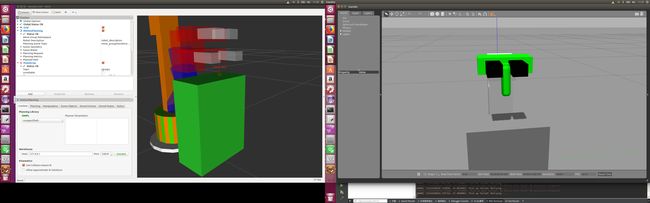
gazebo仿真 机械臂抓取和放置 使用ros_control插件
仿真截图
rqtgraph
ROS Control教程官方
http://gazebosim.org/tutorials/?tut=ros_control
下图概述了仿真、硬件、控制器和传输之间的关系:
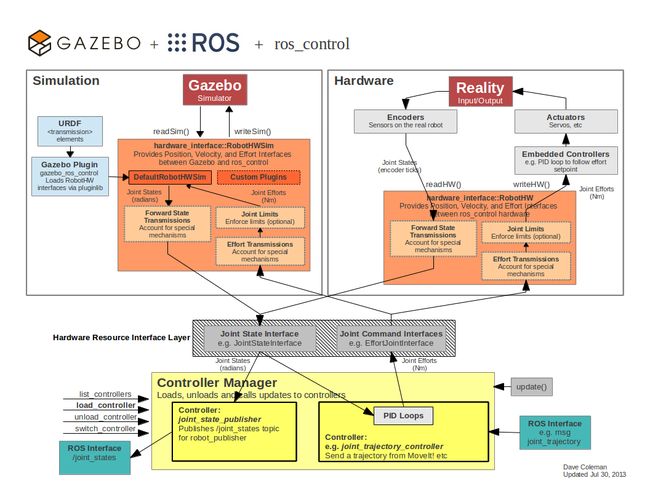
(图片分 gazebo仿真 和真实硬件两部分.两者实现方式是不同的)
Add transmission elements to a URDF
To use ros_control with your robot, you need to add some additional elements to your URDF. The
在URDF文件里添加transmission元素
使用 ros_control 必须要在urdf里添加一些可选元素
Add the gazebo_ros_control plugin
...
The default plugin XML should be added to your URDF:
默认插件xml:
/MYROBOT
The gazebo_ros_control
Default gazebo_ros_control Behavior
By default, without a
The default behavior provides the following ros_control interfaces:
默认情况下提供了下面的控制接口:
hardware_interface::JointStateInterface
hardware_interface::EffortJointInterface
hardware_interface::VelocityJointInterface - not fully implemented
Advanced: custom gazebo_ros_control Simulation Plugins
高级:自定义gazebo_ros_control仿真插件
The gazebo_ros_control Gazebo plugin also provides a pluginlib-based interface to implement custom interfaces between Gazebo and ros_control for simulating more complex mechanisms (nonlinear springs, linkages, etc).
提供基础库接口实现自定义接口
These plugins must inherit gazebo_ros_control::RobotHWSim which implements a simulated ros_control hardware_interface::RobotHW. RobotHWSim provides API-level access to read and command joint properties in the Gazebo simulator.
自定义插件必须继承自gazebo_ros_control::RobotHWSim实现了模拟ros_control hardware_interface::RobotHW...
The respective RobotHWSim sub-class is specified in a URDF model and is loaded when the robot model is loaded. For example, the following XML will load the default plugin (same behavior as when using no
自己的RobotHWSim子类在urdf里定义.模型加载完子类也被加载.
/MYROBOT
gazebo_ros_control/DefaultRobotHWSim
.........
