深入理解Android音视频同步机制(二)ExoPlayer的avsync逻辑
- 深入理解Android音视频同步机制(一)概述
- 深入理解Android音视频同步机制(二)ExoPlayer的avsync逻辑
- 深入理解Android音视频同步机制(三)NuPlayer的avsync逻辑
- 深入理解Android音视频同步机制(四)MediaSync的使用与原理
- 深入理解Android音视频同步机制(五)如何从零开始写一个音视频同步的播放器
对于此前没有看过ExoPlayer的朋友,我们在这里先用下面的时序图简单介绍一下ExoPlayer在音视频同步这块的基本流程:

图中
ExoPlayerImplInternal是Exoplayer的主loop所在处,这个大loop不停的循环运转,将下载、解封装的数据送给AudioTrack和MediaCodec去播放。
MediaCodecAudioRenderer和MediaCodecVideoRenderer分别是处理音频和视频数据的类,在MediaCodecAudioRenderer中会调用AudioTrack的write方法,写入音频数据,同时还会调用AudioTrack的getTimeStamp、getPlaybackHeadPosition、getLantency方法来获得“Audio当前播放的时间”。在MediaCodecVideoRenderer中会调用MediaCodec的几个关键API,例如通过调用releaseOutputBuffer方法来将视频帧送显。在MediaCodecVideoRenderer类中,会依据avsync逻辑调整视频帧的pts,并且控制着丢帧的逻辑。
VideoFrameReleaseTimeHelper可以获取系统的vsync时间和间隔,并且利用vsync信号调整视频帧的送显时间。
下面我会先简要的介绍ExoPlayer avsync逻辑中的关键点,最后再进行详细的代码分析。
Video部分
1.利用pts和系统时间计算预计送显时间(视频帧应该在这个时间点显示)
MediaCodecVideoRenderer#processOutputBuffer
//计算 “当前帧的pts(bufferPresentationTimeUs )” 与“Audio当前播放时间(positionUs )”之间的时间间隔,
//最后还减去了一个elapsedSinceStartOfLoopUs的值,代表的是程序运行到此处的耗时,
//减去这个值可以看做一种使计算值更精准的做法
long elapsedSinceStartOfLoopUs = (SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() * 1000) - elapsedRealtimeUs;
earlyUs = bufferPresentationTimeUs - positionUs - elapsedSinceStartOfLoopUs;
// Compute the buffer's desired release time in nanoseconds.
// 用当前系统时间加上前面计算出来的时间间隔,即为“预计送显时间”
long systemTimeNs = System.nanoTime();
long unadjustedFrameReleaseTimeNs = systemTimeNs + (earlyUs * 1000);
2、利用vsync对预计送显时间进行调整
MediaCodecVideoRenderer#processOutputBuffer
long adjustedReleaseTimeNs = frameReleaseTimeHelper.adjustReleaseTime(
bufferPresentationTimeUs, unadjustedFrameReleaseTimeNs);
adjustReleaseTime方法里面干了几件事:
a.计算ns级别的平均帧间隔时间,因为vsync的精度是ns
b.寻找距离当前送显时间点(unadjustedFrameReleaseTimeNs)最近(可能是在送显时间点之前,也可能是在送显时间点之后)的vsync时间点,我们的目标是在这个vsync时间点让视频帧显示出去
c.上面计算出的是我们的目标vsync显示时间,但是要提前送,给后面的显示流程以时间,所以再减去一个vsyncOffsetNs时间,这个时间是写死的,定义为.8*vsyncDuration,减完之后的这个值就是真正给MediaCodec.releaseOutputBuffer方法的时间戳
这里其实有问题:首先是这里的0.8系数设置的是否合理,其次是否能有办法验证这一帧真的在这一个vsync信号时间点显示出去了。按照mediacodec.releaseOutputbuffer的说法注释,应该在两个vsync信号之前调用release方法,但是从目前的做法来看并没有follow注释的说法。
调研之后,我们发现,利用dumpsys SurfaceFlinger --latency SurfaceView方法我们可以知道每一帧的desiredPresentationTime和actualPresentationTime,经过实测,在一些平台上这两个值得差距在一个vsync时间以上,一般为22ms左右,所以ExoPlayer里面设置的这个0.8的系数也许不甚合理。其次我们观察了NuPlayer的avsync逻辑,发现在NuPlayer中就是严格按照releaseOutputbuffer注释所说的,提前两个vsync时间调用release方法。
上面的提到的注释内容如下
/**
* If you are done with a buffer, use this call to update its surface timestamp
* and return it to the codec to render it on the output surface. If you
* have not specified an output surface when configuring this video codec,
* this call will simply return the buffer to the codec.
*
* The timestamp may have special meaning depending on the destination surface.
*
*
* SurfaceView specifics
* If you render your buffer on a {@link android.view.SurfaceView},
* you can use the timestamp to render the buffer at a specific time (at the
* VSYNC at or after the buffer timestamp). For this to work, the timestamp
* needs to be reasonably close to the current {@link System#nanoTime}.
* Currently, this is set as within one (1) second. A few notes:
*
*
* - the buffer will not be returned to the codec until the timestamp
* has passed and the buffer is no longer used by the {@link android.view.Surface}.
*
- buffers are processed sequentially, so you may block subsequent buffers to
* be displayed on the {@link android.view.Surface}. This is important if you
* want to react to user action, e.g. stop the video or seek.
*
- if multiple buffers are sent to the {@link android.view.Surface} to be
* rendered at the same VSYNC, the last one will be shown, and the other ones
* will be dropped.
*
- if the timestamp is not "reasonably close" to the current system
* time, the {@link android.view.Surface} will ignore the timestamp, and
* display the buffer at the earliest feasible time. In this mode it will not
* drop frames.
* 注意这里!!!!!!
*
- for best performance and quality, call this method when you are about
* two VSYNCs' time before the desired render time. For 60Hz displays, this is
* about 33 msec.
*
*
*
* Once an output buffer is released to the codec, it MUST NOT
* be used until it is later retrieved by {@link #getOutputBuffer} in response
* to a {@link #dequeueOutputBuffer} return value or a
* {@link Callback#onOutputBufferAvailable} callback.
*
* @param index The index of a client-owned output buffer previously returned
* from a call to {@link #dequeueOutputBuffer}.
* @param renderTimestampNs The timestamp to associate with this buffer when
* it is sent to the Surface.
* @throws IllegalStateException if not in the Executing state.
* @throws MediaCodec.CodecException upon codec error.
*/
public final void releaseOutputBuffer(int index, long renderTimestampNs)
3、丢帧和送显
MediaCodecVideoRenderer#processOutputBuffer
//计算实际送显时间与当前系统时间之间的时间差
earlyUs = (adjustedReleaseTimeNs - systemTimeNs) / 1000;
//将上面计算出来的时间差与预设的门限值进行对比
if (shouldDropOutputBuffer(earlyUs, elapsedRealtimeUs)) {
dropOutputBuffer(codec, bufferIndex);
return true;
}
…
if (earlyUs < 50000) {
//视频帧来的太晚会被丢掉, 来的太早则先不予显示,进入下次loop,再行判断
renderOutputBufferV21(codec, bufferIndex, adjustedReleaseTimeNs);
如果earlyUs 时间差为正值,代表视频帧应该在当前系统时间之后被显示,换言之,代表视频帧来早了,反之,如果时间差为负值,代表视频帧应该在当前系统时间之前被显示,换言之,代表视频帧来晚了。如果超过一定的门限值,即该视频帧来的太晚了,则将这一帧丢掉,不予显示。按照预设的门限值,视频帧比预定时间来的早了50ms以上,则进入下一个间隔为10ms的循环,再继续判断,否则,将视频帧送显。
小结
1.我们平时一般理解avsync就是比较audio pts和video pts,也就是比较码流层面的“播放”时间,来早了就等,来晚了就丢帧,但为了更精确地计算这个差值,exoplayer里面一方面统计了函数调用的一些耗时,一方面实际上是在比较系统时间和当前视频帧的送显时间来判断要不要丢帧,也就是脱离了码流层面
2.既然牵涉到实际送显时间的计算,就需要将播放时间映射到vsync时间上,也就有了cloestVsync的计算,也有了提前80% vsync信号间隔时间送显的做法,同时因为vsync信号时间的精度为ns,为了更好匹配这一精度,而没有直接用ms精度的码流pts值,而是另外计算了ns级别的视频帧间隔时间
Audio部分
1.1.get current play time – 使用AudioTrack.getTimeStamp方法
AudioTrack#getCurrentPositionUs(boolean sourceEnded)
positionUs = framesToDurationUs(AudioTimestamp.framePosition)
+ systemClockUs – AudioTimestamp.nanoTime/1000
对getTimeStamp方法的调用是以500ms为间隔的,所以AudioTimestamp.nanoTime是上次调用时拿到的结果,systemClockUs – AudioTimestamp.nanoTime得到的就是距离上次调用所经过的系统时间,framesToDurationUs(AudioTimestamp.framePosition)代表的是上次调用时获取到的“Audio当前播放的时间”,二者相加即为当前系统时间下的“Audio当前播放的时间”
