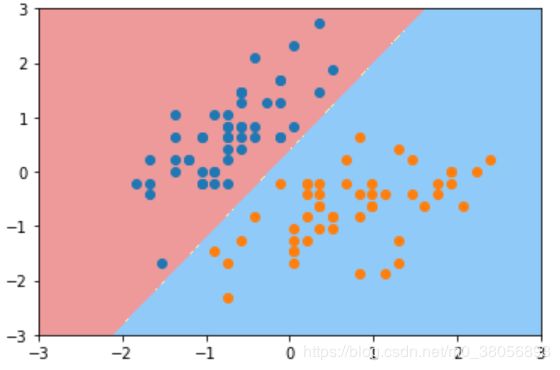
C越大,容错空间越小;C越小,容错空间越大。
① C取较大的数值时:
svc = LinearSVC(C=1e9)
svc.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(svc, axis=[-3, 3, -3, 3])
plt.scatter(X_standard[y == 0, 0], X_standard[y == 0, 1])
plt.scatter(X_standard[y == 1, 0], X_standard[y == 1, 1])
plt.show()② C取较小的数值时:
svc2 = LinearSVC(C=0.01)
svc2.fit(X_standard, y)
plot_decision_boundary(svc2, axis=[-3, 3, -3, 3])
plt.scatter(X_standard[y == 0, 0], X_standard[y == 0, 1])
plt.scatter(X_standard[y == 1, 0], X_standard[y == 1, 1])
plt.show()(8)定义一个绘制svc决策边界的函数
def plot_svc_decision_boundary(model, axis):
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)),
np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100))
)
x_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
y_predict = model.predict(x_new).reshape(x0.shape)
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A', '#FFF59D', '#90CAF9'])
plt.contourf(x0,x1,y_predict, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap)
w = model.coef_[0]
b = model.intercept_[0]
# 决策边界直线方程: w0 * x0 + w1 * x1 + b = 0
# => x1 = -b / w1 - w0 * x0 / w1
plot_x = np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], 200)
up_y = -b/w[1] - w[0]/w[1] * plot_x + 1/w[1]
down_y = -b/w[1] - w[0]/w[1] * plot_x - 1/w[1]
# 过滤
up_index = (up_y >= axis[2]) & (up_y <= axis[3])
down_index = (down_y >= axis[2]) & (down_y <= axis[3])
plt.plot(plot_x[up_index], up_y[up_index], color='black')
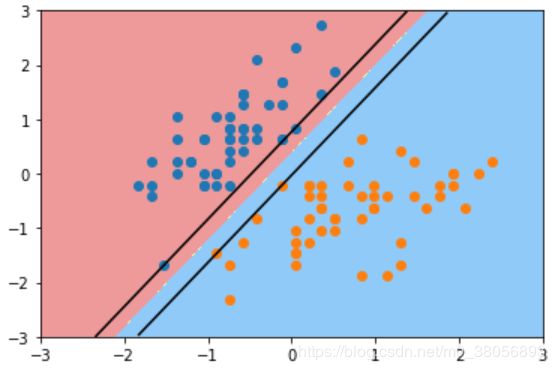
plt.plot(plot_x[down_index], down_y[down_index], color='black')(9)绘制图像,观察svc1和svc2区别
① svc1
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc, axis=[-3, 3, -3, 3])
plt.scatter(X_standard[y == 0, 0], X_standard[y == 0, 1])
plt.scatter(X_standard[y == 1, 0], X_standard[y == 1, 1])
plt.show()
② svc2
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc2, axis=[-3, 3, -3, 3])
plt.scatter(X_standard[y == 0, 0], X_standard[y == 0, 1])
plt.scatter(X_standard[y == 1, 0], X_standard[y == 1, 1])
plt.show()