Java多线程系列--“JUC集合”06之 ConcurrentSkipListSet
概要
本章对Java.util.concurrent包中的ConcurrentSkipListSet类进行详细的介绍。内容包括:
ConcurrentSkipListSet介绍
ConcurrentSkipListSet原理和数据结构
ConcurrentSkipListSet函数列表
ConcurrentSkipListSet源码(JDK1.7.0_40版本)
ConcurrentSkipListSet示例
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3498634.html
ConcurrentSkipListSet介绍
ConcurrentSkipListSet是线程安全的有序的集合,适用于高并发的场景。
ConcurrentSkipListSet和TreeSet,它们虽然都是有序的集合。但是,第一,它们的线程安全机制不同,TreeSet是非线程安全的,而ConcurrentSkipListSet是线程安全的。第二,ConcurrentSkipListSet是通过ConcurrentSkipListMap实现的,而TreeSet是通过TreeMap实现的。
ConcurrentSkipListSet原理和数据结构
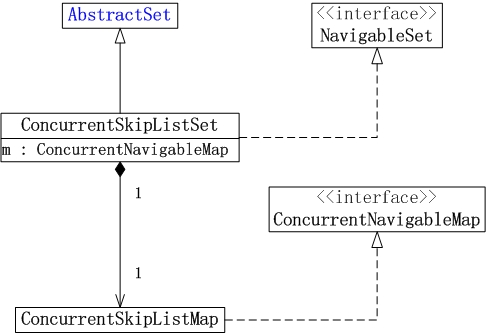
ConcurrentSkipListSet的数据结构,如下图所示:
说明:
(01) ConcurrentSkipListSet继承于AbstractSet。因此,它本质上是一个集合。
(02) ConcurrentSkipListSet实现了NavigableSet接口。因此,ConcurrentSkipListSet是一个有序的集合。
(03) ConcurrentSkipListSet是通过ConcurrentSkipListMap实现的。它包含一个ConcurrentNavigableMap对象m,而m对象实际上是ConcurrentNavigableMap的实现类ConcurrentSkipListMap的实例。ConcurrentSkipListMap中的元素是key-value键值对;而ConcurrentSkipListSet是集合,它只用到了ConcurrentSkipListMap中的key!
ConcurrentSkipListSet函数列表
// 构造一个新的空 set,该 set 按照元素的自然顺序对其进行排序。 ConcurrentSkipListSet() // 构造一个包含指定 collection 中元素的新 set,这个新 set 按照元素的自然顺序对其进行排序。 ConcurrentSkipListSet(Collection<? extends E> c) // 构造一个新的空 set,该 set 按照指定的比较器对其元素进行排序。 ConcurrentSkipListSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) // 构造一个新 set,该 set 所包含的元素与指定的有序 set 包含的元素相同,使用的顺序也相同。 ConcurrentSkipListSet(SortedSet<E> s) // 如果此 set 中不包含指定元素,则添加指定元素。 boolean add(E e) // 返回此 set 中大于等于给定元素的最小元素;如果不存在这样的元素,则返回 null。 E ceiling(E e) // 从此 set 中移除所有元素。 void clear() // 返回此 ConcurrentSkipListSet 实例的浅表副本。 ConcurrentSkipListSet<E> clone() // 返回对此 set 中的元素进行排序的比较器;如果此 set 使用其元素的自然顺序,则返回 null。 Comparator<? super E> comparator() // 如果此 set 包含指定的元素,则返回 true。 boolean contains(Object o) // 返回在此 set 的元素上以降序进行迭代的迭代器。 Iterator<E> descendingIterator() // 返回此 set 中所包含元素的逆序视图。 NavigableSet<E> descendingSet() // 比较指定对象与此 set 的相等性。 boolean equals(Object o) // 返回此 set 中当前第一个(最低)元素。 E first() // 返回此 set 中小于等于给定元素的最大元素;如果不存在这样的元素,则返回 null。 E floor(E e) // 返回此 set 的部分视图,其元素严格小于 toElement。 NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement) // 返回此 set 的部分视图,其元素小于(或等于,如果 inclusive 为 true)toElement。 NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) // 返回此 set 中严格大于给定元素的最小元素;如果不存在这样的元素,则返回 null。 E higher(E e) // 如果此 set 不包含任何元素,则返回 true。 boolean isEmpty() // 返回在此 set 的元素上以升序进行迭代的迭代器。 Iterator<E> iterator() // 返回此 set 中当前最后一个(最高)元素。 E last() // 返回此 set 中严格小于给定元素的最大元素;如果不存在这样的元素,则返回 null。 E lower(E e) // 获取并移除第一个(最低)元素;如果此 set 为空,则返回 null。 E pollFirst() // 获取并移除最后一个(最高)元素;如果此 set 为空,则返回 null。 E pollLast() // 如果此 set 中存在指定的元素,则将其移除。 boolean remove(Object o) // 从此 set 中移除包含在指定 collection 中的所有元素。 boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) // 返回此 set 中的元素数目。 int size() // 返回此 set 的部分视图,其元素范围从 fromElement 到 toElement。 NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive, E toElement, boolean toInclusive) // 返回此 set 的部分视图,其元素从 fromElement(包括)到 toElement(不包括)。 NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) // 返回此 set 的部分视图,其元素大于等于 fromElement。 NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement) // 返回此 set 的部分视图,其元素大于(或等于,如果 inclusive 为 true)fromElement。 NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive)
ConcurrentSkipListSet源码(JDK1.7.0_40版本)
ConcurrentSkipListSet.java的完整源码如下:

1 /* 2 * ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms. 3 * 4 * 5 * 6 * 7 * 8 * 9 * 10 * 11 * 12 * 13 * 14 * 15 * 16 * 17 * 18 * 19 * 20 * 21 * 22 * 23 */ 24 25 /* 26 * 27 * 28 * 29 * 30 * 31 * Written by Doug Lea with assistance from members of JCP JSR-166 32 * Expert Group and released to the public domain, as explained at 33 * http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ 34 */ 35 36 package java.util.concurrent; 37 import java.util.*; 38 import sun.misc.Unsafe; 39 40 /** 41 * A scalable concurrent {@link NavigableSet} implementation based on 42 * a {@link ConcurrentSkipListMap}. The elements of the set are kept 43 * sorted according to their {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering}, 44 * or by a {@link Comparator} provided at set creation time, depending 45 * on which constructor is used. 46 * 47 * <p>This implementation provides expected average <i>log(n)</i> time 48 * cost for the <tt>contains</tt>, <tt>add</tt>, and <tt>remove</tt> 49 * operations and their variants. Insertion, removal, and access 50 * operations safely execute concurrently by multiple threads. 51 * Iterators are <i>weakly consistent</i>, returning elements 52 * reflecting the state of the set at some point at or since the 53 * creation of the iterator. They do <em>not</em> throw {@link 54 * ConcurrentModificationException}, and may proceed concurrently with 55 * other operations. Ascending ordered views and their iterators are 56 * faster than descending ones. 57 * 58 * <p>Beware that, unlike in most collections, the <tt>size</tt> 59 * method is <em>not</em> a constant-time operation. Because of the 60 * asynchronous nature of these sets, determining the current number 61 * of elements requires a traversal of the elements, and so may report 62 * inaccurate results if this collection is modified during traversal. 63 * Additionally, the bulk operations <tt>addAll</tt>, 64 * <tt>removeAll</tt>, <tt>retainAll</tt>, <tt>containsAll</tt>, 65 * <tt>equals</tt>, and <tt>toArray</tt> are <em>not</em> guaranteed 66 * to be performed atomically. For example, an iterator operating 67 * concurrently with an <tt>addAll</tt> operation might view only some 68 * of the added elements. 69 * 70 * <p>This class and its iterators implement all of the 71 * <em>optional</em> methods of the {@link Set} and {@link Iterator} 72 * interfaces. Like most other concurrent collection implementations, 73 * this class does not permit the use of <tt>null</tt> elements, 74 * because <tt>null</tt> arguments and return values cannot be reliably 75 * distinguished from the absence of elements. 76 * 77 * <p>This class is a member of the 78 * <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html"> 79 * Java Collections Framework</a>. 80 * 81 * @author Doug Lea 82 * @param <E> the type of elements maintained by this set 83 * @since 1.6 84 */ 85 public class ConcurrentSkipListSet<E> 86 extends AbstractSet<E> 87 implements NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { 88 89 private static final long serialVersionUID = -2479143111061671589L; 90 91 /** 92 * The underlying map. Uses Boolean.TRUE as value for each 93 * element. This field is declared final for the sake of thread 94 * safety, which entails some ugliness in clone() 95 */ 96 private final ConcurrentNavigableMap<E,Object> m; 97 98 /** 99 * Constructs a new, empty set that orders its elements according to 100 * their {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering}. 101 */ 102 public ConcurrentSkipListSet() { 103 m = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<E,Object>(); 104 } 105 106 /** 107 * Constructs a new, empty set that orders its elements according to 108 * the specified comparator. 109 * 110 * @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this set. 111 * If <tt>null</tt>, the {@linkplain Comparable natural 112 * ordering} of the elements will be used. 113 */ 114 public ConcurrentSkipListSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) { 115 m = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<E,Object>(comparator); 116 } 117 118 /** 119 * Constructs a new set containing the elements in the specified 120 * collection, that orders its elements according to their 121 * {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering}. 