Python开发【第二章】python入门
第一句python代码
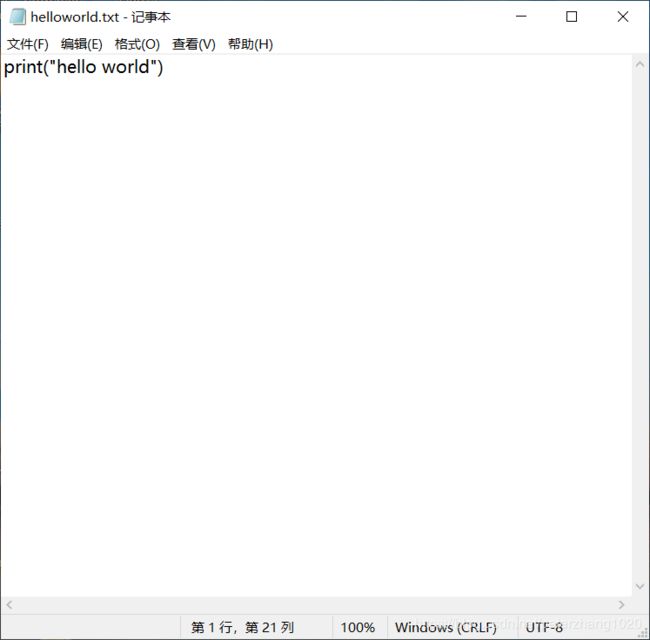
python代码:新建一个记事本,输入print(“hello world”),保存,重命名为helloworld.py。
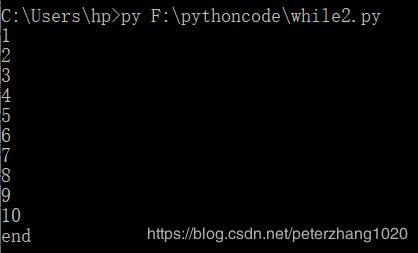
代码的执行:1.在桌面状态下,win+R,输入cmd打开DOS命令窗口,输入python+文件路径\文件名.py,回车执行。
2.桌面状态下win+R,输入cmd,打开终端窗口,输入python,回车;输入Python语句,回车执行。
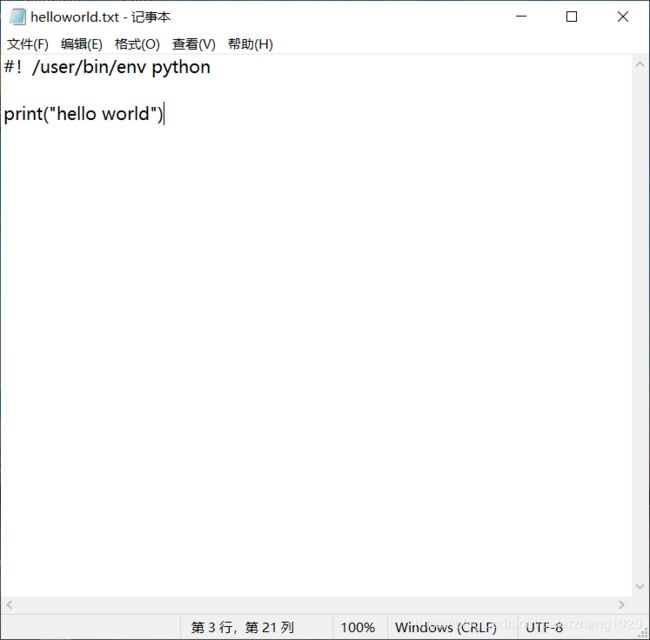
Linux中代码的注意事项:文件内部在第一行加#!/user/bin/env python。
 输入:input(’>>>’)
输入:input(’>>>’)
python 2中代码注意事项:如果使用python2,且代码中含汉字,则需要加# -- coding:utf8 --。
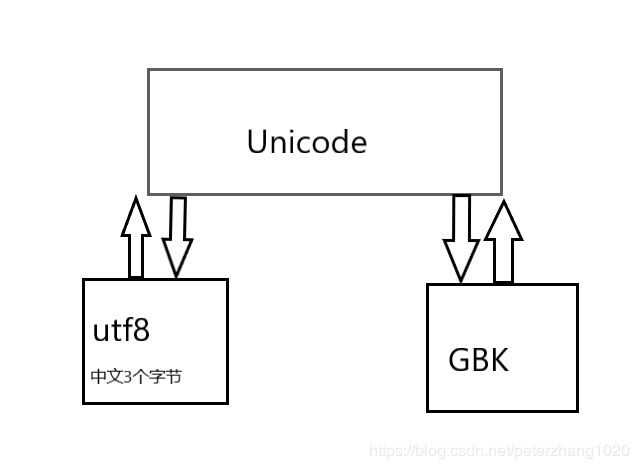
python2需要注意编码格式,python3则不需要。(编码格式:ASCLL,8个字节;
Unicode,16字节;utf-8,尽可能的少)
变量
变量的定义及组成:定义:代指某一个变化的值。
组成:变量只能由字母数字下划线组成,但是不能以数字开头。
变量名命名规范:变量名不能是关键字,最好不要与python内部的东西重复。
变量名命名的时候要有意义,便于确认。
不能使用的变量名:‘and’, ‘as’, ‘assert’, ‘break’, ‘class’, ‘continue’, ‘def’, ‘del’, ‘elif’, ‘else’, ‘except’, ‘exec’, ‘finally’, ‘for’, ‘from’, ‘global’, ‘if’, ‘import’, ‘in’, ‘is’, ‘lambda’, ‘not’, ‘or’, ‘pass’, ‘print’, ‘raise’, ‘return’, ‘try’, ‘while’, ‘with’, ‘yield’。