为什么要以500ms为间隔调用getTimeStamp方法?参见API注释,如下
/**
* Poll for a timestamp on demand.
*
* If you need to track timestamps during initial warmup or after a routing or mode change,
* you should request a new timestamp periodically until the reported timestamps
* show that the frame position is advancing, or until it becomes clear that
* timestamps are unavailable for this route.
*
* After the clock is advancing at a stable rate,
* query for a new timestamp approximately once every 10 seconds to once per minute.
* 注意这里!!!!!
* Calling this method more often is inefficient.
* It is also counter-productive to call this method more often than recommended,
* because the short-term differences between successive timestamp reports are not meaningful.
* If you need a high-resolution mapping between frame position and presentation time,
* consider implementing that at application level, based on low-resolution timestamps.
*
* The audio data at the returned position may either already have been
* presented, or may have not yet been presented but is committed to be presented.
* It is not possible to request the time corresponding to a particular position,
* or to request the (fractional) position corresponding to a particular time.
* If you need such features, consider implementing them at application level.
*
* @param timestamp a reference to a non-null AudioTimestamp instance allocated
* and owned by caller.
* @return true if a timestamp is available, or false if no timestamp is available.
* If a timestamp if available,
* the AudioTimestamp instance is filled in with a position in frame units, together
* with the estimated time when that frame was presented or is committed to
* be presented.
* In the case that no timestamp is available, any supplied instance is left unaltered.
* A timestamp may be temporarily unavailable while the audio clock is stabilizing,
* or during and immediately after a route change.
* A timestamp is permanently unavailable for a given route if the route does not support
* timestamps. In this case, the approximate frame position can be obtained
* using {@link #getPlaybackHeadPosition}.
* However, it may be useful to continue to query for
* timestamps occasionally, to recover after a route change.
*/
// Add this text when the "on new timestamp" API is added:
// Use if you need to get the most recent timestamp outside of the event callback handler.
public boolean getTimestamp(AudioTimestamp timestamp)
1.2.get current play time – 使用AudioTrack.getPlaybackHeadPosition方法
AudioTrack#getCurrentPositionUs(boolean sourceEnded)
//因为 getPlayheadPositionUs() 的粒度只有约20ms, 如果直接拿来用的话精度不够
//要进行采样和平滑演算得到playback position
positionUs = systemClockUs + smoothedPlayheadOffsetUs
= systemClockUs + avg[playbackPositionUs(i) – systemClock(i)]
positionUs -= latencyUs ;
上式中i最大取10,因为getPlayheadPositionUs的精度不足以用来做音视频同步,所以这里通过计算每次getPlayheadPositionUs拿到的值与系统时钟的offset,并且取平均值,来解决精度不足的问题,平滑后的值即为smoothedPlayheadOffsetUs,再加上系统时钟即为“Audio当前播放的时间”。当然,最后要减去通过AudioTrack.getLatency方法获取到的底层delay值,才是最终的结果。
小结
总体来说,音视频同步机制中的同步基准有两种选择:利用系统时间或audio playback position. 如果是video only的流,则利用系统时间,这方面比较简单,不再赘述
a. 如果是用audio position的话, 首先明确是通过下式来计算
startMediaTimeUs + positionUs
式中startMediaTimeUs为码流中拿到的初始audio pts值, positionUs是一个以0为起点的时间值,代表audio 播放了多长时间的数据
b.计算positionUs值则有两个方法, 根据设备支持情况来选择:
b.1.用AudioTimeStamp值来计算,需要注意的是,因为getTimeStamp方法不建议频繁调用,在ExoPlayer中是以500ms为间隔调用的,所以对应的逻辑可以化简为:
positionUs = framePosition/sampleRate + systemClock – nanoTime/1000
b.2. 用audioTrack.getPlaybackHeadPosition方法来计算, 但是因为这个值的粒度只有20ms, 可能存在一些抖动, 所以做了一些平滑处理, 对应的逻辑可以化简为:
positionUs = systemClockUs + smoothedPlayheadOffsetUs - latencyUs
= systemClockUs + avg[playbackPositionUs(i) - systemClock(i)] - latencyUs
= systemClockUs + avg[(audioTrack.getPlaybackHeadPosition/sampleRate)(i) -systemClock(i)] - latencyUs
ExoPlayer avsync逻辑代码精读
还是一样,先来看video部分,avsync逻辑的入口在下面的方法
–
com.google.android.exoplayer2.video.MediaCodecVideoRenderer#processOutputBuffer
protected boolean processOutputBuffer(long positionUs/*当前播放时间,由系统时间或audioClock计算*/, long elapsedRealtimeUs, MediaCodec codec,
ByteBuffer buffer, int bufferIndex, int bufferFlags, long bufferPresentationTimeUs/*当前帧的pts*/,
boolean shouldSkip) {
....
// Compute how many microseconds it is until the buffer's presentation time.
//计算当前帧的pts与当前播放时间之间的时间间隔,需要注意的是,最后还减去了一个elapsedSinceStartOfLoopUs的值,这个值代表的是从当前播放时间更新到程序运行到此处 的耗时,减去这个值可以看做一种使计算值更精准的做法
long elapsedSinceStartOfLoopUs = (SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() * 1000) - elapsedRealtimeUs;
earlyUs = bufferPresentationTimeUs - positionUs - elapsedSinceStartOfLoopUs;
// Compute the buffer's desired release time in nanoseconds.
// 用当前系统时间加上前面计算出来的时间间隔,即为初步计算出来的预计送显时间
long systemTimeNs = System.nanoTime();
long unadjustedFrameReleaseTimeNs = systemTimeNs + (earlyUs * 1000);
// Apply a timestamp adjustment, if there is one.
// 对预计送显时间进行调整, 得到实际送显时间, 调整的逻辑详见下面1.1
long adjustedReleaseTimeNs = frameReleaseTimeHelper.adjustReleaseTime(
bufferPresentationTimeUs, unadjustedFrameReleaseTimeNs);
//计算实际送显时间与当前系统时间之间的时间差, 如果时间差为正值, 代表视频帧应该在当前系统时间之后被显示,换言之,代表视频帧来早了, 反之, 如果时间差为负值, 代表视频帧应该在当前系统时间之前被显示, 换言之, 代表视频帧来晚了
earlyUs = (adjustedReleaseTimeNs - systemTimeNs) / 1000;
//将上面计算出来的时间差与预设的门限值进行对比, 如果超过门限值, 即该视频帧来的太晚了, 则将这一帧丢掉, 不予显示, 详细的对比与丢帧的逻辑如下1.2, 1.3所示
if (shouldDropOutputBuffer(earlyUs, elapsedRealtimeUs)) {
dropOutputBuffer(codec, bufferIndex);
return true;
}
if (Util.SDK_INT >= 21) {
// Let the underlying framework time the release.
if (earlyUs < 50000) {
//视频帧来的太晚会被丢掉, 来的太早同样有问题, 按照预设的门限值, 视频帧比预定时间来的早了50ms以上, 则进入下一个间隔为10ms的循环,再继续判断, 否则, 将视频帧送显, 送显的详细逻辑如下面1.4所示
renderOutputBufferV21(codec, bufferIndex, adjustedReleaseTimeNs);
return true;
}
} else {
....
}
}
....
}
1.1
调整送显时间的逻辑如下
com.google.android.exoplayer2.video.VideoFrameReleaseTimeHelper#adjustReleaseTime
/**
* Adjusts a frame release timestamp.
*
* @param framePresentationTimeUs The frame's presentation time, in microseconds.
* @param unadjustedReleaseTimeNs The frame's unadjusted release time, in nanoseconds and in
* the same time base as {@link System#nanoTime()}.
* @return The adjusted frame release timestamp, in nanoseconds and in the same time base as
