Libevent之信号事件管理
1、原理性介绍:
1、Linux操作系统,对于信号的处理,都是调用先前注册给系统的回调函数,例如通过sigaction(evsignal, &sa, sig->sh_old[evsignal])注册回调了sa里面的回调函数。当对应的信号到来时候,将调用相应的回调函数。
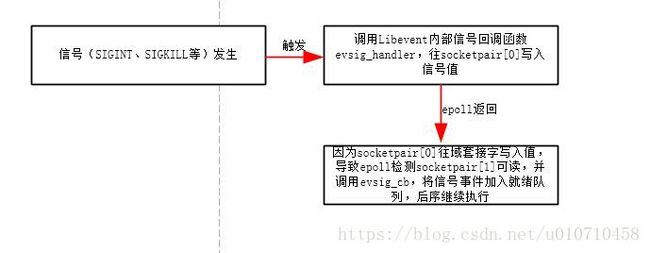
2、Libevent为了将信号事件和IO事件统一起来,即对于信号的处理也通过epoll可以检测到。因此Libevent采用Unix域套接字的方法。创建一个域套接字socketpair[0]、socketpair[1]分别对应读和写。对于socketpair[1]Libevent创建一个内部socketpair[1]可读的事件ev_signal并设定其回调函数是evsig_cb,同时通过epoll监听这个事件。
3、当用户调用event_add添加信号事件的时候,会注册对应的信号回调函数evsig_handler,这个回调函数仅仅是往socketpair[0]里面写入对应的信号值。这时候,这时候epoll可以检测socketpair[1]可读,通过其事件回调函数evsig_cb读取出对应信号的值,并信号对应的事件,添加到就绪队列。然后执行对应的回调函数。通过添加间接层,可以很好的体现Libevent的事件驱动机制,这时候信号也是一个事件。
统一事件源能够工作的一个原因是:多路IO复用函数都是可中断的。即处理完信号后,会从多路IO复用函数中退出,并将errno赋值为EINTR。
2、简单例子
将使用这个简单例子分析全部信号处理流程:
#include 以上代码在SIGINT上面注册三个回调函数,并且各自优先级为0、1、2。
1、首先第一点需要注意,就是需要手动初始化event_base_priority_init的优先级链表个数,也就是初始化struct event_list *activequeues这个数组大小。否则Libevent默认初始化大小为0,为我们定义了优先级,最后肯定会收到系统的SIGSEGV信号,导致程序终止。
int
event_base_priority_init(struct event_base *base, int npriorities)
{
int i;
if (N_ACTIVE_CALLBACKS(base) || npriorities < 1
|| npriorities >= EVENT_MAX_PRIORITIES)
return (-1);
if (npriorities == base->nactivequeues)//
return (0);
if (base->nactivequeues) {
mm_free(base->activequeues);
base->nactivequeues = 0;
}
/* Allocate our priority queues 动态分配优先队列所需要的内存 */
base->activequeues = (struct event_list *)
mm_calloc(npriorities, sizeof(struct event_list));//分配npriorities个struct event_list
if (base->activequeues == NULL) {
event_warn("%s: calloc", __func__);
return (-1);
}
base->nactivequeues = npriorities;
for (i = 0; i < base->nactivequeues; ++i) {//继续初始化nactivequeues个队列,用来分别存储不同优先级的event
TAILQ_INIT(&base->activequeues[i]);
}
return (0);
}此函数很简单,就是分配一个数组,数组里面的元素存储队列头。每一个事件都有一个优先级变量ev_pri,当事件发生时候,通过里面的这个变量,将其加入到activequeues[ev_pri]对应的就绪链表中,实现事件的优先级调用。
2、在同一个事件上面是支持优先级的和IO操作一样,当信号发生时候,优先级高的事件对应的回调函数优先运行。
3、当注册了信号函数,如果用户自己再次重新通过sigaction注册回调函数,那么信号发生,将直接覆盖Libevent帮助我们注册ev_signal,导致统一信号事件源失效。
3、源代码分析
首先安装的Libevent的debug版本,在运行时候,会打印debug信息。其次通过strace -p pid 追踪Libevent运行时候对应的系统调用。可以很清楚的看出Libevent对于信号处理是如何进行的,对于分析代码有重要作用。下面给出跟踪信息及注释。
Libevent自带的调试输出:
//通过strace跟踪Libevent_client,并将跟踪文件输出,以下是Libevent调试输出的结果:
$ strace -o output.txt ./Libevent_client
//第一次调用event_add(sigintEvent1 , NULL);
[debug] event_add: event: 0x15064e0 (fd 2), call 0x4008e6 //调用event_add(sigintEvent1 , NULL);输出的调试信息,因为SIGINT = 2
[debug] evsig_add: 2: changing signal handler //event_add->event_add_internal->evmap_signal_add->evsig_add 注册SIGINT回调函数 evsig_handler
[debug] _evsig_set_handler: evsignal (2) >= sh_old_max (0), resizing//_evsig_set_handler中sig->sh_old扩容,因为对于每一个信号需要存储一个struct sigaction变量
[debug] event_add: event: 0x1506068 (fd 5), EV_READ call 0x7f813c939909//信号事件第一次监听,将pair[1]读端的统一事件源ev_signal加入到epoll。
[debug] Epoll ADD(1) on fd 5 okay. [old events were 0; read change was 1; write change was 0]//ev_signal调用epoll的调试信息,epoll add(指令码为1)操作,pair[1]=5
//第二三次调用event_add(sigintEvent2 , NULL); 仅仅将sigintEvent2加入到信号事件队列
[debug] event_add: event: 0x1506570 (fd 2), call 0x40090a//再次添加SIGINT
[debug] event_add: event: 0x1506600 (fd 2), call 0x40092e//再次添加SIGINT
//调用event_base_dispatch(base);//循环监听
[debug] epoll_dispatch: epoll_wait reports 1 //由于发送了SIGINT信号,回调函数被调用,所以epoll_dispatch里面epoll_wait监听pair[1]返回可读,就绪一个
[debug] event_active: 0x1506068 (fd 5), res 2, callback 0x7f813c939909//event_active_nolock,将pair[1]的回调函数加入就绪队列。res代表触发事件为read
//此时激活队列上就一个事件evsig_cb
[debug] event_process_active: event: 0x1506068, EV_READ call 0x7f813c939909//处理就绪事件,事件的首地址 ,事件可读,调用回调函数evsig_cb(回调函数首地址)
//evsig_cb优先级为0,所以最先被执行,然后将其他三个信号注册函数激活。
//evsig_cb激活三个信号事件后,进而继续执行激活队列上面的事件。
[debug] event_active: 0x15064e0 (fd 2), res 8, callback 0x4008e6//evsig_cb里面将三个信号事件激活,res为8代表信号
[debug] event_active: 0x1506570 (fd 2), res 8, callback 0x40090a
[debug] event_active: 0x1506600 (fd 2), res 8, callback 0x40092e
//在先激活的事件的回调函数,可以激活一些事件。
[debug] event_process_active: event: 0x1506600, call 0x40092e//处理优先级最高的,在第0号优先队列
CB3
[debug] epoll_dispatch: epoll_wait reports 0//为什么此处返回0?