自己的配置gazebo.urdf.xacro
/zzz_arm
rosbook_arm_hardware_gazebo/ROSBookArmHardwareGazebo
0.001
使用默认配置失败信息输出
attaching world object 'coke_can' to link 'grasping_frame'
attached object 'coke_can' to link 'grasping_frame'
Found successful manipution plan!
warn controller handle zzz_arm/fakegazebo_grapper_controller reports status RUNNING
pick up goal failed :Solution found but controller failed during execution.transmission
transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission
${reduction}
hardware_interface/PositionJointInterface
hardware_interface/PositionJointInterface
gazebo 使用的参数配置文件:
joint_trajectory_controllers.yaml
zzz_arm:
fakegazebo_arm_controller:
type: position_controllers/JointTrajectoryController
joints:
- shoulder_zhuan_joint
- upper_arm_joint
- fore_arm_joint
- hand_wan_joint
- hand_zhuan_joint
constraints:
goal_time: &goal_time_constraint 10.0
shoulder_zhuan_joint:
goal: &goal_pos_constraint 0.5
upper_arm_joint:
goal: *goal_pos_constraint
fore_arm_joint:
goal: *goal_pos_constraint
hand_wan_joint:
goal: *goal_pos_constraint
hand_zhuan_joint:
goal: *goal_pos_constraint
gains:
shoulder_zhuan_joint: {p: 1000.0, i: 0.0, d: 0.1, i_clamp: 0.0}
upper_arm_joint: {p: 1000.0, i: 0.0, d: 0.1, i_clamp: 0.0}
fore_arm_joint: {p: 1000.0, i: 0.0, d: 0.1, i_clamp: 0.0}
hand_wan_joint: {p: 1000.0, i: 0.0, d: 0.1, i_clamp: 0.0}
hand_zhuan_joint: {p: 1000.0, i: 0.0, d: 0.1, i_clamp: 0.0}
fakegazebo_grapper_controller:
type: position_controllers/JointTrajectoryController
joints:
- finger_1_joint
- finger_2_joint
constraints:
goal_time: *goal_time_constraint
finger_1_joint:
goal: *goal_pos_constraint
finger_2_joint:
goal: *goal_pos_constraint
gains:
finger_1_joint: {p: 50.0, d: 1.0, i: 0.01, i_clamp: 1.0}
finger_2_joint: {p: 50.0, d: 1.0, i: 0.01, i_clamp: 1.0}
# Publish all joint states -----------------------------------
joint_state_controller:
type: joint_state_controller/JointStateController
publish_rate: 50moveit使用的参数配置文件:
fakegazebo_controllers.yaml
controller_manager_ns: controller_manager
controller_list:
- name: zzz_arm/fakegazebo_arm_controller
action_ns: follow_joint_trajectory
type: FollowJointTrajectory
default: true
joints:
- shoulder_zhuan_joint
- upper_arm_joint
- fore_arm_joint
- hand_wan_joint
- hand_zhuan_joint
- name: zzz_arm/fakegazebo_grapper_controller
action_ns: follow_joint_trajectory
type: FollowJointTrajectory
default: true
joints:
- finger_1_joint
- finger_2_jointrosbook_arm_hardware_gazebo/ROSBookArmHardwareGazebo插件源码
rosbook_arm_hardware_gazebo.cpp
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
namespace rosbook_arm_hardware_gazebo
{
using namespace hardware_interface;
ROSBookArmHardwareGazebo::ROSBookArmHardwareGazebo()
: gazebo_ros_control::RobotHWSim()
{}
bool ROSBookArmHardwareGazebo::initSim(const std::string& robot_namespace,
ros::NodeHandle nh,
gazebo::physics::ModelPtr model,
const urdf::Model* const urdf_model,
std::vector transmissions)
{
using gazebo::physics::JointPtr;
// Cleanup
sim_joints_.clear();
jnt_pos_.clear();
jnt_vel_.clear();
jnt_eff_.clear();
jnt_pos_cmd_.clear();
// Simulation joints
sim_joints_ = model->GetJoints();
n_dof_ = sim_joints_.size();
std::vector jnt_names;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n_dof_; ++i)
{
jnt_names.push_back(sim_joints_[i]->GetName());
}
// Raw data
jnt_pos_.resize(n_dof_);
jnt_vel_.resize(n_dof_);
