【小项目】用Huffman树实现文件压缩并解压
一、前言
如果你学习数据结构,就一定会学到Huffman树,而Huffman编码实际上上就是zip压缩的核心部分,所以,如果已经学习了Huffman树,为何不尝试写一个压缩程序出来呢?
如果你没有学习Huffman树,那咱们就一起先学习一下Huffman树吧。
二、Huffman树压缩文件
定义:Huffman树,又称为最优二叉树,是加权路径长度最短的二叉树。
建立:
这样建立的树,保证所有数据成员都在叶子节点上,且数越小,离根节点越远,越大,离根节点越近,那么这样的特点应用于压缩中是很关键的,我们可以让出现次数少的字符编码长一些,次数多的字符编码短一些。接下来我们看看压缩的步骤吧~
1>统计要压缩的文件中字符出现的次数。
遍历一遍文件,将字符出现的次数统计在一个结构体数组里,数组里包含字符,字符出现的次数,对该字符的编码。
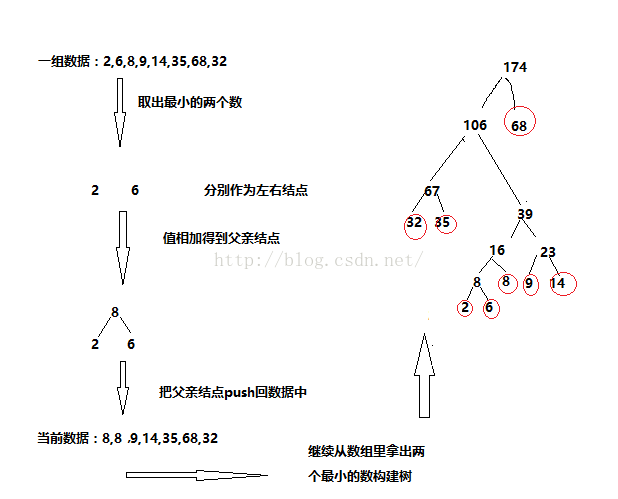
2>用得到的数组构建一个Huffman树。
因为每次要取最小值,所以这里考虑建立一个小堆。
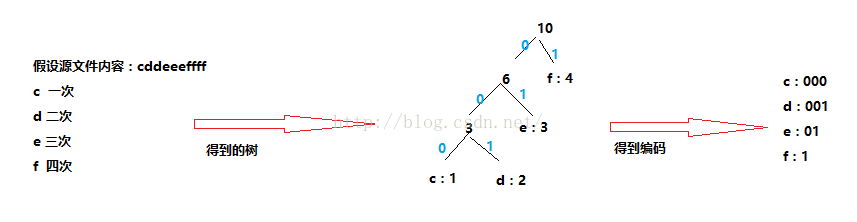
3>得到Huffman编码
怎么得到呢?向右为1,向左为0,就是这么简单,我画图示意一下:
原本用一个char表示的字符,现在只占了几个位,这就是为什么能将文件压缩。
4>向压缩文件里写入Huffman编码。
写入的时候,满8个位写进去,如果最后不足8个位,先补齐,解压的时候要注意,解压到源文件字符数的时候停止即可。源文件的总字符数可以在第一次遍历统计出现的字符个数时统计,还有一种方法就是,仔细观察Huffman树就知道,它的根节点的大小,其实就是所有叶子节点相加的和。所以,根节点的大小就是源文件里所有字符出现的总次数。
至此,压缩就结束了。
但是,怎么解压缩呢?解压缩至少也得已知这样的一颗树才行啊,所以,我们在压缩完成后要建立一个配置文件。
5>建立配置文件
配置文件里要存储源文件字符及出现的次数。有了这样的配置文件,就可以再次构建Huffman树!