* {@link System#nanoTime()}.
*/
public long adjustReleaseTime(long framePresentationTimeUs, long unadjustedReleaseTimeNs) {
long framePresentationTimeNs = framePresentationTimeUs * 1000;
// Until we know better, the adjustment will be a no-op.
//一开始没事干就别瞎调,保持原样
long adjustedFrameTimeNs = framePresentationTimeNs; //调整后的视频帧pts
long adjustedReleaseTimeNs = unadjustedReleaseTimeNs;//调整后的视频帧送显时间
if (haveSync) { //在第一次的时候不走这个if逻辑
// See if we've advanced to the next frame.
if (framePresentationTimeUs != lastFramePresentationTimeUs) {
frameCount++;//下一帧了
adjustedLastFrameTimeNs = pendingAdjustedFrameTimeNs;//上一个帧调整后的pts
}
if (frameCount >= MIN_FRAMES_FOR_ADJUSTMENT) {
// We're synced and have waited the required number of frames to apply an adjustment.
// Calculate the average frame time across all the frames we've seen since the last sync.
// This will typically give us a frame rate at a finer granularity than the frame times
// themselves (which often only have millisecond granularity).
//处于sync状态大于6帧的时间才做调整
//关于何为sync状态: 如果视频帧的pts和他的送显时间之间差了20ms以上,就认为偏移过大,也就认为失去sync了. 在理想的情况下,一个视频帧的pts应该和它的送显时间一一对应,pts本身是个常量,送显时间的计算过程中存在着一个不确定变量,就是 elapsedSinceStartOfLoopUs, 这玩意的理想值永远是0,但实际上并不是,所以会在pts和对应的送显时间之间引入一些偏差,如果这个偏差大于20ms,就认为失去sync了,否则认为还没有失去sync.从一些简单的实验测试结果看,很少会有失去sync的情况出现
// 以6帧作为间隔来计算平均帧间隔的问题是收敛会比较慢,可能算了半天都还有误差.当然好处是能够尽早开始计算,比较适合于码流本身帧间隔就不均匀的情况
//首先计算平均帧间隔
long averageFrameDurationNs = (framePresentationTimeNs - syncFramePresentationTimeNs)
/ frameCount;
// Project the adjusted frame time forward using the average.
//然后根据平均帧间隔,加前一帧的pts,计算出一个ns级别的视频帧pts时间,否则从码流中读出来的pts往往只有ms精度.
long candidateAdjustedFrameTimeNs = adjustedLastFrameTimeNs + averageFrameDurationNs;
if (isDriftTooLarge(candidateAdjustedFrameTimeNs, unadjustedReleaseTimeNs)) {
haveSync = false;
} else {
//如果还在sync的状态,就将ns级别的帧pts作为调整后的视频帧pts
//既然认为还在sync状态,那么送显时间的变化量应该和视频帧pts的变化量相同,所以有下面的式子
adjustedFrameTimeNs = candidateAdjustedFrameTimeNs;
adjustedReleaseTimeNs = syncUnadjustedReleaseTimeNs + adjustedFrameTimeNs
- syncFramePresentationTimeNs;
}
} else {
// We're synced but haven't waited the required number of frames to apply an adjustment.
// Check drift anyway.
// 距离上一次sync之后还没过去6帧,先查查是否有drift too large的问题,即视频帧的pts和他的送显时间之间是否差了20ms以上
if (isDriftTooLarge(framePresentationTimeNs, unadjustedReleaseTimeNs)) {
haveSync = false;
}
}
}
// If we need to sync, do so now.最开始的时候进入这里
if (!haveSync) {
syncFramePresentationTimeNs = framePresentationTimeNs; //sync状态下的视频帧pts
syncUnadjustedReleaseTimeNs = unadjustedReleaseTimeNs; //sync状态下的送显时间
frameCount = 0;
haveSync = true;//相当于默认第一帧是have sync的
onSynced();//do nothing
}
lastFramePresentationTimeUs = framePresentationTimeUs;//记录上一帧的pts
pendingAdjustedFrameTimeNs = adjustedFrameTimeNs;//将要送显帧的pts
if (vsyncSampler == null || vsyncSampler.sampledVsyncTimeNs == 0) {
//vsyncSampler会返回每个vsync信号的时间,正常情况下不会走到这个if逻辑里面
return adjustedReleaseTimeNs;
}
// Find the timestamp of the closest vsync. This is the vsync that we're targeting.
// 寻找距离当前送显时间点最近(可能是在送显时间点之前,也可能是在送显时间点之后)的vsync时间点,我们的目标是在这个vsync时间点让视频帧显示出去,关于这里的计算逻辑请见下面的1.1.1
long snappedTimeNs = closestVsync(adjustedReleaseTimeNs,
vsyncSampler.sampledVsyncTimeNs, vsyncDurationNs);
// Apply an offset so that we release before the target vsync, but after the previous one.
// 上面计算出的是我们的目标vsync显示时间,但是要提前送,给后面的流程以时间,所以再减去vsyncOffsetNs时间,这个时间是写死的,定义为0.8*vsyncDuration,减完之后的这个值就是真正给mediacodec.releaseOutputBuffer方法的时间戳
//这里其实有问题:首先这里的0.8系数设置的是否合理;其次是否能有办法验证这一帧真的在这一个vsync信号时间点显示出去了.按照mediacodec.releaseOutputbuffer的说法,应该在两个vsync信号之前调用release方法,但是从目前的做法来看并没有follow注释的说法
//利用dumpsys SurfaceFlinger --latency SurfaceView方法我们可以知道每一帧的desiredPresentationTime和actualPresentationTime,经过实测,在某些平台上这两个值差距在一个vsync时间以上,一般为22ms左右,所以ExoPlayer里面设置的这个0.8的系数不甚合理。其次我们观察了NuPlayer的avsync逻辑,发现在NuPlayer就是严格按照API注释所说的,提前两个vsync时间调用release方法。
return snappedTimeNs - vsyncOffsetNs;
}
1.1.1
寻找距离当前送显时间最近的vsync时间点的方法如下:
com.google.android.exoplayer2.video.VideoFrameReleaseTimeHelper#closestVsync
private static long closestVsync(long releaseTime, long sampledVsyncTime, long vsyncDuration) {
long vsyncCount = (releaseTime - sampledVsyncTime) / vsyncDuration;
long snappedTimeNs = sampledVsyncTime + (vsyncDuration * vsyncCount);
long snappedBeforeNs;
long snappedAfterNs;
if (releaseTime <= snappedTimeNs) {
// snappedTimeNs-vsyncDuration ---- releaseTime ----- snappedTimeNs
snappedBeforeNs = snappedTimeNs - vsyncDuration;
snappedAfterNs = snappedTimeNs;
} else {
// snappedTimeNs ---- releaseTime ----- snappedTimeNs+vsyncDuration
snappedBeforeNs = snappedTimeNs;
snappedAfterNs = snappedTimeNs + vsyncDuration;
}
long snappedAfterDiff = snappedAfterNs - releaseTime;
long snappedBeforeDiff = releaseTime – snappedBeforeNs;
//后面那个vsync信号离得更近的话,就选后面那个vsync信号,否则选前面那个vsync信号
return snappedAfterDiff < snappedBeforeDiff ? snappedAfterNs : snappedBeforeNs;
}
1.1.2
判断视频帧的pts距离他的送显时间是否有过大的偏移量
com.google.android.exoplayer2.video.VideoFrameReleaseTimeHelper#isDriftTooLarge
private boolean isDriftTooLarge(long frameTimeNs, long releaseTimeNs) {
//如果视频帧的pts和他的送显时间之间差了20ms以上,就认为偏移过大,也就认为失去sync了
//在理想的情况下,一个视频帧的pts应该和它的送显时间一一对应,pts是不会变的,送显时间的计算过程中存在着一个不确定变量,就是 elapsedSinceStartOfLoopUs, 这玩意的理想值永远是0,但实际上并不是,所以会在pts和对应的送显时间之间引入一些偏差,如果这个偏差大于20ms,就认为失去sync了,否则认为还没有失去sync.从一些简单的实验测试结果看,很少会有失去sync的情况出现
long elapsedFrameTimeNs = frameTimeNs - syncFramePresentationTimeNs;
long elapsedReleaseTimeNs = releaseTimeNs - syncUnadjustedReleaseTimeNs;
return Math.abs(elapsedReleaseTimeNs - elapsedFrameTimeNs) > MAX_ALLOWED_DRIFT_NS;
}
1.2
判断丢帧的逻辑如下:
com.google.android.exoplayer2.video.MediaCodecVideoRenderer#shouldDropOutputBuffer
/**
* Returns whether the buffer being processed should be dropped.
*
* @param earlyUs The time until the buffer should be presented in microseconds. A negative value
* indicates that the buffer is late.
* @param elapsedRealtimeUs {@link android.os.SystemClock#elapsedRealtime()} in microseconds,
* measured at the start of the current iteration of the rendering loop.
*/
protected boolean shouldDropOutputBuffer(long earlyUs, long elapsedRealtimeUs) {
/* For fps > 30fps, drop the frame if we're more than 30 ms late rendering the frame.
