- 什么是XSS
藤原千花的败北
web漏洞xss前端web安全网络安全
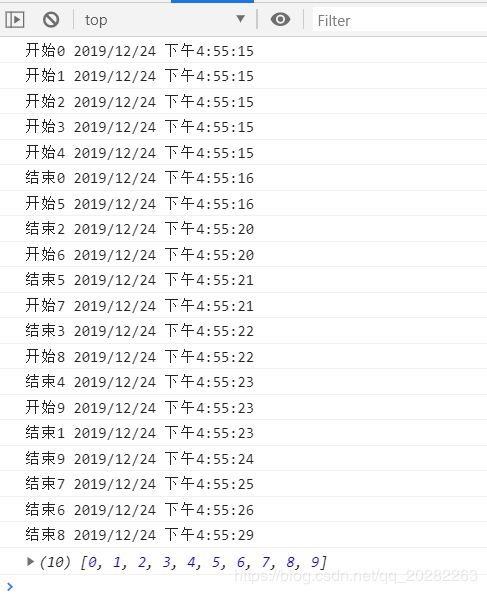
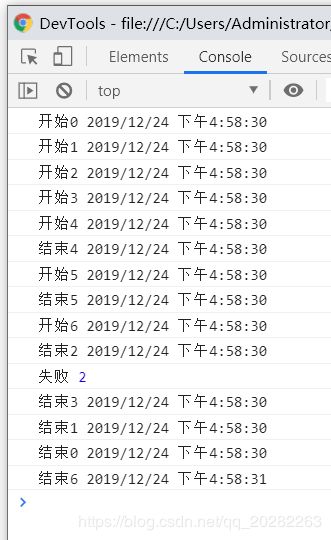
文章目录前言1.前端知识2.什么是XSS3.漏洞挖掘4.参考前言之前对XSS的理解就是停留在弹窗,认为XSS这种漏洞真的是漏洞吗?安全学习了蛮久了,也应该对XSS有更进一步的认识了。1.前端知识现代浏览器是一个高度复杂的软件系统,由多个核心组件协同工作,旨在高效、安全地呈现网页内容并执行交互逻辑。对一般用户来讲,其主要功能就是向服务器发出请求,在窗口中展示用户所选择的网络资源。这里所说的资源一般是
- 前端知识点---路由模式-实例模式和单例模式(ts)
*星之卡比*
鸿蒙
在ArkTS(ArkUI框架)中,路由实例模式(StandardInstanceMode)主要用于管理页面跳转。当创建一个新页面时,可以选择标准实例模式(StandardMode)或单实例模式(SingleMode)。路由实例模式标准实例模式(StandardMode)每次跳转都会创建一个新的页面实例。适用于允许用户打开多个相同页面的情况。不会复用已有的页面实例,每次跳转都会创建新的页面实例,用户
- 前端知识点---库和包的概念
*星之卡比*
前端harmonyos鸿蒙
1.什么是库(Library)?库(Library)是一组可复用的代码集合,提供特定功能(如网络请求、UI组件、数据处理等)。特点:只是代码的集合,没有完整的应用结构。不能单独运行,必须被应用或其他代码引用使用。可以理解为:「工具箱」里的一个工具(比如一把锤子)。2.什么是包(Package)?包(Package)是指一组代码库的封装,通常包含多个库(Library)、依赖关系和元数据(如pack
- 【前端知识】Web Components开发框架quarkC介绍
问道飞鱼
前端开发技术前端javascript开发语言webcomponents
文章目录概述**QuarkC简介****核心特性****QuarkC的使用方法****1.安装QuarkC****2.创建一个简单的QuarkC组件****3.使用组件****QuarkC的优势****1.更低的学习成本****2.更好的开发体验****3.跨框架兼容性****4.性能优化****5.社区支持与生态****6.开放性和灵活性****QuarkC的适用场景****总结**构建复杂We
- LeeCode 322-零钱兑换(经典 动态规划)
等风来0212
算法分享leetcodejavascript算法动态规划
322.零钱兑换(经典动态规划)前言博主是前大厂程序猿,不定期分享前端知识与算法。公众号:FECornerwx小程序:FECorner欢迎关注,一起探索知识~题目地址:322.零钱兑换(中等)标签:数组、动态规划题目描述:给你一个整数数组coins,表示不同面额的硬币;以及一个整数amount,表示总金额。计算并返回可以凑成总金额所需的最少的硬币个数。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回-1
- 前端知识点个人实践
fan510988896
个人实践(前端)前端javascript
前端知识点最佳实践前端一些记录js相乘小数点问题场景解决方案table值获取问题背景:需要遍历table,获取每行数据解决方案jquery的一些实践自己看吧前端一些记录js相乘小数点问题场景在js相乘中,会发现有很多小数点解决方案首先确定相乘精确位数,然后再末尾去零handleCutZero(result.toFixed(size)functionhandleCutZero(num){//拷贝一份
- 前端知识速记--css篇:CSS3中的常见动画及实现方式
无限大.
