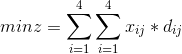运筹优化学习02:Lingo求解带容量约束的车辆路径问题(CVRP)
目录
1 基础知识储备
1.1 LINGO 具有9种逻辑运算符
1.2 lingo的窗口状态解析
1.3 @wrap函数解析
1.3.1 官方解释
1.3.2 示例代码及解释
2 CVRP问题描述与模型
2.1 问题描述
2.2 定义集合和数据段
2.2.1 定义集合
2.2.2 定义数据段
2.2.3 定义目标函数
2.2.4 定义模型约束条件
3 结果演示
带容量约束的车辆路径问题,是使用一组具有核定载重约束的车队为一组顾客点提供服务,要求服务的总路径最短。
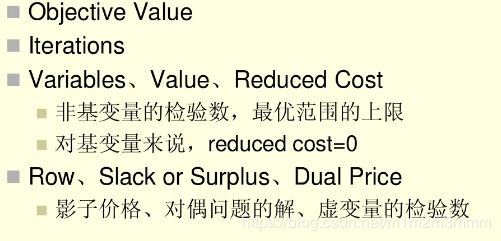
1 基础知识储备
1.1 LINGO 具有9种逻辑运算符
| #not# | 否定该操作数的逻辑值,#not#是一个一元表达式 |
| #eq# | 若两个运算数相等,则为true;否则为flase |
| #ne# | 若两个运算符不相等,则为true;否则为flase |
| #gt# | 若左边的运算符严格大于右边的运算符,则为true;否则为flase |
| #ge# | 若左边的运算符大于或等于右边的运算符,则为true;否则为flase |
| #lt# | 若左边的运算符严格小于右边的运算符,则为true;否则为flase |
| #le# | 若左边的运算符小于或等于右边的运算符,则为true;否则为flase |
| #and# | 仅当两个参数都为true 时,结果为true;否则为flase |
| #or# | 仅当两个参数都为false 时,结果为false;否则为true |
这些运算符的优先级由高到低为
![]()
1.2 lingo的窗口状态解析
1.3 @wrap函数解析
1.3.1 官方解释
@wrap(index,limit)
| @WRAP( INDEX, LIMIT) This allows you to "wrap" an index around the end of a set and continue indexing at the other end of the set. That is, when the last (first) member of a set is reached in a set looping function, use of @WRAP will allow you to wrap the set index to the first (last) member of the set. This is a particularly useful function in cyclical, multiperiod planning models. Formally speaking, @WRAP returns J such that J = INDEX - K * LIMIT, where K is an integer such that J is in the interval [1,LIMIT]. Informally speaking, @WRAP will subtract or add LIMIT to INDEX until it falls in the range 1 to LIMIT. For an example on the use of the @WRAP function in a staff scheduling model, refer to the Primitive Set Example section in Using Sets. |
@wrap函数的确是返回j=index-k*limit,其中k是一个整数,取适当值保证j落在区间[1,limit]内。可是它并不等于做简单的取模再加1的作用。如果硬要在取模方面来说明@wrap函数的话只能这么来解释了:@wrap(index,limit)函数相当于index模limit,如果取模结果不等于0,就返回该结果,否则返回limit。
1.3.2 示例代码及解释
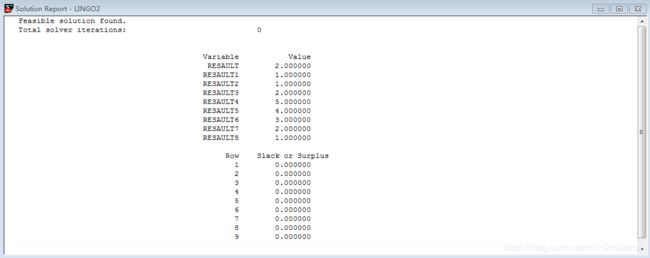
resault = @wrap(10,2);
resault1 = @wrap(10,1);
resault2 = @wrap(10,3);
resault3 = @wrap(10,4);
resault4 = @wrap(10,5);
resault5 = @wrap(10,6);
resault6 = @wrap(10,7);
resault7 = @wrap(10,8);
resault8 = @wrap(10,9);
resault9 = @wrap(10,0); !本行代码会报错误代码86;代码演示结果
最后一行代码的报错及解释:不允许分母为0