122 * 123 * @param c The elements that will comprise the new set 124 * @throws ClassCastException if the elements in <tt>c</tt> are 125 * not {@link Comparable}, or are not mutually comparable 126 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection or any 127 * of its elements are null 128 */ 129 public ConcurrentSkipListSet(Collection<? extends E> c) { 130 m = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<E,Object>(); 131 addAll(c); 132 } 133 134 /** 135 * Constructs a new set containing the same elements and using the 136 * same ordering as the specified sorted set. 137 * 138 * @param s sorted set whose elements will comprise the new set 139 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified sorted set or any 140 * of its elements are null 141 */ 142 public ConcurrentSkipListSet(SortedSet<E> s) { 143 m = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<E,Object>(s.comparator()); 144 addAll(s); 145 } 146 147 /** 148 * For use by submaps 149 */ 150 ConcurrentSkipListSet(ConcurrentNavigableMap<E,Object> m) { 151 this.m = m; 152 } 153 154 /** 155 * Returns a shallow copy of this <tt>ConcurrentSkipListSet</tt> 156 * instance. (The elements themselves are not cloned.) 157 * 158 * @return a shallow copy of this set 159 */ 160 public ConcurrentSkipListSet<E> clone() { 161 ConcurrentSkipListSet<E> clone = null; 162 try { 163 clone = (ConcurrentSkipListSet<E>) super.clone(); 164 clone.setMap(new ConcurrentSkipListMap(m)); 165 } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { 166 throw new InternalError(); 167 } 168 169 return clone; 170 } 171 172 /* ---------------- Set operations -------------- */ 173 174 /** 175 * Returns the number of elements in this set. If this set 176 * contains more than <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt> elements, it 177 * returns <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt>. 178 * 179 * <p>Beware that, unlike in most collections, this method is 180 * <em>NOT</em> a constant-time operation. Because of the 181 * asynchronous nature of these sets, determining the current 182 * number of elements requires traversing them all to count them. 183 * Additionally, it is possible for the size to change during 184 * execution of this method, in which case the returned result 185 * will be inaccurate. Thus, this method is typically not very 186 * useful in concurrent applications. 187 * 188 * @return the number of elements in this set 189 */ 190 public int size() { 191 return m.size(); 192 } 193 194 /** 195 * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this set contains no elements. 196 * @return <tt>true</tt> if this set contains no elements 197 */ 198 public boolean isEmpty() { 199 return m.isEmpty(); 200 } 201 202 /** 203 * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this set contains the specified element. 204 * More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if this set 205 * contains an element <tt>e</tt> such that <tt>o.equals(e)</tt>. 206 * 207 * @param o object to be checked for containment in this set 208 * @return <tt>true</tt> if this set contains the specified element 209 * @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be 210 * compared with the elements currently in this set 211 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null 212 */ 213 public boolean contains(Object o) { 214 return m.containsKey(o); 215 } 216 217 /** 218 * Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present. 219 * More formally, adds the specified element <tt>e</tt> to this set if 220 * the set contains no element <tt>e2</tt> such that <tt>e.equals(e2)</tt>. 221 * If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set 222 * unchanged and returns <tt>false</tt>. 