[debug] event_process_active: event: 0x1506570, call 0x40090a//处理优先级第二高的,在第1号优先队列
CB2
[debug] epoll_dispatch: epoll_wait reports 0
[debug] event_process_active: event: 0x15064e0, call 0x4008e6//处理优先级第三高的 在第2号优先队列
CB1
Hangup//用户发送SIGHUB信号终止Libeventstrace追踪的output.txt:
execve("./Libevent_client", ["./Libevent_client"], [/* 63 vars */]) = 0
brk(NULL) = 0x1506000
access("/etc/ld.so.nohwcap", F_OK) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
access("/etc/ld.so.preload", R_OK) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
open("/home/wangjun/Qt5.7.0/5.7/gcc_64/lib/tls/x86_64/libevent-2.0.so.5", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
stat("/home/wangjun/Qt5.7.0/5.7/gcc_64/lib/tls/x86_64", 0x7ffe290072f0) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
open("/home/wangjun/Qt5.7.0/5.7/gcc_64/lib/tls/libevent-2.0.so.5", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
stat("/home/wangjun/Qt5.7.0/5.7/gcc_64/lib/tls", 0x7ffe290072f0) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
open("/home/wangjun/Qt5.7.0/5.7/gcc_64/lib/x86_64/libevent-2.0.so.5", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
stat("/home/wangjun/Qt5.7.0/5.7/gcc_64/lib/x86_64", 0x7ffe290072f0) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
open("/home/wangjun/Qt5.7.0/5.7/gcc_64/lib/libevent-2.0.so.5", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
stat("/home/wangjun/Qt5.7.0/5.7/gcc_64/lib", {st_mode=S_IFDIR|0775, st_size=20480, ...}) = 0
open("/etc/ld.so.cache", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3
fstat(3, {st_mode=S_IFREG|0644, st_size=95323, ...}) = 0
mmap(NULL, 95323, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, 3, 0) = 0x7f813cd72000
close(3) = 0
access("/etc/ld.so.nohwcap", F_OK) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
open("/usr/lib/libevent-2.0.so.5", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3
read(3, "\177ELF\2\1\1\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\3\0>\0\1\0\0\0\340\312\0\0\0\0\0\0"..., 832) = 832
fstat(3, {st_mode=S_IFREG|0755, st_size=421888, ...}) = 0
mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f813cd71000
mmap(NULL, 2458928, PROT_READ|PROT_EXEC, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_DENYWRITE, 3, 0) = 0x7f813c90c000
mprotect(0x7f813c962000, 2097152, PROT_NONE) = 0
mmap(0x7f813cb62000, 8192, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_FIXED|MAP_DENYWRITE, 3, 0x56000) = 0x7f813cb62000
mmap(0x7f813cb64000, 1328, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_FIXED|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f813cb64000
close(3) = 0
open("/home/wangjun/Qt5.7.0/5.7/gcc_64/lib/libc.so.6", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
access("/etc/ld.so.nohwcap", F_OK) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
open("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3
read(3, "\177ELF\2\1\1\3\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\3\0>\0\1\0\0\0P\t\2\0\0\0\0\0"..., 832) = 832
fstat(3, {st_mode=S_IFREG|0755, st_size=1868984, ...}) = 0
mmap(NULL, 3971488, PROT_READ|PROT_EXEC, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_DENYWRITE, 3, 0) = 0x7f813c542000
mprotect(0x7f813c702000, 2097152, PROT_NONE) = 0
mmap(0x7f813c902000, 24576, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_FIXED|MAP_DENYWRITE, 3, 0x1c0000) = 0x7f813c902000
mmap(0x7f813c908000, 14752, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_FIXED|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f813c908000
close(3) = 0
open("/home/wangjun/Qt5.7.0/5.7/gcc_64/lib/libpthread.so.0", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
access("/etc/ld.so.nohwcap", F_OK) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
open("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpthread.so.0", O_RDONLY|O_CLOEXEC) = 3
read(3, "\177ELF\2\1\1\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\3\0>\0\1\0\0\0\260`\0\0\0\0\0\0"..., 832) = 832