| An undefined arithmetic operation (e.g., 1/0 or @LOG( -1)) occurred while LINGO was solving the model. If you have specified a row name for the constraint, LINGO will print the name of the constraint. If you haven't specified row names in your model, you may want to add them to assist in tracking down this error. Check the referenced constraint for any undefined operations and try to either, 1) rewrite it avoiding operations that can potentially become undefined, or, 2) use the @BND function to restrict variables to ranges where all operations are defined. |
2 CVRP问题描述与模型
2.1 问题描述
假定存在一个车场Depot和3个顾客需求点,4个节点之间的距离和每个顾客点的需求量如下图所示:
我们的任务是安排车辆从depot出发,然后服务完成这三个顾客需求点所需的车辆行驶路径最短
2.2 定义集合和数据段
我们在模型中使用到如下变量:
q_{i}:表示顾客节点的需求量,对应需求向量Q,维度为1*4;其中4为模型涉及的节点个数,并将车场点设置为0;
u_{i}:车辆行驶至节点i时的累积需求量,对应需求量向量U
d_{ij}:表示节点 i 到节点 j 的空间距离,对应距离矩阵DIST
x_{ij}:表示弧段i,j是否为车辆方位,若访问则取值为1,否则取值为0
2.2.1 定义集合
!定义集合;
SETS:
CITY/1..4/: Q, U; !定义需求量向量Q_{i}和累积载重量向量U(i);
CXC(CITY, CITY): DIST, X;!定义距离矩阵d_{ij}和二进制变量x_{ij};
ENDSETS2.2.2 定义数据段
!定义数据段;
DATA:
Q = 0 2 3 5;!需求量向量;
DIST = !距离矩阵;
0 3 4 2
3 0 4 5
4 4 0 7
2 5 7 0;
C = 5;!车辆的最大载重量为5;
ENDDATA2.2.3 定义目标函数
对应Latex源码:
min z = \sum_{i=1}^{4} \sum_{i=1}^{4} x_{ij} * d_{ij}对应Lingo源码:
min = @sum(CXC : X * DIST);2.2.4 定义模型约束条件
(1)限定变量x_{ij}为二进制变量
!设置整数约束;
@for(cxc : @bin(x)); !规定变量x_{ij}为二进制变量,只能取值为0或者1;(2)为x_{ij}赋值:
程序逻辑:
- 第一步,将矩阵X的对角线元素赋值为0;
- 第二步:为非对角线元素赋值
- 若下一个节点为depot节点则设置为x_{ij} = 1,否则为0
- 若为非depot节点,判断累加需求量是否大于车辆约束C,若是设置x_{ij} = 1
对应Lingo源码:
@for(city(k) | k #gt# 1 : x(k,k) = 0;
@sum(city (i) | i #ne# k #and# (i #eq# 1 #or# Q(i) + Q(k) < C) : x(i,k) = 1;
@sum(city (j) | j #ne# k #and# (j #eq# 1 #or# Q(i) + Q(k) < C) : x(k,j) = 1;
@for(city(i) | i #ne# k #and# i #ne# 1 :
U(k) >= U(i) + Q(k) - C + C * (x(k,i) + x(i,k)) - (Q(k) + Q(i)) * x(k,i);
);
U(k) <= C - (C - Q(k)) * x(1, k);
U(k) >= Q(k) + @sum(city(i) | i #gt# 1: Q(i) * x(i,k));
);(3)车辆数目约束
vechileCnt = @SUM( city(i) | i #gt# : Q(i)) / C;
vehicleR = vechileCnt + 1.999 - @wrap(vechileCnt - 0.001, 1);
@sum(city(j) | j #gt# 1 : x(1,j) >= vehicleR;必须有足够的车辆离开车场3 结果演示
| Local optimal solution found.
Row Slack or Surplus |
最优解: 1 --> 4 --> 1; 1-->2-->3-->1
对CVRP的求解过程进行分析,并给出源代码的编写过程,对于代码本身可能还有其他的编码方式,也希望高人无私共享,共同学习
有兴趣共同学习的欢迎关注个人公众账号"学而立行“”
本文模型及代码将在【运筹优化与地理信息】公众号付费发布,如不愿意付费,可移步B站同名帐号,观看手敲代码及演示视频