jnt_eff_.resize(n_dof_);
jnt_pos_cmd_.resize(n_dof_);
// Hardware interfaces
for (size_t i = 0; i < n_dof_; ++i)
{
jnt_state_interface_.registerHandle(
JointStateHandle(jnt_names[i], &jnt_pos_[i], &jnt_vel_[i], &jnt_eff_[i]));
jnt_pos_cmd_interface_.registerHandle(
JointHandle(jnt_state_interface_.getHandle(jnt_names[i]), &jnt_pos_cmd_[i]));
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("Registered joint '" << jnt_names[i] << "' in the PositionJointInterface.");
}
registerInterface(&jnt_state_interface_);
registerInterface(&jnt_pos_cmd_interface_);
// Position joint limits interface
std::vector cmd_handle_names = jnt_pos_cmd_interface_.getNames();
for (size_t i = 0; i < n_dof_; ++i)
{
const std::string name = cmd_handle_names[i];
JointHandle cmd_handle = jnt_pos_cmd_interface_.getHandle(name);
using namespace joint_limits_interface;
boost::shared_ptr urdf_joint = urdf_model->getJoint(name);
JointLimits limits;
SoftJointLimits soft_limits;
if (!getJointLimits(urdf_joint, limits) || !getSoftJointLimits(urdf_joint, soft_limits))
{
ROS_WARN_STREAM("Joint limits won't be enforced for joint '" << name << "'.");
}
else
{
jnt_limits_interface_.registerHandle(
PositionJointSoftLimitsHandle(cmd_handle, limits, soft_limits));
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("Joint limits will be enforced for joint '" << name << "'.");
}
}
// PID controllers
pids_.resize(n_dof_);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n_dof_; ++i)
{
ros::NodeHandle joint_nh(nh, "gains/" + jnt_names[i]);
if (!pids_[i].init(joint_nh))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void ROSBookArmHardwareGazebo::readSim(ros::Time time, ros::Duration period)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < n_dof_; ++i)
{
jnt_pos_[i] += angles::shortest_angular_distance
(jnt_pos_[i], sim_joints_[i]->GetAngle(0u).Radian());
jnt_vel_[i] = sim_joints_[i]->GetVelocity(0u);
jnt_eff_[i] = sim_joints_[i]->GetForce(0u);
}
}
void ROSBookArmHardwareGazebo::writeSim(ros::Time time, ros::Duration period)
{
// Enforce joint limits
jnt_limits_interface_.enforceLimits(period);
// Compute and send commands
for (size_t i = 0; i < n_dof_; ++i)
{
const double error = jnt_pos_cmd_[i] - jnt_pos_[i];
const double effort = pids_[i].computeCommand(error, period);
sim_joints_[i]->SetForce(0u, effort);
}
}
} // namespace rosbook_hardware_gazebo
PLUGINLIB_EXPORT_CLASS(rosbook_arm_hardware_gazebo::ROSBookArmHardwareGazebo, gazebo_ros_control::RobotHWSim) Robot Hardware Interface and Resource Manager.
This class provides a standardized interface to a set of robot hardware interfaces to the controller manager. It performs resource conflict checking for a given set of controllers and maintains a map of hardware interfaces. It is meant to be used as a base class for abstracting custom robot hardware.
机器人硬件接口与资源管理器。
这个类为控制器管理器提供了一组机器人硬件接口的标准化接口。它对给定的控制器集执行资源冲突检查,并维护硬件接口映射。它将被用作抽象自定义机器人硬件的基类。
gazebo仿真抓取时,抓不起来或者很容易滑落的问题.
如图夹住的物体不断下滑甚至掉落.
想必是跟摩擦有关官方 小车轮子对地摩擦的一个例子
http://wiki.ros.org/urdf/Tutorials/Using%20a%20URDF%20in%20GazeboSince the wheels are actually going to touch the ground and thus interact with it physically, we also specify some additional information about the material of the wheels.
当轮子转动,轮子对地就会有一个物理的交互.我们也要指定一些轮子材质的相关信息.
材质信息包含摩擦信息示例如下
Gazebo/Grey
See http://gazebosim.org/tutorials/?tut=ros_urdf for more details.