* For fps <= 30fps, drop the frame if we're more than (1/fps*1000) ms late rendering the frame.
*/
return earlyUs < -frameDropThres;
}
1.3
进行丢帧的逻辑如下:
com.google.android.exoplayer2.video.MediaCodecVideoRenderer#dropOutputBuffer
private void dropOutputBuffer(MediaCodec codec, int bufferIndex) {
TraceUtil.beginSection("dropVideoBuffer");
//注意这里是false就代表不予显示,也就是丢掉这一帧
codec.releaseOutputBuffer(bufferIndex, false);
TraceUtil.endSection();
decoderCounters.droppedOutputBufferCount++;
droppedFrames++;
consecutiveDroppedFrameCount++;
decoderCounters.maxConsecutiveDroppedOutputBufferCount = Math.max(consecutiveDroppedFrameCount,
decoderCounters.maxConsecutiveDroppedOutputBufferCount);
if (droppedFrames == maxDroppedFramesToNotify) {
maybeNotifyDroppedFrames();
}
}
1.4
送显的地方如下:
com.google.android.exoplayer2.video.MediaCodecVideoRenderer#renderOutputBufferV21
private void renderOutputBufferV21(MediaCodec codec, int bufferIndex, long releaseTimeNs) {
maybeNotifyVideoSizeChanged();
TraceUtil.beginSection("releaseOutputBuffer");
codec.releaseOutputBuffer(bufferIndex, releaseTimeNs);
TraceUtil.endSection();
decoderCounters.renderedOutputBufferCount++;
consecutiveDroppedFrameCount = 0;
maybeNotifyRenderedFirstFrame();
}
核心是调用了如下的API
android.media.MediaCodec#releaseOutputBuffer(int, long)
/**
*
* The timestamp may have special meaning depending on the destination surface.
*
*
* SurfaceView specifics
* If you render your buffer on a {@link android.view.SurfaceView},
* you can use the timestamp to render the buffer at a specific time (at the
* VSYNC at or after the buffer timestamp). For this to work, the timestamp
* needs to be reasonably close to the current {@link System#nanoTime}.
* Currently, this is set as within one (1) second. A few notes:
*
* if multiple buffers are sent to the {@link android.view.Surface} to be
* rendered at the same VSYNC, the last one will be shown, and the other ones
* will be dropped.
* if the timestamp is not "reasonably close" to the current system
* time, the {@link android.view.Surface} will ignore the timestamp, and
* display the buffer at the earliest feasible time. In this mode it will not
* drop frames.
* for best performance and quality, call this method when you are about
* two VSYNCs' time before the desired render time. For 60Hz displays, this is
* about 33 msec.
*
*
*
*
* @param index The index of a client-owned output buffer previously returned
* from a call to {@link #dequeueOutputBuffer}.
* @param renderTimestampNs The timestamp to associate with this buffer when
* it is sent to the Surface.
*/
public final void releaseOutputBuffer(int index, long renderTimestampNs)
下面来看audio部分,在上面介绍video的同步逻辑时, 提到了下面的函数processOutputBuffer, 他的一个入参是positionUs, 这个值代表当前音频播放时间,由系统时钟或者audioClock来计算,下面就来看一下它是如何计算出来的, 关键代码如下
–
com.google.android.exoplayer2.ExoPlayerImplInternal#updatePlaybackPositions
private void updatePlaybackPositions() throws ExoPlaybackException {
...
// Update the playback position.
...
} else {
if (rendererMediaClockSource != null && !rendererMediaClockSource.isEnded()) {
//使用audio playback position作为render position,详见2.2
rendererPositionUs = rendererMediaClock.getPositionUs();
standaloneMediaClock.setPositionUs(rendererPositionUs);
} else {
// 使用系统时间作为render position,详见2.1
rendererPositionUs = standaloneMediaClock.getPositionUs();
}
periodPositionUs = playingPeriodHolder.toPeriodTime(rendererPositionUs);
}
...
}
先来看比较简单的方法, 也就是用系统时间计算renderposition的方法
2.1
com.google.android.exoplayer2.util.StandaloneMediaClock#getPositionUs
public long getPositionUs() {
long positionUs = baseUs;
if (started) {
// 可以看到postionUs = baseUs + elapsedSinceBaseMs, 这两个值的计算如下2.1.1
long elapsedSinceBaseMs = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - baseElapsedMs;
if (playbackParameters.speed == 1f) {
positionUs += C.msToUs(elapsedSinceBaseMs);
} else {
positionUs += playbackParameters.getSpeedAdjustedDurationUs(elapsedSinceBaseMs);
}
}
return positionUs;
}
2.1.1
setPosition方法可以看做专用于更新baseUs和baseElapsedMs的方法, 他会在两种情况下被调用: 第一种情况下他只会被调用一次, 也就是在播放刚开始的时候, 前提是所使用的render没有实现getPostionUs方法(这种情况在exoplayer里面实际上并不会出现). 对于这种情况, 在2.1中的计算就比较好理解了. 而第二种情况是在使用audio playback position作为render时间的前提下, 每次都会在 updatePlaybackPositions 中调用 setPosition方法, 传入参数则为audio playback position, 也就是保持和audio playback position对齐
com.google.android.exoplayer2.util.StandaloneMediaClock#setPositionUs
public void setPositionUs(long positionUs) {
baseUs = positionUs;
if (started) {
baseElapsedMs = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
}
}
2.2
看完简单的方法, 接下来我们来看如何通过audio playback时间计算render时间
com.google.android.exoplayer2.audio.MediaCodecAudioRenderer#getPositionUs
public long getPositionUs() {
long newCurrentPositionUs = audioTrack.getCurrentPositionUs(isEnded());
if (newCurrentPositionUs != AudioTrack.CURRENT_POSITION_NOT_SET) {
currentPositionUs = allowPositionDiscontinuity ? newCurrentPositionUs
: Math.max(currentPositionUs, newCurrentPositionUs);
allowPositionDiscontinuity = false;
}
return currentPositionUs;
}
实际上调用的是exoplayer所封装的audioTrack的 getCurrentPositionUs方法
/**
* Returns the playback position in the stream starting at zero, in microseconds, or
* {@link #CURRENT_POSITION_NOT_SET} if it is not yet available.
*
* If the device supports it, the method uses the playback timestamp from
* {@link android.media.AudioTrack#getTimestamp}. Otherwise, it derives a smoothed position by
* sampling the {@link android.media.AudioTrack}'s frame position.
* 从注释来看,这里的一个核心逻辑是: 如果设备支持, 则从 android.media.AudioTrack#getTimestamp方法获取playback timestamp, 这里一方面是要求android api > 19, 一方面要求底层有对应的getTimestamp实现;否则通过对AudioTrack的frame position进行采样和平滑来演算出一个playback postion
*
* @param sourceEnded Specify {@code true} if no more input buffers will be provided.
* @return The playback position relative to the start of playback, in microseconds.
*/
public long getCurrentPositionUs(boolean sourceEnded) {
...
if (audioTrack.getPlayState() == PLAYSTATE_PLAYING) {
//在maybeSampleSyncParams方法中干了三件事, 一方面进行audio track frame position的采样和平滑处理, 一方面对audiotrack.getTimeStamp方法获取的结果进行检验, 一方面获取audiotrack的latency, 详见下面的2.2.1的分析
maybeSampleSyncParams();
}
long systemClockUs = System.nanoTime() / 1000;
long positionUs;
if (audioTimestampSet) {
