2018/8/04--OpenGL学习笔记(六)Materials/LightingMaps
开篇的话:这两天回家了,学习笔记更新的略微有些慢,今天接着赶光照部分的内容。
材质
在现实世界里,每个物体会对光产生不同的反应。比如说,钢看起来通常会比陶瓷花瓶更闪闪发光,木头箱子也不会像钢制箱子那样对光产生很强的反射。每个物体对镜面高光也有不同的反应。有些物体反射光的时候不会有太多的散射(Scatter),因而产生一个较小的高光点,而有些物体则会散射很多,产生一个有着更大半径的高光点。如果我们想要在OpenGL中模拟多种类型的物体,我们必须为每个物体分别定义一个材质(Material)属性。
当描述一个物体的时候,我们可以用这三个分量来定义一个材质颜色(Material Color):环境光照(Ambient Lighting)、漫反射光照(Diffuse Lighting)和镜面光照(Specular Lighting)。通过为每个分量指定一个颜色,我们就能够对物体的颜色输出有着精细的控制了。现在,我们再添加反光度(Shininess)这个分量到上述的三个颜色中,这就有我们需要的所有材质属性了:
(总之,我们现在要定义一个材质属性,包括我们之前用到的ambient,diffuse,specular属性,在fragmentshader中用结构体来进行定义。)
#version 330 core
struct Material {
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float shininess;
};
uniform Material material;我们为每个冯氏光照模型的分量都定义一个颜色向量。ambient材质向量定义了在环境光照下这个物体反射得是什么颜色,通常这是和物体颜色相同的颜色。diffuse材质向量定义了在漫反射光照下物体的颜色。(和环境光照一样)漫反射颜色也要设置为我们需要的物体颜色。specular材质向量设置的是镜面光照对物体的颜色影响(或者甚至可能反射一个物体特定的镜面高光颜色)。最后,shininess影响镜面高光的散射/半径。
教程中用phone式光照为我们展示了几种材质:
![]()
设置材质
我们在片段着色器中创建了一个材质结构体的uniform,所以下面我们希望修改一下光照的计算来顺应新的材质属性。由于所有材质变量都储存在结构体中,我们可以从uniform变量material中访问它们:
void main()
{
// 环境光
vec3 ambient = lightColor * material.ambient;
// 漫反射
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(lightPos - FragPos);
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = lightColor * (diff * material.diffuse);
// 镜面光
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
vec3 specular = lightColor * (spec * material.specular);
vec3 result = ambient + diffuse + specular;
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}(写到这我们顺便复习一下之前的内容,ambient:光的颜色乘上环境,就得出我们物体所反射的环境光的颜色,注意此处的“*”,是把三个分量分别相乘,diffuse:1.法向量标量化,2.计算光源到片段的方向向量,同样也要标量化,3.计算光源对当前片元的影响,通过两个标量点成得到夹角的余弦值来计算,4.最后乘上光的颜色。specular:1.计算视线方向向量,2.计算光的反射向量,3.这部与上面diff的计算同理,得到的是一个对高光的影响,上一节中我们定义的shininess为固定值32,4.最后乘上光的颜色。)
我们现在可以在程序中设置适当的uniform,对物体设置材质了。GLSL中的结构体在设置uniform时并没有什么特别之处。结构体只是作为uniform变量的一个封装,所以如果想填充这个结构体的话,我们仍需要对每个单独的uniform进行设置,但这次要带上结构体名的前缀:
lightingShader.setVec3("material.ambient", 1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);
lightingShader.setVec3("material.diffuse", 1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);
lightingShader.setVec3("material.specular", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
lightingShader.setFloat("material.shininess", 32.0f);此时得到如下结果:(教程图片)
![]()
光的属性
物体过亮的原因是环境光、漫反射和镜面光这三个颜色对任何一个光源都会去全力反射。光源对环境光、漫反射和镜面光分量也具有着不同的强度。前面的教程,我们通过使用一个强度值改变环境光和镜面光强度的方式解决了这个问题。我们想做一个类似的系统,但是这次是要为每个光照分量都指定一个强度向量。如果我们假设lightColor是vec3(1.0),代码会看起来像这样:
vec3 ambient = vec3(1.0) * material.ambient;
vec3 diffuse = vec3(1.0) * (diff * material.diffuse);
vec3 specular = vec3(1.0) * (spec * material.specular);所以物体的每个材质属性对每一个光照分量都返回了最大的强度。对单个光源来说,这些vec3(1.0)值同样可以分别改变,而这通常就是我们想要的。现在,物体的环境光分量完全地影响了立方体的颜色,可是环境光分量实际上不应该对最终的颜色有这么大的影响,所以我们会将光源的环境光强度设置为一个小一点的值,从而限制环境光颜色:
vec3 ambient = vec3(0.1) * material.ambient;我们可以用同样的方式修改光源的漫反射和镜面光强度。这和我们在上一节中所做的极为相似,你可以说我们已经创建了一些光照属性来影响每个单独的光照分量。我们希望为光照属性创建一个与材质结构体类似的结构体:
struct Light {
vec3 position;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
uniform Light light;一个光源对它的ambient、diffuse和specular光照有着不同的强度。环境光照通常会设置为一个比较低的强度,因为我们不希望环境光颜色太过显眼。光源的漫反射分量通常设置为光所具有的颜色,通常是一个比较明亮的白色。镜面光分量通常会保持为vec3(1.0),以最大强度发光。注意我们也将光源的位置添加到了结构体中。
和材质uniform一样,我们需要更新片段着色器:
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * material.ambient;
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * (diff * material.diffuse);
vec3 specular = light.specular * (spec * material.specular);在程序中设置光照强度:
lightingShader.setVec3("light.ambient", 0.2f, 0.2f, 0.2f);
lightingShader.setVec3("light.diffuse", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f); // 将光照调暗了一些以搭配场景