条件语句
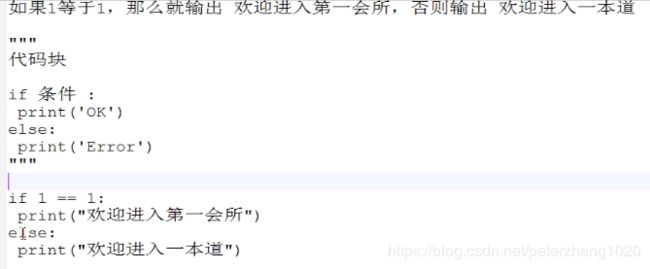
基本结构:
if 条件:
代码块
else:
代码块
 注释:当行注视:# 被注释内容
注释:当行注视:# 被注释内容
多行注释:""" 被注释内容 “”"
嵌套结构:
if 条件1:
if 条件2:
代码块
else:
代码块
else:
代码块
 多个并列的条件语句:
多个并列的条件语句:
多个条件的语句结构:
if 条件1:
代码块
elif 条件2:
代码块
elif 条件3:
代码块
else:
代码块

循环语句
死循环:不停运行的循环
while 1==1:
print(“ok”)
 while循环:
while循环:
whlie 条件:
print(“结果”)
先检测条件,若成立,则输出结果,再返回条件检测,直至条件不符,跳出循环。
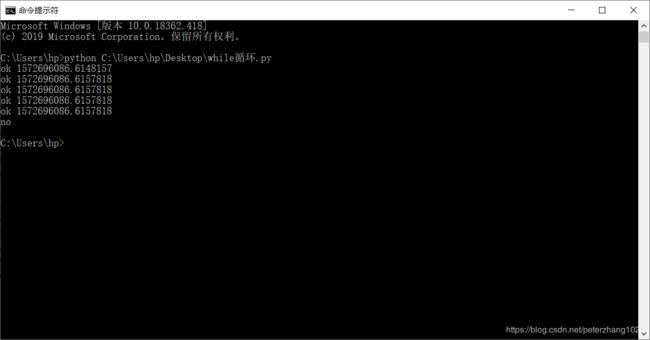
while循环的终止:
import time
count = 0
while count <5:
print(“ok”,time.time())
count = count+1
print(“no”)
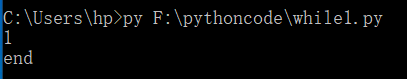
 break的使用:break的作用为跳出整个循环。
break的使用:break的作用为跳出整个循环。
count = 0
while count < 10:
count = count + 1
print(count)
break
print(123)
print(‘end’)
continue的使用:continue的作用为跳出本次循环,进入下一次循环。
count = 0
while count <10:
count = count + 1
print (count)
continue
print(123)
print(‘end’)