【python】用tqdm模块实现进度条显示
tqdm在阿拉伯语中的意思是“进展”,是一个快速、扩展性强的进度条工具库,用户只需要封装任意的迭代器 tqdm(iterator)。
用法
最主要的用法有3种,自动控制、手动控制或者用于脚本或命令行。
详细资料见GitHub: https://github.com/tqdm/tqdm
自动控制运行
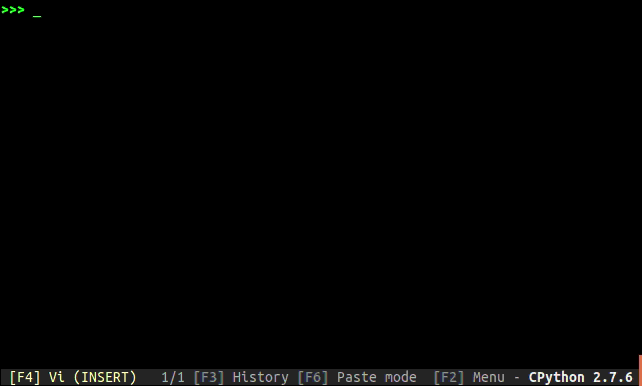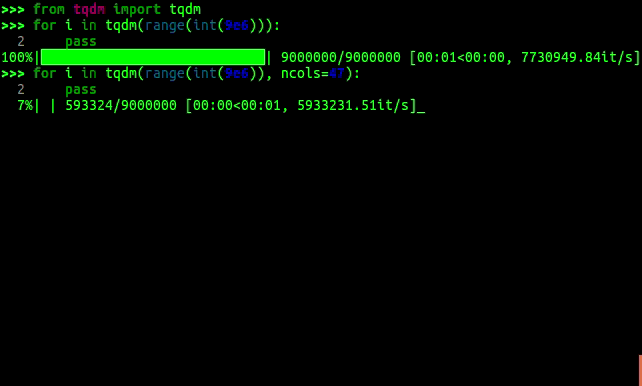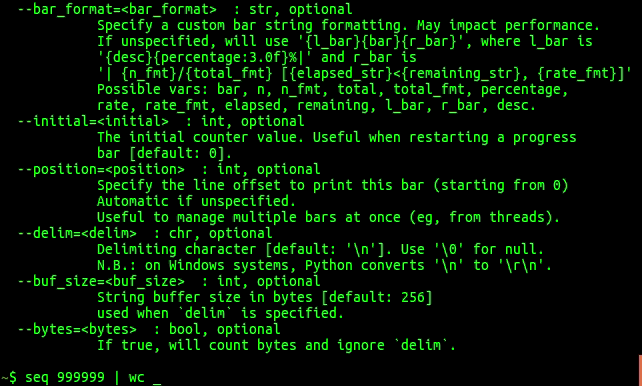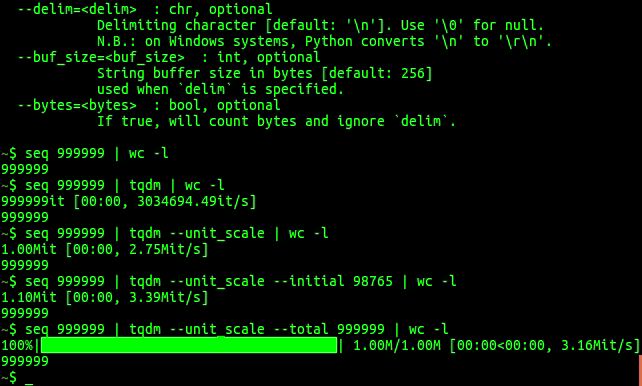
最基本的用法,将tqdm() 直接包装在任意迭代器上。
text = ""
for char in tqdm(["a", "b", "c", "d"]):
text = text + char
time.sleep(0.5)trange(i) 是对tqdm(range(i)) 特殊优化过的实例。
for i in trange(100):
time.sleep(0.1)如果在循环之外实例化,可以允许对tqdm() 手动控制。
pbar = tqdm(["a", "b", "c", "d"])
for char in pbar:
pbar.set_description("Processing %s" % char)手动控制运行
用with 语句手动控制 tqdm() 的更新。
with tqdm(total=100) as pbar:
for i in range(10):
pbar.update(10)或者不用with语句,但是最后需要加上del或者close() 方法。
pbar = tqdm(total=100)
for i in range(10):
pbar.update(10)
pbar.close()tqdm.update()方法用于手动更新进度条,对读取文件之类的流操作非常有用。
E.g.:
>>> t = tqdm(total=filesize) # Initialise
>>> for current_buffer in stream:
... ...