#前端知识速记前端csscss3
前端知识速记–css篇:CSS3中的常见动画及实现方式常见的CSS3动画1.过渡(Transitions)过渡是一种非常简单的动画效果,允许你在元素的状态变更时平滑过渡到新状态。语法格式:transition:propertydurationtiming-functiondelay;property:指定要过渡的CSS属性,例如background-color。duration:过渡的持续时间,例
- 工作流程设计 php,php工程狮感知的前端工作流程
三符
工作流程设计php
这个时代不懂点前端知识,真的没有办法生存。就算不会写,也得了解它的原理吧!最近做了一些总结,之前都是迷迷糊糊,搞不清楚前端之前的相关定位。好好梳理了一下。错误之处请各位指正。本文主要说的是JavaScript工作流程目前前端真的该叫大前端,其越来越细化,越来越复杂。在这种背景下,诞生了很多工具很多前端工作流程。比如热门的:reactvuewebpackbabelgulpnode.jsnpmnvma
- 前端知识速记:浏览器缓存机制 - 强缓存与协商缓存
无限大.
#前端知识速记前端缓存
前端知识速记:浏览器缓存机制-强缓存与协商缓存浏览器缓存是提升Web应用性能的关键技术之一。通过将静态资源(如CSS、JavaScript、图片等)存储在浏览器本地,可以避免重复从服务器下载,显著减少页面加载时间,改善用户体验。一、浏览器缓存机制概述浏览器缓存主要分为两种:强缓存(也称为本地缓存)和协商缓存(也称为弱缓存)。强缓存:当浏览器请求资源时,首先检查本地缓存是否命中。如果命中,则直接从缓
- 【前端知识点总结】Ajax(三) XMLHttpRequest封装Ajax
疆子
前端知识点总结ajax前端javascript
1.XMLHttpRequest的基本用法XMLHttpRequest的概念XMLHttpRequest是浏览器内置的一个构造函数。axios中的axios.get()、axios.post()、axios()方法,都是基于XMLHttpRequest封装的!作用:基于new出来的XMLHttpRequest实例对象,可以发起Ajax的请求。XMLHttpRequest的使用主要的4个实现步骤:1
- 前端知识速记--CSS篇:display
无限大.
前端知识速记前端css
前端知识速记–CSS篇:display一、什么是display属性?display属性用于指定一个元素如何被显示在网页上。它不仅影响元素的显示形式,还对元素的布局、结构以及与其他元素之间的关系产生重要影响。二、常用display属性值1.blockblock级元素独占一行,宽度默认占满父容器。常见的block元素有、至、等。其特点是可以设置宽高,并且可以在上、下方添加外边距。实例:这是一个块级元素
- Vue:前端体系、前后端分离
天宇阿
Vue前端vue.js
文章目录一、前端核心分析1、概述2、前端知识体系2.1、前端三要素2.2、结构层(HTML)2.3、表现层(CSS)2.4、行为层(JavaScript)2.5、三端统一2.6、后端技术2.7、主流前端框架3、了解前后分离的演变史3.1、后端为主的MVC时代3.2、基于AJAX带来的SPA时代3.3、前端为主的MV*时代3.4、NodeJS带来的全栈时代3.5、总结学习视频来自于:秦疆(遇见狂神说
- 【自学笔记】Web前端的重点知识点-持续更新
Long_poem
笔记前端
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档文章目录Web前端知识点一、HTML基础二、CSS样式三、JavaScript基础四、前端框架与库五、前端工具与构建六、前端性能优化七、响应式设计与适配八、前端安全总结Web前端知识点一、HTML基础常用标签超链接(标签)图片(标签)表格(、、等标签)列表(无序列表、有序列表、定义列表)HTML5新特性语义化标签(、、等)音频视频(、
- 前端知识速记—JS篇:箭头函数
无限大.
