二叉平衡树(AVL树)插入、删除的C语言实现
对于AVL树的定义,在教科书和网上的资料都已经十分详细,在这里直接上代码,不做过多赘述。
一、AVL树的结构体
typedef struct AVLTREE {
int data;
int height;
struct AVLTREE* leftChlid;
struct AVLTREE* rightChild;
}AVLTREE;再贴出两个工具函数的代码:
max():返回两个数的最大值
geiHeight():取得节点的高度
int max(int data1, int data2) {
return ((data1 > data2) ? data1 : data2);
}
int getHeight(AVLTREE* root) {
if(root == NULL)
return -1;
else
return root->height;
}其中data为节点的值,而height为节点的高度,而AVL实现起来的难点就在于旋转和对高度这个参数的把控,先来看看AVL旋转的四种情况
二、AVL树的旋转
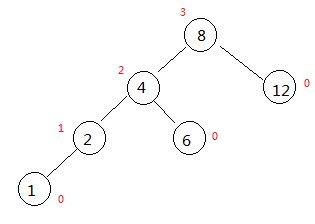
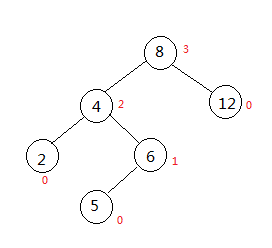
1.LL型
此时二叉平衡树是不平衡的,我们假设叶子节点的高度都为0
那么高度为0的节点有1、6、12,高度为1的节点有2,高度为2的节点有4,高度为3的节点有8
此时,根节点的左孩子高度为2,而右孩子的高度为0,此时树是不平衡的,需要对其进行旋转,贴出LL型的旋转代码:
AVLTREE* left_Left_Rotation(AVLTREE* root) {
AVLTREE* newRoot = NULL;
newRoot = root->leftChlid;
root->leftChlid = newRoot->rightChild;
newRoot->rightChild = root;
root->height = max(getHeight(root->leftChlid),getHeight(root->rightChild)) + 1;
newRoot->height = max(getHeight(newRoot->leftChlid), root->height) + 1;
return newRoot;
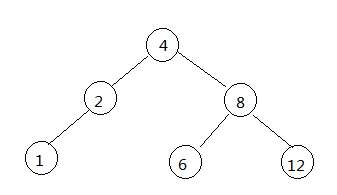
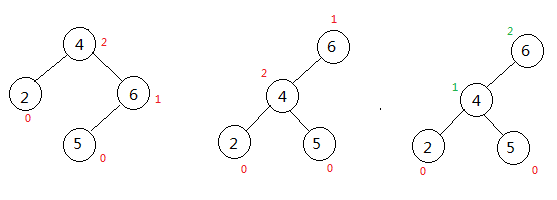
}此时,将根节点8传入,即可完成旋转,下面再给出旋转后的树
对于指针熟悉的朋友来说,旋转时指针的改变是非常容易理解的,而在旋转后重新形成了平衡二叉树,这时每个节点的高度也发生了变化,这时一个令人疑惑的地方,来变量跟踪研究一下:
在代码完成旋转后,会开始执行这两行代码:
root->height = max(getHeight(root->leftChlid),getHeight(root->rightChild)) + 1;
newRoot->height = max(getHeight(newRoot->leftChlid), root->height) + 1;在执行之前,root为节点8,它的高度是3,在执行第一行代码时,取得它左右孩子节点6和节点12的高度,它们高度都为0,那么会将root的高度更新为1。而newRoot为节点4,此时它的高度为2,它的左右孩子分别是节点2和节点8,节点高度都为1,那么此时newRoot节点的高度为2。通过下面的图,查看节点的更新
旋转后,高度为0的节点有1、6、12,高度为1的节点有2、8,而高度为2的节点只有4,不存在不平衡的情况了。
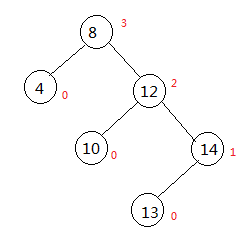
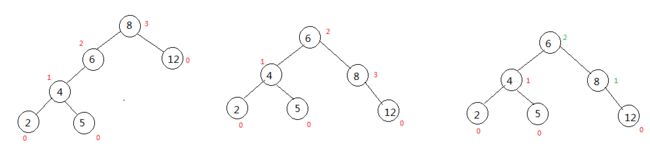
2.RR型
参考图上红点,红点为节点的高度。如果你已经看懂了上面LL型的例子,那么理所当然的能明白,此时节点8的左右孩子高度差变为了2,二叉树需要旋转,给出旋转的代码:
AVLTREE* right_Right_Rotation(AVLTREE* root) {
AVLTREE* newRoot = NULL;
newRoot = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = newRoot->leftChlid;
newRoot->leftChlid = root;
root->height = max(getHeight(root->leftChlid),getHeight(root->rightChild)) + 1;
newRoot->height = max(getHeight(newRoot->rightChild), root->height) + 1;
return newRoot;
}进行旋转过后的树和修正后的高度为如下图:
3.LR型
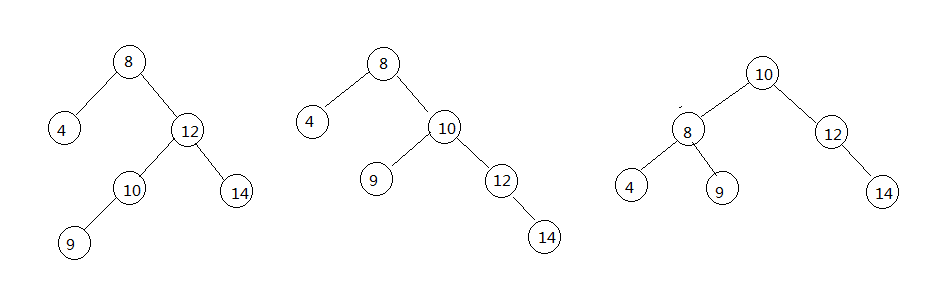
LR型是一种特殊情况,前面两次LL和RR都是单旋转,而LR型和RL型是双旋转,通过下面的图来看看这种情况:
这个时候不能进行单旋转,需要先对根节点的左子树进行一次RR单旋转,然后再对整体进行一次LL单旋转,先给出代码:
AVLTREE* left_Right_Rotation(AVLTREE* root) {