// Calculate the speed-adjusted position using the timestamp (which may be in the future).
// 如果上面拿到了audioTrack.getTimeStamp,就用AudioTrack.getTimestamp方法进行计算,前提是需要设备支持,例如当前很多tv设备上蓝牙音箱的情况下就走不了这个通路
// 关于这块的逻辑,首先需要说明一下audioTrackUtil的几个方法分别是干什么的,详细见下面2.2.2的分析
// 还有一点需要说明的是,在exoplayer里面默认是500ms更新一次audiostamp.
//下面的逻辑可以化简为下式:
//positionUs = framesToDurationUs(AudioTimestamp.framePosition)
// + systemClockUs – AudioTimestamp.nanoTime/1000
long elapsedSinceTimestampUs = systemClockUs - (audioTrackUtil.getTimestampNanoTime() / 1000);
long elapsedSinceTimestampFrames = durationUsToFrames(elapsedSinceTimestampUs);
long elapsedFrames = audioTrackUtil.getTimestampFramePosition() + elapsedSinceTimestampFrames;
positionUs = framesToDurationUs(elapsedFrames);
} else {
//如果上面没拿到AudioTrack.getTimeStamp, 就利用AudioTrack.getPlayheadPostionUs方法来计算
//对getPlayheadPostionUs方法的详细分析见下面2.2.3
if (playheadOffsetCount == 0) {
// The AudioTrack has started, but we don't have any samples to compute a smoothed position.
positionUs = audioTrackUtil.getPositionUs();
} else {
// getPlayheadPositionUs() only has a granularity of ~20 ms, so we base the position off the
// system clock (and a smoothed offset between it and the playhead position) so as to
// prevent jitter in the reported positions.
// 在这里解释了为什么要进行采样和平滑演算得到playback position: 因为 getPlayheadPositionUs()的粒度只有约20ms, 如果直接拿来用的话精度不够
positionUs = systemClockUs + smoothedPlayheadOffsetUs;
}
if (!sourceEnded) {
//如果使用getPositionUs的话,还要再减去一个latencyUs, 它是在maybeSampleSyncParams方法中计算得到的. 这里其实是一个化简的写法, 其实应该展开为
avg[(audioTrack.getPlaybackHeadPosition/sampleRate)(i)] + sysClock – (sysClock + latency)
= avg[(audioTrack.getPlaybackHeadPosition/sampleRate)(i)] - latency
positionUs -= latencyUs;
}
}
//上面算出来的positionUs是从0开始的audio播放时长,需要加上一个时间基,也就是startMediaTimeUs才能得到实际的audio playback position.startMediaTimeUs的计算详见2.2.5
return startMediaTimeUs + applySpeedup(positionUs);
}
2.2.1
maybeSampleSyncParams是一个比较关键的方法, 包含了playback position的平滑,TimeStamp的获取,和Latency的获取
com.google.android.exoplayer2.audio.AudioTrack#maybeSampleSyncParams
/**
* Updates the audio track latency and playback position parameters.
*/
private void maybeSampleSyncParams() {
//从AudioTrack获取playbackPosition, 详见下面2.2.3的分析
long playbackPositionUs = audioTrackUtil.getPositionUs();
if (playbackPositionUs == 0) {
// The AudioTrack hasn't output anything yet.
return;
}
long systemClockUs = System.nanoTime() / 1000;
if (systemClockUs - lastPlayheadSampleTimeUs >= MIN_PLAYHEAD_OFFSET_SAMPLE_INTERVAL_US) {
// Take a new sample and update the smoothed offset between the system clock and the playhead.
//采样的时间间隔是30ms
//下面的采样逻辑可以化简为
//smoothedPlayheadOffsetUs = avg[playbackPositionUs(i) – systemClock(i)],i最大取10,
//意义在于,平均掉playbackPostionUs可能存在的抖动
playheadOffsets[nextPlayheadOffsetIndex] = playbackPositionUs - systemClockUs;
nextPlayheadOffsetIndex = (nextPlayheadOffsetIndex + 1) % MAX_PLAYHEAD_OFFSET_COUNT;
if (playheadOffsetCount < MAX_PLAYHEAD_OFFSET_COUNT) {
playheadOffsetCount++;
}
lastPlayheadSampleTimeUs = systemClockUs;
smoothedPlayheadOffsetUs = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < playheadOffsetCount; i++) {
smoothedPlayheadOffsetUs += playheadOffsets[i] / playheadOffsetCount;
}
}
...
if (systemClockUs - lastTimestampSampleTimeUs >= MIN_TIMESTAMP_SAMPLE_INTERVAL_US) {
//以500ms为间隔获取audioTrack timeStamp,关于AudioTrack.getTimeStamp方法,详见下面2.2.2的分析
audioTimestampSet = audioTrackUtil.updateTimestamp();
if (audioTimestampSet) {
// Perform sanity checks on the timestamp.
//如果获取到了新的AudioTimeStamp,则在下面做三个校验
long audioTimestampUs = audioTrackUtil.getTimestampNanoTime() / 1000;
long audioTimestampFramePosition = audioTrackUtil.getTimestampFramePosition();
if (audioTimestampUs < resumeSystemTimeUs) {
// The timestamp corresponds to a time before the track was most recently resumed.
//首先确定获取到的时间不是已经过去的时间
audioTimestampSet = false;
} else if (Math.abs(audioTimestampUs - systemClockUs) > MAX_AUDIO_TIMESTAMP_OFFSET_US) {
// The timestamp time base is probably wrong.
//再确认获取到的时间与当前系统时间差的不太大,阈值为5s
String message = "Spurious audio timestamp (system clock mismatch): "
+ audioTimestampFramePosition + ", " + audioTimestampUs + ", " + systemClockUs + ", "
+ playbackPositionUs + ", " + getSubmittedFrames() + ", " + getWrittenFrames();
if (failOnSpuriousAudioTimestamp) {
throw new InvalidAudioTrackTimestampException(message);
}
Log.w(TAG, message);
audioTimestampSet = false;
} else if (Math.abs(framesToDurationUs(audioTimestampFramePosition) - playbackPositionUs)
> MAX_AUDIO_TIMESTAMP_OFFSET_US) {
// The timestamp frame position is probably wrong.
//再确认通过getTimeStamp和getPlaybackHeadPostion方法获取到的时间差的不太大,阈值同样为5s
String message = "Spurious audio timestamp (frame position mismatch): "
+ audioTimestampFramePosition + ", " + audioTimestampUs + ", " + systemClockUs + ", "
+ playbackPositionUs + ", " + getSubmittedFrames() + ", " + getWrittenFrames();
if (failOnSpuriousAudioTimestamp) {
throw new InvalidAudioTrackTimestampException(message);
}
Log.w(TAG, message);
audioTimestampSet = false;
}
}
if (getLatencyMethod != null && !passthrough) {
try {
// Compute the audio track latency, excluding the latency due to the buffer (leaving
// latency due to the mixer and audio hardware driver).
// 从AudioTrack获得latency,详细的分析请见下面2.2.4
// 需要注意的是,这里还减掉了一个bufferSizeUs,只留下mixer和audio hardware driver引发的延迟
// bufferSizeUs的计算在audioTrack.configure方法中可以看到
latencyUs = (Integer) getLatencyMethod.invoke(audioTrack, (Object[]) null) * 1000L
- bufferSizeUs;
// Sanity check that the latency is non-negative.
latencyUs = Math.max(latencyUs, 0);
// Sanity check that the latency isn't too large.
if (latencyUs > MAX_LATENCY_US) {
Log.w(TAG, "Ignoring impossibly large audio latency: " + latencyUs);
latencyUs = 0;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// The method existed, but doesn't work. Don't try again.
getLatencyMethod = null;
}
}
lastTimestampSampleTimeUs = systemClockUs;
}
}
计算bufferSizeUs
public void configure(String mimeType, int channelCount, int sampleRate,
@C.PcmEncoding int pcmEncoding, int specifiedBufferSize, int[] outputChannels){
…
if (specifiedBufferSize != 0) {
….
} else if (passthrough) {
….
} else {