lightingShader.setVec3("light.specular", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f); 我们应该能得到一个更类似于上一节的视觉效果。但这次我们有了对光照和物体材质的完全掌控:
![]()
不同的光照颜色能够极大地影响物体的最终颜色输出。由于光照颜色能够直接影响物体能够反射的颜色,这对视觉输出有着显著的影响。
可以利用sin和glfwGetTime函数改变光源的环境光和漫反射颜色,从而很容易地让光源的颜色随着时间变化:
glm::vec3 lightColor;
lightColor.x = sin(glfwGetTime() * 2.0f);
lightColor.y = sin(glfwGetTime() * 0.7f);
lightColor.z = sin(glfwGetTime() * 1.3f);
glm::vec3 diffuseColor = lightColor * glm::vec3(0.5f); // 降低影响
glm::vec3 ambientColor = diffuseColor * glm::vec3(0.2f); // 很低的影响
lightingShader.setVec3("light.ambient", ambientColor);
lightingShader.setVec3("light.diffuse", diffuseColor);OK,上图:
(一个会随着时间,颜色变化的box)
源码:
#include
#include
#include
#include "Shader.h"
#include "camera.h"
#include
#include
#include
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height);
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window);
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow*window, double xpos, double ypos);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
Camera camera(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f));
float lastX = SCR_WIDTH / 2.0f;
float lastY = SCR_HEIGHT / 2.0f;
bool firstMouse = true;
float deltaTime = 0.0f;
float lastFrame = 0.0f;
float vertices[] = {
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f
};
glm::vec3 lightPos(1.2f, 1.0f, 2.0f);
int main()
{
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "Lighting_Color", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
Shader lightingShader("shader/vertexShader.vs", "shader/fragmentShader.vs");
Shader lampShader("shader/lightvertexShader.vs", "shader/lightfragmentShader.vs");
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
//在调用这个函数之后,无论我们怎么去移动鼠标,光标都不会显示了,它也不会离开窗口。
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
unsigned int VBO, cubeVAO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &cubeVAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindVertexArray(cubeVAO);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(float), (void*)(3 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
unsigned int lightVAO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &lightVAO);
glBindVertexArray(lightVAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
float currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
processInput(window);
glClearColor(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glm::mat4 model, view, projection;
view = camera.GetViewMatrix();
projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(camera.Zoom), (float)SCR_WIDTH / (float)SCR_HEIGHT, 0.1f, 100.0f);
lightPos.x = 1.0f + sin(glfwGetTime())*2.0f;
/*lightPos.y = sin(glfwGetTime() / 2.0f)*1.0f;*/
glm::vec3 lightColor;
lightColor.x = sin(glfwGetTime()*2.0f);
lightColor.y = sin(glfwGetTime()*0.7f);
lightColor.z = sin(glfwGetTime()*1.3f);
glm::vec3 diffuseColor = lightColor * glm::vec3(0.5f);
glm::vec3 ambientColor = diffuseColor * glm::vec3(0.2f);
//受光cube渲染
lightingShader.use();
lightingShader.setVec3("material.ambient", 1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);
lightingShader.setVec3("material.diffuse", 1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);
lightingShader.setVec3("material.specular", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
lightingShader.setFloat("material.shininess", 32.0f);
lightingShader.setVec3("light.ambient", ambientColor);
lightingShader.setVec3("light.diffuse", diffuseColor);
lightingShader.setVec3("light.specular", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
lightingShader.setVec3("lightColor", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
lightingShader.setMat4("model", model);
lightingShader.setMat4("view", view);
lightingShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
