python深度学习——用keras实现神经风格迁移
用keras实现神经风格迁移
from keras.preprocessing.image import load_img, img_to_array
import numpy as np
from keras.applications import vgg19
from keras import backend as K
from scipy.optimize import fmin_l_bfgs_b
# from scipy.misc import imsave
import imageio
import time
# This is the path to the image you want to transform.
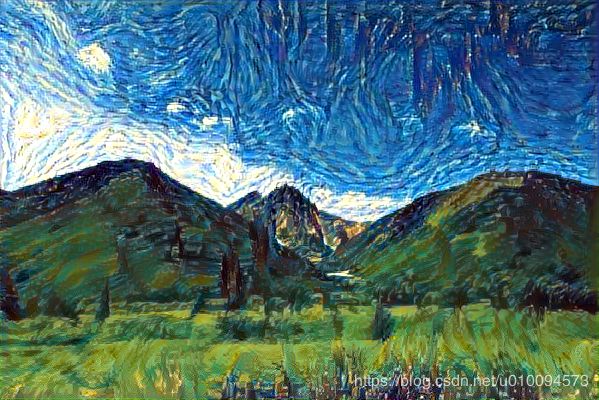
target_image_path = '/mnt/projects/deeplearn/codes/test8_2.jpg'
# This is the path to the style image.
style_reference_image_path = '/mnt/projects/deeplearn/codes/8_3style.jpg'
# Dimensions of the generated picture.
width, height = load_img(target_image_path).size
img_height = 400
img_width = int(width * img_height / height)
def preprocess_image(image_path):
img = load_img(image_path, target_size=(img_height, img_width))
img = img_to_array(img)
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
img = vgg19.preprocess_input(img)
return img
def deprocess_image(x):
# Remove zero-center by mean pixel
x[:, :, 0] += 103.939
x[:, :, 1] += 116.779
x[:, :, 2] += 123.68
# 'BGR'->'RGB'
x = x[:, :, ::-1]
x = np.clip(x, 0, 255).astype('uint8')
return x
target_image = K.constant(preprocess_image(target_image_path))
style_reference_image = K.constant(preprocess_image(style_reference_image_path))
# This placeholder will contain our generated image
combination_image = K.placeholder((1, img_height, img_width, 3))
# We combine the 3 images into a single batch
input_tensor = K.concatenate([target_image,
style_reference_image,
combination_image], axis=0)
# We build the VGG19 network with our batch of 3 images as input.
# The model will be loaded with pre-trained ImageNet weights.
model = vgg19.VGG19(input_tensor=input_tensor,
weights='imagenet',
include_top=False)
print('Model loaded.')
def content_loss(base, combination):
return K.sum(K.square(combination - base))
def gram_matrix(x):
features = K.batch_flatten(K.permute_dimensions(x, (2, 0, 1)))
gram = K.dot(features, K.transpose(features))
return gram
def style_loss(style, combination):
S = gram_matrix(style)
C = gram_matrix(combination)
channels = 3
size = img_height * img_width
return K.sum(K.square(S - C)) / (4. * (channels ** 2) * (size ** 2))
def total_variation_loss(x):
a = K.square(
x[:, :img_height - 1, :img_width - 1, :] - x[:, 1:, :img_width - 1, :])
b = K.square(
x[:, :img_height - 1, :img_width - 1, :] - x[:, :img_height - 1, 1:, :])
return K.sum(K.pow(a + b, 1.25))
# Dict mapping layer names to activation tensors
outputs_dict = dict([(layer.name, layer.output) for layer in model.layers])
# Name of layer used for content loss
content_layer = 'block5_conv2'
# Name of layers used for style loss
style_layers = ['block1_conv1',
'block2_conv1',
'block3_conv1',
'block4_conv1',
'block5_conv1']
# Weights in the weighted average of the loss components
total_variation_weight = 1e-4
style_weight = 1.
content_weight = 0.025
# Define the loss by adding all components to a `loss` variable
loss = K.variable(0.)
layer_features = outputs_dict[content_layer]
target_image_features = layer_features[0, :, :, :]
combination_features = layer_features[2, :, :, :]
loss += content_weight * content_loss(target_image_features,
combination_features)
for layer_name in style_layers:
layer_features = outputs_dict[layer_name]
style_reference_features = layer_features[1, :, :, :]
combination_features = layer_features[2, :, :, :]
sl = style_loss(style_reference_features, combination_features)
loss += (style_weight / len(style_layers)) * sl
loss += total_variation_weight * total_variation_loss(combination_image)
# Get the gradients of the generated image wrt the loss
grads = K.gradients(loss, combination_image)[0]
# Function to fetch the values of the current loss and the current gradients
fetch_loss_and_grads = K.function([combination_image], [loss, grads])
class Evaluator(object):
def __init__(self):
self.loss_value = None
self.grads_values = None
def loss(self, x):
assert self.loss_value is None
x = x.reshape((1, img_height, img_width, 3))
outs = fetch_loss_and_grads([x])
loss_value = outs[0]
grad_values = outs[1].flatten().astype('float64')
self.loss_value = loss_value
self.grad_values = grad_values
return self.loss_value
def grads(self, x):
assert self.loss_value is not None
grad_values = np.copy(self.grad_values)
self.loss_value = None
self.grad_values = None
return grad_values
evaluator = Evaluator()
result_prefix = 'style_transfer_result'
iterations = 20
# Run scipy-based optimization (L-BFGS) over the pixels of the generated image
# so as to minimize the neural style loss.
# This is our initial state: the target image.
# Note that `scipy.optimize.fmin_l_bfgs_b` can only process flat vectors.
x = preprocess_image(target_image_path)
x = x.flatten()
for i in range(iterations):
print('Start of iteration', i)
start_time = time.time()
x, min_val, info = fmin_l_bfgs_b(evaluator.loss, x,
fprime=evaluator.grads, maxfun=20)
print('Current loss value:', min_val)
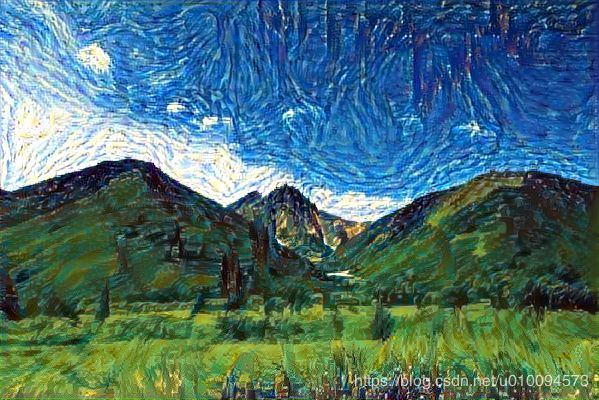
# Save current generated image
img = x.copy().reshape((img_height, img_width, 3))
img = deprocess_image(img)
fname = result_prefix + '_at_iteration_%d.png' % i
imageio.imsave(fname, img)
end_time = time.time()
print('Image saved as', fname)
print('Iteration %d completed in %ds' % (i, end_time - start_time))