三、解压缩
1>读取配置文件,重新构建Huffman树
2>读取压缩文件
由压缩时的原理可知,此时读到1指针向右移动,0向左移,到叶子节点停下,将字符还原。不停的循环,直到文件结束或者总字符数变为0.这里就能体现出,Huffman压缩是一种无损的压缩,如果代码没有问题,它会原原本本的还原源文件。
解压到这里成功。可以先使用小文件测试,若没有问题则找个大点的文件,还有各类格式的文件都拿来压一压测一下。
四、我遇到的问题
1>编译时不通过,一大堆的错误,我找了半天!最后发现是一个很简单的问题,我的Huffman树使用的是C++模板实现的,模板不能分离编译,而我在压缩时建立Huffman树是在另一个文件中进行的,所以编译不通过。
解决方法:.h后缀改成.hpp,重新包一下头文件ok。
2>文件的打开方式。这里打开文件一定要用二进制形式,"wb","rb".因为二进制打开和文本打开其实是有区别的。文本方式打开,会对‘\n’进行特殊处理,那如果这个字符本身就是'\n'.这就会出现问题,所以使用二进制打开,特点:不进行任何处理,是什么就是什么。
3>压缩后解压缩的图片打不开,经过我反复查找,终于发现是配置文件里对‘\0’的处理问题,我在写配置文件起初是用一个string把字符和它出现的次数连接起来放进去。比如:a,3 这样带来的问题是 \0,200 写的时候是以c字符串的形式写的,所以遇见'\0'就终止了,那么在解压缩的时候就会出问题。
解决方法:先把字符放进去,再把剩下的构建成string对象放进去。
五、源码
1>Huffman树
#pragma once
#include
#include"Heap.h"
#include"Press.h"
using namespace std;
template
struct HuffmanTreeNode
{
typedef HuffmanTreeNode Node;
T _weight;
Node* _left;
Node* _right;
Node* _parent;
HuffmanTreeNode(const T& w)
:_weight(w),
_left(NULL),
_right(NULL),
_parent(NULL)
{}
};
template
class HuffmanTree
{
public:
typedef HuffmanTreeNode Node;
HuffmanTree()
:_root(NULL)
{}
~HuffmanTree()
{
_destory(_root);
}
Node* GetRoot()
{
return _root;
}
template
struct Less
{
bool operator()(const T& left, const T&right)
{
return left->_weight < right->_weight;
}
};
HuffmanTree(T* a, int size,T invalid) //构建Huffman树
{
Heap> hp; //建小堆
for (int i = 0; i1)
{
Node* left = hp.Top();
hp.Pop();
Node* right = hp.Top();
hp.Pop();
Node* parent = new Node(left->_weight + right->_weight);
hp.Push(parent);
parent->_left = left;
parent->_right = right;
left->_parent = parent;
right->_parent = parent;
}
_root = hp.Top();
}
protected:
void _destory(Node* root)
{
if (NULL == root)
return;
_destory(root->_left);
_destory(root->_right);
delete root;
}
private:
Node* _root;
}; #pragma once
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include"Huffman.hpp"
typedef long long type;
struct weight //权值里应该包含字符出现的次数以及对应的字符和Huffman编码
{
unsigned char _ch;
type _count;
string _code;
weight(type count = 0)
: _ch(0)
,_count(count)
, _code("")
{}
weight operator+(const weight& w)
{
type tmp = _count + w._count;
return weight(tmp);
}
bool operator<(const weight& w)
{
return _count < w._count;
}
bool operator!=(const weight& w)
{
return !(_count == w._count);
}
};
class HuffmanPress
{
public:
HuffmanPress()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
_infos[i]._ch = (unsigned char)i;
}
}
bool FilePress(const char* filename)
{
//统计出每个字符出现的次数。
FILE* fOut = fopen(filename, "rb");
assert(fOut);
int ch = fgetc(fOut);
type charcount = 0; //统计出字符出现的总次数
while (ch != EOF)
{
if (feof(fOut))
break;
_infos[ch]._count++;
ch = fgetc(fOut);
charcount++;
}
weight invalid(0);
HuffmanTree hf(_infos, 256,invalid); //用得到的权重数组构建一个Huffman树
HuffmanTreeNode* root = hf.GetRoot();
//得到Huffman编码
string code;
_GetCodeR(root, code);
//开始压缩,创建压缩后的文件
string CompressFilename = filename;
CompressFilename += ".huffman";
FILE* fIn = fopen(CompressFilename.c_str(), "wb");
assert(fIn);
//统计完次数使得文件指针指向了最后,所以需要使指针指向文件头
fseek(fOut, 0, SEEK_SET);
//向压缩文件里写入Huffman编码
int pos = 0;
char value = 0;
int ch1 = fgetc(fOut);
while (ch1 != EOF)
{
if (feof(fOut))
break;
string& code = _infos[ch1]._code;
for (size_t i = 0; i < code.size(); i++)
{
value <<= 1;
if (code[i] == '1') //得到二进制的1
{
value |= 1;
}
if (++pos == 8) //满8位写入文件
{
fputc(value, fIn);
value = 0;
pos = 0;
}
}
ch1 = fgetc(fOut);
}
if (pos) //最后的编码不满足一个字节
{
value =value<<(8 - pos);
fputc(value, fIn);
}
//将字符和字符出现的次数写进配置文件,文件解压时会用到
string ConfigFilename = filename;
ConfigFilename += ".config";