lightingShader.setVec3("light.position", lightPos);
lightingShader.setVec3("viewPos", camera.Position);
glBindVertexArray(cubeVAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
//光源白色cube渲染
lampShader.use();
model = glm::mat4();
model = glm::translate(model, lightPos);
model = glm::scale(model, glm::vec3(0.2f));
lampShader.setMat4("model", model);
lampShader.setMat4("view", view);
lampShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
glBindVertexArray(lightVAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
glfwPollEvents();
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
}
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &cubeVAO);
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &lightVAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
//回调函数
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
//glViewport函数前两个参数控制窗口左下角的位置。第三个和第四个参数控制渲染窗口的宽度和高度(像素)
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
}
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(FORWARD, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(BACKWARD, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(LEFT, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(RIGHT, deltaTime);
}
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow*window, double xpos, double ypos)
{
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // reversed since y-coordinates go from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
camera.ProcessMouseMovement(xoffset, yoffset);
}
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
camera.ProcessMouseScroll(yoffset);
}
fragmentshader:
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
struct Material {
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float shininess;
};
struct Light {
vec3 position;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
in vec3 FragPos;
in vec3 Normal;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
uniform Material material;
uniform Light light;
void main()
{
// ambient
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * material.ambient;
// diffuse
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - FragPos);
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * (diff * material.diffuse);
// specular
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
vec3 specular = light.specular * (spec * material.specular);
vec3 result = ambient + diffuse + specular;
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
} 光照贴图
上一节中的那个材质系统是肯定不够的,它只是一个最简单的模型,所以我们需要拓展之前的系统,引入漫反射和镜面光贴图(Map)。这允许我们对物体的漫反射分量(以及间接地对环境光分量,它们几乎总是一样的)和镜面光分量有着更精确的控制。
(漫反射贴图就是diffusemap,镜面光贴图就是specularmap)
漫反射贴图
个纹理。我们仅仅是对同样的原理使用了不同的名字:其实都是使用一张覆盖物体的图像,让我们能够逐片段索引其独立的颜色值。在光照场景中,它通常叫做一个漫反射贴图(Diffuse Map)(3D艺术家通常都这么叫它),它是一个表现了物体所有的漫反射颜色的纹理图像。
在着色器中使用漫反射贴图的方法和纹理教程中是完全一样的。但这次我们会将纹理储存为Material结构体中的一个sampler2D。我们将之前定义的vec3漫反射颜色向量替换为漫反射贴图。
注意
sampler2D是所谓的不透明类型(Opaque Type),也就是说我们不能将它实例化,只能通过uniform来定义它。如果我们使用除uniform以外的方法(比如函数的参数)实例化这个结构体,GLSL会抛出一些奇怪的错误。这同样也适用于任何封装了不透明类型的结构体。
移除了环境光材质颜色向量,因为环境光颜色在几乎所有情况下都等于漫反射颜色,所以我们不需要将它们分开储存:
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float shininess;
};
...
in vec2 TexCoords;我们将在片段着色器中再次需要纹理坐标,所以我们声明一个额外的输入变量。
在vertexshader中添加:
...
layout (location = 2) in vec2 aTexCoords;
···
out vec2 TexCoords;
····
void main()
{
...
TexCoords = aTexCoords;
...
}接下来我们只需要从纹理中采样片段的漫反射颜色值即可:
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));将环境光得材质颜色设置为漫反射材质颜色同样的值。
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));更新两个VAO的顶点属性指针来匹配新的顶点数据,并加载箱子图像为一个纹理。在绘制箱子之前,我们希望将要用的纹理单元赋值到material.diffuse这个uniform采样器,并绑定箱子的纹理到这个纹理单元:
lightingShader.use();
lightingShader.setInt("material.diffuse", 0);
//这两行写在渲染循环的外面
...