fstat(3, {st_mode=S_IFREG|0755, st_size=138696, ...}) = 0
mmap(NULL, 2212904, PROT_READ|PROT_EXEC, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_DENYWRITE, 3, 0) = 0x7f813c325000
mprotect(0x7f813c33d000, 2093056, PROT_NONE) = 0
mmap(0x7f813c53c000, 8192, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_FIXED|MAP_DENYWRITE, 3, 0x17000) = 0x7f813c53c000
mmap(0x7f813c53e000, 13352, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_FIXED|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f813c53e000
close(3) = 0
mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f813cd70000
mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f813cd6f000
mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f813cd6e000
arch_prctl(ARCH_SET_FS, 0x7f813cd6f700) = 0
mprotect(0x7f813c902000, 16384, PROT_READ) = 0
mprotect(0x7f813c53c000, 4096, PROT_READ) = 0
mprotect(0x7f813cb62000, 4096, PROT_READ) = 0
mprotect(0x600000, 4096, PROT_READ) = 0
mprotect(0x7f813cd8a000, 4096, PROT_READ) = 0
munmap(0x7f813cd72000, 95323) = 0
set_tid_address(0x7f813cd6f9d0) = 6847
set_robust_list(0x7f813cd6f9e0, 24) = 0
rt_sigaction(SIGRTMIN, {0x7f813c32ab50, [], SA_RESTORER|SA_SIGINFO, 0x7f813c336390}, NULL, 8) = 0
rt_sigaction(SIGRT_1, {0x7f813c32abe0, [], SA_RESTORER|SA_RESTART|SA_SIGINFO, 0x7f813c336390}, NULL, 8) = 0
rt_sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK, [RTMIN RT_1], NULL, 8) = 0
getrlimit(RLIMIT_STACK, {rlim_cur=8192*1024, rlim_max=RLIM64_INFINITY}) = 0
brk(NULL) = 0x1506000
brk(0x1527000) = 0x1527000
getuid() = 1000
geteuid() = 1000
getgid() = 1000
getegid() = 1000
epoll_create(32000) = 3
fcntl(3, F_GETFD) = 0
fcntl(3, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC) = 0
getuid() = 1000
geteuid() = 1000
getgid() = 1000
getegid() = 1000
socketpair(PF_LOCAL, SOCK_STREAM, 0, [4, 5]) = 0
fcntl(4, F_GETFD) = 0
fcntl(4, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC) = 0
fcntl(5, F_GETFD) = 0
fcntl(5, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC) = 0
fcntl(4, F_GETFL) = 0x2 (flags O_RDWR)
fcntl(4, F_SETFL, O_RDWR|O_NONBLOCK) = 0
fcntl(5, F_GETFL) = 0x2 (flags O_RDWR)
fcntl(5, F_SETFL, O_RDWR|O_NONBLOCK) = 0
getuid() = 1000
geteuid() = 1000
getgid() = 1000
getegid() = 1000
write(2, "[debug] event_add: event: 0x1506"..., 61) = 61
write(2, "[debug] evsig_add: 2: changing s"..., 46) = 46
write(2, "[debug] _evsig_set_handler: evsi"..., 69) = 69
rt_sigaction(SIGINT, {0x7f813c93a321, ~[RTMIN RT_1], SA_RESTORER|SA_RESTART, 0x7f813c5774b0}, {SIG_DFL, [], 0}, 8) = 0
write(2, "[debug] event_add: event: 0x1506"..., 74) = 74
epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, 5, {EPOLLIN, {u32=5, u64=5}}) = 0//往epoll加入sockpair[1]监听读
write(2, "[debug] Epoll ADD(1) on fd 5 oka"..., 94) = 94
write(2, "[debug] event_add: event: 0x1506"..., 61) = 61
write(2, "[debug] event_add: event: 0x1506"..., 61) = 61//写往标准输出
epoll_wait(3, 0x15062f0, 32, -1) = -1 EINTR (Interrupted system call)//epoll_wait第一次返回,因为用户的SIGINT
--- SIGINT {si_signo=SIGINT, si_code=SI_USER, si_pid=6776, si_uid=1000} ---
sendto(4, "\2", 1, 0, NULL, 0) = 1//调用evsig_handler往pair[0]写入2
rt_sigreturn({mask=[]}) = -1 EINTR (Interrupted system call)
/*
epoll_wait第二次返回1,表示用户的SIGINT已经来了,然后在epoll_wait里面将evsig_cb加入就绪事件。
然后执行event_process_active执行就绪优先级最高的事件,也就是执行evsig_cb。evsig_cb从pair[1]中读出所有
信号值,然后将信号值对应的所有事件加入就绪队列。
*/
epoll_wait(3, [{EPOLLIN, {u32=5, u64=5}}], 32, -1) = 1//因为pair[0]写入,导致pair[1]可读,因此epoll_wait返回1
write(2, "[debug] epoll_dispatch: epoll_wa"..., 45) = 45//libevent的调试代码,写入标准客户端
write(2, "[debug] event_active: 0x1506068 "..., 71) = 71
write(2, "[debug] event_process_active: ev"..., 77) = 77
recvfrom(5, "\2", 1024, 0, NULL, NULL) = 1//处理pair[1]可读事件的回调函数evsig_cb。
recvfrom(5, 0x7f813cb64120, 1024, 0, NULL, NULL) = -1 EAGAIN (Resource temporarily unavailable)
/*
因为pair[1]是非阻塞的,要确保将pair[1]缓冲区所有数据读出,必须通过while(1)调用,确保返回错误并且错误码是EINTR或EAGAIN或EWOULDBLOCK才保证好数据读完。
这里返回了EAGAIN,所以数据已经读完了。
这里就是阻塞和非阻塞调用recvfrom的区别。