root->leftChlid = right_Right_Rotation(root->leftChlid);
return left_Left_Rotation(root);
}可以看出,双旋转是对单旋转的调用,再读懂上面代码的基础上,理解双旋转也不是什么难事。首先对根节点的左子树进行旋转:
根节点的左子树旋转后:
这个时候树还是不平衡的,但是我们这个时候可以将整个树进行一次LL单旋转,旋转并且修正过后如下图:
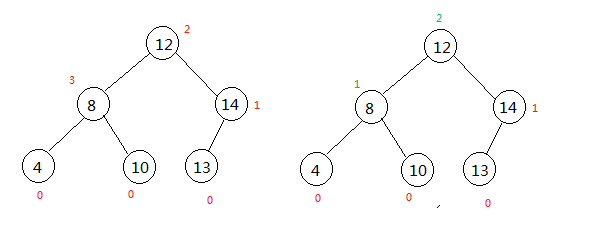
4.RL型
如果看懂了LR型,那么RL型的也就非常容易了,先贴出代码:
AVLTREE* right_Left_Rotation(AVLTREE* root) {
root->rightChild = left_Left_Rotation(root->rightChild);
return right_Right_Rotation(root);
}下图即为旋转后的图:
三、AVL树的插入
如果节点为空,那么创建一个节点下面也分别给出了当要插入的节点大于或小于或等于当前节点的情况
当一个节点的左右孩子高度差为2时,说明树需要旋转
至于是单旋转还是双旋转,得看插入的位置是左子树还是右子树
然后根据相应结构,选择单旋转或者双旋转
建议手动过一遍这里的代码,在插入过程需要旋转时,不妨画出树的结构然后就很容易的看出端倪了
AVLTREE* insertPoint(int data, AVLTREE* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
root = (AVLTREE *)malloc(sizeof(AVLTREE));
root->data = data;
root->height = 0;
root->leftChlid = root->rightChild = NULL;
} else if(data < root->data) {
root->leftChlid = insertPoint(data, root->leftChlid);
if(getHeight(root->leftChlid) - getHeight(root->rightChild) == 2) {
if(data < root->leftChlid->data)
root = left_Left_Rotation(root);
else
root = left_Right_Rotation(root);
}
} else if(data > root->data) {
root->rightChild = insertPoint(data, root->rightChild);
if(getHeight(root->rightChild) - getHeight(root->leftChlid) == 2) {
if(data > root->rightChild->data)
root = right_Right_Rotation(root);
else
root = right_Left_Rotation(root);
}
} else if(data == root->data) {
return NULL;
}
root->height = max(getHeight(root->leftChlid), getHeight(root->rightChild)) + 1;
return root;
}四、AVL树的删除
AVL树的删除分为以下三种情况:
1.删除的节点没有左右孩子,即删除叶子节点
2.删除的节点有左右孩子(包括根节点)
3.删除的节点只有一个孩子(只有左孩子或者右孩子)
分析好这几种情况,可以手工过一遍代码,但是要特别注意被让递归搞坏了思路,得一步步来
AVLTREE* deletePoint(int data, AVLTREE* root) {
// 根为空 或者 没有要删除的节点,直接返回NULL
if(root == NULL || data == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
// 待删除的节点在root的左子树
if(data < root->data) {
root->leftChlid = deletePoint(data, root->leftChlid);
// 删除节点后,若AVL树失去平衡,则进行相应的调节
if(abs(getHeight(root->rightChild) - getHeight(root->leftChlid)) == 2) {
AVLTREE* p = root->rightChild;
if(getHeight(p->leftChlid) > getHeight(p->rightChild)) {
root = right_Left_Rotation(root);
} else {
root = right_Right_Rotation(root);
}
}
// 待删除的节点在root的右子树
} else if(data > root->data) {
root->rightChild = deletePoint(data, root->rightChild);
// 删除节点后,若AVL树失去平衡,则进行相应的调节
if(abs(getHeight(root->leftChlid) - getHeight(root->rightChild)) == 2) {
AVLTREE* p = root->leftChlid;