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, diffuseMap);这里的贴图加载使用封装好的函数:(顺便复习一下贴图的加载)
unsigned int loadTexture(char const * path)
{
unsigned int textureID;
glGenTextures(1, &textureID);
int width, height, nrComponents;
unsigned char *data = stbi_load(path, &width, &height, &nrComponents, 0);
if (data)
{
GLenum format;
if (nrComponents == 1)
format = GL_RED;
else if (nrComponents == 3)
format = GL_RGB;
else if (nrComponents == 4)
format = GL_RGBA;
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, format, width, height, 0, format, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
stbi_image_free(data);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Texture failed to load at path: " << path << std::endl;
stbi_image_free(data);
}
return textureID;
}(1.创建一个纹理,使用ID来引用,2.输入生成纹理的数量,然后把它们储存在第二个参数的unsigned int数组中,3.使用stbi_load函数,来加载图片,4.如果data不为空,定义一个GL枚举变量,nrComponents是颜色通道数,5.绑定纹理,6.glTexImage2D,见下,7.调用glGenerateMipmap。这会为当前绑定的纹理自动生成所有需要的多级渐远纹理。8.纹理过滤,9.释放图像的内存)
glTexImage2D:
- 第一个参数指定了纹理目标(Target)。设置为GL_TEXTURE_2D意味着会生成与当前绑定的纹理对象在同一个目标上的纹理(任何绑定到GL_TEXTURE_1D和GL_TEXTURE_3D的纹理不会受到影响)。
- 第二个参数为纹理指定多级渐远纹理的级别,如果你希望单独手动设置每个多级渐远纹理的级别的话。这里我们填0,也就是基本级别。
- 第三个参数告诉OpenGL我们希望把纹理储存为何种格式。我们的图像只有
RGB值,因此我们也把纹理储存为RGB值。 - 第四个和第五个参数设置最终的纹理的宽度和高度。我们之前加载图像的时候储存了它们,所以我们使用对应的变量。
- 下个参数应该总是被设为
0(历史遗留的问题)。 - 第七第八个参数定义了源图的格式和数据类型。我们使用RGB值加载这个图像,并把它们储存为
char(byte)数组,我们将会传入对应值。 - 最后一个参数是真正的图像数据。
最后返回一个ID。
OK,接下来我们加载图片:
unsigned int diffuseMap = loadTexture("container2.png");编译:
![]()
高光贴图
(高光贴图(specularmap)就是要告诉我们哪里需要有高光,哪里没有)
镜面高光的强度可以通过图像每个像素的亮度来获取。镜面光贴图上的每个像素都可以由一个颜色向量来表示,比如说黑色代表颜色向量vec3(0.0),灰色代表颜色向量vec3(0.5)。在片段着色器中,我们接下来会取样对应的颜色值并将它乘以光源的镜面强度。一个像素越「白」,乘积就会越大,物体的镜面光分量就会越亮。
采样高光贴图
我们在渲染之前先把它绑定到合适的纹理单元上:
lightingShader.setInt("material.specular", 1);
...
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, specularMap);更新片段着色器的材质属性,让其接受一个sampler2D而不是vec3作为镜面光分量:
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
sampler2D specular;
float shininess;
};希望采样镜面光贴图,来获取片段所对应的镜面光强度:
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * vec3(texture(material.specular, TexCoords));
FragColor = vec4(ambient + diffuse + specular, 1.0);(同diffusemap贴图加载一样)
unsigned int specularMap = loadTexture("lighting_maps_specular_color.png");
lightingShader.setInt("material.specular", 1);![]()
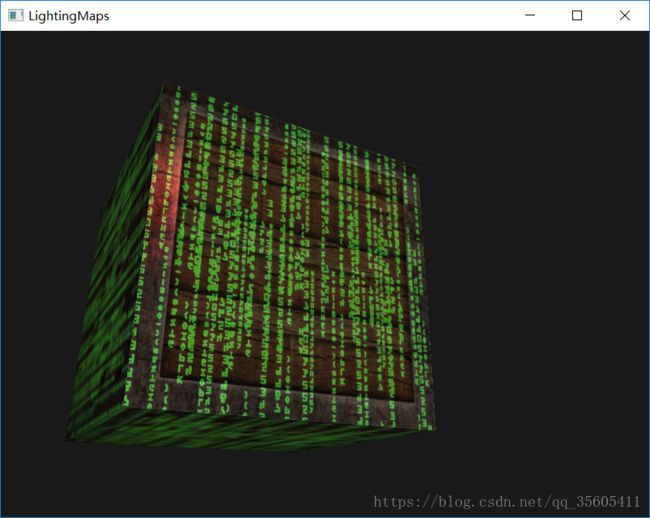
之后做了课后练习,用的是一张彩色的镜面光贴图,并且加了一张自发光贴图(Emission Map)
这是我最终的效果:
源码:
#include
#include
#include
#include "Shader.h"
#include "camera.h"
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "stb_image.h"
#include
#include
#include
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height);
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window);
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow*window, double xpos, double ypos);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
unsigned int loadTexture(const char *path);
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
Camera camera(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f));
float lastX = SCR_WIDTH / 2.0f;
float lastY = SCR_HEIGHT / 2.0f;
bool firstMouse = true;
float deltaTime = 0.0f;
float lastFrame = 0.0f;
float vertices[] = {
// positions // normals // texture coords
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f
};
glm::vec3 lightPos(1.2f, 1.0f, 2.0f);
int main()
{
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LightingMaps", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
Shader lightingShader("shader/2.4_vertexShader.vs", "shader/2.4_fragmentShader.vs");
Shader lampShader("shader/2.4_lightvertexShader.vs", "shader/2.4_lightfragmentShader.vs");
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
//在调用这个函数之后,无论我们怎么去移动鼠标,光标都不会显示了,它也不会离开窗口。
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
unsigned int VBO, cubeVAO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &cubeVAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindVertexArray(cubeVAO);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)(3 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)(6 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
unsigned int lightVAO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &lightVAO);
glBindVertexArray(lightVAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
unsigned int diffuseMap = loadTexture("container2.png");
//unsigned int specularMap = loadTexture("container2_specular.png");
unsigned int specularMap = loadTexture("lighting_maps_specular_color.png");
unsigned int emissionMap = loadTexture("matrix.jpg");
lightingShader.use();
lightingShader.setInt("material.diffuse", 0);
lightingShader.setInt("material.specular", 1);
lightingShader.setInt("material.emission", 2);
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
float currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
processInput(window);
glClearColor(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