//从audioTrack拿到minBufferSize, 关于getMinBufferSize,详见2.2.6
int minBufferSize =
android.media.AudioTrack.getMinBufferSize(sampleRate, channelConfig, outputEncoding);
Assertions.checkState(minBufferSize != ERROR_BAD_VALUE);
//乘上一个系数,取值4
int multipliedBufferSize = minBufferSize * BUFFER_MULTIPLICATION_FACTOR;
int minAppBufferSize = (int) durationUsToFrames(MIN_BUFFER_DURATION_US) * outputPcmFrameSize;
int maxAppBufferSize = (int) Math.max(minBufferSize,
durationUsToFrames(MAX_BUFFER_DURATION_US) * outputPcmFrameSize);
//bufferSizeUs取值在[250ms,750ms]之间
bufferSize = multipliedBufferSize < minAppBufferSize ? minAppBufferSize
: multipliedBufferSize > maxAppBufferSize ? maxAppBufferSize
: multipliedBufferSize;
}
bufferSizeUs = passthrough ? C.TIME_UNSET : framesToDurationUs(bufferSize / outputPcmFrameSize);
...
}
2.2.2
如果走了getTimeStamp通路,可以看到关键的两个方法getTimestampNanoTime和getTimestampFramePosition返回的分别是AudioTimestamp类的两个变量,而AudioTimestamp就是通过audioTrack.getTimestamp方法获得的
com.google.android.exoplayer2.audio.AudioTrack.AudioTrackUtilV19
private static class AudioTrackUtilV19 extends AudioTrackUtil {
private final AudioTimestamp audioTimestamp;
private long rawTimestampFramePositionWrapCount;
private long lastRawTimestampFramePosition;
private long lastTimestampFramePosition;
public AudioTrackUtilV19() {
audioTimestamp = new AudioTimestamp();
}
....
@Override
public boolean updateTimestamp() {
boolean updated = audioTrack.getTimestamp(audioTimestamp);
if (updated) {
long rawFramePosition = audioTimestamp.framePosition;
if (lastRawTimestampFramePosition > rawFramePosition) {
// The value must have wrapped around.
rawTimestampFramePositionWrapCount++;
}
lastRawTimestampFramePosition = rawFramePosition;
lastTimestampFramePosition = rawFramePosition + (rawTimestampFramePositionWrapCount << 32);
}
return updated;
}
@Override
public long getTimestampNanoTime() {
return audioTimestamp.nanoTime;
}
@Override
public long getTimestampFramePosition() {
return lastTimestampFramePosition;
}
}
AudioTimestamp的定义如下,它有两个关键的变量,分别是framePostition和nanoTime, 都是从HAL层拿到的值
android.media.AudioTimestamp
/**
* Structure that groups a position in frame units relative to an assumed audio stream,
* together with the estimated time when that frame enters or leaves the audio
* processing pipeline on that device. This can be used to coordinate events
* and interactions with the external environment.
*
* The time is based on the implementation's best effort, using whatever knowledge
* is available to the system, but cannot account for any delay unknown to the implementation.
*
* @see AudioTrack#getTimestamp AudioTrack.getTimestamp(AudioTimestamp)
* @see AudioRecord#getTimestamp AudioRecord.getTimestamp(AudioTimestamp, int)
*/
public final class AudioTimestamp
{
...
/**
* Position in frames relative to start of an assumed audio stream.
* When obtained through
* {@link AudioTrack#getTimestamp AudioTrack.getTimestamp(AudioTimestamp)},
* the low-order 32 bits of position is in wrapping frame units similar to
* {@link AudioTrack#getPlaybackHeadPosition AudioTrack.getPlaybackHeadPosition()}.
* 从HAL层拿到的值,代表刚播放完的,或者已经在pipeline中马上就要播放的帧的位置
*/
public long framePosition;
/**
* Time associated with the frame in the audio pipeline.
* When obtained through
* {@link AudioTrack#getTimestamp AudioTrack.getTimestamp(AudioTimestamp)},
* this is the estimated time when the frame was presented or is committed to be presented,
* with a timebase of {@link #TIMEBASE_MONOTONIC}.
* 上面framePostion对应帧的播放时间或者将要被播出的时间,以系统时间表示
*/
public long nanoTime;
}
而AudioTrack.getTimeStamp方法的定义如下,注意注释中提到的,这个方法返回的值不一定总是变化的,同时注释还提到不要频繁调用它,否则会有性能上的问题
android.media.AudioTrack#getTimestamp
/**
* Poll for a timestamp on demand.
*
* If you need to track timestamps during initial warmup or after a routing or mode change,
* you should request a new timestamp periodically until the reported timestamps
* show that the frame position is advancing, or until it becomes clear that
* timestamps are unavailable for this route.
*
* After the clock is advancing at a stable rate,
* query for a new timestamp approximately once every 10 seconds to once per minute.
* Calling this method more often is inefficient.
* It is also counter-productive to call this method more often than recommended,
* because the short-term differences between successive timestamp reports are not meaningful.
* If you need a high-resolution mapping between frame position and presentation time,
* consider implementing that at application level, based on low-resolution timestamps.
*
* The audio data at the returned position may either already have been
* presented, or may have not yet been presented but is committed to be presented.
* It is not possible to request the time corresponding to a particular position,
* or to request the (fractional) position corresponding to a particular time.
* If you need such features, consider implementing them at application level.
*
* @param timestamp a reference to a non-null AudioTimestamp instance allocated
* and owned by caller.
* @return true if a timestamp is available, or false if no timestamp is available.
* If a timestamp if available,
* the AudioTimestamp instance is filled in with a position in frame units, together
* with the estimated time when that frame was presented or is committed to
* be presented.
* In the case that no timestamp is available, any supplied instance is left unaltered.
* A timestamp may be temporarily unavailable while the audio clock is stabilizing,
* or during and immediately after a route change.
* A timestamp is permanently unavailable for a given route if the route does not support
* timestamps. In this case, the approximate frame position can be obtained
* using {@link #getPlaybackHeadPosition}.
* However, it may be useful to continue to query for
* timestamps occasionally, to recover after a route change.
*/
// Add this text when the "on new timestamp" API is added:
// Use if you need to get the most recent timestamp outside of the event callback handler.
public boolean getTimestamp(AudioTimestamp timestamp)
我们可以再往framework里面看看这个方法是如何获取到framePosition和nanoTime的,这里看的是Android M
frameworks/av/media/libmedia/AudioTrack.cpp

