咱们来看看爬虫三大库---BeautifulSoup库(精简版)
文章目录
- 前言:
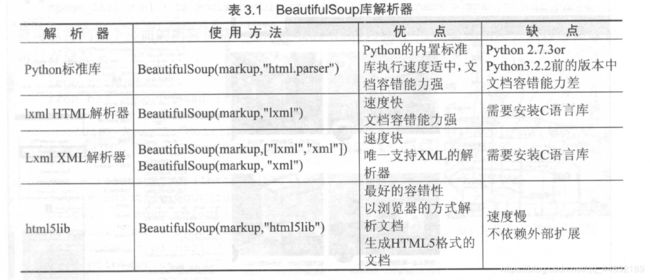
- BeautifulSoup库除了支持Python标准库中的HTML解析器外,还支持一一些第三方的解析器。如下表中列出了BeautifulSoup 库的主要解析器及相应的优缺点。
- 爬取小猪短租房信息代码实现:
前言:
BeautifulSoup库是一个非常流行的Python模块。通过BeautifulSoup库可以轻松地解析Requests库请求的网页,并把网页源代码解析为Soup文档,以便过滤提取数据。
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import time
res = requests.get ('http://bj.xiaozhu.com/')
print (res.text)
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/83.0.4103.97 Safari/537.36'
}
res = requests.get ('http://bj.xiaozhu.com/',headers=headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(res. text, 'html.parser' )
print (soup .prettify()) #BeautifulSoup库解析得到的Soup文档按照标准缩进格式的结构输出,为结构化的数据,为数据的过滤提取做好准备。
BeautifulSoup库除了支持Python标准库中的HTML解析器外,还支持一一些第三方的解析器。如下表中列出了BeautifulSoup 库的主要解析器及相应的优缺点。
注意: BeautifulSoup 库官方推荐使用lxml 作为解析器,因为效率更高。解析得到的Soup文档可以使用==find()和find_all()方法及selector()==方法定位需要的元素了。find()和find_ all)0两 个方法用法相似,BeautifulSoup 文档中对这两个方法的定义是这样的:
find_ all (tag, attibutes, recursive, text, limit, keywords)
find(tag,attibutes, recursive, text, keywords)
通过一个例子来了解一下:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import time
res = requests.get ('http://bj.xiaozhu.com/')
print (res.text)
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/83.0.4103.97 Safari/537.36'
}
res = requests.get ('http://bj.xiaozhu.com/',headers=headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(res. text, 'html.parser' )
print (soup .prettify())
prices = soup.select('#page_list > ul > li > div.result_btm_con.lodgeunitname > div:nth-child(1) > span > i')
for price in prices:
print(price)
爬取小猪短租房信息代码实现:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
import time
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/83.0.4103.97 Safari/537.36'
}
def judgment_sex(class_name):
if class_name == ['member_ico1']:
return '女'
else:
return '男'
def get_links(url): #定义获取详细页url的函数
wb_data = requests.get(url,headers=headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(wb_data.text,'lxml')
links = soup.select('#page_list > ul > li > a')
for link in links:
href = link.get("href")
get_info(href)
def get_info(url): #获取定义网页信息的函数
wb_data = requests.get(url,headers=headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(wb_data.text,'lxml')
tittles = soup.select('div.pho_info > h4')
addresses = soup.select('span.pr5')
prices = soup.select('#pricePart > div.day_l > span')
imgs = soup.select('#floatRightBox > div.js_box.clearfix > div.member_pic > a > img')
names = soup.select('#floatRightBox > div.js_box.clearfix > div.w_240 > h6 > a')
sexs = soup.select('#floatRightBox > div.js_box.clearfix > div.member_pic > div')
for tittle, address, price, img, name, sex in zip(tittles,addresses,prices,imgs,names,sexs):
data = {
'tittle':tittle.get_text().strip(),
'address':address.get_text().strip(),
'price':price.get_text(),
'img':img.get("src"),
'name':name.get_text(),
'sex':judgment_sex(sex.get("class"))
}
print(data) #获取信息并通过字典的信息打印
if __name__ == '__main__':
urls = ['http://bj.xiaozhu.com/search-duanzufang-p{}-0/'.format(number) for number in range(1,14)]
for single_url in urls:
get_links(single_url)
time.sleep(2)
代码分析:
(1)第1~3行导入程序需要的库,Requests 库用于请求网页获取网页数据。BeautifulSoup用于解析网页数据。time 库的sleep0方法可以让程序暂停。
(2)第5~8行通过Chrome浏览器的开发者工具,复制User-Agent,用于伪装为浏览器,便于爬虫的稳定性。
(3)第16~22行定义了get_ links()函数, 用于获取进入详细页的链接。传入URL后,进行请求和解析。通过Chrome浏览器的“检查”并“Copy selector”,可以找到进入详细页的URL链接,但URL链接并不是嵌套在标签中,而是在标签的属性信息中,如图所示。

前面说到可用get.text()方法获取标签中的文本信息,但标签中的属性信息需要通过get’attr()方法获取得到,如上图所示,URL 链接在href中,这时用get( href )便可得到网页的URL。最后调用getinfo()函数,转入的参数为获取到的网页详细页的链接。
(4)第24~42行定义get_info()函数,用于获取网页信息并输出信息。传入URL后,进行请求和解析。通过Chrome浏览器的“检查”并“Copy selector”获取相应的信息,由于信息数据为列表数据结构,可以通过多重循环,构造出字典数据结构,输出并打印出来。
(5)第10~14行定义judgment_ sex()函数, 用于判断房东的性别。通过Chrome 浏览器的“检查”可以发现,女房东的信息为
(6)第44~49行为程序的主入口,通过对网页URL的观察,利用列表的推导式构造13个URL,并依次调用**get_ links()函 数,time.sleep(2)的意思是每循环一次, 让程序暂停2秒,**防止请求网页频率过快而导致爬虫失败。
后续会有更多的爬虫案例与大家分享。感谢支持!!