if(getHeight(p->rightChild) > getHeight(p->leftChlid)) {
root = left_Right_Rotation(root);
} else {
root = left_Left_Rotation(root);
}
}
// root就是要删除的节点
} else if(data == root->data) {
//左右孩子非空
if(root->leftChlid && root->rightChild) {
if(getHeight(root->leftChlid) > getHeight(root->rightChild)) {
// 如果root的左子树比右子树高;
// 则找出root的左子树中的最大节点
// 将该最大节点的值赋值给root
// 删除该最大节点
// 这类似于用root的左子树中最大节点做root的替身
// 删除root的左子树中最大节点之后,AVL树仍然是平衡的
AVLTREE* max = getMaxNum(root->leftChlid);
root->data = max->data;
root->leftChlid = deletePoint(max->data, root->leftChlid);
} else {
// 如果root的左子树比右子树低;
// 则找出root的左子树中的最小节点
// 将该最小节点的值赋值给root
// 删除该最小节点
// 这类似于用root的右子树中最小节点做root的替身
// 删除root的左子树中最小节点之后,AVL树仍然是平衡的
AVLTREE* min = getMinNum(root->rightChild);
root->data = min->data;
root->rightChild = deletePoint(min->data, root->rightChild);
}
}
else {
//这种情况为左孩子为空右孩子不为空、或者右孩子为空左孩子不为空、左右孩子都为空时的处理方法
//直接通过一个三目运算,即可完美解决
AVLTREE* temp = root;
root = root->leftChlid ? root->leftChlid : root->rightChild;
destroy(temp);
}
}
return root;
}五、源代码与总结
在正确理解思路后,其实AVL树并不难,在编写时要注意递归函数编写的严谨性即可,以下是源代码:
#include
#include
#include
typedef struct AVLTREE {
int data;
int height;
struct AVLTREE* leftChlid;
struct AVLTREE* rightChild;
}AVLTREE;
typedef unsigned char boolean;
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
static int i = 1;
void showBtreeByLeft(AVLTREE* head);
void showBtreeByMid(AVLTREE* head);
AVLTREE* left_Left_Rotation(AVLTREE* root);
AVLTREE* right_Right_Rotation(AVLTREE* root);
AVLTREE* left_Right_Rotation(AVLTREE* root);
AVLTREE* right_Left_Rotation(AVLTREE* root);
AVLTREE* insertPoint(int data, AVLTREE* root);
AVLTREE* deletePoint(int data, AVLTREE* root);
int getHeight(AVLTREE* root);
int max(int data1, int data2);
AVLTREE* getMaxNum(AVLTREE* root);
AVLTREE* getMinNum(AVLTREE* root);
void destroy(AVLTREE* root);
void destroy(AVLTREE* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
return;
}
root->leftChlid = NULL;
root->rightChild = NULL;
root = NULL;
}
AVLTREE* getMinNum(AVLTREE* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
while(root->leftChlid != NULL) {
root = root->leftChlid;
}
return root;
}
AVLTREE* getMaxNum(AVLTREE* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
while(root->rightChild != NULL) {
root = root->rightChild;
}
return root;
}
int max(int data1, int data2) {
return ((data1 > data2) ? data1 : data2);
}