frameworks/av/media/libmedia/IAudioTrack.cpp

frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/Tracks.cpp
binder调过来的

然后调用PlaybackThread里Track的getTimeStamp

这里timestamp里的mPosition和mTime都由mLatchQ获取。
不过在Android7.0以后就不用mLatchD、mLatchQ了。

frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/Threads.cpp

mLatchD赋给mLatchQ

frameworks/av/media/libnbaio/AudioStreamOutSink.cpp

后边就调到Hal了,mLatchD的mTimestamp就是hal返回的。
hardware/mstar/audio/audio_hw_6_0/audio_hw.cpp

2.2.3
如果走了getPlaybackPosition通路, 调用的是下面的方法
com.google.android.exoplayer2.audio.AudioTrack.AudioTrackUtil#getPositionUs
/**
* Returns the duration of played media since reconfiguration, in microseconds.
*/
public long getPositionUs() {
return (getPlaybackHeadPosition() * C.MICROS_PER_SECOND) / sampleRate;
}
利用下面方法的返回值进行计算
com.google.android.exoplayer2.audio.AudioTrack.AudioTrackUtil#getPlaybackHeadPosition
/**
* {@link android.media.AudioTrack#getPlaybackHeadPosition()} returns a value intended to be
* interpreted as an unsigned 32 bit integer, which also wraps around periodically. This method
* returns the playback head position as a long that will only wrap around if the value exceeds
* {@link Long#MAX_VALUE} (which in practice will never happen).
*
* @return The playback head position, in frames.
*/
public long getPlaybackHeadPosition() {
...
long rawPlaybackHeadPosition = 0xFFFFFFFFL & audioTrack.getPlaybackHeadPosition();
...
if (lastRawPlaybackHeadPosition > rawPlaybackHeadPosition) {
// The value must have wrapped around.
rawPlaybackHeadWrapCount++;
}
lastRawPlaybackHeadPosition = rawPlaybackHeadPosition;
return rawPlaybackHeadPosition + (rawPlaybackHeadWrapCount << 32);
}
实际调用的是
android.media.AudioTrack#getPlaybackHeadPosition
/**
* Returns the playback head position expressed in frames.
* Though the "int" type is signed 32-bits, the value should be reinterpreted as if it is
* unsigned 32-bits. That is, the next position after 0x7FFFFFFF is (int) 0x80000000.
* This is a continuously advancing counter. It will wrap (overflow) periodically,
* for example approximately once every 27:03:11 hours:minutes:seconds at 44.1 kHz.
* It is reset to zero by {@link #flush()}, {@link #reloadStaticData()}, and {@link #stop()}.
* If the track's creation mode is {@link #MODE_STATIC}, the return value indicates
* the total number of frames played since reset,
* not the current offset within the buffer.
*/
public int getPlaybackHeadPosition()
它返回的是AudioFlinger里面的共享内存的位置,跟一下framework里面的实现如下
/frameworks/av/media/libmedia/AudioTrack.cpp
status_t AudioTrack::getPosition(uint32_t *position)
{
if (position == NULL) {
return BAD_VALUE;
}
AutoMutex lock(mLock);
if (isOffloadedOrDirect_l()) {
...
} else {
if (mCblk->mFlags & CBLK_INVALID) {
(void) restoreTrack_l("getPosition");
// FIXME: for compatibility with the Java API we ignore the restoreTrack_l()
// error here (e.g. DEAD_OBJECT) and return OK with the last recorded server position.
}
// IAudioTrack::stop() isn't synchronous; we don't know when presentation completes
*position = (mState == STATE_STOPPED || mState == STATE_FLUSHED) ?
0 : updateAndGetPosition_l();
}
....
uint32_t AudioTrack::updateAndGetPosition_l()
{
// This is the sole place to read server consumed frames
uint32_t newServer = mProxy->getPosition();
int32_t delta = newServer - mServer;
mServer = newServer;
// TODO There is controversy about whether there can be "negative jitter" in server position.
// This should be investigated further, and if possible, it should be addressed.
// A more definite failure mode is infrequent polling by client.
// One could call (void)getPosition_l() in releaseBuffer(),
// so mReleased and mPosition are always lock-step as best possible.
// That should ensure delta never goes negative for infrequent polling
// unless the server has more than 2^31 frames in its buffer,
// in which case the use of uint32_t for these counters has bigger issues.
if (delta < 0) {
ALOGE("detected illegal retrograde motion by the server: mServer advanced by %d", delta);
delta = 0;
}
return mPosition += (uint32_t) delta;
}
/frameworks/av/include/private/media/AudioTrackShared.h
// Proxy used by AudioTrack client, which also includes AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread::OutputTrack
class AudioTrackClientProxy : public ClientProxy
// Proxy seen by AudioTrack client and AudioRecord client
class ClientProxy : public Proxy {
...
size_t getPosition() {
return mEpoch + mCblk->mServer;
}
...
}
// Important: do not add any virtual methods, including ~
struct audio_track_cblk_t
{
...
uint32_t mServer; // Number of filled frames consumed by server (mIsOut),
// or filled frames provided by server (!mIsOut).
// It is updated asynchronously by server without a barrier.
// The value should be used
// "for entertainment purposes only",
// which means don't make important decisions based on it.
...
}
2.2.4
如果走了getPlaybackPosition通路,还要在position基础上减去latency
android.media.AudioTrack#getLatency
/**
* Returns this track's estimated latency in milliseconds. This includes the latency due
* to AudioTrack buffer size, AudioMixer (if any) and audio hardware driver.
* getlatency返回的值包含了三部分:AudioTrack buffer size, AudioMixer带来的延迟以及audio hardware driver带来的延迟
* DO NOT UNHIDE. The existing approach for doing A/V sync has too many problems. We need
* a better solution.
* 注释中也提到这个返回值可能是有问题的,这可能也是api19后来增加了AudioTimeStamp类的原因
* @hide
*/
public int getLatency() {
return native_get_latency();
}
直接调用的jni
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_media_AudioTrack.cpp