详细部分:
List of elements that are individually parsed:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| material | value | Material of visual element |
| gravity | bool | Use gravity |
| dampingFactor | double | Exponential velocity decay of the link velocity - takes the value and multiplies the previous link velocity by (1-dampingFactor). |
| maxVel | double | maximum contact correction velocity truncation term. |
| minDepth | double | minimum allowable depth before contact correction impulse is applied |
| mu1 | double | Friction coefficients μ for the principal contact directions along the contact surface as defined by theOpen Dynamics Engine (ODE) (see parameter descriptions inODE's user guide) |
| mu2 | ||
| fdir1 | string | 3-tuple specifying direction of mu1 in the collision local reference frame. |
| kp | double | Contact stiffness k_p and damping k_d for rigid body contacts as defined by ODE (ODE uses erp and cfm but there is amapping between erp/cfm and stiffness/damping) |
| kd | ||
| selfCollide | bool | If true, the link can collide with other links in the model. |
| maxContacts | int | Maximum number of contacts allowed between two entities. This value overrides the max_contacts element defined in physics. |
| laserRetro | double | intensity value returned by laser sensor. |
Similar to , any arbitrary blobs that are not parsed according to the table above are inserted into the the corresponding element in the SDF. This is particularly useful for plugins, as discussed in theROS Motor and Sensor Plugins tutorial.
Friction coefficients μ for the principal contact directions along the contact surface as defined by the Open Dynamics Engine (ODE) http://www.ode.org/ (see parameter descriptions in ODE's user guide) http://www.ode.org/ode-latest-userguide.html#sec_7_3_7
由ODE定义的接触面的主要接触方向上的摩擦系数μ
Contact stiffness k_p and damping k_d for rigid body contacts as defined by ODE (ODE uses erp and cfm but there is a mapping between erp/cfm and stiffness/damping)
由ODE定义的刚体接触的接触强度k_p和阻尼k_d (ODE使用 erp和cfm ,erp/cfm 和 stiffness/damping之间是有映射关系的)
什么是ODE?
Introduction
The Open Dynamics Engine (ODE) is a free, industrial quality library for simulating articulated rigid body dynamics. Proven applications include simulating ground vehicles, legged creatures, and moving objects in VR environments. It is fast, flexible and robust, and has built-in collision detection. ODE is being developed by Russell Smith( http://www.q12.org/) with help from several contributors.(http://ode.org/)
......似乎要跑题
转回来修改设置
urdf 内抓手材质的设置
2000.0
1000.0
10000000.0
1.0
2000.0
1000.0
10000000.0
1.0
仿真环境中物体以及被抓物体的材质设置
grasp.world
model://sun
model://ground_plane
0.001
1
1000
0 0 -9.81
0.175 0.0 0.2165 0 0 0
0.001
0.00016
0
0
0.00016
0
0.00006
model://coke_can/meshes/coke_can.dae
0.095 0.095 0.18
10
100.0
100.0
10000000.0
1.0
0.001
0.1
model://coke_can/meshes/coke_can.dae
0.095 0.095 0.18
0
0
true
0.15 0.0 0.1 0 -0 1.5707963265
1
0.166667
0
0
0.166667
0
0.166667
0.15 0.08 0.2
10
0.6
0.6
0.15 0.08 0.2
0
0
gazebo 仿真尝试抓取圆柱体,立方体,和mesh可乐罐
经测试,在同样的设置下圆柱最容易滑落,立方体次之.可乐罐最不容易掉落.
gazebo与ros_control学习 (1)
http://blog.csdn.net/sunbibei/article/details/53665876
学习机械臂的一些文章
http://www.360doc.com/content/16/0825/16/7821691_585865831.shtml
Gazebo与ros_control(1):让模型动起来
http://blog.csdn.net/yaked/article/details/51412781
Gazebo与ros_control(2):七自由度机械臂和两轮差速运动小车
http://blog.csdn.net/yaked/article/details/51417742
Gazebo与ros_control(3):Moveit输出规划轨迹到Gazebo
http://blog.csdn.net/yaked/article/details/51436262
Gazebo与ros_control(4):举一反三,实战youBot
http://blog.csdn.net/yaked/article/details/51483531