... t.update(len(current_buffer))
>>> t.close()参数解析
这里给出了class tqdm的初始化参数列表。
https://github.com/tqdm/tqdm#documentation
class tqdm(object):
"""
Decorate an iterable object, returning an iterator which acts exactly
like the original iterable, but prints a dynamically updating
progressbar every time a value is requested.
"""
def __init__(self, iterable=None, desc=None, total=None, leave=True,
file=None, ncols=None, mininterval=0.1,
maxinterval=10.0, miniters=None, ascii=None, disable=False,
unit='it', unit_scale=False, dynamic_ncols=False,
smoothing=0.3, bar_format=None, initial=0, position=None,
postfix=None):- desc : str, optional。进度条的前缀
- miniters : int, optional。迭代过程中进度显示的最小更新间隔。
- unit : str, optional。定义每个迭代的单元。默认为
"it",即每个迭代,在下载或解压时,设为"B",代表每个“块”。 - unit_scale : bool or int or float, optional。默认为
False,如果设置为1或者True,会自动根据国际单位制进行转换 (kilo, mega, etc.) 。比如,在下载进度条的例子中,如果为False,数据大小是按照字节显示,设为True之后转换为Kb、Mb。 - total:总的迭代次数,不设置则只显示统计信息,没有图形化的进度条。设置为
len(iterable),会显示黑色方块的图形化进度条。
【例子】实时显示下载进度
这里要用到urllib.request模块中的urlretrieve()方法。
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename=None, reporthook=None, data=None)filename以此文件名保存在当前文件夹中,如果未提供此参数,则生成临时文件。
如果存在reporthook,即钩子函数 / 回调函数。钩子函数将在建立网络连接时调用一次,之后每次读取块后调用一次。
该钩子将传递三个参数,到目前为止传输的块的数量,以字节为单位的块大小以及文件的总大小。
这里有一篇讲钩子函数的文章,python学习之路–hook(钩子原理和使用)。
源码在此,tqdm_wget.py,也可以按照下面的方法实现。
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
from tqdm import tqdm
class TqdmUpTo(tqdm):
# Provides `update_to(n)` which uses `tqdm.update(delta_n)`.
last_block = 0
def update_to(self, block_num=1, block_size=1, total_size=None):
'''
block_num : int, optional
到目前为止传输的块 [default: 1].
block_size : int, optional
每个块的大小 (in tqdm units) [default: 1].
total_size : int, optional
文件总大小 (in tqdm units). 如果[default: None]保持不变.
'''
if total_size is not None:
self.total = total_size
self.update((block_num - self.last_block) * block_size)
self.last_block = block_num
eg_link = "https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-python.tar.gz"
file = eg_link.split('/')[-1]
with TqdmUpTo(unit='B', unit_scale=True, unit_divisor=1024, miniters=1,
desc=file) as t: # 继承至tqdm父类的初始化参数
urlretrieve(eg_link, filename=file, reporthook=t.update_to, data=None)【例子】实时显示解压进度
针对zip文件的解压缩使用zipfile.ZipFile()方法,但是ZipFile()方法不支持回调函数,只能考虑逐文件解压,将tqdm()包装到迭代器上。
可以用ZipFile.namelist()返回整个压缩文件的名字列表,然后逐个解压。
...
if not isdir('dir_path'):
with ZipFile('imgs.zip', 'r') as zipf:
for name in tqdm(zipf.namelist()[:1000],desc='Extract files', unit='files'):
zipf.extract(name, path='dir_path')
zipf.close()
...逐文件解压会增加解压时间:
同样解压10000张图片,zipf.extractall()方法耗时 8.81s;上述方法耗时 9.86s,多花时间 12%。
其他实现方法可以参考 Monitor ZIP File Extraction Python。
关于解压缩速度对比,可以参考这篇文章,Fastest way to unzip a zip file in Python。