lightingShader.use();
lightingShader.setVec3("light.position", lightPos);
lightingShader.setVec3("viewPos", camera.Position);
// light properties
lightingShader.setVec3("light.ambient", 0.2f, 0.2f, 0.2f);
lightingShader.setVec3("light.diffuse", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
lightingShader.setVec3("light.specular", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
// material properties
lightingShader.setVec3("material.specular", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
lightingShader.setFloat("material.shininess", 64.0f);
// view/projection transformations
glm::mat4 projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(camera.Zoom), (float)SCR_WIDTH / (float)SCR_HEIGHT, 0.1f, 100.0f);
glm::mat4 view = camera.GetViewMatrix();
lightingShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
lightingShader.setMat4("view", view);
// world transformation
glm::mat4 model;
lightingShader.setMat4("model", model);
// bind diffuse map
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, diffuseMap);
//bind specular map
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, specularMap);
//bind emission mao
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE2);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, emissionMap);
// render the cube
glBindVertexArray(cubeVAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
// also draw the lamp object
lampShader.use();
lampShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
lampShader.setMat4("view", view);
model = glm::mat4();
lightPos.x = 1.0f + sin(glfwGetTime())*2.0f;
model = glm::translate(model, lightPos);
model = glm::scale(model, glm::vec3(0.2f)); // a smaller cube
lampShader.setMat4("model", model);
glBindVertexArray(lightVAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
glfwPollEvents();
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
}
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &cubeVAO);
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &lightVAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
//回调函数
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
//glViewport函数前两个参数控制窗口左下角的位置。第三个和第四个参数控制渲染窗口的宽度和高度(像素)
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
}
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(FORWARD, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(BACKWARD, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(LEFT, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(RIGHT, deltaTime);
}
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow*window, double xpos, double ypos)
{
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // reversed since y-coordinates go from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
camera.ProcessMouseMovement(xoffset, yoffset);
}
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
camera.ProcessMouseScroll(yoffset);
}
unsigned int loadTexture(char const * path)
{
unsigned int textureID;
glGenTextures(1, &textureID);
int width, height, nrComponents;
unsigned char *data = stbi_load(path, &width, &height, &nrComponents, 0);
if (data)
{
GLenum format;
if (nrComponents == 1)
format = GL_RED;
else if (nrComponents == 3)
format = GL_RGB;
else if (nrComponents == 4)
format = GL_RGBA;
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, format, width, height, 0, format, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
stbi_image_free(data);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Texture failed to load at path: " << path << std::endl;
stbi_image_free(data);
}
return textureID;
}
fragmentshader:
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
sampler2D specular;
sampler2D emission;
//vec3 specular;
float shininess;
};
struct Light {
vec3 position;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
in vec3 FragPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec2 TexCoords;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
uniform Material material;
uniform Light light;
void main()
{
// ambient
//vec3 ambient = light.ambient * texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb;
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
// diffuse
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - FragPos);
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);
//vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords).rgb;
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
// specular
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
//vec3 specular = light.specular * (spec * material.specular);
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * vec3(texture(material.specular, TexCoords));
//emission
vec3 emission = texture(material.emission, TexCoords).rgb;
vec3 result = ambient + diffuse + specular + emission;
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
} 末尾顺便提一下,从这篇开始发现我的shader命名加上了2.4的前缀,原因前面有提到过,,,,惨痛的回忆!