*/
write(2, "[debug] event_active: 0x15064e0 "..., 65) = 65//调用evmap_signal_active,将信号对应的事件加入就绪队列
write(2, "[debug] event_active: 0x1506570 "..., 65) = 65
write(2, "[debug] event_active: 0x1506600 "..., 65) = 65
write(2, "[debug] event_process_active: ev"..., 64) = 64//执行信号优先级最高的回调函数。
fstat(1, {st_mode=S_IFCHR|0620, st_rdev=makedev(136, 1), ...}) = 0
write(1, "CB3\n", 4) = 4//执行完毕
epoll_wait(3, [], 32, 0) = 0
write(2, "[debug] epoll_dispatch: epoll_wa"..., 45) = 45
write(2, "[debug] event_process_active: ev"..., 64) = 64
write(1, "CB2\n", 4) = 4
epoll_wait(3, [], 32, 0) = 0
write(2, "[debug] epoll_dispatch: epoll_wa"..., 45) = 45
write(2, "[debug] event_process_active: ev"..., 64) = 64
write(1, "CB1\n", 4) = 4
epoll_wait(3, 0x15062f0, 32, -1) = -1 EINTR (Interrupted system call)//阻塞于此,直到用户键入SIGHUP信号
--- SIGHUP {si_signo=SIGHUP, si_code=SI_USER, si_pid=6776, si_uid=1000} ---
+++ killed by SIGHUP +++ //strace提示由于接受SIGHUB信号结束进程。event_base里面两个成员变量
//event-internal.h文件
struct event_base {
/** Function pointers used to describe the backend that this event_base
* uses for signals */
//执行用户添加和删除信号的内部调用函数
const struct eventop *evsigsel;
/*
sig里面包含socketpair[1]读事件,以及注册信号时候需要用到的结构体
sigaction(evsignal, &sa, sig->sh_old[evsignal])中需要用到的struct sigaction,来存储信号先前注册过得回调函数,用户删除自己信号后恢复原来处理操作。看APUE可以清楚此过程。
*/
struct evsig_info sig;
...
//用户注册信号事件的链表,保存全部信号
struct event_signal_map sigmap;
...
}; static const struct eventop evsigops = {//处理信号的IO复用
"signal",
NULL,
evsig_add,//添加信号 函数指针
evsig_del,//移除信号 函数指针操作
NULL,
NULL,
0, 0, 0
};
struct evsig_info {
/* Event watching ev_signal_pair[1] */
struct event ev_signal;//内部事件,在信号第一次注册时候,会加入epoll
/* Socketpair used to send notifications from the signal handler */
evutil_socket_t ev_signal_pair[2];//保存socketpair
/* True iff we've added the ev_signal event yet. */
int ev_signal_added;//标记ev_signal是否已经添加epoll
/* Count of the number of signals we're currently watching. */
int ev_n_signals_added;//记录多少个信号被添加
/* Array of previous signal handler objects before Libevent started
* messing with them. Used to restore old signal handlers.
* 保存sigaction之前的回调函数。对于一个信号仅仅需要一个struct sigaction保存先前配置,而Linux信号总共32个,所以这里将sh_old_max设定为32个比较好。sh_old执向一个指针数组,指针数组里面的成员指向一个struct sigaction。所以可以通过sh_old及sh_old_max管理全部的struct sigaction。这里设计很聪明。
*/
struct sigaction **sh_old;
//保存的是捕抓函数的函数指针,又因为是数组。所以是二级指针
/* Size of sh_old. */
int sh_old_max;
};和信号处理有关的结构体就是上面,那么Libevent如何做到上述示意图的统一信号源处理。
初始化工作
在event.c里面会调用base->evbase = base->evsel->init(base);初始化epoll。
static void *
epoll_init(struct event_base *base)
{
int epfd;
struct epollop *epollop;
/* Initialize the kernel queue. (The size field is ignored since
* 2.6.8.) */
if ((epfd = epoll_create(32000)) == -1) {//1、如果返回-1,则出错,2、查看错误码,是什么错误。这是判断套路
if (errno != ENOSYS)
event_warn("epoll_create");
return (NULL);
}
//将epoll实例文件描述符 设为FD_CLOEXEC属性,也就是程序exec即关闭文件描述符
evutil_make_socket_closeonexec(epfd);
if (!(epollop = mm_calloc(1, sizeof(struct epollop)))) {//分配epollop内存
close(epfd);
return (NULL);
}
epollop->epfd = epfd;//记录epfd实例文件描述符
/* Initialize fields */
epollop->events = mm_calloc(INITIAL_NEVENT, sizeof(struct epoll_event));//分配32个用于设定fd对应的感兴趣事件结构体
if (epollop->events == NULL) {//出错,则释放内存
mm_free(epollop);
close(epfd);
return (NULL);
}
epollop->nevents = INITIAL_NEVENT;//32个
//我们暂不考虑changelist
if ((base->flags & EVENT_BASE_FLAG_EPOLL_USE_CHANGELIST) != 0 ||
((base->flags & EVENT_BASE_FLAG_IGNORE_ENV) == 0 &&
evutil_getenv("EVENT_EPOLL_USE_CHANGELIST") != NULL))
base->evsel = &epollops_changelist;
//建立UNIX套接字(非阻塞),用于UNIX信号响应,
//初始化sockpair[1]读端
//sockpair[2]写端
evsig_init(base);
return (epollop);//返回初始化epoll相关的结构体,为后续使用做准备,这个地址存储在event_base.evbase中
}从上面可以看到epoll调用了evsig_init函数初始化Unix域套接字。
//创建socketpair并将socketpair的一个读端与ev_signal相关联
int
evsig_init(struct event_base *base)
{
/*
* Our signal handler is going to write to one end of the socket
* pair to wake up our event loop. The event loop then scans for
* signals that got delivered.