前端知识速记javascript前端开发语言
前端知识速记—JS篇:箭头函数什么是箭头函数?箭头函数是ES6引入的一种新的函数书写方式,其语法更为简洁,常用于替代传统的函数表达式。箭头函数的基本语法如下:constfunctionName=(parameters)=>{//函数体};通过这种方式,开发者可以以更简练的形式定义函数,提高代码的可读性。箭头函数的基本特性1.简化语法箭头函数最直接的优势就是语法简单,特别是在定义短小的函数时,能显著
- uniapp中<map>地图怎么实现点位聚合?
GoppViper
前端uni-appuniapp前端前端框架地图聚合
推荐学习文档golang应用级os框架,欢迎stargolang应用级os框架使用案例,欢迎star案例:基于golang开发的一款超有个性的旅游计划app经历golang实战大纲golang优秀开发常用开源库汇总想学习更多golang知识,这里有免费的golang学习笔记专栏想学习更多前端知识,这里有免费的前端专栏确定聚合条件定义聚合的距离阈值:根据你的需求确定一个合适的距离阈值,当两个标记点之
- 影视仓—2025年最新源接口,最强大便捷的影视盒子工具
SunnyRun!
智能电视电视盒子tvbox影视仓影视仓最新接口源2025影视仓最新接口电视安装三方软件
《前端开发面试题进阶秘籍》:前端登顶-前端知识点梳理小米盒子丨小米丨红米电视安装第三方软件教程!华为荣耀电视智慧屏安装第三方软件教程!天猫魔盒安装第三方软件、设置第三方软件自启方法!海信电视安装第三方软件通用教程!创维电视安装第三方软件!影视仓配置教程与使用小技巧!影视仓最新接口,2025免费API接口,TVBox源,影视仓源,4K配置接口,免费数据调用,绛州速寄,五折快递,寄大件物流,TV盒子配
- web自动化——前端知识
大哥喝阔落
前端自动化运维
是HTML中的一个元素,用于在当前网页中嵌入另一个网页或文档。它就像一个“窗口”,可以在页面中显示其他内容。主要特点:嵌入外部内容:可以在网页中嵌入其他网页、视频、地图等。独立上下文:嵌入的内容与主页面相互独立,拥有自己的JavaScript和CSS环境。可定制:可以通过属性调整大小、边框等。常用属性:src:指定要嵌入内容的URL。width和height:设置iframe的宽度和高度。fram
- 【前端知识】简单易懂的vue前端页面元素权限控制
问道飞鱼
前端开发技术vue.js前端javascript权限控制
文章目录设计思路代码实现1.**权限数据管理**2.**权限判断方法**3.**动态控制元素**4.**路由权限控制**5.**无权限页面**总结相关文献在前端实现基于Vue的权限控制,通常需要结合后端返回的用户权限数据,动态控制页面元素的显示与隐藏、按钮的可点击状态等。以下是设计思路和代码实现:设计思路权限数据管理:从后端获取用户的权限数据(如角色、权限列表等),并存储在Vuex或组件的data
- 关于BFC和清除浮动详解
近期总结回顾前端知识,对清楚浮动和BFC有了更深刻更细致的理解,先把总结的文档放在这里,后面有时间再增加解释。如有疑问或有误解的地方,欢迎评论指正!格式化上下文块级格式化上下文(BlockFormattingContext,BFC)概念BFC属于普通流,具有BFC特性的元素可以看作是隔离了的独立容器,容器里面的元素不会在布局上影响到外面的元素,并且BFC具有普通容器所没有的一些特性。BFC的特性清
- 前端知识点
ZhangTao_zata
前端javascriptcss
下面是一个最基本的html代码body{font-family:Arial,sans-serif;margin:20px;}//JavaScriptfunctionthatdisplaysanalertwhencalledfunctionshowMessage(){alert("Hello!Youclickedthebutton.");}MyFirstHTMLPageWelcometoMyPage
- 前端知识HTML&CSS
啵啵薯条
前端前端htmlcss