直接调用的native 层,在h文件里
frameworks/av/include/media/AudioTrack.h

frameworks/av/media/libmedia/AudioTrack.cpp

mLatency在createTrack_l时赋值,afLatency从AudioFlinger获取,AudioFlinger又从hal获取frameCount从AudioTrack.cpp获得
frameworks/av/media/libmedia/AudioTrack.cpp

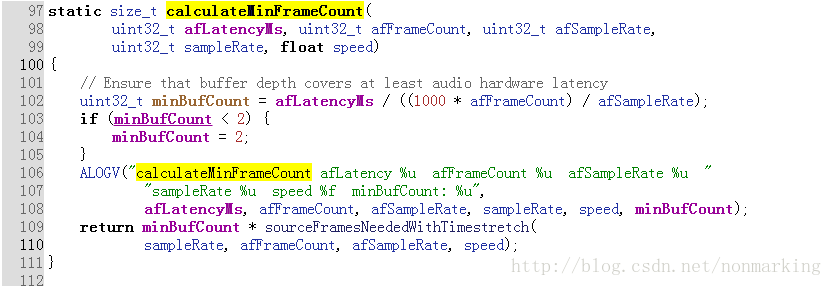
frameworks/av/include/media/AudioResamplerPublic.h


如上两部分代码是计算framecount,如果src采样率、 dst采样率 都为 48K,播放速度speed默认为1,dstFramesRequired为afFrameCount是1024
frameCount =(1024*1 + 1 +1) * 2 = 2052
2.2.5
在handleBuffer中计算startMediaTimeUs, 在他的基础上再加上postionUs
com.google.android.exoplayer2.audio.AudioTrack#handleBuffer
public boolean handleBuffer(ByteBuffer buffer, long presentationTimeUs)
throws InitializationException, WriteException {
…
if (startMediaTimeState == START_NOT_SET) {
//startMediaTimeState的初始状态是START_NOT_SET,将第一个进来的audio pts时间赋个startMediaTimeUs,修改startMediaTimeState状态为IN_SYNC
startMediaTimeUs = Math.max(0, presentationTimeUs);
startMediaTimeState = START_IN_SYNC;
} else {
// Sanity check that presentationTimeUs is consistent with the expected value.
//在这里会根据之前给audioTrack的buffer计算出对应的frameSize,计算的方法见下面getSubmittedFrames, 再加上startMediaTimeUs即可估计当前到来的audio pts
long expectedPresentationTimeUs = startMediaTimeUs
+ framesToDurationUs(getSubmittedFrames());
if (startMediaTimeState == START_IN_SYNC
&& Math.abs(expectedPresentationTimeUs - presentationTimeUs) > 200000
&& !needsWrongSampleRateWorkarounds()) {
//如果估计的pts值和实际到来的值差了200ms以上,就认为遇到了discont.相应的修改状态为NEED_SYNC
Log.e(TAG, "Discontinuity detected [expected " + expectedPresentationTimeUs + ", got "
+ presentationTimeUs + "]");
startMediaTimeState = START_NEED_SYNC;
}
if (startMediaTimeState == START_NEED_SYNC) {
// Adjust startMediaTimeUs to be consistent with the current buffer's start time and the
// number of bytes submitted.
// 如果遇到了discont.则将startMediaTimeUs对齐到当前buffer的实际其实时间上,在把状态改为IN_SYNC
startMediaTimeUs += (presentationTimeUs - expectedPresentationTimeUs);
startMediaTimeState = START_IN_SYNC;
listener.onPositionDiscontinuity();
}
}
if (passthrough) {
submittedEncodedFrames += framesPerEncodedSample;
} else {
//在这里更新submittedPcmBytes
submittedPcmBytes += buffer.remaining();
}
inputBuffer = buffer;
}
if (passthrough) {
// Passthrough buffers are not processed.
writeBuffer(inputBuffer, presentationTimeUs);
} else {
processBuffers(presentationTimeUs);
}
if (!inputBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
inputBuffer = null;
return true;
}
return false;
}
private long getSubmittedFrames() {
return passthrough ? submittedEncodedFrames : (submittedPcmBytes / pcmFrameSize);
}
2.2.6
android.media.AudioTrack#getMinBufferSize
/**
* Returns the estimated minimum buffer size required for an AudioTrack
* object to be created in the {@link #MODE_STREAM} mode.
* The size is an estimate because it does not consider either the route or the sink,
* since neither is known yet. Note that this size doesn't
* guarantee a smooth playback under load, and higher values should be chosen according to
* the expected frequency at which the buffer will be refilled with additional data to play.
* For example, if you intend to dynamically set the source sample rate of an AudioTrack
* to a higher value than the initial source sample rate, be sure to configure the buffer size
* based on the highest planned sample rate.
* @param sampleRateInHz the source sample rate expressed in Hz.
* {@link AudioFormat#SAMPLE_RATE_UNSPECIFIED} is not permitted.
* @param channelConfig describes the configuration of the audio channels.
* See {@link AudioFormat#CHANNEL_OUT_MONO} and
* {@link AudioFormat#CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO}
* @param audioFormat the format in which the audio data is represented.
* See {@link AudioFormat#ENCODING_PCM_16BIT} and
* {@link AudioFormat#ENCODING_PCM_8BIT},
* and {@link AudioFormat#ENCODING_PCM_FLOAT}.
* @return {@link #ERROR_BAD_VALUE} if an invalid parameter was passed,
* or {@link #ERROR} if unable to query for output properties,
* or the minimum buffer size expressed in bytes.
*/
static public int getMinBufferSize(int sampleRateInHz, int channelConfig, int audioFormat)
往framework里面去看
frameworks/base/media/java/android/media/AudioTrack.java

第一步:从java调到AudioTrack的jni接口
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_media_AudioTrack.cpp

这里frameCount从AudioTrack.cpp获得,如果channelCount 为2, bytesPerSample为2(位宽16是2个字节)
所以是buffersize = frameCount * 4;
关注公众号,掌握更多多媒体领域知识与资讯
![]()
文章帮到你了?可以扫描如下二维码进行打赏,打赏多少您随意~
![]()