*/
if (evutil_socketpair(
AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, base->sig.ev_signal_pair) == -1) {
#ifdef WIN32
/* Make this nonfatal on win32, where sometimes people
have localhost firewalled. */
event_sock_warn(-1, "%s: socketpair", __func__);
#else
event_sock_err(1, -1, "%s: socketpair", __func__);
#endif
return -1;
}
//子进程不能访问该socketpair
evutil_make_socket_closeonexec(base->sig.ev_signal_pair[0]);
evutil_make_socket_closeonexec(base->sig.ev_signal_pair[1]);
base->sig.sh_old = NULL;
base->sig.sh_old_max = 0;
evutil_make_socket_nonblocking(base->sig.ev_signal_pair[0]);
evutil_make_socket_nonblocking(base->sig.ev_signal_pair[1]);
//将ev_signal_pair[1]与ev_signal这个event相关联。ev_signal_pair[1]为读端
//在ev_signal_pair[1]上新建一个监听事件,sig.ev_signal内存以及分配了。
event_assign(&base->sig.ev_signal, base, base->sig.ev_signal_pair[1],
EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, evsig_cb, base);
//当socketpair[1]可读,那么调用evsig_cb处理
base->sig.ev_signal.ev_flags |= EVLIST_INTERNAL;//事件设定为内部使用。
event_priority_set(&base->sig.ev_signal, 0);
//ev_signal优先集最高,最先被执行,evsig_cb将已经发生的信号的回调函数加入到就绪队列
base->evsigsel = &evsigops;//专门处理信号的IO复用变量
return 0;
}首先创建一个套接字,fd[0]用于写,fd[1]用于读。通过event_assign将fd[1]的读事件ev_signal初始化,这里注意其优先级为最高优先级0。其次属性为EV_PERSIST,所以epoll会一直监听,不会取消。
并将两个文件描述符设定为非阻塞,因为非阻塞,所以recv需要在while里面读取,这点后面会有说明。
event_new信号事件
event_new工作很简单,如果属性设定为EV_SIGNAL|EV_PERSIST,那么就通过event_assign将其初始化而已。里面添加一些标志位,事件属性等等。
struct event *
event_new(struct event_base *base, evutil_socket_t fd, short events, void (*cb)(evutil_socket_t, short, void *), void *arg)
{
struct event *ev;
ev = mm_malloc(sizeof(struct event));
if (ev == NULL)
return (NULL);
if (event_assign(ev, base, fd, events, cb, arg) < 0) {
mm_free(ev);
return (NULL);
}
return (ev);
}
int
event_assign(struct event *ev, struct event_base *base, evutil_socket_t fd, short events, void (*callback)(evutil_socket_t, short, void *), void *arg)
{
if (!base)
base = current_base;//事件管理器
_event_debug_assert_not_added(ev);
ev->ev_base = base;
ev->ev_callback = callback;//设定事件回调函数
ev->ev_arg = arg;//设定回调参数
ev->ev_fd = fd;//设定fd,定时器没有fd则为-1
ev->ev_events = events;//事件类型,为0是啥意思?
ev->ev_res = 0;
ev->ev_flags = EVLIST_INIT;//event信息状态转为初始化标记
ev->ev_ncalls = 0;
ev->ev_pncalls = NULL;
if (events & EV_SIGNAL) {//检测是否设置错误,信号不支持读和写
if ((events & (EV_READ|EV_WRITE)) != 0) {
event_warnx("%s: EV_SIGNAL is not compatible with "
"EV_READ or EV_WRITE", __func__);
return -1;
}
ev->ev_closure = EV_CLOSURE_SIGNAL;
} else {//检测错误
if (events & EV_PERSIST) {
evutil_timerclear(&ev->ev_io_timeout);
ev->ev_closure = EV_CLOSURE_PERSIST;
} else {
ev->ev_closure = EV_CLOSURE_NONE;
}
}
min_heap_elem_init(ev);//堆元素索引初始化为-1,也就是没有元素
if (base != NULL) {
/* by default, we put new events into the middle priority */
ev->ev_pri = base->nactivequeues / 2;//设定为中间优先级
}
_event_debug_note_setup(ev);
return 0;
}event_add信号事件
前面的代码已经完成了“创建socketpair并将socketpair的一个读端与ev_signal相关联”。接下来看其他的工作。假如要对一个绑定了某个信号的event调用event_add函数,那么在event_add的内部会调用event_add_internal函数。而event_add_internal函数又会调用evmap_signal_add函数。
/*
参数:ev:指向要注册的事件;
tv:超时时间;
函数将ev注册到ev->ev_base上,事件类型由ev->ev_events指明,如果注册成功,ev
将被插入到已注册链表中,如果tv不是NULL,则会同时注册定时事件,将ev添加到timer 堆上。
如果其中有一步操作失败,那么函数保证没有事件会被注册,可以讲这相当于一个原子
操作。这个函数也体现了libevent细节之处的巧妙设计,且仔细看程序代码,部分有省略,
注释直接附在代码中。
*/
int
event_add(struct event *ev, const struct timeval *tv)
{
int res;
if (EVUTIL_FAILURE_CHECK(!ev->ev_base)) {//必须首先设定ev_base
event_warnx("%s: event has no event_base set.", __func__);
return -1;
}
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(ev->ev_base, th_base_lock);//为了支持多线程操作
res = event_add_internal(ev, tv, 0);
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(ev->ev_base, th_base_lock);
return (res);
}
static inline int
event_add_internal(struct event *ev, const struct timeval *tv,
int tv_is_absolute)
{
.....
res = evmap_signal_add(base, (int)ev->ev_fd, ev);//加入到信号队列
.....