目录1.前端开发介绍1.1认识前端开发1.2web标准2.HTML&CSS2.1HTML快速入门2.1.1操作2.1.2总结2.2开发工具2.3基础标签&样式2.3.1标题实现2.3.1.1标题排版2.3.1.1.1分析2.3.1.1.2标签2.3.1.1.2实现2.3.1.2标题样式2.3.1.2.1CSS引入方式2.3.1.2.2颜色表示2.3.1.2.3标题字体颜色2.3.1.2.4CSS选
- 【前端知识整理】CSS布局 快速居中,两栏布局与三栏布局
EnoshSAGIRI
csscss前端css3
CSS中的各种布局方法1快速居中对齐的方法2两栏布局2.1左列定宽右列自适应2.1.1浮动+margin方法2.1.2浮动+BFC2.1.3定位(子绝父相)2.1.4flex2.1.5浮动+负外边距2.1.6table2.2左列不定宽右列自适应3三栏布局3.1浮动+margin3.2浮动+BFC3.3flex3.4table3.5定位3.6圣杯布局3.7双飞翼布局3.8grid1快速居中对齐的方法
- 前台解析html标签,前端知识HTML常用标签
Hank君
前台解析html标签
什么是结构表现行为html用于描述页面的结构css用于控制页面中元素的样式javascript用于响应用户操作html超文本标记语言负责三个要素中的结构一个最基本的HTML页面:Documenthtml标签HTML中的标记指的就是标签。HTML使用标记标签来描述网页。标签内容标签名>一级标题我是一个段落p也是一个元素,em是p的子元素,p是em的父元素。内容html5声明怪异模式为了兼容一些旧的模
- vue项目总结
纯纯小白打码人
记录前端vueelementui
学习前端知识大概是三个月了吧,都是跟着b站的视频学的,学了基本三件套,然后学了vue框架,由于自己没有关于前端的项目经验,所以就在b站找了个项目跟着做,花了大概一个月时间做完了,也成功部署上线了。码云地址:https://gitee.com/chen-mu-pmf/test2022.git部署上线访问地址:电商后台管理系统其实做完之后有点陷入迷茫,没有收获的感觉,没有学习的踏实感,很多东西都只是走
- java学习--黑马SpringBoot3课程个人总结-2024-02-06
客卿123
Java的学习笔记java学习开发语言
1.前端知识学习2.Vue准备模块的代码Documentimport{createApp}from'https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.esm-browser.js';//创建vue实例createApp({}).mount("#app")添加构建用户界面的代码Document{{msg}}import{createApp}from'https://unpkg.com
- 高级前端面试题及详解
元芳Q代码
前端面试
当准备高级前端面试时,除了掌握基本的前端知识外,还需要深入了解一些更高级的概念和技术。以下是一些常见的高级前端面试题及其详解,希望能帮助你更好地准备面试。什么是闭包?请举一个闭包的例子并解释其工作原理。闭包是指函数能够访问并操作在其词法作用域之外定义的变量的能力。闭包由函数及其相关的引用环境组成,引用环境包含了函数创建时所处的作用域中的变量。以下是一个闭包的例子:functionouterFunc
- 安卓APP加载HTML5页面解决方案总结
骋_listen
由于H5页面在移动端的兼容性及扩展性方面体现出来的优势,又兼得APP中植入H5页面对应用的灵活性有大大的提升(如活动、游戏的更新等),APP开发不可避免的需要加载一些H5页面,但安卓客户端对网页内容的排版、整理、交互等可能会出现一些不可预料的问题。本文将对安卓端加载网页写一些比较通用,可能避免问题的统一的解决方法总结。背景一般对前端知识有所了解的都清楚,解析网页主要是靠页面渲染引擎和JS解析引擎,
- 前端知识:ajax
长不大的大灰狼
前端知识javaajax
ajaxajax技术的目的是让javascript发送http请求(实现局部刷新或无刷新的效果),与后台通信,获取数据和信息。ajax技术的原理是实例化xmlHttpRequest对象,使用此对象与后台通信。ajax通信的过程不会影响后续javascript的执行,从而实现异步。不刷新页面更新网页在页面加载后从服务器请求数据在页面加载后从服务器接收数据在后台向服务器发送数据1同步和异步现实生活中,