int getHeight(AVLTREE* root) {
if(root == NULL)
return -1;
else
return root->height;
}
AVLTREE* deletePoint(int data, AVLTREE* root) {
// 根为空 或者 没有要删除的节点,直接返回NULL
if(root == NULL || data == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
// 待删除的节点在root的左子树
if(data < root->data) {
root->leftChlid = deletePoint(data, root->leftChlid);
// 删除节点后,若AVL树失去平衡,则进行相应的调节
if(abs(getHeight(root->rightChild) - getHeight(root->leftChlid)) == 2) {
AVLTREE* p = root->rightChild;
if(getHeight(p->leftChlid) > getHeight(p->rightChild)) {
root = right_Left_Rotation(root);
} else {
root = right_Right_Rotation(root);
}
}
// 待删除的节点在root的右子树
} else if(data > root->data) {
root->rightChild = deletePoint(data, root->rightChild);
// 删除节点后,若AVL树失去平衡,则进行相应的调节
if(abs(getHeight(root->leftChlid) - getHeight(root->rightChild)) == 2) {
AVLTREE* p = root->leftChlid;
if(getHeight(p->rightChild) > getHeight(p->leftChlid)) {
root = left_Right_Rotation(root);
} else {
root = left_Left_Rotation(root);
}
}
// root就是要删除的节点
} else if(data == root->data) {
//左右孩子非空
if(root->leftChlid && root->rightChild) {
if(getHeight(root->leftChlid) > getHeight(root->rightChild)) {
// 如果root的左子树比右子树高;
// 则找出root的左子树中的最大节点
// 将该最大节点的值赋值给root
// 删除该最大节点
// 这类似于用root的左子树中最大节点做root的替身
// 删除root的左子树中最大节点之后,AVL树仍然是平衡的
AVLTREE* max = getMaxNum(root->leftChlid);
root->data = max->data;
root->leftChlid = deletePoint(max->data, root->leftChlid);
} else {
// 如果root的左子树比右子树低;
// 则找出root的左子树中的最小节点
// 将该最小节点的值赋值给root
// 删除该最小节点
// 这类似于用root的右子树中最小节点做root的替身
// 删除root的左子树中最小节点之后,AVL树仍然是平衡的
AVLTREE* min = getMinNum(root->rightChild);
root->data = min->data;
root->rightChild = deletePoint(min->data, root->rightChild);
}
}
else {
//这种情况为左孩子为空右孩子不为空、或者右孩子为空左孩子不为空、左右孩子都为空时的处理方法
//直接通过一个三目运算,即可完美解决
AVLTREE* temp = root;
root = root->leftChlid ? root->leftChlid : root->rightChild;
destroy(temp);
}
}
return root;
}
/*
如果节点为空,那么创建一个节点
下面也分别给出了当要插入的节点大于或小于或等于当前节点的情况
当一个节点的左右孩子高度差为2时,说明树需要旋转
至于是单旋转还是双旋转,得看插入的位置是左子树还是右子树
然后根据相应结构,选择单旋转或者双旋转
建议手动过一遍这里的代码,在插入过程需要旋转时,不妨画出树的结构
然后就很容易的看出端倪了
*/
AVLTREE* insertPoint(int data, AVLTREE* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
root = (AVLTREE *)malloc(sizeof(AVLTREE));
root->data = data;
root->height = 0;
root->leftChlid = root->rightChild = NULL;
} else if(data < root->data) {
root->leftChlid = insertPoint(data, root->leftChlid);
if(getHeight(root->leftChlid) - getHeight(root->rightChild) == 2) {