}int
evmap_signal_add(struct event_base *base, int sig, struct event *ev)
{
const struct eventop *evsel = base->evsigsel;//信号添加函数
struct event_signal_map *map = &base->sigmap;
struct evmap_signal *ctx = NULL;//ctx = map->entries[fd] = 双向队列头结点
if (sig >= map->nentries) {//sig或fd大于个数,则扩容
if (evmap_make_space(
map, sig, sizeof(struct evmap_signal *)) == -1)
return (-1);
}
//如果ctx为NULL
GET_SIGNAL_SLOT_AND_CTOR(ctx, map, sig, evmap_signal, evmap_signal_init,
base->evsigsel->fdinfo_len);
if (TAILQ_EMPTY(&ctx->events)) {//注意 信号回调函数注册一次即可。因为同一个信号可以绑定多个事件,所以回调函数注册一次即可。
if (evsel->add(base, ev->ev_fd, 0, EV_SIGNAL, NULL)//调用evsig_add,注册一次信号回调函数即可。
== -1)
return (-1);
}//
//将所有有相同信号值的event连起来
TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&ctx->events, ev, ev_signal_next);//将ev,插入尾端
return (1);
}上述evsel->add(base, ev->ev_fd, 0, EV_SIGNAL, NULL)就是调用了base->evsigsel里面的add函数,base->evsigsel在前面的evsig_init里面初始化,所以这里也就是调用evsig_add。
static int
evsig_add(struct event_base *base, evutil_socket_t evsignal, short old, short events, void *p)
{
struct evsig_info *sig = &base->sig;
(void)p;
//NSIG是信号的个数。定义在系统头文件中
EVUTIL_ASSERT(evsignal >= 0 && evsignal < NSIG);
/* catch signals if they happen quickly */
//加锁保护。但实际其锁变量为NULL。所以并没有保护。应该会在以后的版本有所改正
//在2.1.4-alpha版本中,就已经改进了这个问题。为锁变量分配了锁
EVSIGBASE_LOCK();
//如果有多个event_base,那么捕抓信号这个工作只能由其中一个完成。
if (evsig_base != base && evsig_base_n_signals_added) {
event_warnx("Added a signal to event base %p with signals "
"already added to event_base %p. Only one can have "
"signals at a time with the %s backend. The base with "
"the most recently added signal or the most recent "
"event_base_loop() call gets preference; do "
"not rely on this behavior in future Libevent versions.",
base, evsig_base, base->evsel->name);
}
evsig_base = base;
evsig_base_n_signals_added = ++sig->ev_n_signals_added;
evsig_base_fd = base->sig.ev_signal_pair[0];//写端
EVSIGBASE_UNLOCK();
event_debug(("%s: %d: changing signal handler", __func__, (int)evsignal));
if (_evsig_set_handler(base, (int)evsignal, evsig_handler) == -1) {//注册信号捕捉函数
goto err;
}
//event_base第一次监听信号事件。要添加ev_signal也就是sockerpair[1]的读端要加入到event_base中
if (!sig->ev_signal_added) {
if (event_add(&sig->ev_signal, NULL))
goto err;
sig->ev_signal_added = 1;//标记ev_signal添加到了epoll。
}
return (0);
err:
EVSIGBASE_LOCK();
--evsig_base_n_signals_added;
--sig->ev_n_signals_added;
EVSIGBASE_UNLOCK();
return (-1);
}该函数重点是设定信号对应的回调函数_evsig_set_handler,以及将ev_signal添加到epoll。
int
_evsig_set_handler(struct event_base *base,
int evsignal, void (__cdecl *handler)(int))
{
//如果有sigaction就优先使用之
#ifdef _EVENT_HAVE_SIGACTION
struct sigaction sa;
#else
ev_sighandler_t sh;
#endif
struct evsig_info *sig = &base->sig;
void *p;
/*
* resize saved signal handler array up to the highest signal number.
* a dynamic array is used to keep footprint on the low side.