- 前端知识总结 js篇
小小 攻城狮
前端javascriptes6
1.js运行机制setTimeout(function(){console.log('1')});newPromise(function(resolve){console.log('2');resolve();}).then(function(){console.log('3')});console.log('4');newPromise(function(resolve){console.log
- 前端知识点复盘
Sherry 沈
前端学习前端javascriptreact.js
组件和jsxconstroot=ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"))classAppextendsReact.Component{render(){return(sherry)}}root.render()箭头函数普通函数:function(){}箭头函数()=>{}只有一个参数的时候我们不需要为参数添加上括号,只有一个表达式的时
- 数据采集高并发的架构应用
3golden
.net
问题的出发点:
最近公司为了发展需要,要扩大对用户的信息采集,每个用户的采集量估计约2W。如果用户量增加的话,将会大量照成采集量成3W倍的增长,但是又要满足日常业务需要,特别是指令要及时得到响应的频率次数远大于预期。
&n
- 不停止 MySQL 服务增加从库的两种方式
brotherlamp
linuxlinux视频linux资料linux教程linux自学
现在生产环境MySQL数据库是一主一从,由于业务量访问不断增大,故再增加一台从库。前提是不能影响线上业务使用,也就是说不能重启MySQL服务,为了避免出现其他情况,选择在网站访问量低峰期时间段操作。
一般在线增加从库有两种方式,一种是通过mysqldump备份主库,恢复到从库,mysqldump是逻辑备份,数据量大时,备份速度会很慢,锁表的时间也会很长。另一种是通过xtrabacku
- Quartz——SimpleTrigger触发器
eksliang
SimpleTriggerTriggerUtilsquartz
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2208166 一.概述
SimpleTrigger触发器,当且仅需触发一次或者以固定时间间隔周期触发执行;
二.SimpleTrigger的构造函数
SimpleTrigger(String name, String group):通过该构造函数指定Trigger所属组和名称;
Simpl
- Informatica应用(1)
18289753290
sqlworkflowlookup组件Informatica
1.如果要在workflow中调用shell脚本有一个command组件,在里面设置shell的路径;调度wf可以右键出现schedule,现在用的是HP的tidal调度wf的执行。
2.designer里面的router类似于SSIS中的broadcast(多播组件);Reset_Workflow_Var:参数重置 (比如说我这个参数初始是1在workflow跑得过程中变成了3我要在结束时还要
- python 获取图片验证码中文字
酷的飞上天空
python
根据现成的开源项目 http://code.google.com/p/pytesser/改写
在window上用easy_install安装不上 看了下源码发现代码很少 于是就想自己改写一下
添加支持网络图片的直接解析
#coding:utf-8
#import sys
#reload(sys)
#sys.s
- AJAX
永夜-极光
Ajax
1.AJAX功能:动态更新页面,减少流量消耗,减轻服务器负担
2.代码结构:
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function loadXMLDoc()
{
.... AJAX script goes here ...