if(data < root->leftChlid->data)
root = left_Left_Rotation(root);
else
root = left_Right_Rotation(root);
}
} else if(data > root->data) {
root->rightChild = insertPoint(data, root->rightChild);
if(getHeight(root->rightChild) - getHeight(root->leftChlid) == 2) {
if(data > root->rightChild->data)
root = right_Right_Rotation(root);
else
root = right_Left_Rotation(root);
}
} else if(data == root->data) {
return NULL;
}
root->height = max(getHeight(root->leftChlid), getHeight(root->rightChild)) + 1;
return root;
}
AVLTREE* right_Left_Rotation(AVLTREE* root) {
root->rightChild = left_Left_Rotation(root->rightChild);
return right_Right_Rotation(root);
}
AVLTREE* left_Right_Rotation(AVLTREE* root) {
root->leftChlid = right_Right_Rotation(root->leftChlid);
return left_Left_Rotation(root);
}
AVLTREE* right_Right_Rotation(AVLTREE* root) {
AVLTREE* newRoot = NULL;
newRoot = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = newRoot->leftChlid;
newRoot->leftChlid = root;
root->height = max(getHeight(root->leftChlid),getHeight(root->rightChild)) + 1;
newRoot->height = max(getHeight(newRoot->rightChild), root->height) + 1;
return newRoot;
}
AVLTREE* left_Left_Rotation(AVLTREE* root) {
AVLTREE* newRoot = NULL;
newRoot = root->leftChlid;
root->leftChlid = newRoot->rightChild;
newRoot->rightChild = root;
root->height = max(getHeight(root->leftChlid),getHeight(root->rightChild)) + 1;
newRoot->height = max(getHeight(newRoot->leftChlid), root->height) + 1;
return newRoot;
}
void showBtreeByMid(AVLTREE* head) {
if(head == NULL) {
return;
}
showBtreeByMid(head->leftChlid);
printf("%d ", head->data);
showBtreeByMid(head->rightChild);
}
void showBtreeByLeft(AVLTREE* head) {
if(head == NULL) {
return;
}
printf("%d ", head->data);
showBtreeByLeft(head->leftChlid);
showBtreeByLeft(head->rightChild);
}
void main(void) {
AVLTREE* root = NULL;
root = insertPoint(20,root);
root = insertPoint(10,root);
root = insertPoint(25,root);
root = insertPoint(8,root);
root = insertPoint(24,root);
root = insertPoint(30,root);
root = insertPoint(29,root);
printf("\n");
printf("按先序输出可得:\n");
showBtreeByLeft(root);
printf("\n");
printf("按中序输出可得:\n");
showBtreeByMid(root);
printf("\n");
root = deletePoint(24,root);
printf("\n");
printf("按先序输出可得:\n");
showBtreeByLeft(root);
printf("\n");
printf("按中序输出可得:\n");
showBtreeByMid(root);
printf("\n");
}