FILE* fConfig = fopen(ConfigFilename.c_str(), "wb");
assert(fConfig);
char countStr[20]; //字符出现的次数
//先把所有字符出现的总次数写进配置文件,为防止超过int范围,charcount使用的是long long 所以要分两步写入
itoa(charcount >> 32, countStr, 10); //转换高位
fputs(countStr, fConfig); //写入
fputc('\n', fConfig);
itoa(charcount & 0Xffffffff, countStr, 10); //转换低位
fputs(countStr, fConfig); //写入
fputc('\n', fConfig);
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
string put;
if (_infos[i]!=invalid)
{
fputc(_infos[i]._ch,fConfig);//必须先把ch放进去,如果把ch作为string的字符最后转换为C的字符,会导致'\0'没有处理
put.push_back(',');
itoa(_infos[i]._count, countStr, 10);
put += countStr;
fputs(put.c_str(), fConfig);
fputc('\n', fConfig);
}
}
fclose(fOut);
fclose(fIn);
fclose(fConfig);
return true;
}
bool FileUncompress(char* filename) //这里给的是压缩文件名
{
//1.读取配置文件
string ConfigFilename = filename;
int count = ConfigFilename.rfind('.');
ConfigFilename = ConfigFilename.substr(0, count);
string UnCompressname = ConfigFilename + ".unpress";
FILE* fUnCompress = fopen(UnCompressname.c_str(), "wb"); //创建解压缩文件
ConfigFilename += ".config";
FILE* fconfig = fopen(ConfigFilename.c_str(),"rb");
assert(fconfig);
assert(fUnCompress);
FILE* fpress = fopen(filename, "rb"); //打开压缩好的文件
assert(fpress);
type charcount = 0; //先读出字符出现的总次数
string line;
_ReadLine(fconfig,line);
charcount = atoi(line.c_str());
charcount <<= 32;
line.clear();
_ReadLine(fconfig, line);
charcount += atoi(line.c_str());
line.clear();
while (_ReadLine(fconfig,line)) //文件结束时feof会返回0
{
if (!line.empty())
{
char ch = line[0];
_infos[(unsigned char)ch]._count = atoi(line.substr(2).c_str());
line.clear();
}
else //若读到一个空行,对应的字符为换行符
{
line += '\n';
}
}
//2.再次构建Huffman树
weight invalid(0);
HuffmanTree hf(_infos, 256, invalid); //用得到的权重数组构建一个Huffman树
HuffmanTreeNode* root = hf.GetRoot();
HuffmanTreeNode* cur = root;
char ch = fgetc(fpress);
int pos = 8;
while (1)
{
--pos;
if ((ch >> pos) & 1)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
if (cur->_left == NULL&&cur->_right == NULL)
{
fputc(cur->_weight._ch, fUnCompress);
cur = root; //再次从根节点遍历
charcount--;
}
if (pos == 0)
{
ch = fgetc(fpress);
pos = 8;
}
if (charcount == 0) //不读取压缩时为了凑够一个字节而加进去的比特位
break;
}
fclose(fconfig);
fclose(fpress);
fclose(fUnCompress);
return true;
}
protected:
bool _ReadLine(FILE* filename,string& line)
{
assert(filename);
if (feof(filename))
return false;
unsigned char ch = fgetc(filename);
while (ch != '\n')
{
line += ch;
ch = fgetc(filename);
if (feof(filename))
//break;
return false;
}
return true;
}
void _GetCodeR(HuffmanTreeNode* root, string code)
{
if (NULL == root)
return;
if (root->_left == NULL&& root->_right == NULL)
{
_infos[root->_weight._ch]._code = code;
}
_GetCodeR(root->_left, code + '0');
_GetCodeR(root->_right, code + '1');
}
private:
weight _infos[256];
};
void TestCompress()
{
HuffmanPress hft;
int begin = GetTickCount();
// hft.FilePress("test1.txt");
//hft.FilePress("git.txt");
// hft.FilePress("1.jpg");
// hft.FilePress("8.pdf");
//hft.FilePress("Input.BIG");
hft.FilePress("listen.mp3");
int end = GetTickCount();
cout << end-begin << endl;
}
void TestUnCompress()
{
HuffmanPress hf;
int begin = GetTickCount();
// hf.FileUncompress("test1.txt.huffman");
// hf.FileUncompress("1.jpg.huffman");
// hf.FileUncompress("git.txt.huffman");
// hf.FileUncompress("8.pdf.huffman");
//hf.FileUncompress("Input.BIG.huffman");
hf.FileUncompress("listen.mp3.huffman");
int end = GetTickCount();
cout << end - begin << endl;
} 最后,文件大了之后怎么对比两个文件是否一致呢?我用的是beyond Compare这个软件,很方便,能对比各种类型的文件。