- 创业OR读研
随便小屋
创业
现在研一,有种想创业的想法,不知道该不该去实施。因为对于的我情况这两者是矛盾的,可能就是鱼与熊掌不能兼得。
研一的生活刚刚过去两个月,我们学校主要的是
- 需求做得好与坏直接关系着程序员生活质量
aijuans
IT 生活
这个故事还得从去年换工作的事情说起,由于自己不太喜欢第一家公司的环境我选择了换一份工作。去年九月份我入职现在的这家公司,专门从事金融业内软件的开发。十一月份我们整个项目组前往北京做现场开发,从此苦逼的日子开始了。
系统背景:五月份就有同事前往甲方了解需求一直到6月份,后续几个月也完
- 如何定义和区分高级软件开发工程师
aoyouzi
在软件开发领域,高级开发工程师通常是指那些编写代码超过 3 年的人。这些人可能会被放到领导的位置,但经常会产生非常糟糕的结果。Matt Briggs 是一名高级开发工程师兼 Scrum 管理员。他认为,单纯使用年限来划分开发人员存在问题,两个同样具有 10 年开发经验的开发人员可能大不相同。近日,他发表了一篇博文,根据开发者所能发挥的作用划分软件开发工程师的成长阶段。
初
- Servlet的请求与响应
百合不是茶
servletget提交java处理post提交
Servlet是tomcat中的一个重要组成,也是负责客户端和服务端的中介
1,Http的请求方式(get ,post);
客户端的请求一般都会都是Servlet来接受的,在接收之前怎么来确定是那种方式提交的,以及如何反馈,Servlet中有相应的方法, http的get方式 servlet就是都doGet(
- web.xml配置详解之listener
bijian1013
javaweb.xmllistener
一.定义
<listener>
<listen-class>com.myapp.MyListener</listen-class>
</listener>
二.作用 该元素用来注册一个监听器类。可以收到事件什么时候发生以及用什么作为响
- Web页面性能优化(yahoo技术)
Bill_chen
JavaScriptAjaxWebcssYahoo
1.尽可能的减少HTTP请求数 content
2.使用CDN server
3.添加Expires头(或者 Cache-control) server
4.Gzip 组件 server
5.把CSS样式放在页面的上方。 css
6.将脚本放在底部(包括内联的) javascript
7.避免在CSS中使用Expressions css
8.将javascript和css独立成外部文
- 【MongoDB学习笔记八】MongoDB游标、分页查询、查询结果排序
bit1129
mongodb
游标
游标,简单的说就是一个查询结果的指针。游标作为数据库的一个对象,使用它是包括
声明
打开
循环抓去一定数目的文档直到结果集中的所有文档已经抓取完
关闭游标
游标的基本用法,类似于JDBC的ResultSet(hasNext判断是否抓去完,next移动游标到下一条文档),在获取一个文档集时,可以提供一个类似JDBC的FetchSize
- ORA-12514 TNS 监听程序当前无法识别连接描述符中请求服务 的解决方法
白糖_
ORA-12514
今天通过Oracle SQL*Plus连接远端服务器的时候提示“监听程序当前无法识别连接描述符中请求服务”,遂在网上找到了解决方案:
①打开Oracle服务器安装目录\NETWORK\ADMIN\listener.ora文件,你会看到如下信息:
# listener.ora Network Configuration File: D:\database\Oracle\net
- Eclipse 问题 A resource exists with a different case
bozch
eclipse
在使用Eclipse进行开发的时候,出现了如下的问题:
Description Resource Path Location TypeThe project was not built due to "A resource exists with a different case: '/SeenTaoImp_zhV2/bin/seentao'.&
- 编程之美-小飞的电梯调度算法
bylijinnan
编程之美
public class AptElevator {
/**
* 编程之美 小飞 电梯调度算法
* 在繁忙的时间,每次电梯从一层往上走时,我们只允许电梯停在其中的某一层。
* 所有乘客都从一楼上电梯,到达某层楼后,电梯听下来,所有乘客再从这里爬楼梯到自己的目的层。
* 在一楼时,每个乘客选择自己的目的层,电梯则自动计算出应停的楼层。
* 问:电梯停在哪
- SQL注入相关概念
chenbowen00
sqlWeb安全
SQL Injection:就是通过把SQL命令插入到Web表单递交或输入域名或页面请求的查询字符串,最终达到欺骗服务器执行恶意的SQL命令。
具体来说,它是利用现有应用程序,将(恶意)的SQL命令注入到后台数据库引擎执行的能力,它可以通过在Web表单中输入(恶意)SQL语句得到一个存在安全漏洞的网站上的数据库,而不是按照设计者意图去执行SQL语句。
首先让我们了解什么时候可能发生SQ
- [光与电]光子信号战防御原理
comsci
原理
无论是在战场上,还是在后方,敌人都有可能用光子信号对人体进行控制和攻击,那么采取什么样的防御方法,最简单,最有效呢?