*/
//一个信号对应一个struct sigaction变量。event_base通过sh_old管理所有的struct sigaction变量。
//数组的一个元素就存放一个信号。信号值等于其下标
if (evsignal >= sig->sh_old_max) {//不够内存。重新分配 struct sigaction*
int new_max = evsignal + 1;
event_debug(("%s: evsignal (%d) >= sh_old_max (%d), resizing",
__func__, evsignal, sig->sh_old_max));
p = mm_realloc(sig->sh_old, new_max * sizeof(*sig->sh_old));
if (p == NULL) {
event_warn("realloc");
return (-1);
}
memset((char *)p + sig->sh_old_max * sizeof(*sig->sh_old),
0, (new_max - sig->sh_old_max) * sizeof(*sig->sh_old));//新分配的内存区域清0
sig->sh_old_max = new_max;
sig->sh_old = p;
}
/* allocate space for previous handler out of dynamic array */
//注意sh_old是一个二级指针。元素是一个一级指针。为这个一级指针分配内存
sig->sh_old[evsignal] = mm_malloc(sizeof *sig->sh_old[evsignal]);//struct sigaction变量内存
if (sig->sh_old[evsignal] == NULL) {
event_warn("malloc");
return (-1);
}
/* save previous handler and setup new handler */
#ifdef _EVENT_HAVE_SIGACTION
memset(&sa, 0, sizeof(sa));
sa.sa_handler = handler;
sa.sa_flags |= SA_RESTART;
sigfillset(&sa.sa_mask);
if (sigaction(evsignal, &sa, sig->sh_old[evsignal]) == -1) {//注册信号,并将先前handler保存在sig->sh_old[evsignal]
event_warn("sigaction");
mm_free(sig->sh_old[evsignal]);
sig->sh_old[evsignal] = NULL;
return (-1);
}
#else
if ((sh = signal(evsignal, handler)) == SIG_ERR) {
event_warn("signal");
mm_free(sig->sh_old[evsignal]);
sig->sh_old[evsignal] = NULL;
return (-1);
}
//signal返回之前的信号捕抓函数,当用户event_del这个信号监听后,就可以恢复了原始值。
*sig->sh_old[evsignal] = sh;
#endif
return (0);
}_evsig_set_handler主要工作就是将evsig_handler注册为信号发生时候的处理函数。
//内部使用的信号发送回调函数
//
static void __cdecl
evsig_handler(int sig)
{
int save_errno = errno;
#ifdef WIN32
int socket_errno = EVUTIL_SOCKET_ERROR();
#endif
ev_uint8_t msg;
if (evsig_base == NULL) {
event_warnx(
"%s: received signal %d, but have no base configured",
__func__, sig);
return;
}
#ifndef _EVENT_HAVE_SIGACTION
signal(sig, evsig_handler);
#endif
/* Wake up our notification mechanism */
msg = sig;
send(evsig_base_fd, (char*)&msg, 1, 0);//向socketpair[0]写入信号值
errno = save_errno;
#ifdef WIN32
EVUTIL_SET_SOCKET_ERROR(socket_errno);
#endif
}evsig_handler工作很简单,就是在信号发生时候,将往pair[0]里面写入对应的信号值,写入之后ev_signal事件对应的回调函数将被调用。
/* Callback for when the signal handler write a byte to our signaling socket */
//event_base应该已经监听到socketpair可读了,并且会为调用回调函数evsig_cb
static void
evsig_cb(evutil_socket_t fd, short what, void *arg)
{
static char signals[1024];
ev_ssize_t n;
int i;
int ncaught[NSIG];
struct event_base *base;
base = arg;
memset(&ncaught, 0, sizeof(ncaught));
while (1) {
//读取socketpair中的数据。从中可以知道有哪些信号发生了,因为发送过来了信号fd
//已经socketpair的读端已经设置为非阻塞的。所以不会被阻塞在
//recv函数中。这个循环要把socketpair的所有数据都读取出来
n = recv(fd, signals, sizeof(signals), 0);//读取所以字节数,一字节对应一个信号发生了
if (n == -1) {
int err = evutil_socket_geterror(fd);
if (! EVUTIL_ERR_RW_RETRIABLE(err))//EINTR和EAGAIN
event_sock_err(1, fd, "%s: recv", __func__);
break;
} else if (n == 0) {
/* XXX warn? */
break;
}
//遍历数据数组,把每一个字节当作一个信号
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ev_uint8_t sig = signals[i];
if (sig < NSIG)
ncaught[sig]++;//记录该信号发生的次数,
}
}
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
for (i = 0; i < NSIG; ++i) {
if (ncaught[i])//有信号发生就为之调用evmap_signal_active
evmap_signal_active(base, i, ncaught[i]);
}
/*
evsig_cb这个回调函数并不是用户为监听一个信号调用event_new时设置的用户回调函数.
而是Libevent内部为了处理信号而设置的内部回调函数
*/
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
}通过while(1)循环读出socketpair[1]上的数据,直到recv返回EAGAIN就可以确保数据读取完毕了。然后通过evmap_signal_active将信号值对应的事件链接到就绪队列中。然后就可以执行其对应的回调函数了。
之处,统一了事件源,将二者组合在一起。
激活信号事件
void
evmap_io_active(struct event_base *base, evutil_socket_t fd, short events)
{
struct event_io_map *io = &base->io;
struct evmap_io *ctx;
struct event *ev;
#ifndef EVMAP_USE_HT
EVUTIL_ASSERT(fd < io->nentries);
#endif
GET_IO_SLOT(ctx, io, fd, evmap_io);//找到fd对应事件链表,的桶子
EVUTIL_ASSERT(ctx);
TAILQ_FOREACH(ev, &ctx->events, ev_io_next) {//将链表里面全部为events的事件,加入到就绪队列。利用事件里面的节点加入链表即可。
if (ev->ev_events & events)
event_active_nolock(ev, ev->ev_events & events, 1);
}
}
void
event_active_nolock(struct event *ev, int res, short ncalls)
{
struct event_base *base;
event_debug(("event_active: %p (fd "EV_SOCK_FMT"), res %d, callback %p",
ev, EV_SOCK_ARG(ev->ev_fd), (int)res, ev->ev_callback));
/* We get different kinds of events, add them together */
if (ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_ACTIVE) {
ev->ev_res |= res;
return;
}
base = ev->ev_base;
EVENT_BASE_ASSERT_LOCKED(base);
ev->ev_res = res;
if (ev->ev_pri < base->event_running_priority)
base->event_continue = 1;
if (ev->ev_events & EV_SIGNAL) {
#ifndef _EVENT_DISABLE_THREAD_SUPPORT
if (base->current_event == ev && !EVBASE_IN_THREAD(base)) {
++base->current_event_waiters;
EVTHREAD_COND_WAIT(base->current_event_cond, base->th_base_lock);
}
#endif
ev->ev_ncalls = ncalls;
ev->ev_pncalls = NULL;
}
event_queue_insert(base, ev, EVLIST_ACTIVE);
if (EVBASE_NEED_NOTIFY(base))
evthread_notify_base(base);
}
evmap_io_active调用event_active_nolock循环将信号上面注册的事件加入到就绪队列。通过evmap_signal_active、event_active_nolock和event_queue_insert这三个函数的调用后,就可以把一个event插入到激活队列了。
由于这些函数的执行本身就是在Libevent处理event的回调函数之中的(Libevent正在处理内部的信号处理event)。所以并不需要从event_base_loop里的while循环里面再次执行一次evsel->dispatch(),才能执行到这次信号event。即无需等到下一次处理激活队列,就可以执行该信号event了。分析如下:
首先要明确,现在执行上面三个函数相当于在执行event的回调函数。所以其是运行在event_process_active函数之中的。
/*
* Active events are stored in priority queues. Lower priorities are always
* process before higher priorities. Low priority events can starve high
* priority ones.