223 * 224 * @param e element to be added to this set 225 * @return <tt>true</tt> if this set did not already contain the 226 * specified element 227 * @throws ClassCastException if <tt>e</tt> cannot be compared 228 * with the elements currently in this set 229 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null 230 */ 231 public boolean add(E e) { 232 return m.putIfAbsent(e, Boolean.TRUE) == null; 233 } 234 235 /** 236 * Removes the specified element from this set if it is present. 237 * More formally, removes an element <tt>e</tt> such that 238 * <tt>o.equals(e)</tt>, if this set contains such an element. 239 * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this set contained the element (or 240 * equivalently, if this set changed as a result of the call). 241 * (This set will not contain the element once the call returns.) 242 * 243 * @param o object to be removed from this set, if present 244 * @return <tt>true</tt> if this set contained the specified element 245 * @throws ClassCastException if <tt>o</tt> cannot be compared 246 * with the elements currently in this set 247 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null 248 */ 249 public boolean remove(Object o) { 250 return m.remove(o, Boolean.TRUE); 251 } 252 253 /** 254 * Removes all of the elements from this set. 255 */ 256 public void clear() { 257 m.clear(); 258 } 259 260 /** 261 * Returns an iterator over the elements in this set in ascending order. 262 * 263 * @return an iterator over the elements in this set in ascending order 264 */ 265 public Iterator<E> iterator() { 266 return m.navigableKeySet().iterator(); 267 } 268 269 /** 270 * Returns an iterator over the elements in this set in descending order. 271 * 272 * @return an iterator over the elements in this set in descending order 273 */ 274 public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() { 275 return m.descendingKeySet().iterator(); 276 } 277 278 279 /* ---------------- AbstractSet Overrides -------------- */ 280 281 /** 282 * Compares the specified object with this set for equality. Returns 283 * <tt>true</tt> if the specified object is also a set, the two sets 284 * have the same size, and every member of the specified set is 285 * contained in this set (or equivalently, every member of this set is 286 * contained in the specified set). This definition ensures that the 287 * equals method works properly across different implementations of the 288 * set interface. 289 * 290 * @param o the object to be compared for equality with this set 291 * @return <tt>true</tt> if the specified object is equal to this set 292 */ 293 public boolean equals(Object o) { 294 // Override AbstractSet version to avoid calling size() 295 if (o == this) 296 return true; 297 if (!(o instanceof Set)) 298 return false; 299 Collection<?> c = (Collection<?>) o; 300 try { 301 return containsAll(c) && c.containsAll(this); 302 } catch (ClassCastException unused) { 303 return false; 304 } catch (NullPointerException unused) { 305 return false; 306 } 307 } 308 309 /** 310 * Removes from this set all of its elements that are contained in 311 * the specified collection. If the specified collection is also 312 * a set, this operation effectively modifies this set so that its 313 * value is the <i>asymmetric set difference</i> of the two sets. 314 * 315 * @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this set 316 * @return <tt>true</tt> if this set changed as a result of the call 317 * @throws ClassCastException if the types of one or more elements in this 318 * set are incompatible with the specified collection 319 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection or any 320 * of its elements are null 321 */ 322 public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { 323 // Override AbstractSet version to avoid unnecessary call to size() 324 boolean modified = false; 325 for (Iterator<?> i = c.