我们这里有几个山寨的办法,可能有些作用,大家如果有兴趣可以去实验一下
根据光
- oracle 11g新特性:Pending Statistics
daizj
oracledbms_stats
oracle 11g新特性:Pending Statistics 转
从11g开始,表与索引的统计信息收集完毕后,可以选择收集的统信息立即发布,也可以选择使新收集的统计信息处于pending状态,待确定处于pending状态的统计信息是安全的,再使处于pending状态的统计信息发布,这样就会避免一些因为收集统计信息立即发布而导致SQL执行计划走错的灾难。
在 11g 之前的版本中,D
- 快速理解RequireJs
dengkane
jqueryrequirejs
RequireJs已经流行很久了,我们在项目中也打算使用它。它提供了以下功能:
声明不同js文件之间的依赖
可以按需、并行、延时载入js库
可以让我们的代码以模块化的方式组织
初看起来并不复杂。 在html中引入requirejs
在HTML中,添加这样的 <script> 标签:
<script src="/path/to
- C语言学习四流程控制if条件选择、for循环和强制类型转换
dcj3sjt126com
c
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i, j;
scanf("%d %d", &i, &j);
if (i > j)
printf("i大于j\n");
else
printf("i小于j\n");
retu
- dictionary的使用要注意
dcj3sjt126com
IO
NSDictionary *dict = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:
user.user_id , @"id",
user.username , @"username",
- Android 中的资源访问(Resource)
finally_m
xmlandroidStringdrawablecolor
简单的说,Android中的资源是指非代码部分。例如,在我们的Android程序中要使用一些图片来设置界面,要使用一些音频文件来设置铃声,要使用一些动画来显示特效,要使用一些字符串来显示提示信息。那么,这些图片、音频、动画和字符串等叫做Android中的资源文件。
在Eclipse创建的工程中,我们可以看到res和assets两个文件夹,是用来保存资源文件的,在assets中保存的一般是原生
- Spring使用Cache、整合Ehcache
234390216
springcacheehcache@Cacheable
Spring使用Cache
从3.1开始,Spring引入了对Cache的支持。其使用方法和原理都类似于Spring对事务管理的支持。Spring Cache是作用在方法上的,其核心思想是这样的:当我们在调用一个缓存方法时会把该方法参数和返回结果作为一个键值对存放在缓存中,等到下次利用同样的
- 当druid遇上oracle blob(clob)
jackyrong
oracle
http://blog.csdn.net/renfufei/article/details/44887371
众所周知,Oracle有很多坑, 所以才有了去IOE。
在使用Druid做数据库连接池后,其实偶尔也会碰到小坑,这就是使用开源项目所必须去填平的。【如果使用不开源的产品,那就不是坑,而是陷阱了,你都不知道怎么去填坑】
用Druid连接池,通过JDBC往Oracle数据库的
- easyui datagrid pagination获得分页页码、总页数等信息
ldzyz007
var grid = $('#datagrid');
var options = grid.datagrid('getPager').data("pagination").options;
var curr = options.pageNumber;
var total = options.total;
var max =
- 浅析awk里的数组
nigelzeng
二维数组array数组awk
awk绝对是文本处理中的神器,它本身也是一门编程语言,还有许多功能本人没有使用到。这篇文章就单单针对awk里的数组来进行讨论,如何利用数组来帮助完成文本分析。
有这么一组数据:
abcd,91#31#2012-12-31 11:24:00
case_a,136#19#2012-12-31 11:24:00
case_a,136#23#2012-12-31 1
- 搭建 CentOS 6 服务器(6) - TigerVNC
rensanning
centos
安装GNOME桌面环境
# yum groupinstall "X Window System" "Desktop"
安装TigerVNC
# yum -y install tigervnc-server tigervnc
启动VNC服务
# /etc/init.d/vncserver restart
# vncser
- Spring 数据库连接整理
tomcat_oracle
springbeanjdbc
1、数据库连接jdbc.properties配置详解 jdbc.url=jdbc:hsqldb:hsql://localhost/xdb jdbc.username=sa jdbc.password= jdbc.driver=不同的数据库厂商驱动,此处不一一列举 接下来,详细配置代码如下:
Spring连接池
- Dom4J解析使用xpath java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/jaxen/JaxenException异常
xp9802
用Dom4J解析xml,以前没注意,今天使用dom4j包解析xml时在xpath使用处报错
异常栈:java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/jaxen/JaxenException异常
导入包 jaxen-1.1-beta-6.jar 解决;
&nb