*/
static int
event_process_active(struct event_base *base)
{
/* Caller must hold th_base_lock */
struct event_list *activeq = NULL;
int i, c = 0;
/*
for循环是从二级链表中查找一个优先级最高的队列,然后从优先级最高的队列中挑选排在第一个的事件进行处理
*/
for (i = 0; i < base->nactivequeues; ++i) {
if (TAILQ_FIRST(&base->activequeues[i]) != NULL) {
base->event_running_priority = i;
activeq = &base->activequeues[i];
c = event_process_active_single_queue(base, activeq);
if (c < 0) {
base->event_running_priority = -1;
return -1;
} else if (c > 0)
break; /* Processed a real event; do not
* consider lower-priority events */
/* If we get here, all of the events we processed
* were internal. Continue. */
}
}
event_process_deferred_callbacks(&base->defer_queue,&base->event_break);
base->event_running_priority = -1;
return c;
}
/*
Helper for event_process_active to process all the events in a single queue,
releasing the lock as we go. This function requires that the lock be held
when it's invoked. Returns -1 if we get a signal or an event_break that
means we should stop processing any active events now. Otherwise returns
the number of non-internal events that we processed.
*/
static int
event_process_active_single_queue(struct event_base *base,
struct event_list *activeq)
{
struct event *ev;
int count = 0;
EVUTIL_ASSERT(activeq != NULL);
/*
先将就绪事件从激活队列中删除,然后再执行事件里面的回调函数
*/
for (ev = TAILQ_FIRST(activeq); ev; ev = TAILQ_FIRST(activeq)) {//注意这里始终从TAILQ_FIRST第一个元素开始取,防止在回调函数里面,激活事件加入到当前就绪队列。
if (ev->ev_events & EV_PERSIST)
event_queue_remove(base, ev, EVLIST_ACTIVE);
else
event_del_internal(ev);
if (!(ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_INTERNAL))
++count;
event_debug((
"event_process_active: event: %p, %s%scall %p",
ev,
ev->ev_res & EV_READ ? "EV_READ " : " ",
ev->ev_res & EV_WRITE ? "EV_WRITE " : " ",
ev->ev_callback));
#ifndef _EVENT_DISABLE_THREAD_SUPPORT
base->current_event = ev;
base->current_event_waiters = 0;
#endif
switch (ev->ev_closure) {
case EV_CLOSURE_SIGNAL:
event_signal_closure(base, ev);
break;
case EV_CLOSURE_PERSIST:
event_persist_closure(base, ev);//执行回调函数
break;
default:
case EV_CLOSURE_NONE:
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
(*ev->ev_callback)(
ev->ev_fd, ev->ev_res, ev->ev_arg);
break;
}
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
#ifndef _EVENT_DISABLE_THREAD_SUPPORT
base->current_event = NULL;
if (base->current_event_waiters) {
base->current_event_waiters = 0;
EVTHREAD_COND_BROADCAST(base->current_event_cond);
}
#endif
if (base->event_break)
return -1;
if (base->event_continue)
break;
}
return count;
}
Libevent在处理内部的那个信号处理event的回调函数时,其实是在event_process_active_single_queue的一个循环里面。因为Libevent内部的信号处理event的优先级最高优先级,并且在前面的将用户信号event插入到队列(即event_queue_insert),在插入到队列的尾部。所以无论用户的这个信号event的优先级是多少,都是在Libevent的内部信号处理event的后面。所以在遍历上面两个函数的里外两个循环时,肯定会执行到用户的信号event。
执行已激活信号event
//event.c文件
static inline void
event_signal_closure(struct event_base *base, struct event *ev)
{
short ncalls;
int should_break;
/* Allows deletes to work */
ncalls = ev->ev_ncalls;
if (ncalls != 0)
ev->ev_pncalls = &ncalls;
//while循环里面会调用用户设置的回调函数。该回调函数可能会执行很久
//所以要解锁先.
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
//如果该信号发生了多次,那么就需要多次执行回调函数
while (ncalls) {
ncalls--;
ev->ev_ncalls = ncalls;
if (ncalls == 0)
ev->ev_pncalls = NULL;
(*ev->ev_callback)(ev->ev_fd, ev->ev_res, ev->ev_arg);
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
//其他线程调用event_base_loopbreak函数中断之
should_break = base->event_break;
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
if (should_break) {
if (ncalls != 0)
ev->ev_pncalls = NULL;
return;
}
}
} 可以看到,如果对应的信号发生了多次,那么该信号event的回调函数将被执行多次。