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) 326 if (remove(i.next())) 327 modified = true; 328 return modified; 329 } 330 331 /* ---------------- Relational operations -------------- */ 332 333 /** 334 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 335 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null 336 */ 337 public E lower(E e) { 338 return m.lowerKey(e); 339 } 340 341 /** 342 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 343 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null 344 */ 345 public E floor(E e) { 346 return m.floorKey(e); 347 } 348 349 /** 350 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 351 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null 352 */ 353 public E ceiling(E e) { 354 return m.ceilingKey(e); 355 } 356 357 /** 358 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 359 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null 360 */ 361 public E higher(E e) { 362 return m.higherKey(e); 363 } 364 365 public E pollFirst() { 366 Map.Entry<E,Object> e = m.pollFirstEntry(); 367 return (e == null) ? null : e.getKey(); 368 } 369 370 public E pollLast() { 371 Map.Entry<E,Object> e = m.pollLastEntry(); 372 return (e == null) ? null : e.getKey(); 373 } 374 375 376 /* ---------------- SortedSet operations -------------- */ 377 378 379 public Comparator<? super E> comparator() { 380 return m.comparator(); 381 } 382 383 /** 384 * @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc} 385 */ 386 public E first() { 387 return m.firstKey(); 388 } 389 390 /** 391 * @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc} 392 */ 393 public E last() { 394 return m.lastKey(); 395 } 396 397 /** 398 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 399 * @throws NullPointerException if {@code fromElement} or 400 * {@code toElement} is null 401 * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} 402 */ 403 public NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, 404 boolean fromInclusive, 405 E toElement, 406 boolean toInclusive) { 407 return new ConcurrentSkipListSet<E> 408 (m.subMap(fromElement, fromInclusive, 409 toElement, toInclusive)); 410 } 411 412 /** 413 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 414 * @throws NullPointerException if {@code toElement} is null 415 * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} 416 */ 417 public NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) { 418 return new ConcurrentSkipListSet<E>(m.headMap(toElement, inclusive)); 419 } 420 421 /** 422 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 423 * @throws NullPointerException if {@code fromElement} is null 424 * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} 425 */ 426 public NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) { 427 return new ConcurrentSkipListSet<E>(m.tailMap(fromElement, inclusive)); 428 } 429 430 /** 431 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 432 * @throws NullPointerException if {@code fromElement} or 433 * {@code toElement} is null 434 * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} 435 */ 436 public NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) { 437 return subSet(fromElement, true, toElement, false); 438 } 439 440 /** 441 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 442 * @throws NullPointerException if {@code toElement} is null 443 * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} 444 */ 445 public NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement) { 446 return headSet(toElement, false); 447 } 448 449 /** 450 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 451 * @throws NullPointerException if {@code fromElement} is null 452 * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} 453 */ 454 public NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement) { 455 return tailSet(fromElement, true); 456 } 457 458 /** 459 * Returns a reverse order view of the elements contained in this set. 460 * The descending set is backed by this set, so changes to the set are 461 * reflected in the descending set, and vice-versa. 462 * 463 * <p>The returned set has an ordering equivalent to 464 * <tt>{@link Collections#reverseOrder(Comparator) Collections.reverseOrder}(comparator())</tt>. 465 * The expression {@code s.descendingSet().descendingSet()} returns a 466 * view of {@code s} essentially equivalent to {@code s}. 467 * 468 * @return a reverse order view of this set 469 */ 470 public NavigableSet<E> descendingSet() { 471 return new ConcurrentSkipListSet(m.descendingMap()); 472 } 473 474 // Support for resetting map in clone 475 private void setMap(ConcurrentNavigableMap<E,Object> map) { 476 UNSAFE.putObjectVolatile(this, mapOffset, map); 477 } 478 479 private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE; 480 private static final long mapOffset; 481 static { 482 try { 483 UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe(); 484 Class k = ConcurrentSkipListSet.class; 485 mapOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset 486 (k.getDeclaredField("m")); 487 } catch (Exception e) { 488 throw new Error(e); 489 } 490 } 491 }
ConcurrentSkipListSet是通过ConcurrentSkipListMap实现的,它的接口基本上都是通过调用ConcurrentSkipListMap接口来实现的。这里就不再对它的源码进行分析了。
ConcurrentSkipListSet示例
1 import java.util.*; 2 import java.util.concurrent.*; 3 4 /* 5 * ConcurrentSkipListSet是“线程安全”的集合,而TreeSet是非线程安全的。 6 * 7 * 下面是“多个线程同时操作并且遍历集合set”的示例 8 * (01) 当set是ConcurrentSkipListSet对象时,程序能正常运行。 9 * (02) 当set是TreeSet对象时,程序会产生ConcurrentModificationException异常。 10 * 11 * @author skywang 12 */ 13 public class ConcurrentSkipListSetDemo1 { 14 15 // TODO: set是TreeSet对象时,程序会出错。 16 //private static Set<String> set = new TreeSet<String>(); 17 private static Set<String> set = new ConcurrentSkipListSet<String>(); 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 20 // 同时启动两个线程对set进行操作! 21 new MyThread("a").start(); 22 new MyThread("b").start(); 23 } 24 25 private static void printAll() { 26 String value = null; 27 Iterator iter = set.iterator(); 28 while(iter.hasNext()) { 29 value = (String)iter.next(); 30 System.out.print(value+", "); 31 } 32 System.out.println(); 33 } 34 35 private static class MyThread extends Thread { 36 MyThread(String name) { 37 super(name); 38 } 39 @Override 40 public void run() { 41 int i = 0; 42 while (i++ < 10) { 43 // “线程名” + "序号" 44 String val = Thread.currentThread().getName() + (i%6); 45 set.add(val); 46 // 通过“Iterator”遍历set。 47 printAll(); 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 }
(某一次)运行结果:
a1, b1,
a1, a1, a2, b1,
b1, a1, a2, a3, b1,
a1, a2, a3, a1, a4, b1, b2,
a2, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, b1, b2,
a3, a0, a4, a5, a1, b1, a2, b2,
a3, a0, a4, a1, a5, a2, b1, a3, b2, a4, b3,
a5, a0, b1, a1, b2, a2, b3,
a3, a0, a4, a1, a5, a2, b1, a3, b2, a4, b3, a5, b4,
b1, a0, b2, a1, b3, a2, b4,
a3, a0, a4, a1, a5, a2, b1, a3, b2, a4, b3, a5, b4, b1, b5,
b2, a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, b3, b1, b4, b2, b5,
b3, a0, b4, a1, b5,
a2, a0, a3, a1, a4, a2, a5, a3, b0, a4, b1, a5, b2, b0, b3, b1, b4, b2, b5, b3,
b4, a0, b5,
a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, b0, b1, b2, b3, b4, b5,
a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, b0, b1, b2, b3, b4, b5,
a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, b0, b1, b2, b3, b4, b5,
a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, b0, b1, b2, b3, b4, b5,
结果说明:
示例程序中,启动两个线程(线程a和线程b)分别对ConcurrentSkipListSet进行操作。以线程a而言,它会先获取“线程名”+“序号”,然后将该字符串添加到ConcurrentSkipListSet集合中;接着,遍历并输出集合中的全部元素。 线程b的操作和线程a一样,只不过线程b的名字和线程a的名字不同。
当set是ConcurrentSkipListSet对象时,程序能正常运行。如果将set改为TreeSet时,程序会产生ConcurrentModificationException异常。
更多内容